共享内存
共享内存
一、共享内存的概念
共享内存是Linux系统进程间通信的一种方式,是在Unix系统的system-V版本引入的一种IPC对象,除了共享内存外,其他的IPC对象还包含消息队列、信号量组。
共享内存其实就是指多个进程可以共享物理内存中的同一段内存区域,只不过还需要把物理内存映射到进程的私有虚拟地址空间中,这样多个进程就可以对同一块内存进行访问,效率非常高。
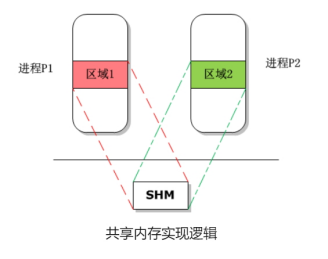
二、申请共享内存
共享内存其实是物理内存中的一段内存空间,而物理内存是由内核进行维护的,所以进程必须向操作系统申请一块物理内存,Linux系统提供了一个名称叫做shmget()的函数接口,利用该接口可以向内核申请物理内存。
shmget()函数的第一个参数指的是key_t类型的键值,和消息队列类似,一般用户可以使用ftok()函数生成一个唯一的键值key。
shmget()函数的第二个参数指的是要申请的共享内存段的大小,由参数size指定,size的大小可以是宏定义PAGE_SIZE的倍数。
shmget()函数的第三个参数指的是共享内存段的标志,其中IPC_CREAT指的是如果共享内存不存在则创建,IPC_EXCL指的是如果共享内存存在则表示函数调用失败。
返回结果:可以看到,函数调用成功,则返回创建成功的共享内存的标识符,函数调用失败,则返回-1。
注意事项:可以看到,申请成功的共享内存段里面存储的内容会被自动初始化为0,并且内核会为每一块创建的共享内存分配一个shmid_ds结构体来记录共享内存的属性和信息。
三、共享内存的映射和控制
用户申请成功共享内存之后是无法直接访问的,因为缺少共享内存的入口地址,另外,由于申请的是物理内存,所以还需要把申请的物理内存映射到进程的内存空间,这样用户就可以通过共享内存入口的虚拟地址来直接访问共享内存空间。
Linux系统提供了一个名称叫做shmat()的函数接口,用户利用该接口可以实现把共享内存映射到进程的内存空。Linux系统来提供了一个名称叫做shmdt()的函数接口,用户利用该接口可以解除映射。
Linux系统内核需要对创建成功的共享内存进行维护,所以会记录每块共享内存的属性和信息,Linux系统提供了一个名称叫做shmctl()的函数接口,用户可以调用该函数实现设置共享内存的属性、获取共享内存的属性、删除共享内存等相关操作。
四、练习
设计三个程序,要求三个程序申请一块共享内存,并分别映射到各自进程的地址空间,进程A和进程B对共享内存段中的数据进行修改,然后进程C不断输出共享内存段中的数据,并观察效果,要求实现进程间的互斥,避免竞争。
进程A
/***************************************************
*
* file name: shmA.c
* author : zzlyx1239.126.com
* date : 2025/04/3
* brief : 进程A,用于对共享内存中的数据进行修改
* note : None
*
* CopyRight(c) 2025 zzlyx1239.126.com All Reserved
***************************************************/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
char *pshm;
void sign_hander(int)
{
sprintf(pshm,"I am ProcessA,My PID = %d",getpid());
}
int main()
{
//1.打开共享内存段,如果不存在则创建,如果存在则打开
int shm_id = shmget(ftok(".",10),256,IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0644);
if (-1 == shm_id)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmget error,errno:%d,%s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
shm_id = shmget(ftok(".",10),256,0644);
}
//2.把共享内存段连接到进程空间 shmat() 默认是可读可写 默认会初始化为0
pshm = (char *)shmat(shm_id,NULL,0);
if (pshm == (void *)-1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmat error,errno:%d,%s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//3.向共享内存中写入数据
signal(SIGUSR1,sign_hander);
while(1);
shmdt(pshm);
return 0;
}
进程B
/***************************************************
*
* file name: shmB.c
* author : zzlyx1239.126.com
* date : 2025/04/3
* brief : 进程B,用于对共享内存中的数据进行修改
* note : None
*
* CopyRight(c) 2025 zzlyx1239.126.com All Reserved
***************************************************/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
char *pshm;
void sign_hander(int)
{
sprintf(pshm,"I am ProcessB,My PID = %d",getpid());
}
int main()
{
//1.打开共享内存段,如果不存在则创建,如果存在则打开
int shm_id = shmget(ftok(".",10),256,IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0644);
if (-1 == shm_id)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmget error,errno:%d,%s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
shm_id = shmget(ftok(".",10),256,0644);
}
//2.把共享内存段连接到进程空间 shmat() 默认是可读可写 默认会初始化为0
pshm = (char *)shmat(shm_id,NULL,0);
if (pshm == (void *)-1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmat error,errno:%d,%s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//3.向共享内存中写入数据
signal(SIGUSR2,sign_hander);
while(1);
shmdt(pshm);
return 0;
}
进程C
/***************************************************
*
* file name: shmC.c
* author : zzlyx1239.126.com
* date : 2025/04/3
* brief : 进程C,用于对共享内存中的数据进行修改
* note : None
*
* CopyRight(c) 2025 zzlyx1239.126.com All Reserved
***************************************************/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
int main()
{
//1.打开共享内存段,如果不存在则创建,如果存在则打开
int shm_id = shmget(ftok(".",10),256,IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0644);
if (-1 == shm_id)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmget error,errno:%d,%s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
shm_id = shmget(ftok(".",10),256,0644);
}
//2.把共享内存段连接到进程空间 shmat() 默认是可读可写 默认会初始化为0
char *pshm = (char *)shmat(shm_id,NULL,0);
if (pshm == (void *)-1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmat error,errno:%d,%s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//3.手动输入进程A和进程B的pid
int PidA, PidB;
printf("please input the PID of processA\n");
scanf("%d", &PidA);
printf("please input the PID of processB\n");
scanf("%d", &PidB);
while(1)
{
// 给进程A发送信号
kill(PidA, SIGUSR1);
sleep(2);
// 输出读到的数据
printf("%s\n", pshm);
// 给进程B发送信号
kill(PidB, SIGUSR2);
sleep(2);
// 输出读到的数据
printf("%s\n", pshm);
}
shmdt(pshm);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号