读书报告
numpy基本函数 scipy pandas
numpy的导入 使用用例
import numpy as np
import numpy as np print np.random.rand(4,4)
>>> import numpy as np #生成数据 >>> x=np.arange(10) >>> x array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) #数据保存 >>> np.save('save_x',x) #读取保存的数据 >>> np.load('save_x.npy') array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
scipy计算矩阵的逆
>>> arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) >>> iarr = linalg.inv(arr) >>> iarr array([[-2. , 1. ], [ 1.5, -0.5]]) >>>np.allclose(np.dot(arr, iarr), np.eye(2))
pandas
import pandas as pd
import pandas food_info = pandas.read_csv(file_name) n_rows = food_info.head(n) column_names = food_info.columns dimensions = food_info.shape
数据加减乘除操作
div_1000 = food_info["Iron_(mg)"] / 1000 #对该列每一个数据进行除法操作 add_100 = food_info["Iron_(mg)"] + 100 sub_100 = food_info["Iron_(mg)"] - 100 mult_2 = food_info["Iron_(mg)"] * 2 # 两列数据对应元素做乘法 water_energy = food_info["Water_(g)"] * food_info["Energ_Kcal"]
matplotlib
抛物线y=x^2
x1=np.arange(-np.pi,np.pi,0.01) y1=x1**2 plt.plot(x1,y1)
正弦曲线
x=np.linspace(-np.pi,np.pi,100) y=np.sin(x) plt.plot(x,y)
x = np.linspace(0, np.pi) y_sin = np.sin(x) y_cos = np.cos(x) ax1.plot(x, y_sin) ax2.plot(x, y_sin, 'go--', linewidth=2, markersize=12) ax3.plot(x, y_cos, color='red', marker='+', linestyle='dashed')
#线
矩阵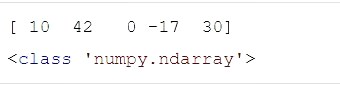
import numpy as np ls1 = [10, 42, 0, -17, 30] nd1 =np.array(ls1) print(nd1) print(type(nd1))
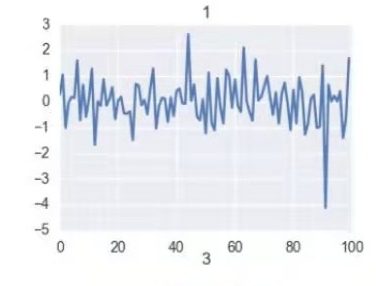
fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1) y = np.random.randn(100) plt.plot(y); ax.set_title('1') y = np.random.rand(5) x = np.arange(5) ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2) plt.bar(x, y) ax.set_title('2'); y = np.random.rand(5) y = y / np.sum(y) y[y < .05] = .05 ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3) plt.pie(y) ax.set_title('3') plt.draw() plt.show()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号