文件
- 打开文件
要打开文件,可使用函数open,它位于自动导入的模块io中。
>>> f = open('/opt/python/123')
文件模式
调用函数open时,如果只指定文件名,将获得一个可读取的文件对象。如果要写入文件,必须通过指定模式来显示的指出这一点。
函数open的参数mode的最常见取值
值 描述
'r' 读取模式(默认值)
'w' 写入模式
'x' 独占写入模式
'a' 附加模式
'b' 二进制模式(与其他模式结合使用)
't' 文本模式(默认值,与其他模式结合使用)
'+' 读写模式(与其他模式结合使用)
文件的基本方法
读取和写入
1 >>> f = open('/opt/python/123','w') 2 >>> f.write('hehe, ') 3 6 4 >>> f.write('hahaha!') 5 7 6 >>> f.close()
1 >>> f = open('/opt/python/123', 'r') 2 >>> f.read() 3 'hehe, hahaha!'
使用管道重定向输出
计算sys.stdin中包含多少个单词
#123.txt
hehe, hahaha!
#12.py
import sys
text = sys.stdin.read()
words = text.split()
wordcount = len(words)
print('Wordcount:', wordcount)
执行结果
cat 123 | python 12.py |sort
关闭文件
要确保文件得以关闭,可使用一条try/finally语句,并在finally子句中调用close.
#在这里打开文件
try:
#将数据写入到文件中
finally:
file.close()
实际上,有一条专门为此设计的语句,那就是with语句。
with open("somefile.txt") as somefile:
do_something(somefile)
with语句让你能够打开文件并将其赋给一个变量(这里是somefile).在语句体中,你将数据写入文件(还可能做其他事情)。到达该语句末尾时,将自动关闭文件。
使用文件的基本方法
read(n)
1 >>> f = open(r'/opt/python/123') 2 >>> f.read(7) 3 'hello h' 4
read() 5 >>> f = open(r'/opt/python/123') 6 >>> print(f.read()) 7 hello hellohello hello 8
readline() 9 >>> f = open(r'/opt/python/123') 10 >>> for i in range(3): 11 ... print(str(i) + ': ' + f.readline(), end='') 12 ... 13 0: hello hellohello hello 14 1: hehehehehe 15 2: hahahaha
readlines()
16 >>> import pprint
17 >>> pprint.pprint(open(r'/opt/python/123').readlines())
18 ['hello hellohello hello\n', 'hehehehehe\n', 'hahahaha\n']
writelines(list):
1 >>> f = open(r'/opt/python/123') 2 >>> lines = f.readlines() 3 >>> f.close() 4 >>> lines[1] = "xiaoming\n" 5 >>> f = open(r'/opt/python/123', 'w') 6 >>> f.writelines(lines) 7 >>> f.close() 8 >>> f = open(r'/opt/python/123') 9 >>> f.read() 10 'hello hellohello hello\nxiaoming\nhahahaha\n'
- 迭代文件内容
使用fileinput实现延迟行迭代
使用fileinput迭代行
1 import fileinput 2 for line in fileinput.input('/opt/python/123'): 3 print(line)
执行结果
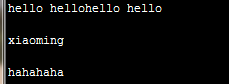
文件迭代器
迭代文件
1 with open('/opt/python/123') as f: 2 for line in f: 3 print(line) 4
在不将文件对象赋给变量的情况下迭代文件 5 import sys 6 7 for line in open('/opt/python/123'): 8 print(line)
1 >>> f = open('/opt/python/123', 'w') 2 >>> print('Firsh', 'line', file=f) 3 >>> print('Second', 'line', file=f) 4 >>> print('Third', 'and final', 'line', file=f) 5 >>> f.close() 6 >>> lines = list(open('/opt/python/123')) 7 >>> lines 8 ['Firsh line\n', 'Second line\n', 'Third and final line\n'] 9 >>> first, second, third = open('/opt/python/123') 10 >>> first 11 'Firsh line\n' 12 >>> second 13 'Second line\n' 14 >>> third 15 'Third and final line\n'




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号