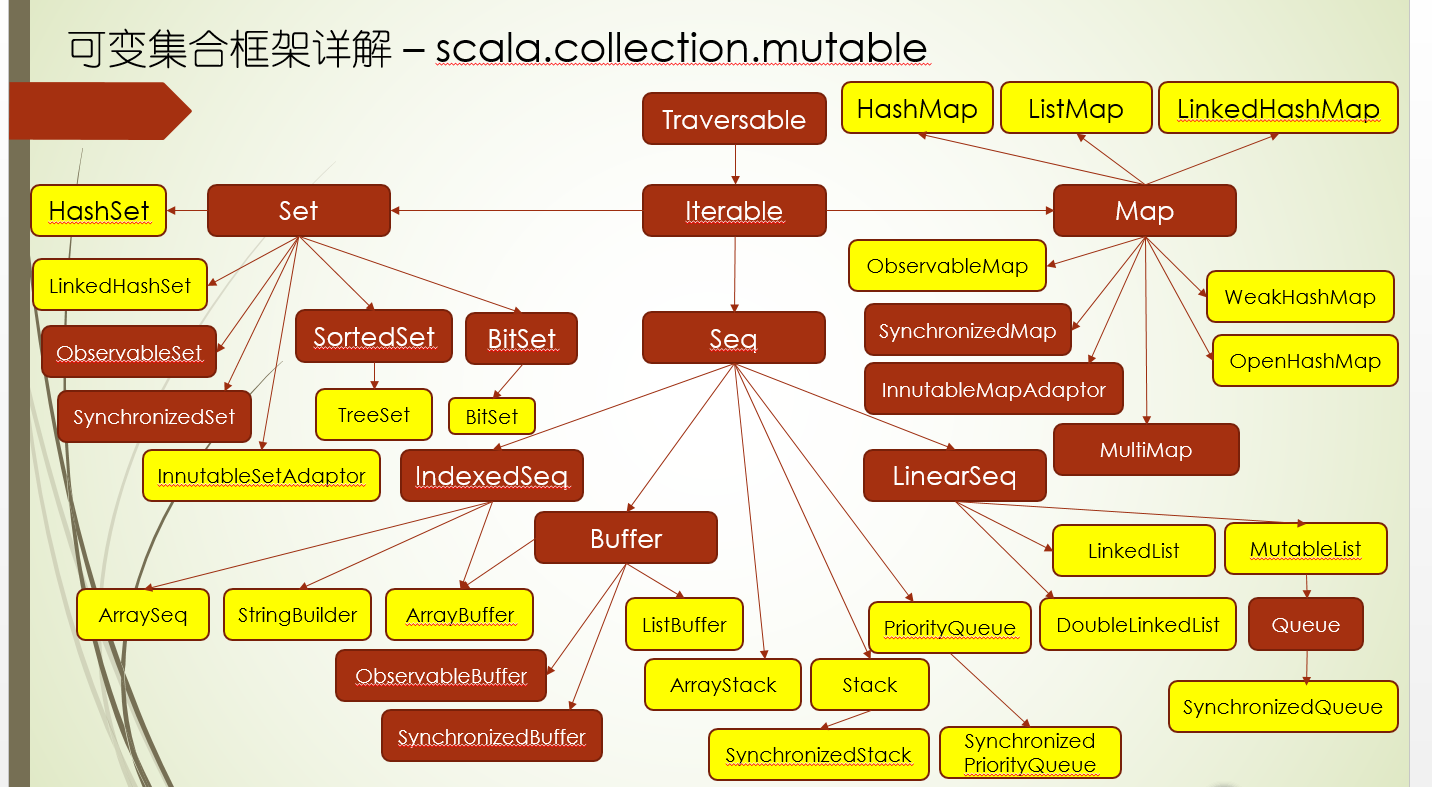
scala集合
Traversable
常用的方法都在这里,其中注意的是foreach也定义在这
package com.twq.collection.framework
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/10.
*/
object TraversableTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1、Traversable 中只定义了一个抽象方法: def foreach[U](f: Elem => U)
// 这个方法的功能就是遍历集合中的每一个元素,然后将函数f应用在每一个元素上
// Elem表示集合元素的类型,U表示函数f的返回类型,函数f的结果值将会丢弃
//2、Traversable所有的方法分类以及含义
val xs = Traversable(1, 2, 4, 1)
//抽象方法(Abstract Method)
xs foreach println
//添加方法(Addition)
// 将两个Traversable拼接在一起,或者将Iterator中的所有元素拼接到Traversable中
val ys = Traversable(2, 3)
xs ++ ys
//映射方法(Maps)
// 将一个方法应用到集合中的每一个元素,然后返回新的集合
xs map (i => (i + 1).toString())
xs flatMap (_.to(5))
xs collect { case i if (i == 2) => i * 3 }
//转换方法(Conversions)
//将Traversable转换成更具体的集合
val x = Traversable(2, 3)
x.toArray
x.toList
x.toIterable
x.toSeq
x.toIndexedSeq
x.toStream
x.toSet
//x.toMap // x必须是key value类型的集合
//拷贝方法(Copying)
//将集合元素拷贝到Buffer或者Array中
val buff = new ArrayBuffer[Int]()
xs.copyToBuffer(buff)
val arr = new Array[Int](4)
xs.copyToArray(arr, 1, 2) //从拷贝xs前面两个元素到arr中(从arr的下标为2开始)
//大小信息方法(Size info)
xs.isEmpty
xs.nonEmpty
xs.size
xs.hasDefiniteSize //如果Traversable知道有有限的长度则返回true
//检索元素方法(Element Retrieval)
//对于head和last不是所有的集合返回都是固定值,比如Set,因为Set是无序的
xs.head
xs.headOption
xs.last
xs.lastOption
xs find(_ == 3)
//子集合方法(Subcollections)
xs.tail //除了xs.head的所有的元素集合
xs.tails //Seq(1, 2, 4, 1).tails = Iterator( List(1, 2, 4, 1),List(2, 4, 1),List(4, 1),List(1),Nil)
xs.init //除了xs.last的所有元素的集合
xs.slice(1, 3) //List(2, 4)
xs.take(2)
xs.drop(2) //除了take(2)外的其他元素的集合
xs.takeWhile(_ == 1) //从集合的头开始提取符合条件的数据,一旦碰到不符合的数据元素则退出
xs.dropWhile(_ == 1) //从集合的头开始删除符合条件的数据,一旦碰到不符合的数据元素则退出
xs.filter(_ == 2) //过滤出符合条件的元素的集合
xs.withFilter(_ == 2) //不是严格意义上上的filter,不像filter那样会产生新的集合
xs.filterNot(_ == 2) //过滤出不符合条件的元素的集合
//切分方法(Subdivisions)
//在指定的位置对集合介个, 返回 pair of collections (xs take n, xs drop n)
xs.splitAt(3) //res20: (Seq[Int], Seq[Int]) = (List(1, 2, 4),List(1))
//根据指定的条件对集合进行切割, 返回 pair of collections (xs takeWhile p, xs.dropWhile p)
xs.span(_ == 1) //res22: (Seq[Int], Seq[Int]) = (List(1),List(2, 4, 1))
//返回集合对,第一个集合包括了符合条件的元素的集合,第二个集合包括了不符合条件的元素的集合
//(xs filter p, xs.filterNot p)
xs.partition(_ == 1) //res24: (Seq[Int], Seq[Int]) = (List(1, 1),List(2, 4))
//按照f来group集合成Map
xs.groupBy(_ + 1) //res25: scala.collection.immutable.Map[Int,Seq[Int]] = Map(2 -> List(1, 1), 5 -> List(4), 3 -> List(2))
//元素判断方法(Element Conditions)
xs.forall(_ > 0) //判断集合xs中的所有元素是否大于0
xs.exists(_ > 2) //判断集合xs中是否有大于2的元素
xs.count(_ > 2) //计算集合xs中大于2的数量
//折叠方法(Folds)
//对集合中的连续的元素应用二元操作
(0 /: xs)(_ + _)
xs.foldLeft(0)(_ + _)
(xs :\ 0)(_ + _)
xs.foldRight(0)(_ + _)
xs.reduceLeft(_ + _)
xs.reduceRight(_ + _)
//Specific Folds
xs.sum
xs.product // 元素累乘
xs.min
xs.max
//Strings
val sb = new StringBuilder
xs.addString(sb, "[", ",", "]")
xs.mkString("[", ",", "]")
xs.stringPrefix
//Views
//lazy计算特性的集合
xs.view(1, 3)
}
}
Iterable
提供了外部迭代器方法iterator
package com.twq.collection.framework
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/11/15.
*/
object IterableTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1、trait Iterable提供了iterator方法,可以返回一个用来遍历集合元素的外部迭代器
//2、iterator有两个方法,一个是hasNext,一个是next
//如果集合中还有元素的话,则hasNext返回true,否则返回false
//next返回下一个元素,如果没有下一个元素就会抛异常
//Iterable的超类Traversable中的foreach方法的实现如下:
/**
* def foreach[U](f: Elem => U): Unit = {
val it = iterator
while (it.hasNext) f(it.next())
}
*/
//3、Iterable另一个主要的优点是:有能力的高效的合作迭代两个集合
val names = Iterable("kity", "myte")
val ages = Iterable(32, 34)
val n = names.iterator
val a = ages.iterator
while (n.hasNext && a.hasNext) {
println(s"${n.next()} age is ${a.next()}")
}
//下面的代码效果和上面的是一样的
names.iterator zip ages.iterator map {case
(n, a) => s"${n} age is ${a}"} foreach println
//4、当在可变集合中使用外部迭代器的时候,迭代器背后的集合可能在迭代器不知道的情况下改变了
val x = collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer(1, 2, 3)
val i = x.iterator
//删除x中的所有元素
x.remove(0, 3)
i.hasNext //true
i.next() //java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: 0
//5、Iterable应该用在明确需要外部迭代器,但不需要随机访问的应用场景
//6、所有的方法
val xs = Iterable(1, 2, 4, 2, 3)
//抽象方法(Abstract Method)
val iterator = xs.iterator
while (iterator.hasNext) {
println(iterator.next())
}
//Other Iterators
xs.grouped(2) //res31: Iterator[Iterable[Int]] = Iterator(Iterable(1, 2), Iterable(4, 2), Iterable(3))
xs.grouped(2).toList //res32: List[Iterable[Int]] = List(List(1, 2), List(4, 2), List(3))
xs.sliding(2).toList //res35: List[Iterable[Int]] = List(List(1, 2), List(2, 4), List(4, 2), List(2, 3))
//Subcollections
xs.takeRight(3)
xs.dropRight(3)
//Zippers
val ys = Iterable(3, 1, 1)
xs.zip(ys)
xs.zipAll(ys, 99, 999) // 后面指定的两个元素分别 代表 xs和ys的 空补元素
xs.zipWithIndex
//Comparison
xs sameElements ys //false
}
}
WhyTraversable
package com.twq.collection.framework
import java.io.{BufferedReader, File, FileReader}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/10.
*/
object WhyTraversable {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1、Iterable缺点一:有一些非标准的集合很难实现外部迭代器,就比如:FileLineTraversable
//FileLineTraversable需要知道迭代是否已经完成,完成的话则需要关闭资源,这个利用外部迭代器很难做到
//所以继承Iterable的都是标准的集合
}
}
class FileLineTraversable(file: File) extends Traversable[String] {
//1、trait Traversable就定义了一个接口,就是foreach
//这个属于内部迭代,无法提供高效的随机访问能力
override def foreach[U](f: (String) => U): Unit = {
println("Opening file")
val input = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))
try {
var line = input.readLine()
while (line != null) {
f(line)
line = input.readLine()
}
println("Done iteration file")
} finally {
println("Closing file")
input.close()
}
}
override def toString(): String = s"{Lines of ${file.getAbsolutePath}}"
}
Arrays
package com.twq.collection.framework.seq
import scala.reflect.ClassTag
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/10.
*/
object ArraysTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//Array是一种特殊的集合。Scala中的数组和Java中的数组是一对一的,比如:
//Array[Int]对应着java中int[],Array[String]对应着java中的String[]等
//但是scala中的Array比java中的数组功能更强大:
//1、Scala中的Array是带有类型参数的,比如Array[T] ==> T[]
//在构建泛型数组的时候需要让编译器将泛型类型告知运行时。因为:
// (1)运行时需要根据类型来构建不同的jvm数组
// (2)所有的泛型在运行的时候都是擦除的
def evenElems[T : ClassTag](xs: Vector[T]): Array[T] = {
val arr = new Array[T]((xs.length + 1) / 2)
for (i <- 0 until xs.length by 2)
arr(i / 2) = xs(i)
arr
}
//2、Scala中的Array是兼容Seq的,比如:
def test(seq: Seq[Int]) = seq.foreach(println)
test(Array(1, 2, 3)) //可以将Array传给Seq
val a1 = Array(1, 2, 3)
val seq: Seq[Int] = a1
//这个是因为在scala.LowPriorityImplicits中含有一个隐式转换,
// 这个隐式转换将Array[T]转换成WrappedArray[T]类型,而WrappedArray[T]是Seq的子类
//3、Scala中的Array支持Seq中的所有方法,比如:
val a2 = a1 map (_ * 3)
val a3 = a2 filter (_ % 2 != 0)
a3.reverse
//这个是因为在scala.PreDef中存在一个隐式转换,
// 这个隐式转换是将Array[T]类型转换称ArrayOps[T]类型,ArrayOps并不是Seq的子类,但是包含了Seq中的所有方法
//4、两个问题:
//4.1、为什么会存在两个隐式转换呢?
//第一个转成WrappedArray[T]是为了使得Array兼容Seq。如果你调用WrappedArray[T]中的方法,那么返回的就是WrappedArray[T]
val seqTmp: Seq[Int] = a1
seqTmp.reverse //res2: Seq[Int] = WrappedArray(3, 2, 1).... 这个并不是我们想要的
val ops: collection.mutable.ArrayOps[Int] = a1
ops.reverse // res3: Array[Int] = Array(3, 2, 1) 这个才是我们想要的
scala.Predef
//4.2、有两个隐式转换的话,那怎么能找对是哪个隐式转换呢?
//两个隐式转换的查找是有优先级的:
//scala.LowPriorityImplicits是scala.PreDef的父类,所以隐式查找的时候会去先查找scala.PreDef中的隐式转换
//所以对于Array方法的调用,肯定会先找到scala.PreDef中的隐式转换
//对于Array兼容Seq则会找到scala.LowPriorityImplicits中的隐式转换,因为ArrayOps并不是Seq的子类
}
}
Buffers可变集合
package com.twq.collection.framework.seq
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/10.
*/
object BuffersTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//可变集合Buffer是Seq的一个子类
//它不仅允许更新元素的更新,而且允许元素的插入和删除
//ListBuffer 和 ArrayBuffer
//5、可变集合Buffer的方法
val buffer = scala.collection.mutable.Buffer(1, 2, 3, 1, 4) //Buffer的默认实现是ArrayBuffer
//Additions
buffer += 99
buffer += (88, 100)
buffer ++= Seq(1, 2, 3)
101 +=: buffer
Seq(1, 2, 3) ++=: buffer
buffer.insert(3, 99999)
buffer.insertAll(2, Seq(22, 33))
//Removals
buffer -= 99
buffer.remove(3)
buffer.remove(3, 4) // 索引位置 移除个数
buffer.trimStart(4) // 从头开始算 裁掉4个
buffer.trimEnd(2) // 从尾开始算 裁掉2个
buffer.clear()
//Cloning
buffer.clone()
}
}
Seq
package com.twq.collection.framework.seq
import scala.annotation.tailrec
import scala.collection.LinearSeq
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/11/15.
* Seq是一个有长度且其元素都有一个固定的下标值(从0开始)的Iterable
*/
object SeqTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1、trait Seq是通过length和apply两个接口方法定义的,代表连续有序(有序并不代表排序sorted)的集合
//apply是根据序号进行索引操作,而length则是返回集合的大小
//Seq不对索引或者length做任何的性能保证,仅用来将有序集合和Set/Map区分开
//也就是说,如果元素插入集合的顺序是重要的,并且允许重复元素,那么就使用Seq
//比如:记录采用的音频数据,其记录的顺序对于数据的处理是非常重要的
val x = Seq(2, 1, 30, -2, 20, 1, 2, 1)
x.tails map (_.take(2)) filter (_.length > 1) map (_.sum) toList
//res4: List[Int] = List(3, 31, 28, 18, 21, 3, 2)
//效果和上面是一样的,我们推荐使用sliding,而不是tails
x.sliding(2).map(_.sum).toList
//res4: List[Int] = List(3, 31, 28, 18, 21, 3, 2)
//2、所有的方法
val seq = Seq(1, 2, 4, 2, 1, 1) //Seq的默认实现是不可变集合List
//Indexing and Length
seq(2)
seq.apply(2)
seq.isDefinedAt(4) //判断是否存在这个索引
seq.length
seq.lengthCompare(4) //如果seq的长度比4小则返回-1,长度比4大则返回1,否则返回0
seq.indices // 所有的下标
//Index Search
seq.indexOf(3) //获取元素的下标
seq.lastIndexOf(1)
seq.indexOfSlice(Seq(2, 1), 2) //从seq的下标为2的位置开始,返回Seq(2, 1)在seq中的位置
seq.lastIndexOfSlice(Seq(2, 1), 2) //到2为止
seq.indexWhere(_ == 1, 2) //从seq的下标为2的位置开始,返回符合条件的下标
seq.segmentLength(_ == 1, 2) //从seq的下标为2的位置开始,返回连续符合条件的元素的个数,如果碰到不符合条件的元素则直接返回
seq.prefixLength(_ == 1) //返回连续符合条件的元素的个数,如果碰到不符合条件的元素则直接返回
//Additions
3 +: seq
seq :+ 3
seq.padTo(10, 3) // 扩充seq 不足补3
//Updates
seq.patch(2, Seq(88, 99), 3) //从seq的下标2开始将seq长度为3的元素集合替换为Seq(88, 99)
seq.updated(2, 100)
//Sorting
seq.sorted
seq.sortWith(_ < _)
seq.sortBy(_ % 2)
val person = Seq(People("kk", 23), People("mm", 21), People("mssm", 81))
implicit object PersonOrdering extends Ordering[People] {
override def compare(x: People, y: People): Int = x.age - y.age
}
person.sorted
//Reversals
seq.reverse
seq.reverseIterator //和seq.reverse.iterator一样,但是会更加的高效
seq.reverseMap(_ + 3)
//Comparisons
val ys = Seq(2, 3, 1, 1)
seq.startsWith(ys, 2) //seq 偏移2个元素 是否以ys开始
seq.endsWith(ys)
seq.contains(3)
seq.containsSlice(ys)
(seq.corresponds(ys))((x, y) => x + y == 4) //判断两个序列的元素对应起来是否符合条件
//Multiset Operations
seq.intersect(ys)
seq.diff(ys)
seq.union(ys)
seq.distinct
//3、trait LinearSeq表示能够分割为头元素 + 尾集合的集合,是Seq的子类
//定义了三个方法:isEmpty(集合是否非空)、head(非空集合的第一个元素)
// 和tail(去掉第一个元素剩下的所有元素的集合)
//这种集合类型通过头元素分割集合的尾递归算法非常的理想
val linearSeq = LinearSeq(1, 2, 3)
linearSeq.head
linearSeq.tail
linearSeq.isEmpty
val tree = Branch(1, Leaf(2), Branch(3, Leaf(4), NilTree))
traverse(tree)(println)
//当需要把一个普通递归的算法转化成尾递归或者循环算法时,
// 在堆(heap)上手工创建一个栈(stack),然后用这个栈来完成实际功能是一种常见的做法
//在使用函数式风格的尾递归算法时,LinearSeq是一个恰当的选择
//List是常用的LinearSeq的实现集合
//4、IndexedSeq也是Seq的子类,它在随机访问的时候更为高效
val indexedSeq = IndexedSeq(1, 2, 3) //默认情况下是创建一个不可变的Vector
indexedSeq.updated(1, 5)//将集合中下标为1的值改成5,生成一个新的集合
//访问IndexedSeq
indexedSeq.apply(1)
indexedSeq(2)
//Array和ArrayBuffer是常用的IndexedSeq的实现集合
//Vector同时支持高效的线形访问和随机访问,如果场景需要线形访问和随机访问的话,则用Vector
//5、LinearSeq和IndexedSeq都包含可变和不可变的
val immutableLinearSeq = scala.collection.immutable.LinearSeq(1, 2, 3)
val mutableLinearSeq = scala.collection.mutable.LinearSeq(1, 2, 3)
val immutableIndexedSeq = scala.collection.immutable.IndexedSeq(1, 2, 3)
val mutableIndexedSeq = scala.collection.mutable.IndexedSeq(1, 2, 3)
//可变和不可变都有updated方法,都是返回一个新的Seq集合
immutableIndexedSeq.updated(1, 5)
mutableIndexedSeq.updated(1, 5)
//update只有是可变集合有,改变原集合,不产生新的集合
mutableIndexedSeq.update(1, 5)
//immutableIndexedSeq.update(1, 5) 不存在的方法
}
def traverse[A, U](t: BinaryTree[A])(f: A => U): Unit = {
@tailrec
def traverseHelper(current: BinaryTree[A],
next: LinearSeq[BinaryTree[A]]): Unit = {
current match {
case Branch(value, lhs, rhs) =>
f(value)
traverseHelper(lhs, rhs +: next)
case Leaf(value) if !next.isEmpty =>
f(value)
traverseHelper(next.head, next.tail)
case Leaf(value) =>
f(value)
case NilTree if !next.isEmpty =>
traverseHelper(next.head, next.tail)
case NilTree => ()
}
}
traverseHelper(t, LinearSeq())
}
}
sealed trait BinaryTree[+A]
case object NilTree extends BinaryTree[Nothing]
case class Branch[+A](value: A,
lhs: BinaryTree[A],
rhs: BinaryTree[A]) extends BinaryTree[A]
case class Leaf[+A](value: A) extends BinaryTree[A]
case class People(name: String, age: Int)
Streams
package com.twq.collection.framework.seq
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/10.
*/
class StreamsTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1、Stream结构和List是一样的,但是它是延迟计算的,只有被访问到的元素才会计算
// 所以呢Stream可以无限长,Stream的性能和List是一样的
//2、List是用 :: 操作符来拼接元素,而Stream使用 #:: 来拼接元素
val str = 1 #:: 2 #:: 3 #:: Stream.empty
//3、例子:求斐波那契数列
//如果将下面的 #:: 修改成 :: 将会导致死循环
def fibFrom(a: Int, b: Int): Stream[Int] =
a #:: fibFrom(b, a + b)
val fibs = fibFrom(1, 1).take(7)
fibs.foreach(println)
fibs.toList
}
}
Strings
package com.twq.collection.framework.seq
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/10.
*/
object StringsTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val str = "hello"
str.reverse
str.map(_.toUpper)
str drop 3
str slice (1, 4)
val s: Seq[Char] = str
//为什么String有如上的功能呢?是因为存在两个隐式转换
//第一个是低级别的隐式转换:将String类型转换成WrappedString类型,
// WrappedString是immutable.IndexedSeq的子类
//第二个是高级别的隐式转换:将String类型转换成StringOps对象,
// StringOps对象中含有immutable.IndexedSeq中的所有方法
}
}
Vectors
package com.twq.collection.framework.seq
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/10.
*/
class VectorsTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1、对List的头进行增删改查是一件不耗时的操作,但是对List的非头部分的增删改查是一件比较耗时的操作
//而vector则是可以高效的支持任意位置的增删改查
val vec = scala.collection.immutable.Vector.empty
val vec2 = vec :+ 1 :+ 2
val vec3 = 100 +: vec2
vec3(0)
//2、vector是不可变的
val vec4 = Vector(1, 2, 3)
vec4 updated (2, 4) //返回新的vector,而vec4不改变
//3、因为vector可以高效的支持任意位置的增删改查,所以IndexedSeq的默认实现就是vector
collection.immutable.IndexedSeq(1, 2, 3)
//4、vector的数据结构
//TODO
}
}
Map
package com.twq.collection.framework.map
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/11/16.
*/
object MapTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1、在scala.Predef中定义了一个隐式转换,把A -> B 的表达式转换为元组(A, B)
val errorCodes = Map(1 -> "NOES", 2 -> "KTHXBAI", 3 -> "ZOMG")
//2、Map能用作从键类型到值类型的偏函数
val result = List(1, 3) map errorCodes //result: List[String] = List(NOES, ZOMG)
//3、Map还提供了当键不存在时返回默认值的能力
val addresses = Map("katy" -> "someplace 123").withDefaultValue("default place")
addresses("john") //default place
//4、在scala社区中一般习惯直接用通用的Map类型
//所有的方法:
val ms = Map("x" -> 24, "y" -> 25, "z" -> 26) //默认类型是scala.collection.immutable.Map
//Lookups
ms.get("x")
ms("x")
ms.getOrElse("c", 33)
ms.contains("c")
ms.isDefinedAt("d") //Same as contains
//Additions and Updates
ms + ("c" -> 33)
ms + ("c" -> 33, "d" -> 34)
ms ++ Map("f" -> 32, "h" -> 88)
ms.updated("x", 23) //效果和ms + (k -> v)一样
//Removals
ms - "c"
ms - ("x", "y", "d")
ms -- (Seq("c", "d"))
//Subcollections
ms.keys
ms.keySet
ms.keysIterator
ms.values
ms.valuesIterator
//Transformation
ms.filterKeys(_.contains("c"))
ms.mapValues(_ + 4)
//可变的Map的方法:
val mutableMap = scala.collection.mutable.Map("x" -> 24, "y" -> 25, "z" -> 26) // scala.collection.mutable.Map
//Additions and Updates
mutableMap("x") = 99
mutableMap += ("c" -> 98)
mutableMap += ("d" -> 98, "m" -> 77)
mutableMap ++= Map("l" -> 2)
mutableMap.put("v", 23)
mutableMap.getOrElseUpdate("l", 8)
//可以用于缓存,如下:
val cache = collection.mutable.Map[String, String]()
def cachedF(s: String) = cache.getOrElseUpdate(s, f(s)) //第二个参数是by-name参数,用的时候才会取计算
cachedF("abd")
cachedF("abd")
def cachedF_1(arg: String) = cache get arg match {
case Some(result) => result
case None =>
val result = f(arg)
cache(arg) = result
result
}
//Removals
mutableMap -= "c"
mutableMap -= ("x", "y", "d")
mutableMap --= (Seq("c", "d"))
mutableMap.remove("v")
mutableMap.retain((key, value) => key != "d")
mutableMap.clear()
//Transformation
mutableMap.transform((key, value) => value + 23)
//Cloning
mutableMap.clone()
}
def f(x: String) = {
println("taking my time.");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2)
x.reverse
}
}
Set
package com.twq.collection.framework.set
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/11/15.
*/
object SetTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//Set 提供了:
// 1、高效的检查集合是否包含某元素的实现
// 2、元素去重的功能
//set的另一个特性: 可以用作过滤函数
(0 to 100) filter Set(2, 3, 4) //Set(2, 3, 4)就是一个过滤函数
//所有的方法:
val fruit = Set("apple", "orange", "peach", "banana") //默认实现是scala.collection.immutable.Set
//Tests
fruit.contains("apple")
fruit("apple") //和fruit.contains("apple")功能是一样的
fruit.subsetOf(Set("apple", "orange", "peach", "banana", "tes"))
//Additions
fruit + "pear"
fruit + ("pear", "grape")
fruit ++ Seq("grape")
//Removals
fruit - "pear"
fruit - ("pear", "grape")
fruit -- Seq("grape")
fruit.empty
//Binary Operations
fruit & Set("orange")
fruit.intersect(Set("orange"))
fruit | Set("orange")
fruit.union(Set("orange"))
fruit &~ Set("orange")
fruit.diff(Set("orange"))
//可变Set新增的方法
val mutableSet = scala.collection.mutable.Set(1, 2, 3, 4, 1)
//Additions
mutableSet += 99
mutableSet += (88, 109)
mutableSet ++= Seq(22, 11, 23)
mutableSet.add(999)
//Removals
mutableSet -= 99
mutableSet -= (88, 109)
mutableSet --= Seq(22, 11, 23)
mutableSet.remove(999)
mutableSet.retain(_ > 10) //保留大于10的元素
mutableSet.clear()
//Update
mutableSet(999999) = true
mutableSet.update(999999, true) //两者功能是一样的
//Cloning
mutableSet.clone()
}
}
Views
package com.twq.collection.framework.view
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/10.
*/
object ViewsTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//view 的作用
val v = Vector(1 to 10: _*)
val result1 = v.map(_ + 1) // strict
val result2 = result1.map(_ * 2)
val vv = v.view
val result3 = vv.map(_ + 1) // non-strict(lazy)
val result4 = result3.map(_ * 2)
result4.force
//view的两个使用场景
//1、消除中间结果,提升性能
def isPalindrome(x: String) = x == x.reverse
def findPalindrome(s: Seq[String]) = s find isPalindrome
val words = Seq("test", "tttt", "man", "sd", "444", "45", "", "")
findPalindrome(words take 100000) //会产生中间结果
findPalindrome(words.view take 100000) //不会产生中间结构
//2、view和可变集合的配合
val arr = (0 to 9).toArray
val subarr = arr.view.slice(3, 6)
def negate(xs: collection.mutable.Seq[Int]) =
for (i <- 0 until xs.length) xs(i) = -xs(i)
negate(subarr)
arr //部分元素被修改了
//对于数据量比较少的集合的操作,建议使用strict模式,而不要采用view的模式
//因为对于数据量少的集合使用view的开销可能还比产生中间结果的要大
}
}
与java进行转换
package com.twq.collection.framework.conversions
import scala.collection.mutable
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/12/22.
*/
object Conversions {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
import scala.collection.JavaConversions._
/**
* 双向转换
* Iterator <--> java.util.Iterator
* Iterator <--> java.util.Enumeration
* Iterable <--> java.util.Iterable
* Iterable <--> java.util.Collection
* mutable.Buffer <--> java.util.List
* mutable.Set <--> java.util.Set
* mutable.Map <--> java.util.Map
*/
val jul: java.util.List[Int] = ArrayBuffer(1, 2, 3)
val buf: mutable.Buffer[Int] = jul
val m: java.util.Map[String, Int] = mutable.HashMap("abc" -> 1, "hello" -> 2)
val map: mutable.Map[String, Int] = m
/*
单向转换
* Seq --> java.util.List
* mutable.Seq --> java.util.List
* Set --> java.util.Set
* Map --> java.util.Map
*/
val javaul: java.util.List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3)
javaul.add(2)
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号