第十话-Java类
类创建

构造器
package com.xie.oop;
public class Person {
String name;
//无参构造器
//1. 使用new关键字,本质就是调用构造器
//2. 主要用来初始化
public Person(){
this.name = "aa";
}
//有参构造器
public Person(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.xie.oop;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person("bbbb");
System.out.println(person.name);
}
}
快捷键Alt+Insert
Alt+Insert按键可以快速生成构造器、Getter、Setter、Override等方法。
创建对象内存分析
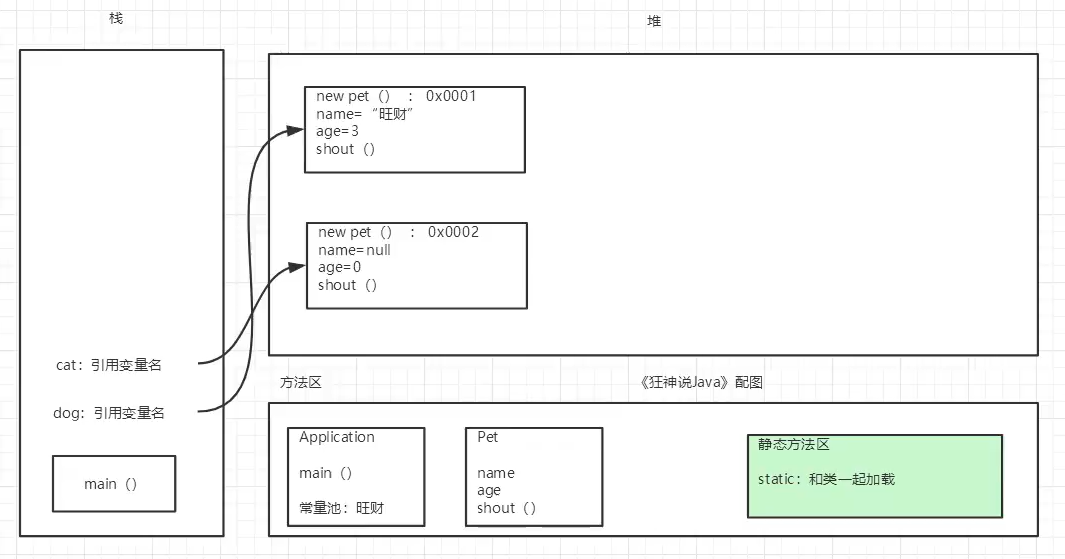
说明:
- 方法区:加载类和静态方法(类中可以直接被调用不需要实例对象调用)
- 栈:栈最里面是main方法,程序入口
- 栈:存放声明的对象名和内存地址
- 堆:对象对应的实际内存地址,存放对象的各种属性值、方法等。
封装
package com.xie.oop;
public class Student {
//属性私有,通过get、set来设置值、取值
private String name;
private int id;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
package com.xie.oop;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("aaa");
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
继承
package com.xie.oop.demo01;
public class Person {
//public //继承用public修饰
//private //无法继承private修饰的属性和方法
private int aa = 11000;
public int getAa() {
return aa;
}
public void setAa(int aa) {
this.aa = aa;
}
public int money = 1000;
public void say(){
System.out.println("say some thing");
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo01;
public class Student extends Person{
}
package com.xie.oop.demo01;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.say();
System.out.println(student.money);
System.out.println(student.getAa());
}
}
快捷键Ctrl + h
Ctrl + h,显示父子类继承关系
super
- super只能在继承条件下才可以使用
- super代表父类对象的应用,super.属性名,super.方法(),可以调用父类的属性或方法,只能使用在方法中。
- super()调用父类的构造方法,只能放在构造方法的第一个。
- super()只能出现在构造方法中
- super()和this()不能放在一个构造方法中,this():调用当前类的构造方法
- this代表当前类对象的应用。
package com.xie.oop.demo02;
public class Person {
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person-Construtor");
}
protected String name = "xiexieyc";
public void test(){
System.out.println("Person-test");
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo02;
public class Student extends Person{
public Student() {
super();//调用父类构造方法,默认会省略。
System.out.println("Student-Construtor");
}
private String name = "aaa";
public void test(){
String name = "bbb";
System.out.println(name+"--"+this.name+"--"+super.name);
super.test();
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo02;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.test();
}
}
方法重写
- 重写需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的非静态方法
- 方法名必须相同
- 参数列表必须相同
- 修饰符:范围可以扩大;default-->pretected-->public
- 抛出的异常:范围可以被缩小,但不能扩大;Exceptoin-->ClassNotFoundException
- 只有方法体不同
package com.xie.oop.demo03;
public class A {
public static void stest(){
System.out.println("a-stest");
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("a-test");
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo03;
public class B extends A{
public static void stest(){
System.out.println("b-stest");
}
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("b-test");
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo03;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
b.test();
b.stest();
//静态方法调用只和左边的定义类型有关
//非静态方法可以重写,重写后会调用子类方法
//父类声明后,父类的引用指向子类
A a = new B();
a.test();
a.stest();
}
}
多态
- 多态是方法的多态,属性没有多态
- 父类和子类要有联系,否则类型转换异常!ClassCastException
- 存在条件:继承关系,方法重写,父类引用指向子类对象。 Father f1 = new Son();
- 无法重写的方法:static(静态)、final(常量)、private(私有)修饰的方法
package com.xie.oop.demo04;
public class Person {
public void run(){
System.out.println("Person-run");
}
public void say(){
System.out.println("Person-say");
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo04;
public class Student extends Person{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Student-run");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("Student-eat");
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo04;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//父类引用指向子类
//student可以调用自己或父类继承的方法
//person不能调用子类独有的方法,除非强制转换
Student student = new Student();
Person person = new Student();
Object object = new Student();
student.say();
person.say();
student.run();
person.run();
student.eat();
((Student) person).eat();
}
}
instanceof和类型转换
package com.xie.oop.demo04;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object object = new Student();
System.out.println(object instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Object);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher);//false
System.out.println(object instanceof String);//false
System.out.println("-------------");
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println(person instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(person instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(person instanceof Object);//true
System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher);//false
//System.out.println(person instanceof String);//编译报错
System.out.println("-------------");
Student student = new Student();
System.out.println(student instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(student instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(student instanceof Object);//true
//System.out.println(student instanceof Teacher);//编译报错
System.out.println("-------------");
Person p = new Person();
System.out.println(p instanceof Student);//false
System.out.println(p instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(p instanceof Object);//true
}
}
- 父类引用指向子类的对象
- 把子类转换为父类,向上转型
- 把父类转换为子类,向下转型,强制转换
- 方便调用方法,较少重复代码
static关键字详解
- 静态变量和方法可以类名直接访问
package com.xie.oop.demo05;
public class Student {
//静态变量和方法可以类名直接访问
private static int age;
private double score;
public static void go(){}
public void run(){}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println(s1.age);
System.out.println(s1.score);
System.out.println(Student.age);
//System.out.println(Student.score);会报错
s1.run();
s1.go();
Student.go();
go();
//run();//会报错
}
}
- 静态代码块
package com.xie.oop.demo05;
public class Person {
//2
{
System.out.println("匿名代码块");
}
//1 只执行一次
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
//3
public Person(){
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person1 = new Person();
System.out.println("=============");
Person person2 = new Person();
}
}
- 静态导入包
package com.xie.oop.demo05;
//静态导入包
import static java.lang.Math.random;
import static java.lang.Math.PI;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.random());
System.out.println(random());
System.out.println(PI);
}
}
抽象类
- 不能new这个抽象类,只能靠子类去实现,约束的作用
- 抽象类可以写普通的方法
- 抽象方法必须在抽象类中
package com.xie.oop.demo06;
public abstract class Action {
public void doSomething(){
System.out.println("普通方法");
};
//抽象方法,没有方法的实现
public abstract void doSomething2();
}
package com.xie.oop.demo06;
//继承抽象类的子类,必须实现所有抽象类的抽象方法,除非子类也是抽象类
public class A extends Action{
@Override
public void doSomething2() {
System.out.println("重写抽象方法");
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo06;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.doSomething();
a.doSomething2();
Action b = new A();
b.doSomething();
b.doSomething2();
}
}
接口
- 起到约束作用,定义一些方法,让不同人实现
- 方法默认修饰:public abstract
- 属性默认修饰:public static final
- 接口不能被实例化,没有构造方法
- implements可以实现多个接口
- 必须重写接口的方法
package com.xie.oop.demo7;
public interface UserService {
//默认public static final修饰,很少这样用
int AGE = 99;
//默认public abstract修饰
void add(String name);
void update(String name);
void delete(String name);
void query(String name);
}
package com.xie.oop.demo7;
public interface TimeService {
void time();
}
package com.xie.oop.demo7;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService,TimeService{
@Override
public void add(String name) {
}
@Override
public void update(String name) {
}
@Override
public void delete(String name) {
}
@Override
public void query(String name) {
}
@Override
public void time() {
}
}
内部类
package com.xie.oop.demo08;
public class Outer {
private int id =10 ;
private void out(){
System.out.println("外部类的方法");
}
class Inner{
public void in(){
System.out.println("内部类的方法");
}
public void getId(){
System.out.println(id);
}
public void test(){
out();
}
}
}
package com.xie.oop.demo08;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer outer = new Outer();
Outer.Inner inner = outer.new Inner();
inner.in();
inner.getId();
inner.test();
}
}
- 内部类用static修饰,则不能调用外部类的非static属性和方法
- 一个java文件中可以有多个class类,但只能有一个public class
- 局部内部类
package com.xie.oop.demo08;
public class Outer2 {
public void method(){
//局部内部类
class Inner{
public void in(){
}
}
}
}
- 匿名内部类
package com.xie.oop.demo08;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类
new Apple().eat();
new UserService() {
@Override
public void hello() {
}
};
}
}
class Apple{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("111");
}
}
interface UserService{
void hello();
}
以上仅供参考,如有疑问,留言联系




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号