WordCount
2018-03-23 14:12 萌萌哒的小泽 阅读(260) 评论(1) 收藏 举报1、github链接:https://github.com/xiaozemmd/WordCount
2、psp表格如下:
|
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时 |
实际耗时 |
|
(分钟) |
(分钟) |
||
|
Planning |
计划 |
10 |
10 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
30 |
|
Development |
开发 |
40 |
60 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
60 |
100 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
60 |
100 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
40 |
50 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
60 |
40 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
100 |
60 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
300 |
200 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
50 |
50 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
100 |
120 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
70 |
80 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
80 |
120 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
50 |
50 |
|
|
合计 |
890 |
1120 |
3、解题思路:本次测试需要自己编码,本来计数器并不是一个很难的项目,但是迫于java并不是很熟悉,代码部分只能参考已完成的,自己则完成测试部分。
4、测试:按要求测试一段文字中的字符数、单词总数、总行数,并输出到指定文件中:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的单词总数
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的总行数
wc.exe -o outputFile.txt //将结果输出到指定文件outputFile.txt
并完成高级功能:
wc.exe -s //递归处理目录下符合条件的文件
wc.exe -a file.c //返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)
wc.exe -e stopList.txt // 停用词表,统计文件单词总数时,不统计该表中的单词
5、代码分析:此次代码引用的邹会江同学的代码。
(1)统计字符数:
public int charCounts(File f) throws Exception{
String str;
int charCount = 0;
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));//当前工程目录下
while((str=br.readLine())!=null){
charCount += str.length();
}
File fs=new File("result.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fs, true);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.println(f.getName()+",字符数: "+charCount);
pw.flush();//flush实际上就是将所有的写入的流,一次性输出到文件中,之后进行关闭即可。如果没关闭流,也没进行flush,此时的内容并未写入到文件的。
fw.flush();
pw.close();
fw.close();
return charCount;
(2)统计单词数:
public int wordCounts(File f) throws Exception{
String str;
int wordCount = 0;
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
while((str=br.readLine())!=null){
wordCount += str.split(",| ").length;
}
File fs=new File("result.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fs, true);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.println(f.getName()+",单词数: "+wordCount);
pw.flush();//flush实际上就是将所有的写入的流,一次性输出到文件中,之后进行关闭即可。如果没关闭流,也没进行flush,此时的内容并未写入到文件的。
fw.flush();
pw.close();
fw.close();
return wordCount;
(3)统计总行数:
public int lineCounts(File f) throws Exception{
String str;
int lineCount = 0;
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
while((str=br.readLine())!=null){
lineCount++;
}
File fs=new File("result.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fs, true);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.println(f.getName()+",总行数: "+lineCount);
pw.flush();//flush实际上就是将所有的写入的流,一次性输出到文件中,之后进行关闭即可。如果没关闭流,也没进行flush,此时的内容并未写入到文件的。
fw.flush();
pw.close();
fw.close();
return lineCount;
(4)递归处理目录下符合条件的文件
public ArrayList<File> recursion(String filedir) throws Exception{
//ArrayList<File> listFiles=new ArrayList<File>();
File file=new File(filedir);
File []files=file.listFiles();
if(files==null)return null;
for(File f:files){
if(f.isFile()){
if(f.getName().endsWith(".c")){
fileList.add(f);
}
}else if(f.isDirectory()){
recursion(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
return fileList;
}
(5)public void complex(File f) throws Exception{
String str;
boolean nodeflag = false;
int codeLine = 0;
int spaceLine = 0;
int nodeLine = 0;
BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
while((str=br.readLine())!=null){
if(str.matches("\\s*/\\*.*")&&str.matches(".*\\*/\\s*")){
nodeLine++;
continue;
}
else if(str.matches("\\s*|}\\s*|\\{\\s*")){
spaceLine++;
}
else if(str.matches("//.*")){
nodeLine++;
}else if(str.matches("\\s*/\\*.*")){
nodeLine++;
nodeflag = true;
}else if(str.matches(".*\\*/\\s*")){
nodeLine++;
nodeflag = false;
}else if(nodeflag)nodeLine++;
else codeLine++;
}
File fs=new File("result.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fs, true);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.println(f.getName()+",代码行/空行/注释行: "+codeLine+"/"+spaceLine+"/"+nodeLine);
pw.flush();//flush实际上就是将所有的写入的流,一次性输出到文件中,之后进行关闭即可。如果没关闭流,也没进行flush,此时的内容并未写入到文件的。
fw.flush();
pw.close();
fw.close();
}
(6)停用词表:
public void stopWords(File f) throws Exception{
String str;
int wordCount=0;
int stopWord=0;
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
while((str=br.readLine())!=null){
String []line= str.split(",| ");
wordCount+=line.length;
for(int i=0;i<line.length;i++){
if(line[i].equals("while"))stopWord++;
if(line[i].equals("if"))stopWord++;
if(line[i].equals("switch"))stopWord++;
}
}
int count =wordCount-stopWord;
File fs=new File("result.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fs, true);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.println(f.getName()+",单词数: "+count);
pw.flush();//flush实际上就是将所有的写入的流,一次性输出到文件中,之后进行关闭即可。如果没关闭流,也没进行flush,此时的内容并未写入到文件的。
fw.flush();
pw.close();
fw.close();
}
(7)main函数:
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
Chance zhj=new Chance();
int n= args.length;
boolean sj = false;
boolean ej = false;
String filename=null;
String outputname= args[n-1];
for(int i=0; i<args.length; i++){
if(args[i].equals("-s")){
sj= true;
}
if(args[i].equals("-e")){
ej= true;
}
}//判断是否递归获取当前目录下的文件,和是否使用停用词表
for(int i=0; i<args.length; i++){
if(args[i].endsWith(".c")){
filename=args[i];
}
}
File g = new File(filename);
//记录操作目标文件
if(sj){
zhj.fileList=zhj.recursion(".");//当前工程目录
for(int i=0; i<args.length; i++){
if(args[i].equals("-a")){
for(File f:zhj.fileList){
zhj.complex(f);
}
}
if(args[i].equals("-l")){
for(File f:zhj.fileList){
zhj.lineCounts(f);
}
}
if(args[i].equals("-c")){
for(File f:zhj.fileList){
zhj.charCounts(f);
}
}
if(args[i].equals("-w")){
if(ej){
for(File f:zhj.fileList){
zhj.stopWords(f);
}
}else{
for(File f:zhj.fileList){
zhj.wordCounts(f);
}
}
}
if(args[i].equals("-o")){
String str;
File fs=new File(outputname);
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter(fs,true);
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(fw);
//读取result.txt文件
BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(new FileReader("result.txt"));
while((str=br.readLine())!=null){
//将数据复制到output.txt文件中
pw.println(str);
}
pw.flush();//flush实际上就是将所有的写入的流,一次性输出到文件中,之后进行关闭即可。如果没关闭流,也没进行flush,此时的内容并未写入到文件的。
fw.flush();
pw.close();
fw.close();
}
}
}
if(!sj){
for(int i=0; i<args.length; i++){
if(args[i].equals("-a")){
zhj.complex(g);
}
if(args[i].equals("-c")){
zhj.charCounts(g);
}
if(args[i].equals("-w")){
if(ej){
zhj.stopWords(g);
}else{
zhj.wordCounts(g);
}
}
if(args[i].equals("-l")){
zhj.lineCounts(g);
}
if(args[i].equals("-o")){
String str;
File fs=new File(outputname);
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter(fs,true);
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(fw);
//读取result.txt文件
BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(new FileReader("result.txt"));
while((str=br.readLine())!=null){
//将数据复制到output.txt文件中
pw.println(str);
}
pw.flush();//flush实际上就是将所有的写入的流,一次性输出到文件中,之后进行关闭即可。如果没关闭流,也没进行flush,此时的内容并未写入到文件的。
fw.flush();
pw.close();
fw.close();
}
}
}
}
}
利用exe4j将jar包转换成exe文件,通过控制台调用exe文件并对其传参:
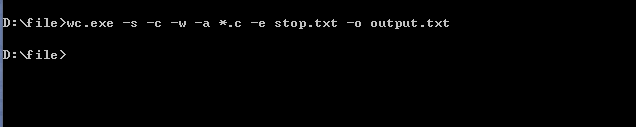

参考文献:
https://blog.csdn.net/sunkun2013/article/details/13167099
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/10/22/2220872.html
手把手教你如何把jar文件,打包成jar文件以及转换为exe可执行文件


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号