移除元素
第一个想法就是利用两个for循环暴力解决
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int size = nums.size();
int writeIndex = 0; // 用来记录当前应该写入的索引位置
for (int readIndex = 0; readIndex < size; readIndex++) {
if (nums[readIndex] != val) { // 发现不需要移除的元素,则写入到当前位置
nums[writeIndex] = nums[readIndex];
writeIndex++; // 写入位置后移
}
}
return writeIndex; // 返回新的数组大小
}
};
int main() {
// 示例输入
vector<int> nums = {3, 2, 2, 3};
int val = 3;
// 创建Solution对象并调用removeElement函数
Solution solution;
int newLength = solution.removeElement(nums, val);
// 输出结果
cout << "New array size: " << newLength << endl;
cout << "New array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < newLength; i++) {
cout << nums[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
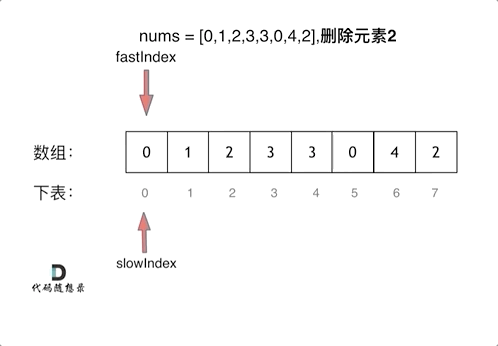
第二个双指针法(快慢指针法): 通过一个快指针和慢指针在一个for循环下完成两个for循环的工作。
定义快慢指针
快指针:寻找新数组的元素 ,新数组就是不含有目标元素的数组
慢指针:指向更新 新数组下标的位置
#include <stdio.h>
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val) {
int i = 0; // 指向当前有效元素的下一个位置
for (int j = 0; j < numsSize; j++) {
if (nums[j] != val) {
nums[i] = nums[j]; // 将不等于val的元素移到前面
i++; // 有效元素个数增加
}
}
return i; // 返回新数组的长度
}
int main() {
int nums[] = {3, 2, 2, 3};
int val = 3;
int numsSize = sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0]);
int newLength = removeElement(nums, numsSize, val);
printf("新的数组长度为: %d\n", newLength);
for (int i = 0; i < newLength; i++) {
printf("%d ", nums[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号