mybaits源码分析--事务管理(八)
一、事务管理
写到这也快进入收尾阶段了了,在介绍MyBatis中的事务管理时不可避免的要接触到DataSource的内容,所以接下来会分别来介绍DataSource和Transaction两块内容。
1. DataSource
在数据持久层中,数据源是一个非常重要的组件,其性能直接关系到整个数据持久层的性能,在实际开发中我们常用的数据源有 Apache Common DBCP,C3P0,Druid 等,MyBatis不仅可以集成第三方数据源,还提供的有自己实现的数据源。在MyBatis中提供了两个 javax.sql.DataSource 接口的实现,分别是 PooledDataSource 和UnpooledDataSource .
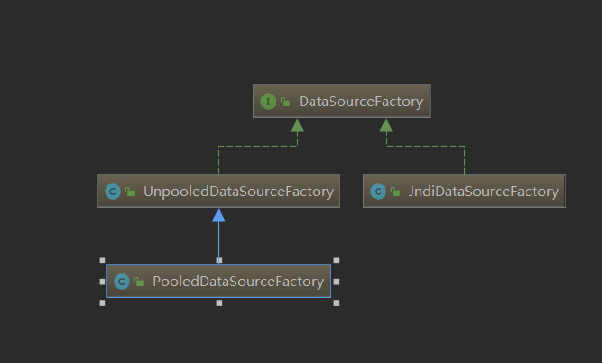
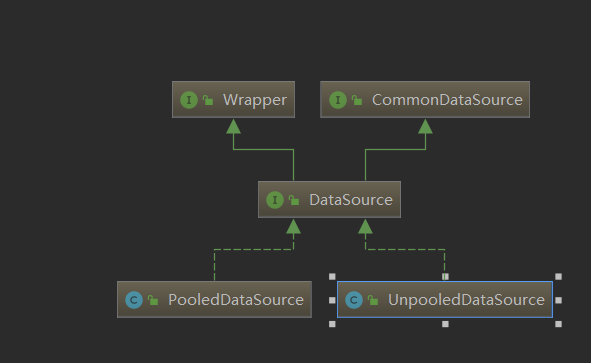
1.1 DataSourceFactory
DataSourceFactory是用来创建DataSource对象的,接口中声明了两个方法,作用如下
public interface DataSourceFactory { // 设置 DataSource 的相关属性,一般紧跟在初始化完成之后 void setProperties(Properties props); // 获取 DataSource 对象 DataSource getDataSource(); }
DataSourceFactory接口的两个具体实现是 UnpooledDataSourceFactory 和PooledDataSourceFactory 这两个工厂对象的作用通过名称我们也能发现是用来创建不带连接池的数据源对象和创建带连接池的数据源对象,先来看下 UnpooledDataSourceFactory 中的方法
@Override public void setProperties(Properties properties) { Properties driverProperties = new Properties(); // 创建 DataSource 对应的 MetaObject 对象 MetaObject metaDataSource = SystemMetaObject.forObject(dataSource); // 遍历 Properties 集合,该集合中配置了数据源需要的信息 for (Object key : properties.keySet()) { // 获取属性名称 String propertyName = (String) key; if (propertyName.startsWith(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX)) { // 以 "driver." 开头的配置项是对 DataSource 的配置 String value = properties.getProperty(propertyName); driverProperties.setProperty(propertyName.substring(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH), value); } else if (metaDataSource.hasSetter(propertyName)) { // 有该属性的 setter 方法 String value = (String) properties.get(propertyName); Object convertedValue = convertValue(metaDataSource, propertyName, value); // 设置 DataSource 的相关属性值 metaDataSource.setValue(propertyName, convertedValue); } else { throw new DataSourceException("Unknown DataSource property: " + propertyName); } } if (driverProperties.size() > 0) { // 设置 DataSource.driverProperties 的属性值 metaDataSource.setValue("driverProperties", driverProperties); } }
UnpooledDataSourceFactory的getDataSource方法实现比较简单,直接返回DataSource属性记录的 UnpooledDataSource 对象
1.2 UnpooledDataSource
UnpooledDataSource 是 DataSource接口的其中一个实现,但是 UnpooledDataSource 并没有提供数据库连接池的支持,看下他的具体实现;UnpooledDataSource 中获取Connection的方法最终都会调用 doGetConnection() 方法。
public class UnpooledDataSource implements DataSource { private ClassLoader driverClassLoader; // 加载Driver的类加载器 private Properties driverProperties; // 数据库连接驱动的相关信息 // 缓存所有已注册的数据库连接驱动 private static Map<String, Driver> registeredDrivers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private String driver; private String url; private String username; private String password; private Boolean autoCommit;// 是否自动提交 private Integer defaultTransactionIsolationLevel; // 事务隔离级别 private Integer defaultNetworkTimeout; static { // 从 DriverManager 中获取 Drivers Enumeration<Driver> drivers = DriverManager.getDrivers(); while (drivers.hasMoreElements()) { Driver driver = drivers.nextElement(); // 将获取的 Driver 记录到 Map 集合中 registeredDrivers.put(driver.getClass().getName(), driver); } } public UnpooledDataSource() { } public UnpooledDataSource(String driver, String url, String username, String password) { this.driver = driver; this.url = url; this.username = username; this.password = password; } public UnpooledDataSource(String driver, String url, Properties driverProperties) { this.driver = driver; this.url = url; this.driverProperties = driverProperties; } public UnpooledDataSource(ClassLoader driverClassLoader, String driver, String url, String username, String password) { this.driverClassLoader = driverClassLoader; this.driver = driver; this.url = url; this.username = username; this.password = password; } public UnpooledDataSource(ClassLoader driverClassLoader, String driver, String url, Properties driverProperties) { this.driverClassLoader = driverClassLoader; this.driver = driver; this.url = url; this.driverProperties = driverProperties; } @Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return doGetConnection(username, password); } @Override public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { return doGetConnection(username, password); } @Override public void setLoginTimeout(int loginTimeout) { DriverManager.setLoginTimeout(loginTimeout); } @Override public int getLoginTimeout() { return DriverManager.getLoginTimeout(); } @Override public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter logWriter) { DriverManager.setLogWriter(logWriter); } @Override public PrintWriter getLogWriter() { return DriverManager.getLogWriter(); } public ClassLoader getDriverClassLoader() { return driverClassLoader; } public void setDriverClassLoader(ClassLoader driverClassLoader) { this.driverClassLoader = driverClassLoader; } public Properties getDriverProperties() { return driverProperties; } public void setDriverProperties(Properties driverProperties) { this.driverProperties = driverProperties; } public synchronized String getDriver() { return driver; } public synchronized void setDriver(String driver) { this.driver = driver; } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Boolean isAutoCommit() { return autoCommit; } public void setAutoCommit(Boolean autoCommit) { this.autoCommit = autoCommit; } public Integer getDefaultTransactionIsolationLevel() { return defaultTransactionIsolationLevel; } public void setDefaultTransactionIsolationLevel(Integer defaultTransactionIsolationLevel) { this.defaultTransactionIsolationLevel = defaultTransactionIsolationLevel; } /** * @since 3.5.2 */ public Integer getDefaultNetworkTimeout() { return defaultNetworkTimeout; } /** * Sets the default network timeout value to wait for the database operation to complete. See {@link Connection#setNetworkTimeout(java.util.concurrent.Executor, int)} * * @param defaultNetworkTimeout * The time in milliseconds to wait for the database operation to complete. * @since 3.5.2 */ public void setDefaultNetworkTimeout(Integer defaultNetworkTimeout) { this.defaultNetworkTimeout = defaultNetworkTimeout; } private Connection doGetConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { Properties props = new Properties(); if (driverProperties != null) { props.putAll(driverProperties); } if (username != null) { props.setProperty("user", username); } if (password != null) { props.setProperty("password", password); } return doGetConnection(props); } private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException { initializeDriver(); // 创建真正的数据库连接 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties); // 配置Connection的自动提交和事务隔离级别 configureConnection(connection); return connection; } private synchronized void initializeDriver() throws SQLException { if (!registeredDrivers.containsKey(driver)) { Class<?> driverType; try { if (driverClassLoader != null) { driverType = Class.forName(driver, true, driverClassLoader); } else { driverType = Resources.classForName(driver); } // DriverManager requires the driver to be loaded via the system ClassLoader. // http://www.kfu.com/~nsayer/Java/dyn-jdbc.html Driver driverInstance = (Driver)driverType.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); DriverManager.registerDriver(new DriverProxy(driverInstance)); registeredDrivers.put(driver, driverInstance); } catch (Exception e) { throw new SQLException("Error setting driver on UnpooledDataSource. Cause: " + e); } } } private void configureConnection(Connection conn) throws SQLException { if (defaultNetworkTimeout != null) { conn.setNetworkTimeout(Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(), defaultNetworkTimeout); } // 配置Connection的自动提交 if (autoCommit != null && autoCommit != conn.getAutoCommit()) { conn.setAutoCommit(autoCommit); } // 配置Connection的事务隔离级别 if (defaultTransactionIsolationLevel != null) { conn.setTransactionIsolation(defaultTransactionIsolationLevel); } } private static class DriverProxy implements Driver { private Driver driver; DriverProxy(Driver d) { this.driver = d; } @Override public boolean acceptsURL(String u) throws SQLException { return this.driver.acceptsURL(u); } @Override public Connection connect(String u, Properties p) throws SQLException { return this.driver.connect(u, p); } @Override public int getMajorVersion() { return this.driver.getMajorVersion(); } @Override public int getMinorVersion() { return this.driver.getMinorVersion(); } @Override public DriverPropertyInfo[] getPropertyInfo(String u, Properties p) throws SQLException { return this.driver.getPropertyInfo(u, p); } @Override public boolean jdbcCompliant() { return this.driver.jdbcCompliant(); } @Override public Logger getParentLogger() { return Logger.getLogger(Logger.GLOBAL_LOGGER_NAME); } } @Override public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException { throw new SQLException(getClass().getName() + " is not a wrapper."); } @Override public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException { return false; } @Override public Logger getParentLogger() { // requires JDK version 1.6 return Logger.getLogger(Logger.GLOBAL_LOGGER_NAME); } }
1.3 PooledDataSource
在操作数据库的时候数据库连接的创建过程是非常耗时的,数据库能够建立的连接数量也是非常有限的,所以数据库连接池的使用是非常重要的,使用数据库连接池会给我们带来很多好处,比如可以实现数据库连接的重用,提高响应速度,防止数据库连接过多造成数据库假死,避免数据库连接泄漏等等。先 进入他的工厂对象中来
public class PooledDataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory { public PooledDataSourceFactory() { this.dataSource = new PooledDataSource(); } }
会发现它的工厂对象直接帮我们创建了PooledDataSource对象,会发现PooledDataSource类中的无参构造中本质上就是UnpooledDataSource(),至于为什么这么设计那就要回归到UnpooledDataSource中去了,在UnpooledDataSource类中本来就帮我们设计好了与数据库的连接和关闭
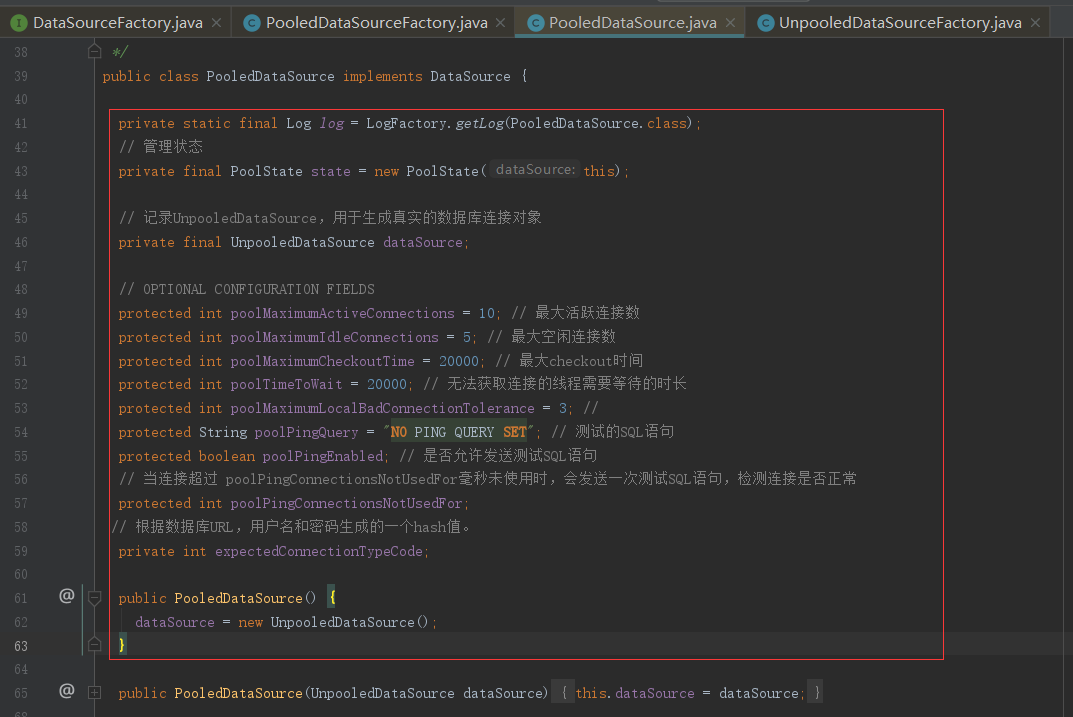
在上图的代码中有一行是管理连接池的信息的
// 管理状态 private final PoolState state = new PoolState(this);
可以点进去看下
public class PoolState { protected PooledDataSource dataSource; // 空闲的连接 protected final List<PooledConnection> idleConnections = new ArrayList<>(); // 活跃的连接 protected final List<PooledConnection> activeConnections = new ArrayList<>(); protected long requestCount = 0; // 请求数据库连接的次数 protected long accumulatedRequestTime = 0; // 获取连接累计的时间 // CheckoutTime 表示应用从连接池中取出来,到归还连接的时长 // accumulatedCheckoutTime 记录了所有连接累计的CheckoutTime时长 protected long accumulatedCheckoutTime = 0; // 当连接长时间没有归还连接时,会被认为该连接超时 // claimedOverdueConnectionCount 记录连接超时的个数 protected long claimedOverdueConnectionCount = 0; // 累计超时时间 protected long accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections = 0; // 累计等待时间 protected long accumulatedWaitTime = 0; // 等待次数 protected long hadToWaitCount = 0; // 无效连接数 protected long badConnectionCount = 0; public PoolState(PooledDataSource dataSource) { this.dataSource = dataSource; } public synchronized long getRequestCount() { return requestCount; } public synchronized long getAverageRequestTime() { return requestCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedRequestTime / requestCount; } public synchronized long getAverageWaitTime() { return hadToWaitCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedWaitTime / hadToWaitCount; } public synchronized long getHadToWaitCount() { return hadToWaitCount; } public synchronized long getBadConnectionCount() { return badConnectionCount; } public synchronized long getClaimedOverdueConnectionCount() { return claimedOverdueConnectionCount; } public synchronized long getAverageOverdueCheckoutTime() { return claimedOverdueConnectionCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections / claimedOverdueConnectionCount; } public synchronized long getAverageCheckoutTime() { return requestCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedCheckoutTime / requestCount; } public synchronized int getIdleConnectionCount() { return idleConnections.size(); } public synchronized int getActiveConnectionCount() { return activeConnections.size(); } @Override public synchronized String toString() { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); builder.append("\n===CONFINGURATION=============================================="); builder.append("\n jdbcDriver ").append(dataSource.getDriver()); builder.append("\n jdbcUrl ").append(dataSource.getUrl()); builder.append("\n jdbcUsername ").append(dataSource.getUsername()); builder.append("\n jdbcPassword ").append(dataSource.getPassword() == null ? "NULL" : "************"); builder.append("\n poolMaxActiveConnections ").append(dataSource.poolMaximumActiveConnections); builder.append("\n poolMaxIdleConnections ").append(dataSource.poolMaximumIdleConnections); builder.append("\n poolMaxCheckoutTime ").append(dataSource.poolMaximumCheckoutTime); builder.append("\n poolTimeToWait ").append(dataSource.poolTimeToWait); builder.append("\n poolPingEnabled ").append(dataSource.poolPingEnabled); builder.append("\n poolPingQuery ").append(dataSource.poolPingQuery); builder.append("\n poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor ").append(dataSource.poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor); builder.append("\n ---STATUS-----------------------------------------------------"); builder.append("\n activeConnections ").append(getActiveConnectionCount()); builder.append("\n idleConnections ").append(getIdleConnectionCount()); builder.append("\n requestCount ").append(getRequestCount()); builder.append("\n averageRequestTime ").append(getAverageRequestTime()); builder.append("\n averageCheckoutTime ").append(getAverageCheckoutTime()); builder.append("\n claimedOverdue ").append(getClaimedOverdueConnectionCount()); builder.append("\n averageOverdueCheckoutTime ").append(getAverageOverdueCheckoutTime()); builder.append("\n hadToWait ").append(getHadToWaitCount()); builder.append("\n averageWaitTime ").append(getAverageWaitTime()); builder.append("\n badConnectionCount ").append(getBadConnectionCount()); builder.append("\n==============================================================="); return builder.toString(); } }
看到上面可以看到很多连接池信息,什么空闭连接数啥的,标注的很清楚就不过多说明,后退一步;上面说了很多连接池的一些属性信息,接下来就是如何管理这些连接池信息;站在客户端的角度来说,当客户端发送一个连接请求时,连接池就会去维护和数据库的一个连接,那么客户端和连接池之间肯定要返回一个Connection对象,至于连接池是怎么返回的呢,那么一般设计肯定要在连接池那边给外部提供一个API接口供调用;接口如下
@Override public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { return popConnection(username, password).getProxyConnection(); }
会发现其中调用了 popConnection 方法,在该方法中 返回的是 PooledConnection 对象,而PooledConnection 对象实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,所以会使用到Java的动态代理;
public Connection getProxyConnection() { return proxyConnection; }
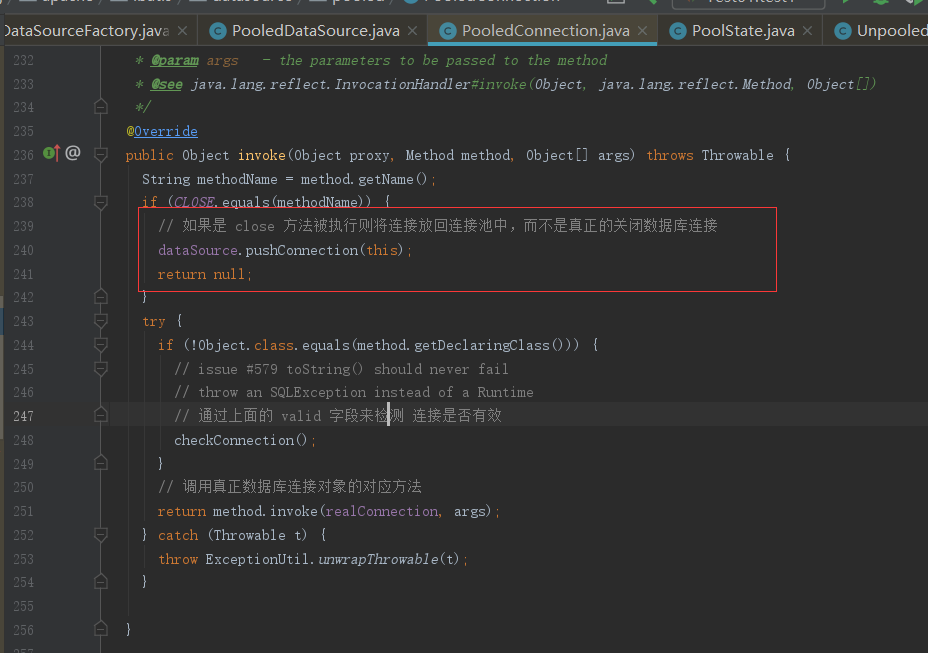
重点关注下这个类中的invoke 方法
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { String methodName = method.getName(); if (CLOSE.equals(methodName)) { // 如果是 close 方法被执行则将连接放回连接池中,而不是真正的关闭数据库连接 dataSource.pushConnection(this); return null; } try { if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // issue #579 toString() should never fail // throw an SQLException instead of a Runtime // 通过上面的 valid 字段来检测 连接是否有效 checkConnection(); } // 调用真正数据库连接对象的对应方法 return method.invoke(realConnection, args); } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } }
还有就是前面提到的 PoolState 对象,它主要是用来管理 PooledConnection 对象状态的组件,通过两个 ArrayList 集合分别管理空闲状态的连接和活跃状态的连接,先点进popConnection方法看下,看下它是怎么管理空闲连接的,其实下面代码就是正真数据库连接的原理
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
while (conn == null) {
synchronized (state) { // 同步
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) { // 检测空闲连接
// Pool has available connection 连接池中有空闲的连接
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);// 获取连接
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {// 当前连接池 没有空闲连接
// Pool does not have available connection
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// 活跃数没有达到最大连接数 可以创建新的连接
// Can create new connection
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {// 活跃数已经达到了最大数 不能创建新的连接
// Cannot create new connection 获取最先创建的活跃连接
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
// 获取该连接的超时时间
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
// 检查是否超时
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
// Can claim overdue connection
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
// 将超时连接移除 activeConnections
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
// 如果超时连接没有提交 则自动回滚
try {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
/*
Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following
statement like nothing happened.
Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help
to not interrupt current executing thread and give current thread a
chance to join the next competition for another valid/good database
connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null.
*/
log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back");
}
}
// 创建 PooledConnection,但是数据库中的真正连接并没有创建
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 将超时的 PooledConnection 设置为无效
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Must wait 无空闲连接,无法创建新连接和无超时连接 那就只能等待
// Must wait
try {
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;// 统计等待次数
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);// 阻塞等待
// 统计累计的等待时间
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (conn != null) {
// ping to server and check the connection is valid or not
// 检查 PooledConnection 是否有效
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 配置 PooledConnection 的相关属性
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;// 进行相关的统计
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
为了更好理解,画了张图
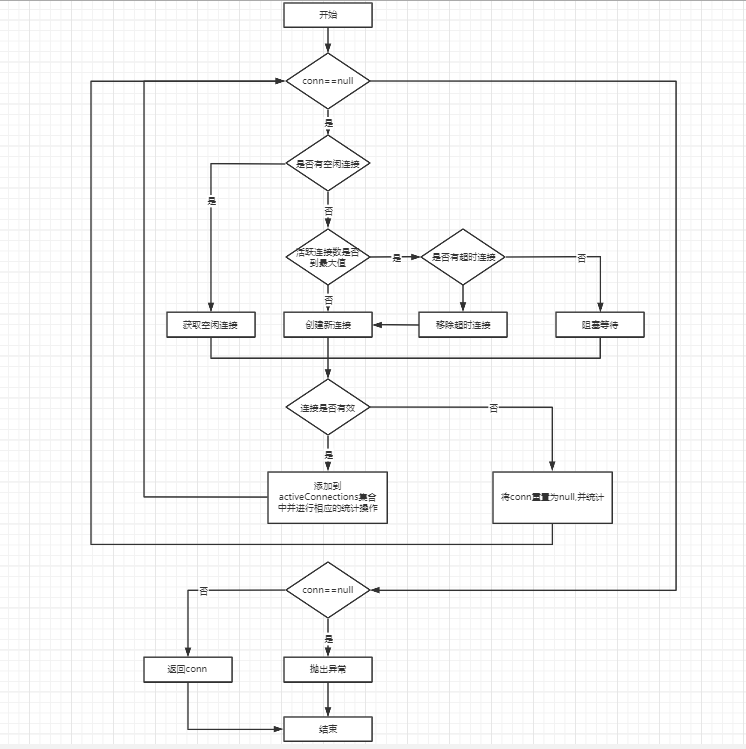
上面是需要连接连接池时的操作,但连接池用完后总要关闭吧,下面要看的就是当我们从连接池中使用完成了数据库的相关操作后,是如何来关闭连接的,通过前面的 invoke 方法的介绍其实我们能够发现,当我们执行代理对象的 close 方法的时候其实是执行的pushConnection 方法。
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException { synchronized (state) { // 从 activeConnections 中移除 PooledConnection 对象 state.activeConnections.remove(conn); if (conn.isValid()) {// 检测 连接是否有效 if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections //是否达到上限 && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode // 该PooledConnection 是否为该连接池的连接 ) { state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();// 累计checkout 时长 if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {// 回滚未提交的事务 conn.getRealConnection().rollback(); } // 为返还连接创建新的 PooledConnection 对象 PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this); // 添加到 空闲连接集合中 state.idleConnections.add(newConn); newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp()); newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp()); conn.invalidate();// 将原来的 PooledConnection 连接设置为无效 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool."); } // 唤醒阻塞等待的线程 state.notifyAll(); } else { // 空闲连接达到上限或者 PooledConnection不属于当前的连接池 state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime(); // 累计checkout 时长 if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) { conn.getRealConnection().rollback(); } // 关闭真正的数据库连接 conn.getRealConnection().close(); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + "."); } // 设置 PooledConnection 无线 conn.invalidate(); } } else { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection."); } // 统计无效的 PooledConnection 对象个数 state.badConnectionCount++; } } }
同样为了把思路搞清,也搞张图
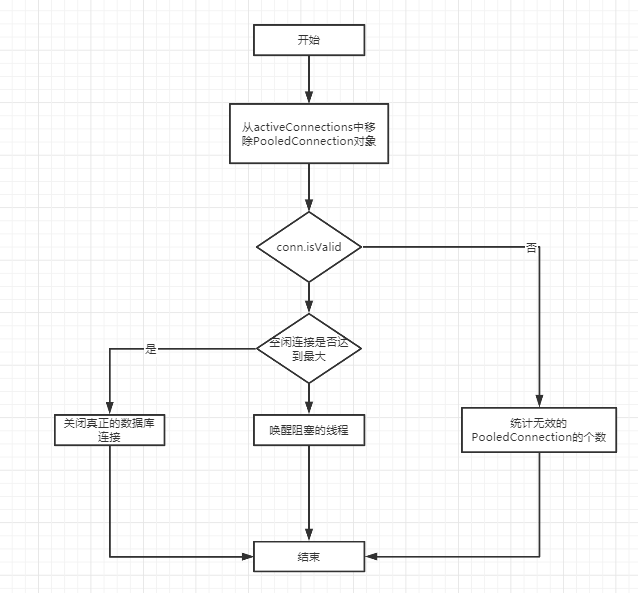
还有就是我们在源码中多处有看到 conn.isValid方法来检测连接是否有效
public boolean isValid() { return valid && realConnection != null && dataSource.pingConnection(this); }
dataSource.pingConnection(this)中会真正的实现数据库的SQL执行操作
protected boolean pingConnection(PooledConnection conn) { boolean result = true; try { result = !conn.getRealConnection().isClosed(); } catch (SQLException e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is BAD: " + e.getMessage()); } result = false; } if (result) { if (poolPingEnabled) { if (poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor >= 0 && conn.getTimeElapsedSinceLastUse() > poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor) { try { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Testing connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " ..."); } Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection(); try (Statement statement = realConn.createStatement()) { statement.executeQuery(poolPingQuery).close(); } if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) { realConn.rollback(); } result = true; if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is GOOD!"); } } catch (Exception e) { log.warn("Execution of ping query '" + poolPingQuery + "' failed: " + e.getMessage()); try { conn.getRealConnection().close(); } catch (Exception e2) { //ignore } result = false; if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is BAD: " + e.getMessage()); } } } } } return result; }
最后一点要注意的是在我们修改了任意的PooledDataSource中的属性的时候都会执行forceCloseAll来强制关闭所有的连接。
public void setPoolMaximumActiveConnections(int poolMaximumActiveConnections) { this.poolMaximumActiveConnections = poolMaximumActiveConnections; forceCloseAll(); }
public void forceCloseAll() { synchronized (state) { // 更新 当前的 连接池 标识 expectedConnectionTypeCode = assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()); // 处理全部的活跃连接 for (int i = state.activeConnections.size(); i > 0; i--) { try { // 获取 获取的连接 PooledConnection conn = state.activeConnections.remove(i - 1); // 标识为无效连接 conn.invalidate(); // 获取真实的 数据库连接 Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection(); if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) { // 回滚未处理的事务 realConn.rollback(); } // 关闭真正的数据库连接 realConn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { // ignore } } // 同样的逻辑处理空闲的连接 for (int i = state.idleConnections.size(); i > 0; i--) { try { PooledConnection conn = state.idleConnections.remove(i - 1); conn.invalidate(); Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection(); if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) { realConn.rollback(); } realConn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { // ignore } } } if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections."); } }
2.Transaction
在实际开发中,控制数据库事务是一件非常重要的工作,MyBatis使用Transaction接口对事务进行了抽象,定义的接口为
public interface Transaction { /** * Retrieve inner database connection. * @return DataBase connection * @throws SQLException */ Connection getConnection() throws SQLException; /** * Commit inner database connection. * @throws SQLException */ void commit() throws SQLException; /** * Rollback inner database connection. * @throws SQLException */ void rollback() throws SQLException; /** * Close inner database connection. * @throws SQLException */ void close() throws SQLException; /** * Get transaction timeout if set. * @throws SQLException */ Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException; }
Transaction接口的实现有两个分别是 JdbcTransaction 和 ManagedTransaction两个
2.1 JdbcTransaction
JdbcTransaction 依赖于JDBC Connection来控制事务的提交和回滚,声明的相关的属性为

在构造方法中会完成除了 Connection 属性外的另外三个属性的初始化,而Connection会延迟初始化,在我们执行getConnection方法的时候才会执行相关的操作。源码比较简单
2.2 ManagedTransaction
ManagedTransaction的实现更加的简单,它同样依赖 DataSource 字段来获取 Connection 对象,但是 commit方法和rollback方法都是空的,事务的提交和回滚都是依赖容器管理的。在实际开发中MyBatis通常会和Spring集成,数据库的事务是交给Spring进行管理的




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号