图像分割系列:OTSU算法
大津法(OTSU法)
介绍
大津法是由日本学者OTSU于1979年提出的一种像素级的图像分割方法,旨在利用阈值将原图像分成前景和背景两类,其思想在于最大化类间方差。当然也可以采用最小化类内方差和最大化类间方差。
原理
假定一幅灰度图像\(I(i,j)\)的灰度区间为\([0,L-1]\),选择一个阈值thresh将图像的像素分为\(C_1\)和\(C_2\)两组。
\[\begin{eqnarray*}
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
C_1\quad I(i,j)\leq \text{thresh} \quad |C_1|=w_1,灰度均值m_1,方差\sigma_1^2\\
C_2\quad I(i,j)>\text{thresh} \quad |C_2|=w_2,灰度均值m_2,方差\sigma_2^2
\end{array}
\right.
\end{eqnarray*}
\]
由此可以得到,以下几个数据。
- 图像总像素\(|I|=w_1+w_2\),图像灰度均值为\(m=\frac{m_1w_1+m_2w_2}{w_1+w_2}\)。
- 类内离散度\(S_w=S_1+S_2\),\(S_w=w_1\sigma_1^2+w_2\sigma_2^2\)。
- 类间离散度\(S_b=w_1(m_1-m)^2+w_2(m_2-m)^2=\frac{w_1w_2}{w_1+w_2}(m_1-m_2)^2\)
说明:网上还有一种版本采用概率的形式,如\(p_1=\frac{w_1}{w_1+w_2}\),同样可以得到相同结果。另外,需要指出此处的类间离散度与Fisher线性判别分析中的定义是有所区别的,LDA采用类间离散度矩阵是\(S_b=(m_1-m_2)(m_1-m_2)^T\)。
分类的判别依据就是类间离散度越大越好,类内离散度越小越好。因此,\(S_b/S_w\)的值越大,则分割效果越好。可以采用遍历方式搜索整个灰度区间,找到最优thresh。这种分割方法也有一个明显的缺点,它没有考虑图像的几何结构,有时分割结果并不能令人满意。
实现
本文给出Python版本的实现方法,先获得图像像素的统计信息,然后遍历像素计算判别值,得到最优分割像素值。
def ThOTSU(img):
A = img.flatten()
A = np.sort(A)
lst, uni_ind = np.unique(A,return_inverse=True)
del A
num = np.diff(uni_ind)
count = []
#统计不同像素的个数
i = 1
for x in num:
if x==0:
i = i+1
else:
count.append(i)
i = 1
else:
count.append(i)
# 初始化均值,方差,类内离散度,类间离散度
w1 = count[0]
w2 = np.sum(count[1:])
m1 = lst[0]
m2 = (lst@count-w1*m1)/w2
thresh = lst[0]
sigma1 = 0
sigma2 = (lst[1:]-m2)**2 @ count[1:] / (w2)
Sw = w2*sigma2
Sb = w1*w2/(w1+w2)*(m1-m2)**2
score = Sb/Sw
# 遍历像素区间寻找最优分割点
for i in range(1,len(lst)-1):
w1_new = w1 + count[i]
w2_new = w2 - count[i]
m1_new = (m1*w1 + lst[i]*count[i])/w1_new
m2_new = (m2*w2 - lst[i]*count[i])/w2_new
sigma1_new = (lst[:i]-m1_new)**2 @ count[:i] / (w1_new)
sigma2_new = (lst[i:]-m2_new)**2 @ count[i:] / (w2_new)
Sw = w1_new*sigma1_new + w2_new*sigma2_new
Sb = w1_new*w2_new/(w1_new+w2_new)*(m1_new-m2_new)**2
if Sb/Sw > score:
score = Sb/Sw
thresh = lst[i]
w1, w2, m1, m2 = w1_new,w2_new,m1_new,m2_new
sigma1, sigma2 = sigma1_new, sigma2_new
return thresh
测试
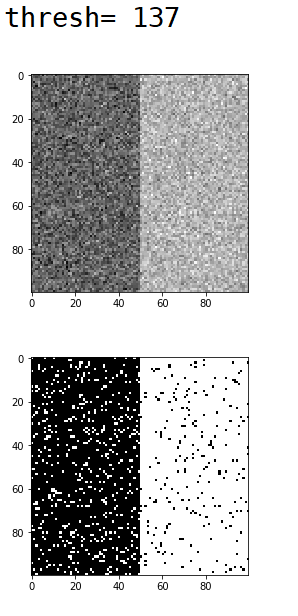
采用仿真,图片左半边像素采用均值为100方差为30的高斯分布,右半边采用均值为180方差为25的高斯分布,随机生成图像。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(1)
part1 = np.random.randn(100,50)*30+100
part1 = np.clip(part1,0,200).astype(np.uint8)
part2 = np.random.randn(100,50)*25+180
part2 = np.clip(part2,100,255).astype(np.uint8)
img = np.concatenate((part1,part2),axis=1)
plt.figure(1)
plt.imshow(img,'gray')
thresh = ThOTSU(img)
img2 = img>thresh
plt.figure(2)
plt.imshow(img2,'gray')
print("thresh=",ThOTSU(img))
得到仿真结果



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号