Java 多线程 学习笔记(2021.10.13~17)
多线程
一、线程简介
任务、进程、线程、多线程
1. 多任务
同时进行两个任务:边玩游戏边听歌
2. 多线程
一条路只能走一辆车,想要一条路走两辆车需要分出很多道,这样太能同时开两辆车(类比)
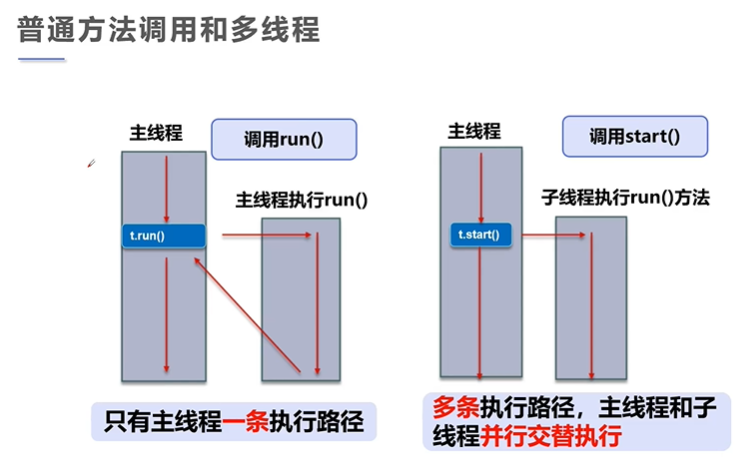
3. 普通方法和多线程
4. 程序、进程、线程
- 运行的程序就是进程
- 一个进程可以有多个线程,如:视频中可以同时看图像,听声音,看弹幕。
- 进程包含至少一个线程,如果是模拟出的多线程,即在一个CPU中快速切换,感觉到是同时执行
5. 核心概念
- 线程就是独立的执行路径;
- 在程序运行时,即使没有自己创建线程,后台也会有多个线程,如主线程,gc线程;main()称之为主线程,为系统的入口,用于执行整个程序;
- 在一个进程中,如果开辟了多个线程,线程的运行由调度器安排调度,调度器是与操作系统紧密相关的,先后顺序是不能认为的干预的。
- 对同一份资源操作时,会存在资源抢夺的问题,需要加入并发控制;线程会带来额外的开销,如cpu调度时间,并发控制开销。
- 每个线程在自己的工作内存交互,内存控制不当会造成数据不一致
二、线程创建
1. 三种创建方式
-
Thread class:继承Thread类(重点)
-
package com.xiaowei9s.lesson01; //创建线程方式一:继承Thread类,重写run方法,调用start开启线程 //总结:线程不一定start后直接执行,由CPU调度 public class ThreadTest1 extends Thread { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadTest1 threadTest1 = new ThreadTest1(); threadTest1.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) { System.out.println("main"+i); } } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) { System.out.println("run"+i); } } } -
Runnable接口:实现Runnable接口(重点)
-
package com.xiaowei9s.lesson01; //创建线程方式一:继承Thread类,重写run方法,调用start开启线程 //总结:线程不一定start后直接执行,由CPU调度 public class ThreadTest3 implements Runnable { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadTest3 threadTest3 = new ThreadTest3(); new Thread(threadTest3).start(); for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) { System.out.println("main"+i); } } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) { System.out.println("run"+i); } } }初时多并发:
package com.xiaowei9s.lesson01; //多个线程同时操作一个对象 //发现问题,线程不安全了 //模拟同时买票 public class ThreadTest4 implements Runnable { private int ticketNum=10; public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadTest4 tt1 = new ThreadTest4(); ThreadTest4 tt2 = new ThreadTest4(); new Thread(tt1,"小明").start(); new Thread(tt1,"老师").start(); new Thread(tt1,"黄牛").start(); } @Override public void run() { while (ticketNum>=0){ try { Thread.sleep(200); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到了第"+ticketNum+"号票"); ticketNum--; } } }龟兔赛跑
package com.xiaowei9s.lesson01; //龟兔赛跑 //跑一百米 //兔子睡觉并且输掉游戏 public class ThreadTest5 implements Runnable{ private String winner; public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadTest5 threadTest5 = new ThreadTest5();//共用一个对象 new Thread(threadTest5,"兔子").start(); new Thread(threadTest5,"乌龟").start(); } private boolean gameOver(int step){//是否结束游戏 if (winner!=null){ return true; } if (step==0){ winner = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println(winner+"赢了"); return true; } return false; } @Override public void run() { int step = 100;//虽然共用一个对象,但是方法是两个,每个线程调用方法时方法时独立得方法,方法内的资源不共用 while(true){ try {//延时 Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if(gameOver(step)){ break; } if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("兔子")&&step%10==0){//兔子跑十下休息以下 try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"还剩"+step+"步"); step--; } } } -
Callable接口:实现Callable接口(了解)
-
package com.xiaowei9s.lesson01; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URL; import java.util.concurrent.*; /* 线程创建方式三,实现Callable接口 优势: 1. 自定义返回值类型 2. 可以抛出异常 */ public class ThreadTest6 implements Callable<Boolean> { public ThreadTest6(String name, String url) { this.name = name; this.url = url; } public String name; public String url; public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { //创建线程池 ExecutorService exs = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); //提交线程 Future<Boolean> submit = exs.submit(new ThreadTest6("1.jpg", "https://pics6.baidu.com/feed/42a98226cffc1e17b881c7a94554b40a728de9bd.jpeg?token=6f6f69fad743d5bf129581dcbe35269f")); Future<Boolean> submit1 = exs.submit(new ThreadTest6("2.jpg","https://pics1.baidu.com/feed/4b90f603738da97767ecd34db795ba108418e3e6.jpeg?token=2695638344602480017c59554e078749")); Future<Boolean> submit2 = exs.submit(new ThreadTest6("3.jpg","https://pics3.baidu.com/feed/377adab44aed2e73899a0cee8ac5e38285d6faca.jpeg?token=2bc485aa1ae4cea267fb997488b209d5")); //获得线程结果 Boolean aBoolean = submit.get(); Boolean aBoolean1 = submit1.get(); Boolean aBoolean2 = submit2.get(); //关闭服务 exs.shutdownNow(); } @Override public Boolean call() throws Exception { MyDownloader downloader = new MyDownloader(); downloader.download(url,name); return true; } class MyDownloader{ public void download(String url,String name){ try { FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name)); System.out.println(name); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
推荐使用Runnable接口,因为Runnable接口可以解耦,继承Thread类有局限性
三、静态代理
让主要的类专注于处理实现关键功能,例如
new Thread(()->System.out.println("run()方法中的事情")).start();
package com.xiaowei9s.lesson02;
public class StaticMode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ToolMan toolMan = new ToolMan(new You());
toolMan.toDo();
}
}
class You implements Work{
@Override
public void toDo() {
System.out.println("你做了关键的事情");
}
}
class ToolMan implements Work{
public ToolMan(Work toWork) {
this.toWork = toWork;
}
public Work toWork;//把工具人帮助的人加入工具人,两个人实现了同一个接口就是静态代理
@Override
public void toDo() {
System.out.println("工具人先做了辅助的事情");
toWork.toDo();
}
}
interface Work{
public void toDo();
}
四、Lambda表达式
- 函数式接口:只包含唯一一个抽象方法,它就是一个函数式接口
- 对于函数式接口,我们可以使用Lambda表达式创建该接口的对象
package com.xiaowei9s.lesson02;
//逐渐导出Lambda表达式
//实现类->匿名内部类->Lambda表达式
public class LambdaDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类
FunMode fm = new FunMode() {
@Override
public void toDo() {
System.out.println("使用匿名内部类实现");
}
};
fm.toDo();
new Test1().toDo();
//Lambda表达式
fm = ()-> System.out.println("使用Lambda表达式实现");
fm.toDo();
}
interface FunMode{//函数式接口
public void toDo();
}
}
///使用实现类
class Test1 implements LambdaDemo.FunMode {
@Override
public void toDo() {
System.out.println("使用实现类实现");
}
}
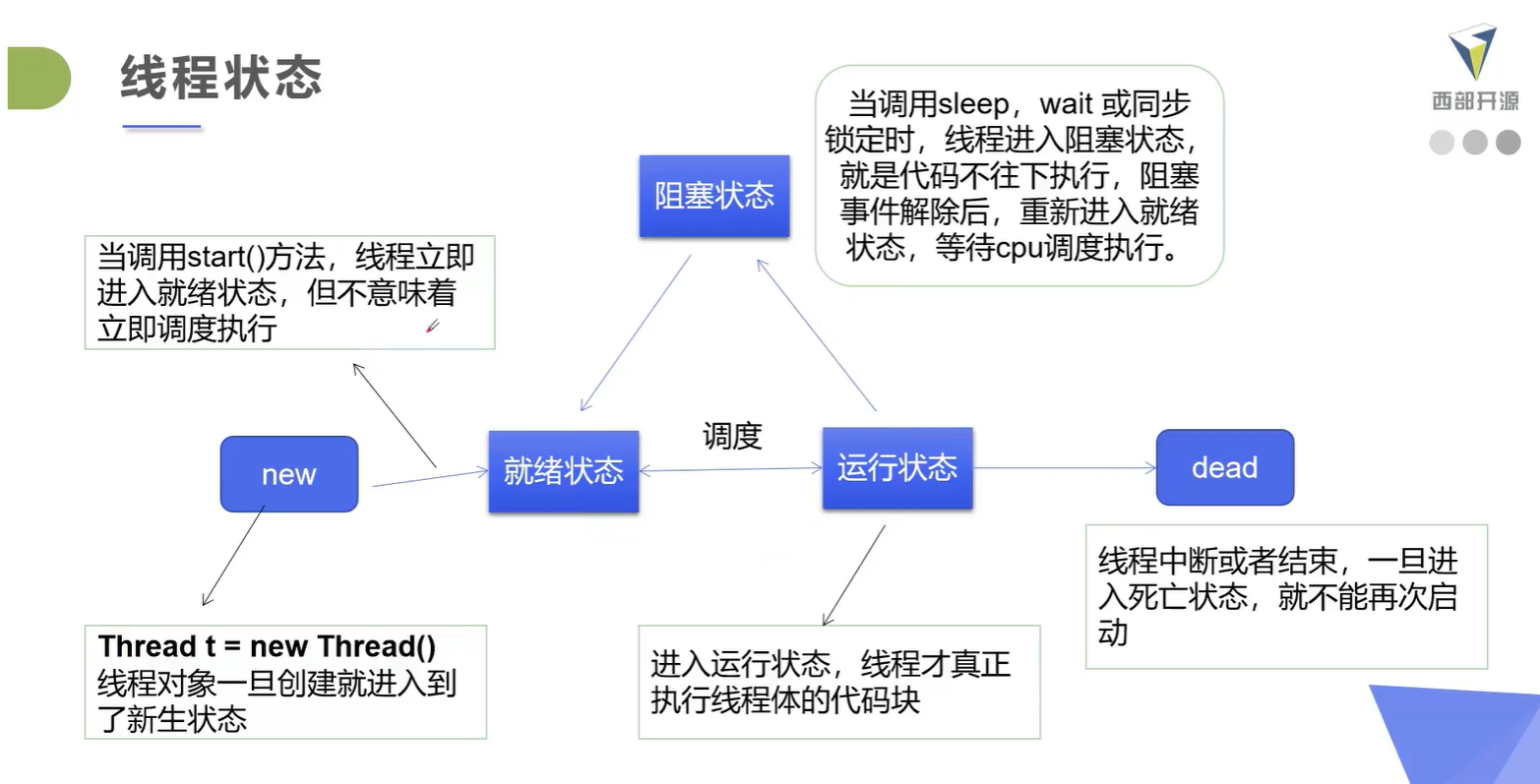
五、线程停止
线程状态:
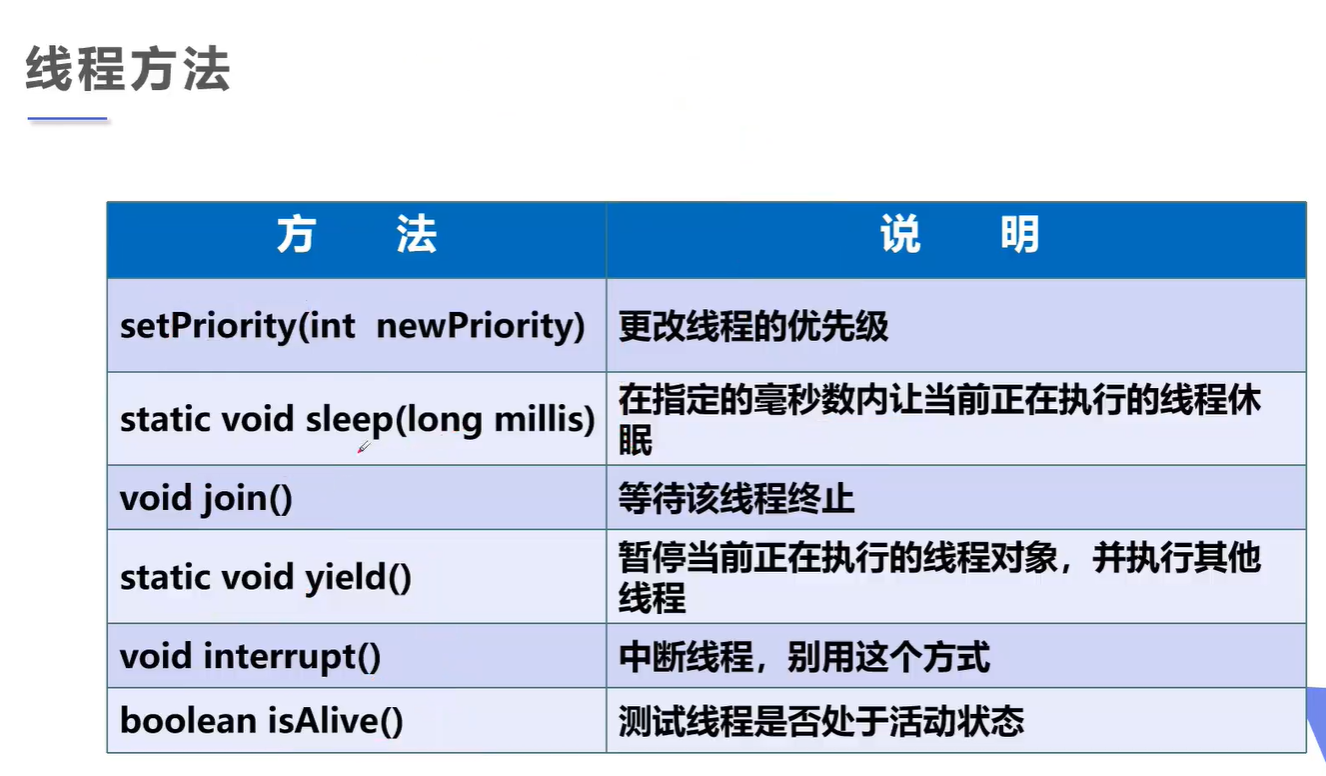
线程方法:
1. 停止线程的方法
-
官方不建议使用JDK中的方法
-
使用一个停止标志位实现线程停止
-
package com.xiaowei9s.lession03; public class TestStop { public static void main(String[] args) { Arun arun = new Arun(); new Thread(arun).start(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { if (i==500){ arun.stop(); System.out.println("stop"); } System.out.println(i); } } } class Arun implements Runnable{ private boolean isStop = true; @Override public void run() { int i = 0; while (isStop){ System.out.println("I am running..."+i++); } System.out.println("ji"); } public void stop(){ this.isStop = false; } }
六、线程休眠
- sleep(时间)表示当前线程休眠时间,单位:毫秒
- sleep存在异常InterruptedExpection;
- sleep时间达到后,线程重新进入就绪状态;
- sleep可以模拟网络延时、倒计时等等;
- 每一个对象都有锁,sleep不会释放锁;(记住、不用理解)
Demo:模拟网络延迟:
package com.xiaowei9s.lession03;
//模拟网络延迟
public class TestSleep implements Runnable{
public int ticket = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestSleep testSleep = new TestSleep();
new Thread(testSleep,"小明").start();
new Thread(testSleep,"小红").start();
new Thread(testSleep,"老师").start();
new Thread(testSleep,"黄牛").start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (ticket>=0){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->买了第"+ticket+"号票");
ticket--;
}
}
}
Demo:模拟时钟:
package com.xiaowei9s.lession03;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestTime {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
while (true){
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(date));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
七、线程礼让
- 让当前进程从运行变成就绪状态
- 当前进程不阻塞,依然拥有资源
- 不一定了礼让成功,变成就绪的起跑线,cpu依然有可能让礼让的线程重新进入运行
package com.xiaowei9s.lession03;
public class TestYeild {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new MyYield(),"A").start();
new Thread(new MyYield(),"B").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始");
Thread.yield();//礼让
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程结束");
}
}
八、线程强制执行(线程插队)
直接加入指定进程,插队!
package com.xiaowei9s.lession03;
public class TestJoin implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
if (i==150){
thread.join();
}
System.out.println(i+"main");
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
九、线程状态检测
线程在停止后,不能再次start()。
package com.xiaowei9s.lession03;
public class TestState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("THE END");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();
while (state!=Thread.State.TERMINATED){
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
十、线程优先级
数字越小,优先级越低,10优先级最高
main线程默认优先级是5
优先级只是意味着cpu调度概率,优先级低也有概率会先执行
优先级设置在start之前
package com.xiaowei9s.lession03;
public class TestPriority implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestPriority testPriority = new TestPriority();
Thread a = new Thread(testPriority, "a");
Thread b = new Thread(testPriority, "b");
Thread c = new Thread(testPriority, "c");
Thread d = new Thread(testPriority, "d");
Thread e = new Thread(testPriority, "e");
Thread f = new Thread(testPriority, "f");
Thread g = new Thread(testPriority, "g");
Thread h = new Thread(testPriority, "h");
Thread i = new Thread(testPriority, "i");
System.out.println("main-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
a.setPriority(1);
b.setPriority(2);
c.setPriority(3);
d.setPriority(4);
e.setPriority(6);
f.setPriority(7);
g.setPriority(8);
h.setPriority(9);
a.start();
b.start();
c.start();
d.start();
e.start();
f.start();
g.start();
h.start();
i.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("this Thread"+Thread.currentThread().getName()
+"-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
十一、守护线程Deamon
一旦线程被设置成守护线程,则主线程不会等待守护线程结束。
使用方法
thread.setDeamon(true);//将该线程设置成守护线程
Demo:
package com.xiaowei9s.lession03;
public class TestDeamon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
You you = new You();
God god = new God();
Thread gt = new Thread(god);
gt.setDaemon(true);
gt.start();
new Thread(you).start();
}
}
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 35000; i++) {
System.out.println("你活了:" + i + "天");
}
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("你的家人朋友守护着你");
}
}
}
十二、线程同步机制
多个线程操作一个资源
1. 并发
同一个对象被多个线程同时操作
在处理线程时多个线程同时访问一个对象,这个时候我们需要线程同步。
线程同步其实就是等待机制,多个线程进入该对象的线程池中等待形成队列,进行顺序访问。
2. 队列和锁
队列:保证访问顺序
锁:保证对象同一时间只能有一个对象访问
锁机制:synchronized,主要就是排它锁
3. 性能问题
进行线程同步会导致性能下降和优先级倒置问题
4. 三大不安全案例
-
不安全的买票
-
package com.xiaowei9s.syn; public class UnsafeTicket { public static void main(String[] args) { BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket(); new Thread(buyTicket,"小明").start(); new Thread(buyTicket,"小黄").start(); new Thread(buyTicket,"小红").start(); } } class BuyTicket implements Runnable{ int numTicket = 10; boolean flag = true; //买票 public void buy(){ if (numTicket<=0){ flag = false; } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买到了"+numTicket--+"票"); } @Override public void run() { while (flag){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } buy(); } } } -
不安全的取钱
-
package com.xiaowei9s.syn; public class UnsafeBank { public static void main(String[] args) { Account account = new Account("结婚基金", 1000); Drawing d1 = new Drawing(account, 500, "老公"); Drawing d2 = new Drawing(account, 800, "老婆"); d1.start(); d2.start(); } } //账户 class Account{ public String name; public int monny; public Account(String name , int monny){ this.name = name; this.monny = monny; } } //银行取钱 class Drawing extends Thread{ Account account; int nowMonny; int getMonny; public Drawing(Account account, int getMonny, String name){ super(name); this.account = account; this.getMonny = getMonny; } //取钱 @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (account.monny - getMonny < 0){ System.out.println("账户里还有" + account.monny + "元,钱不够了"); return; } nowMonny += getMonny; account.monny -= getMonny; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取了" + getMonny+"元,还剩"+account.monny+"元,现在ta有" + nowMonny+"元"); } } -
不安全的列表
-
package com.xiaowei9s.syn; import java.util.ArrayList; public class UnsafeList { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { new Thread(()->{ arrayList.add(1); }).start(); } Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println(arrayList.size()); } }
5. 同步方法
在方法中加入同步方法关键字synchronized,这个方法就变成了同步方法,这个方法只能在获得对象的锁的时候才能运行,执行完成才返回这把锁。这把锁锁的是this,也就是方法体所在的对象。
缺陷:影响效率
比如之前的买票,在run方法加入关键字即可同步
package com.xiaowei9s.syn;
public class UnsafeTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket();
new Thread(buyTicket,"小明").start();
new Thread(buyTicket,"小黄").start();
new Thread(buyTicket,"小红").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable{
int numTicket = 10;
boolean flag = true;
//买票
public void buy(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买到了第"+numTicket--+"票");
if (numTicket==0){
flag = false;
}
}
@Override
public synchronized void run() {//加入关键字
while (flag){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
buy();
}
}
}
6. 同步块
synchronized(Obj){};//Obj是需要监视的对象,也就是对这个对象加上锁
例如银行取钱,我们只需要对账户加上监视,让它同步即可:
package com.xiaowei9s.syn;
public class UnsafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account("结婚基金", 1000);
Drawing d1 = new Drawing(account, 500, "老公");
Drawing d2 = new Drawing(account, 800, "老婆");
d1.start();
d2.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account{
public String name;
public int monny;
public Account(String name , int monny){
this.name = name;
this.monny = monny;
}
}
//银行取钱
class Drawing extends Thread{
Account account;
int nowMonny;
int getMonny;
public Drawing(Account account, int getMonny, String name){
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.getMonny = getMonny;
}
//取钱
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (account){
if (account.monny - getMonny < 0){
System.out.println("账户里还有" + account.monny + "元,钱不够了");
return;
}
nowMonny += getMonny;
account.monny -= getMonny;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取了"
+ getMonny+"元,还剩"+account.monny+"元,现在ta有"
+ nowMonny+"元");
}
}
}
7. CopyOnWriteArrayList
就是一个JUC并发编程中的一个列表类。
他内部实现了一个锁和同步的功能,不用自己去实现同步。
十三、死锁
当一个同步块拥有两个以上的对象的锁的时候有可能发生。
因为一个对象被一个线程占有,而另一个对象被另一个线程占有,两个线程都不愿意放手,就谁都做不了事情。
package com.xiaowei9s.syn;
public class DieLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Key1 key1 = new Key1();
Key2 key2 = new Key2();
LockNeedK1K2 lockNeedK1K2 = new LockNeedK1K2(key1, key2);
new Thread(lockNeedK1K2,"小红").start();
new Thread(lockNeedK1K2,"小黄").start();
}
}
class LockNeedK1K2 implements Runnable{
public LockNeedK1K2(Key1 k1, Key2 k2) {
this.k1 = k1;
this.k2 = k2;
}
public Key1 k1;
public Key2 k2;
@Override
public void run() {
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("小红")){
synchronized (k1){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了第一个密码");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (k2){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了第二个密码");
System.out.println("密码是:" + k1.password1 + k2.password2);
System.out.println("打开了宝箱");
}
}
}
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("小黄")){
synchronized (k2){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了第二个密码");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (k1){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了第一个密码");
System.out.println("密码是:" + k1.password1 + k2.password2);
System.out.println("打开了宝箱");
}
}
}
}
}
class Key1{
String password1 = "123";
}
class Key2{
String password2 = "321";
}
避免死锁:不要在同步块中再次嵌入同步块!
十四、Lock(锁)

demo:
package com.xiaowei9s.syn;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lock1 lock1 = new Lock1();
new Thread(lock1,"hong").start();
new Thread(lock1,"huang").start();
new Thread(lock1,"jun").start();
}
}
class Lock1 implements Runnable{
public int ticket = 10;
public ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
lock.lock();
while (ticket>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ticket);
ticket--;
}
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
十五、线程协作
生产者消费者问题
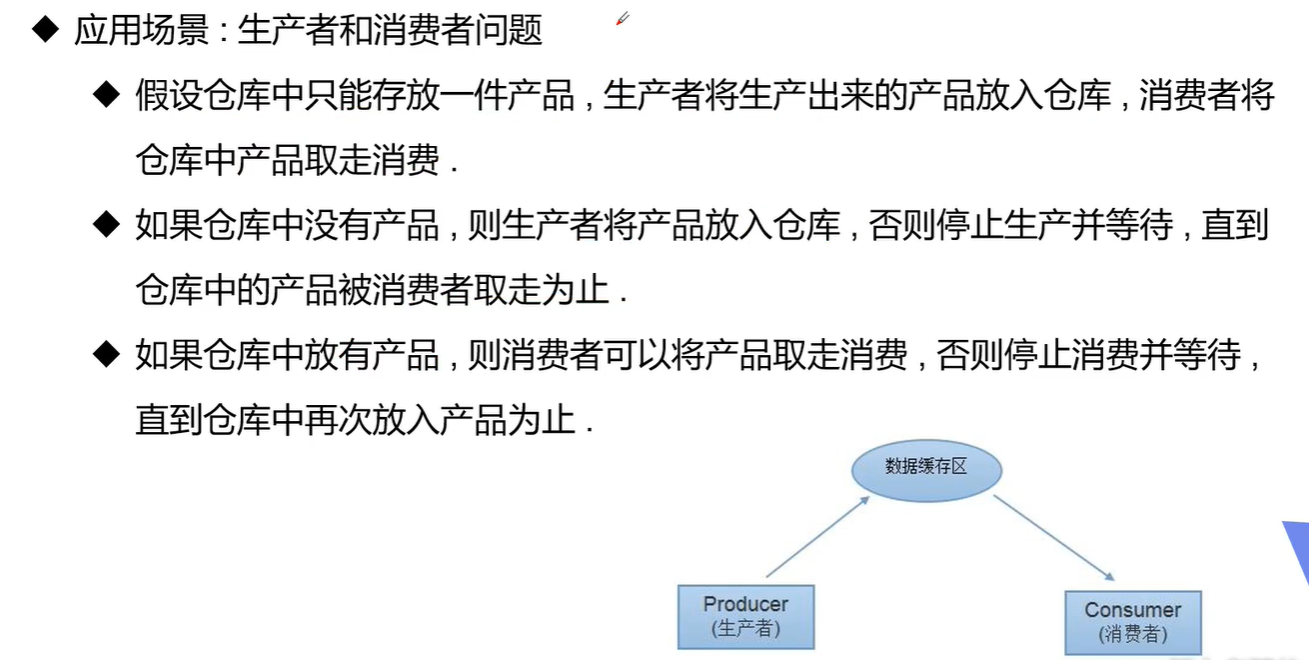
相关方法:
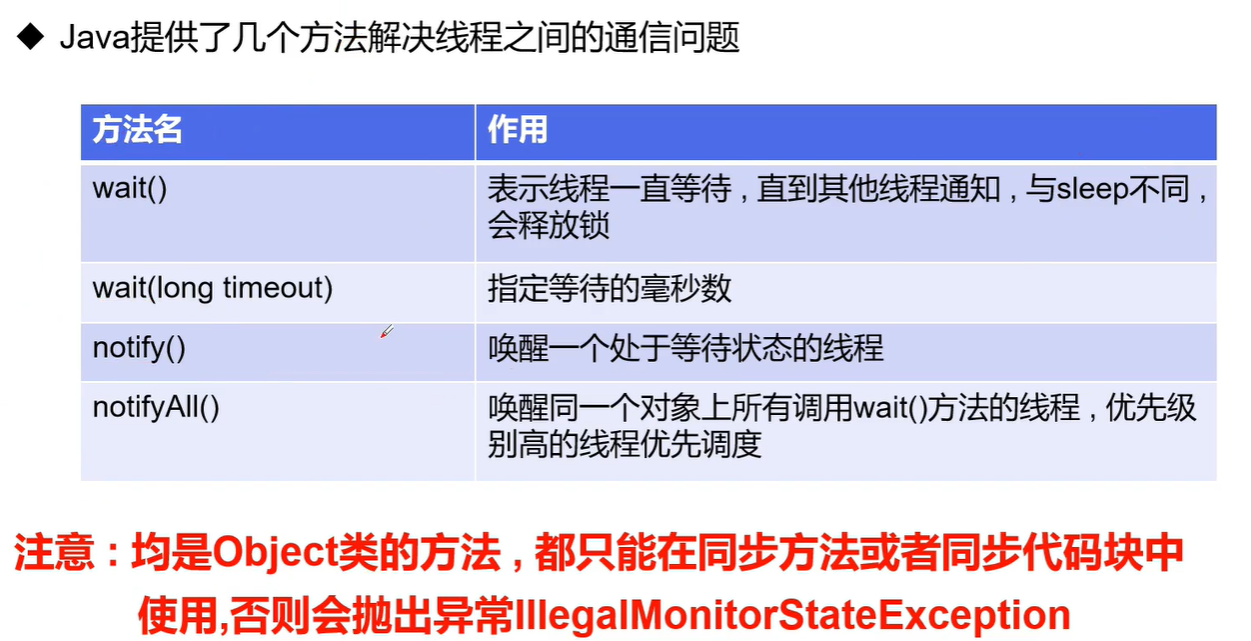
解决方法:
-
缓冲区法,设置缓冲区(管程法)
-
package com.xiaowei9s.syn; public class TestPC { public static void main(String[] args) { SynContain synContain = new SynContain(); new Producer(synContain).start(); new Customer(synContain).start(); } } class Producer extends Thread{ public SynContain synContain; public Producer(SynContain synContain){ this.synContain = synContain; } //生产 @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { try { synContain.add(i); System.out.println("生产了第" + i + "只鸡"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } class Customer extends Thread{ public SynContain synContain; public Customer(SynContain synContain){ this.synContain = synContain; } //消费 @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { try { synContain.minus(i); System.out.println("消费了第" + i + "只鸡"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } class Chichen{ public Chichen(int id) { this.id = id; } int id; } class SynContain{ Chichen[] contain = new Chichen[10]; int count = -1; public synchronized void add(int i) throws InterruptedException { if(count+1<contain.length){ contain[++count] = new Chichen(i); this.notifyAll(); }else if (count>=10){ this.wait(); } } public synchronized void minus(int i) throws InterruptedException { if(count>=0){ contain[count] = null; count--; this.notifyAll(); }else if (count==0){ this.wait(); } } } -
信号灯法:设置信号用于唤醒或等待
-
package com.xiaowei9s.syn; public class TestPC2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Food food = new Food(); new Eater(food).start(); new Cooker(food).start(); } } //厨师 class Cooker extends Thread{ Food food; public Cooker(Food food) { this.food = food; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { try { food.cook(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //顾客 class Eater extends Thread{ Food food; public Eater(Food food) { this.food = food; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { try { food.eat(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //菜品 class Food{ String name = "满汉全席"; boolean flag = false; public synchronized void eat() throws InterruptedException { if (!flag){ this.wait(); } System.out.println("顾客在吃"+name); flag = !flag; this.notifyAll(); } public synchronized void cook() throws InterruptedException { if (flag){ this.wait(); } System.out.println("厨师在做"+name); flag = !flag; this.notifyAll(); } }
十六、使用线程池

使用:

demo:
package com.xiaowei9s.syn;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
executorService.execute(new MyThread());
executorService.execute(new MyThread());
executorService.execute(new MyThread());
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
知识来源:kuangstudy.com


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号