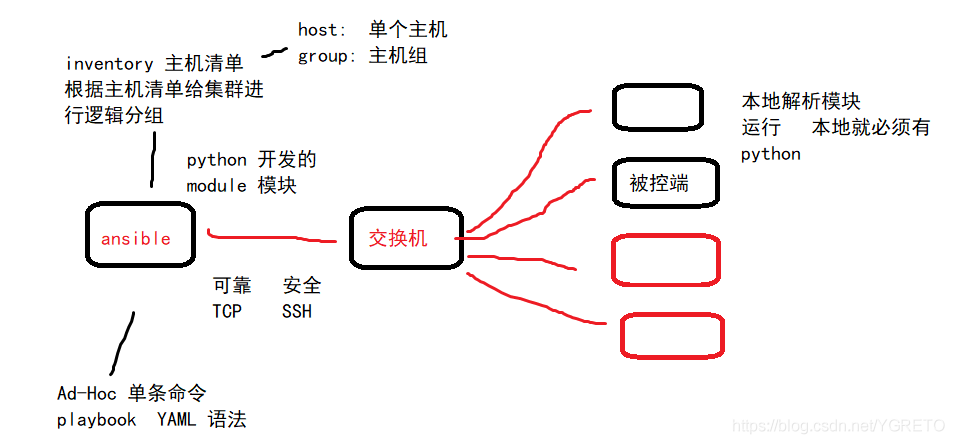
Ansible
Ansible
- 批管理工具,python 开发
- 组织架构
1. 免密互联
- 多台主机之间实现批量管理,需要免密码,免交互
#!/bin/bash
. /etc/init.d/functions
for ip in {5,6,7,8,9,31,41,51,71,81}
do
sshpass -p123456 ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@172.16.1.$ip -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
action "主机172.16.1.$ip" /bin/true
echo ""
else
action "主机172.16.1.$ip" /bin/false
echo ""
fi
done
2. 安装使用
1. 安装
yum install ansible -y
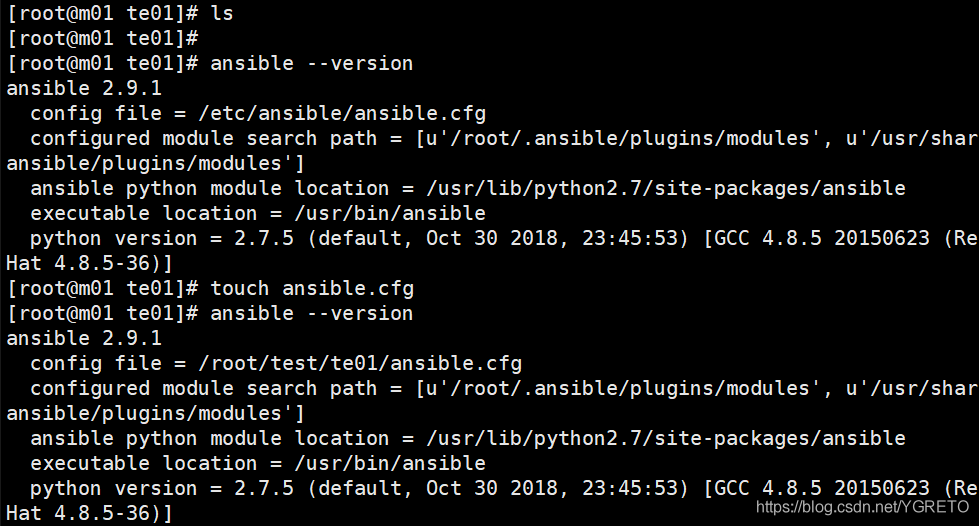
[root@salt01 ~]# ansible --version
ansible 2.9.13
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = [u'/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Apr 2 2020, 13:16:51) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39)]
ansible 的具体使用可以根据他的配置文件来定义,从而实现多项目之间的"隔离"
- ansible 配置文件查找优先级
| 1. ANSIBLE_CONFIG | 是个变量 |
| 2. ~/ansible.cfg | |
| 3. ~/.ansible.cfg | 不常用 |
| 4. /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg | 优先级最低 |
2. 使用
- 隔离
1. 项目之间 以目录间隔,通过修改 ansible.cfg 文件,使隔离
mkdir 项目{1..4} -p
cp /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg 项目1/
cp /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg 项目2/
vim ansible.cfg
inventory = ./hosts
- 定义主机清单
cat hosts
[web]
10.0.0.1
10.0.0.2
ansible web -m ping -i /etc/ansible/hosts
不写hosts文件就 -i指定 hosts文件位置
ansible web -m command -a "df -h"
3. Ad-Hoc
- 即:具体某一模块的playbook的书写方法
- 例:
ansible-doc yum:搜索/EX - 最初的 playbook的书写版本:
- hosts: all
vars:
file_name: xxx
tasks:
- name:
shell:
4. yaml 书写格式
缩进: [强制缩进2空格]
冒号: 以冒号结尾的除外,其他所有冒号后面所有的必须有空格
短横线
- hosts: all [ play 阶段 ]
- tasks: [tasks 阶段]
4.1 常用模块
- 模块:
https://blog.csdn.net/YGRETO/article/details/103575410
5. 剧本的执行原则
检查语法:
ansible-playbook --syntax-check main.yml
模拟执行执行剧本:
ansible-playbook -C main.yml
执行剧本:
ansible-playbook main.yml
建议写一段,执行一段
6. Variables 变量
- 变量有三种:
- 定义变量
- fact变量
- 变量注册
1. 优先级
1.extra
2.playbook
2.1) vars_files
2.2) vars
3.inventory
3.1) host_vars
3.2) group_vars
3.3) group_all
2. 定义变量
- 通过var进行定义变量 [ 只能用在一个主机 ]
- host: web
vars:
- xxx: XXXXX <--与全局定义 也可以在某任务定义
tasks:
.....
- 通过vars_ files来进行定义变量 [ 文件里定义变量,多个主机共享文件,各自调用需要的变量 ]
- hosts: web
vars_files: var.yml <--定义变量的文件
tasks:
- name: touch new files
file:
path: "/tmp/{{ play_var1 }}"
state: touch
----------------------------------
在同一目录下 创建 var.yml 文件 格式如下:
play_var1: play_var1_sb1
- 通过inventory主机清单 [ hosts文件 ] 进行变量定义
用的少
vim ~/hosts
[web]
172.16.1.7
172.16.1.8
[web:vars]
xxx=XXX ---> 定义的变量
- 通过host_ vars对主机进行定义
mkdir host_vars
vim host_vars/172.16.1.7 (或域名) [ 只针对 7 这台主机生效 ]
bianliang: XXX
vim host_vars/172.16.1.8 [ 只针对 8 这台主机生效 ]
bianliang: xxx1
因此可以应用于: keepalived : 一个变量名,不同的变量值
- 通过group_ vars对主机组进行定义
针对hosts的 web 这个组的 所有主机
mkdir group_vars
主机组:
vim group_vars/web
bianliangming: xxx
特殊的: 针对所有的主机组
vim group_vars/all
bianliangming: xxx
- 通过执行playbook时使用-e参数指定变量
剧本中写的变量(没有被定义的),在执行命令的时候定义
在命令行执行
ansible-playbook play.yml -e "XXX=xxx" [ xxx ]:被赋予的值
3. 注册变量
- 注册变量:register
- 当执行剧本的时候,里面有 命令的使用 ,只会显示 change 不会显示具体的内容 ,需要通过变量注册 把命令显示的内容赋值给 register ,然后把 register 打印出来
- 例:
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name:
shell: netstat -lnp
register: System_state
- name: Get System_state
debug: msg={{ System_state }}
将netstat-lnp 赋予 system_state 的 变量名
debug 打印出值
4. fact变量
- ansible 的内置变量
- 全部facts 变量
ansible localhost -m setup
例子:redis 的使用:
配置文件的监听内网的ip地址
bind 172.0.0.1 {{ ansible_eth1.ipv4.address }}
- 常用的facts变量:
https://blog.csdn.net/YGRETO/article/details/103611697 - 全部的facts变量:
https://blog.csdn.net/YGRETO/article/details/104807813
7. 循环
- name: Copy Rsync Configure
copy:
src: "{{ item.src }}" 【src: 变量名】
dest: "{{ item.dest }}" 【dest: 变量名】
mode: "{{ item.mode }}" 【mode: 变量名】
loop: 【下边是字典】
- { src: ./rsyncd.conf.j2 , dest: /etc/rsyncd.conf , mode: '0644' }
【此处src 是 引用上层的变量】
- { src: ./rsync.passwd.j2 , dest: /etc/rsync.passwd , mode: '0600' }
notify: Restart Rsync Server
- name: Systemd Httpd Server
systemd:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: started
enabled: yes
loop: 【下边是列表】
- httpd
- firewalld
8. 判断
1.根据不同的操作系统,安装不同的软件
[root@manager ~/ansible_variables]# cat play_14.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Installed Httpd Server Centos
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
when: ( ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu" )
[root@manager ~/ansible_variables]# cat play_14.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Installed Httpd Server Centos
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
when: ( ansible_distribution == "CentOS" ) and
( ansible_distribution_major_version == "7")
- name: Installed Httpd Server Centos
yum:
name: httpd2
state: present
when: ( ansible_distribution == "CentOS" ) or
( ansible_distribution_major_version != "6")
2.根据不同的主机名称,配置不同的源 all--> web--->nginx_repo
[root@manager ~/ansible_variables]# cat play_15.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: This is when repo
yum_repository:
name: oldxu
description: oldxu
baseurl: http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck: no
when: ( not ansible_hostname is match ("web*") )
9. Handlers
- 触发器 Handlers :
- 特殊Tasks
- 不会被正常的TASKS调用。
- 当有 notify 调用时,才会被执行。
- 无论Handlers被调用多少次,最终只会在正常的Tasks结束后,才执行
- 当遇到多次调用 handlers , handlers 也只执行一次,
当前几个调用的 handlers成功 ,最后一个失败了 ,handlers 也不会触发,[当然也可以强制触发[错误处理里]]
task 文件
- name: config conf
copy:
src:
dest:
notify: restart nginx server [名字一致]
handlers 文件
- name: restart nginx server [名字一致]
systemd:
name: nginx
state: restarted
错误处理
通常 task失败, play 中止,任何在前面被tasks notify的 handlers 都不会执行,
如果 在play中设置了 `force_handlers: yes` handlers 就会强制执行
- hosts: all
force_handlers: yes
tasks:
- name:
。。。。。。。。
10.Tag
- 可以将 tasks 与标签捆绑 --> 可以针对指定的tag 执行
- 可以 tasks 对应一个tag标签 也可以多个 tag标签
例子:[tasks 文件]
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: install
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
tag: installed
使用:tasks较多时,可以针对 指定的tasks 调试
1. 指定 这个标签执行:ansible-playbook main.yml -t installed
2. 指定 除了这个标签都执行:ansible-playbook main.yml --skip-tags installed
11. include 包含
应用: 多个tasks 任务遇到一个相同的任务
注意: 要包含的这个文件是tasks 任务 没有play 主机
例子:
要包含的文件
vim restart_nginx.yml
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
tasks 任务:
- hosts:
tasks:
- name:
command:
- name: restart nginx
include: restart_nginx.yml
12. Ignore_errors 忽略错误
- 应用: 当有tasks 执行失败 ,后续的task 也无法执行,可以 忽略错误 继续执行下面的 task
- hosts:
tasks:
- name:
command:
Ignore_errors: yes
13. change_when
- 没写
14. jianja2
jianja 循环
原先:
upstream cloud {
server 172.16.1.7:80
server 172.16.1.8:80
}
现在: 循环循的是 hosts文件 的web 组
upstream {{ cloud }} {
{% for host in groups['web'] %} 本质也是 for 循环
server {{ host }}:80;
{% endfor %}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name {{ cloud }};
location / {
proxy_pass http://{{ cloud }}
}
}
可以在 group/all 里定义变量 cloud: cloud.zhang.com
jianja 判断
- keepalived
global_defs {
router_id {{ ansible_hostname }}
}
vrrp_instance VIP_1 {
{% if ansible_hostname == "lb01" %}
state MASTER
priority 150
{% elif ansible_hostname == "lb02" %}
state BACKUP
priority 100
{% endif %}
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 1
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.3
}
}
15. Role角色
- 有目录结构的规划 ( 必须的 )
- 大型项目一律 role
- playbook 的 ”规范“
目录结构:
文件一般自己创建
命令获得: ansible-galaxy init nginx
nginx: [ 叫角色 ]
tasks -- tasks 任务
main.yml
handlers -- 触发器
main.yml
vars -- 变量
main.yml
templates -- 模板文件
main.yml
meta -- 依赖关系
files -- 文件 tar | zip
ansible.cfg 角色/ hosts top.yml group/all
vim top.yml
- hosts: web
roles:
- role: 顶层角色 [依赖着nginx 和php 就只写这一个角色就行]
- hosts: lb
- roles:
- role: a
16.模板
- 上面有Keepalived的模板
- nginx_万能模板 :
https://blog.csdn.net/YGRETO/article/details/103672398 - 基础环境的模板
- 包含了:系统的基础优化和ssh 优化
- 见下:
目录结构;
base:
tasks
main.yml
templates
sshd_config.j2
main.yml : base基础优化:`https://blog.csdn.net/YGRETO/article/details/104821207`
sshd_config.j2 : https://blog.csdn.net/YGRETO/article/details/104821569


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号