装饰器,视图系统
装饰器:在不改变原函数的调用方式和函数的情况下,额外的增加功能
1.简单装饰器
import time
def timer(func):
def inner():
print(time.time())
func()
@timer #她等于func1 = timer(func1)
def func1():
print('这是func1')
func1()
2.函数带返回值
import time
def timer(func):
def inner():
print(time.time())
ret = func()
return ret
return inner
@timer
def func1():
print('这是func1')
func1()
3.原函数携带参数
import time
def download(func):
def inner(*args,**kwargs):
print('下载软件')
ret = func(*args,**kwargs)
return ret
return inner
@download
def yue(tools):
print('使用{}约一约'.format(tools))
return '成功了'
print(yue('探探'))
print(yue('陌陌'))
结果图: 
4. 完整的装饰器的写法
def wrapper(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
# 执行被装饰函数之前进行的操作
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 执行被装饰函数之后进行的操作
return ret
return inner
5.改变所有的装饰器使用还是不使用
import time
flag = True#通过修改他改变所有的装饰器使用还是不使用
def timer(func):
def inner(*args,**kwargs):
if flag:
print(time.time())
ret = func(*args,**kwargs)
else:
ret = func(*args,**kwargs)
return ret
return inner
@timer
def func1():
print('func1')
func1()
6.装饰器带参数
import time
def outer(flag):
def timer(func):
def inner(*args,**kwargs):
if flag:
print(time.time())
ret = func(*args,**kwargs)
else:
ret = func(*args,**kwargs)
return ret
return inner
return timer
@outer(True)
def func1():
print('func1')
@outer(False)
def func2():
print('func2')
func1()
func2()
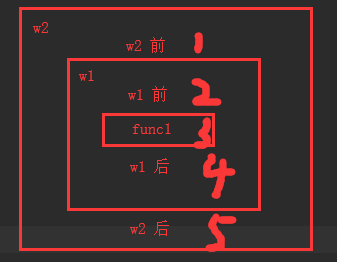
7.多个装饰器装饰同一个函数
def wrapper1(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
print('wrapper1 前') # 2
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
print('wrapper1 后') # 4
return ret
return inner
def wrapper2(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
print('wrapper2 前') # 1
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
print('wrapper2 后') # 5
return ret
return inner
@wrapper2 # func1 = wrapper2(func1) wrapper2.inner func=wrapper1.inner
@wrapper1 # func1 = wrapper1(func1) wrapper1.inner func=func1
def func1():
print('func1') # 3
return 'func1的返回值'
print(func1()) # 6

8. 装饰器修复技术
from functools import wraps
def timer(func):
@wraps(func)
def inner():
print(time.time())
ret = func() # 原来的函数
return ret
return inner
1. CBV和FBV
-
-
CBV(class based view)
定义:
# 增加出版社 CBV
from django.views import View
class AddPublisher(View):
def get(self, request):
pass
def post(self, request):
pass
使用:
url(r'^add_publisher/', views.AddPublisher.as_view()),
CBV的流程
views.AddPublisher.as_view() 程序加载的时候执行 ——》 view函数
给CBV加装饰器
引入模块
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
装饰器
def timer(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
print(func)
print(*args, *kwargs)
start = time.time()
ret = func(request, *args, **kwargs)
end = time.time()
print('时间:{}'.format(end - start))
return ret
return inner
1.加载某个get/post的方法上:
@method_decorator(timer) def get(self, request):
2.加在self.dispatch方法上:
@method_decorator(timer) def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
3. 加在类上:指定post和get,想要指定别的就要在加
@method_decorator(timer, name='post') @method_decorator(timer, name='get') class AddPublisher(View):
-
不使用method_decorator
func: <function AddPublisher.dispatch at 0x00000163735176A8>args :<app01.views.AddPublisher object at 0x00000163735F7EF0> <WSGIRequest: GET '/add_publisher/'>
-
使用method_decorator
func:<function method_decorator.<locals>.dec.<locals>.wrapper.<locals>.bound_func at 0x0000019664B4A378>arsgs: <WSGIRequest: GET '/add_publisher/'>
dispatch
class AddPublisher(View):
http_method_names = ['get']#设置只能get
@method_decorator(timer)
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):#执行自己的方法
ret = super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)#在去执行父类的dispatch
return ret #返回值接收一下
print(request.method) # GET 请求反方式
print(request.GET) # {} [] get()
print(request.POST) # {} [] get()
print(request.FILES)
print(request.path_info,type(request.path_info)) # 路径信息 不包含IP和端口、参数
print(request.get_host())
print(request.get_full_path()) # 路径信息 + 参数
-
form表单的enctype = 'multipart/form-data'
-
request.FILES中获取文件对象
-
使用文件对象的chunks()
-
-

def upload(request): if request.method == 'POST': # print(request.body) file = request.FILES.get('f1') with open(file.name, 'wb') as f: for chunk in file.chunks(): f.write(chunk) return HttpResponse('上传成功') return render(request, 'upload.html')

<body> <form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> {% csrf_token %} 文件:<input type="file" name="f1"> <button>上传</button> </form> </body>
from django.http import JsonResponse
def json_test(request):
data = {'name': 'alex', 'pwd': 'alexdsb'}
return JsonResponse(data) #左边原样输出 添加下面这个跟jsonRes...一样
return HttpResponse(json.dumps(data), content_type='application/json')
只有上边这个是输出k




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号