Pyhon进阶9---类的继承
类的继承
基本概念







定义
格式如下



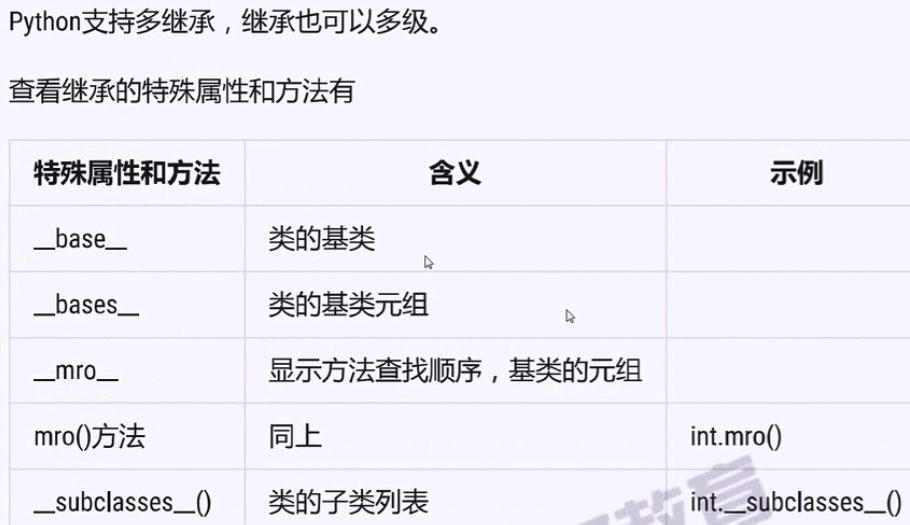
继承中的访问控制
class Animal: __CNOUT = 0 HEIGHT = 0 def __init__(self,age,weight,height): self.__CNOUT =self.__CNOUT + 1 self.age = age self.__weight = weight self.HEIGHT = height def eat(self): print('{} eat'.format(self.__class__.__name__)) def __getweight(self): print(self.__weight) @classmethod def showcount1(cls): print(cls.__CNOUT) @classmethod def __showcount2(cls): print(cls.__CNOUT) class Cat(Animal): NAME = 'CAT' c = Cat(3,5,15) c.eat() c.showcount1()#注意此处的cls.__COUNT仍为0 print(c.NAME) print(c.__dict__)#{'_Animal__CNOUT': 1, 'age': 3, '_Animal__weight': 5, 'HEIGHT': 15} print(Cat.__dict__)#{'__module__': '__main__', 'NAME': 'CAT', '__doc__': None} print(Animal.__dict__)#{'__module__': '__main__', '_Animal__CNOUT': 0, 'HEIGHT': 0,...}

方法的重写、覆盖override

![]()
class Animal: def shout(self): print('Animal shout') class Cat(Animal): #覆盖父类的方法 def shout(self): print('miao') #覆盖自身的方法,显示调用了父类的方法 def shout(self): print(super(Cat, self)) super().shout() a = Animal() a.shout() c =Cat() c.shout() #输出结果: # Animal shout # <super: <class 'Cat'>, <Cat object>> # Animal shout

class Animal: @classmethod def class_method(cls): print('class_method_animal') @staticmethod def static_method(): print('static_method_animal') class Cat(Animal): @classmethod def class_method(cls): print('class_method_cat') @staticmethod def static_method(): print('static_method_cat') c = Cat() c.class_method() c.static_method() #输出结果: # class_method_cat # static_method_cat
![]()
继承中的初始化





示例1
class A: def __init__(self): self.a1 = 'a1' self.__a2 = 's2' print('A init') class B(A): pass b = B() print(b.__dict__) #{'a1': 'a1', '_A__a2': 's2'}
![]()
示例2
class A: def __init__(self): self.a1 = 'a1' self.__a2 = 's2' print('A init') class B(A): def __init__(self): self.b1 = 'b1' print('B init') b = B() print(b.__dict__) #{'b1': 'b1'}
![]()
class A: def __init__(self): self.a1 = 'a1' self.__a2 = 's2' print('A init') class B(A): def __init__(self): # A.__init__(self) # super(B,self).__init__() super().__init__() self.b1 = 'b1' print('B init') b = B() print(b.__dict__) #{'a1': 'a1', '_A__a2': 's2', 'b1': 'b1'}
如何正确初始化

![]()
![]()
![]()
class Animal: def __init__(self,age): print('Animal init') self.age =age def show(self): print(self.age) class Cat(Animal): def __init__(self,age,weight): super().__init__(age)#c.show()结果为11 print('Cat init') self.age = age + 1 self.weight = weight # super().__init__(age)#c.show()结果为10 c = Cat(10,5) c.show()
# c.__dict__ {'age': 11, 'weight': 5}

class Animal: def __init__(self,age): print('Animal init') self.__age =age def show(self): print(self.__age) class Cat(Animal): def __init__(self,age,weight): super().__init__(age) print('Cat init') self.__age = age + 1 self.__weight = weight c = Cat(10,5) c.show() print(c.__dict__)#{'_Animal__age': 10, '_Cat__age': 11, '_Cat__weight': 5}

Python不同版本的类

多继承

多继承弊端


Python多继承实现
class ClassName(基类列表): 类体
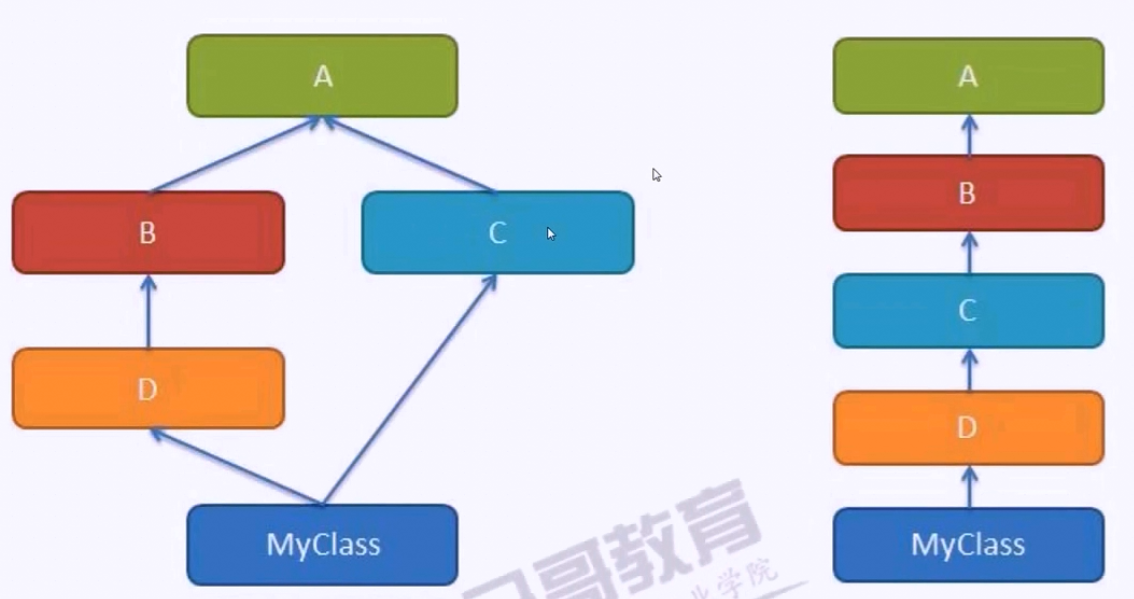

多继承的缺点


Mixin



class Printable: def _print(self): print(self.content) class Document:#假设为第三方库,不允许修改 def __init__(self,content): self.content = content class Word(Document):pass#假设为第三方库,不允许修改 class Pdf(Document):pass#假设为第三方库,不允许修改 class PrintableWord(Printable,Word):pass print(PrintableWord.__dict__) print(PrintableWord.mro()) pw = PrintableWord('test string') pw._print()


def printable(cls): def _print(self): print(self.content,'装饰器') cls.print = _print return cls class Document:#假设为第三方库,不允许修改 def __init__(self,content): self.content = content class Word(Document):pass#假设为第三方库,不允许修改 class Pdf(Document):pass#假设为第三方库,不允许修改 @printable class PrintableWord(Word):pass print(PrintableWord.__dict__)#{'__module__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, 'print': <function printable.<locals>._print at 0x0000000002961730>} PrintableWord('test').print()#test 装饰器
![]()
4.Mixin
#Mixin示例1 class PrintableMixin: def print(self): print(self.content,'Mixin') class Document: def __init__(self,content): self.content = content class Word(Document):pass class Pdf(Document):pass class PrintableWord(PrintableMixin,Word):pass print(PrintableWord.__dict__) print(PrintableWord.mro()) pw = PrintableWord('test\nstring') pw.print()

#Mixin示例2 class PrintableMixin: def print(self): print(self.content,'Mixin') class Document: def __init__(self,content): self.content = content class Word(Document):pass class Pdf(Document):pass class SuperPrintableMixin(PrintableMixin): def print(self): print('~'*20) super().print() #通过继承复用 print('~'*20) class SuperPrintablePdf(SuperPrintableMixin,Pdf):pass print(SuperPrintablePdf.__dict__) print(SuperPrintablePdf.mro()) spp = SuperPrintablePdf('super print pdf') spp.print()
Mixin类

练习

#1.Shape基类,要求所有子类都必须提供面积的计算,子类有三角形、矩形、圆 import math class Shape: @property def area(self): raise NotImplementedError('基类未实现') class Triangle(Shape): def __init__(self,a,b,c): self.a = a self.b = b self.c = c @property def area(self): p = (self.a+self.b+self.c)/2 return math.sqrt(p*(p-self.a)*(p-self.b)*(p-self.c)) class Circle(Shape): def __init__(self,radius): self.radius = radius @property def area(self): return math.pi*self.radius**2 class Rectangle(Shape): def __init__(self,width,height): self.width = width self.height = height @property def area(self): return self.width*self.height # shapes = [Triangle(3,4,5),Rectangle(3,4),Circle(4)] # for s in shapes: # print('The area of {} = {}'.format(s.__class__.__name__,s.area)) #2.圆类的数据可序列化 import json import msgpack def mydump(cls): def _dumps(self, t='json'): if t == 'json': return json.dumps(self.__dict__) elif t == 'msgpack': return msgpack.packb(self.__dict__) else: raise NotImplementedError('没有实现的序列化') cls.dumps = _dumps return cls #使用Mixin类 # class SerializableMixin: # def dumps(self,t='json'): # if t == 'json': # return json.dumps(self.__dict__) # elif t == 'msgpack': # return msgpack.packb(self.__dict__) # else: # raise NotImplementedError('没有实现的序列化') # #使用装饰器 @mydump class SerializableCircleMixin(Circle):pass scm = SerializableCircleMixin(1) print(scm.area)#3.141592653589793 print(scm.__dict__)#{'radius': 1} print(scm.dumps('json'))#{"radius": 1}
作业

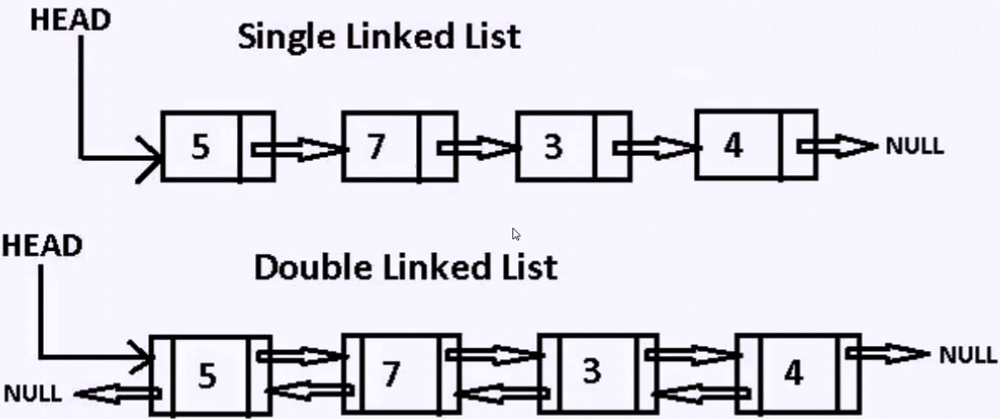
#单链表 class SingleNode: #代表一个节点 def __init__(self,val,next=None): self.val = val self.next = None class LinkedList: #容器类,某种方式存储一个个节点 def __init__(self): self.head = None self.tail = None def append(self,val): node = SingleNode(val) if self.head is None:# 0 self.head = node self.tail = node self.tail.next = node self.tail = node def iternodes(self): while self.head: yield self.head.val self.head = self.head.next
1 #实现双向链表 2 class SingleNode: 3 #代表一个节点 4 def __init__(self,val,next=None,prev=None): 5 self.val = val 6 self.next = next 7 self.prev = prev 8 9 def __repr__(self): 10 return str(self.val) 11 12 class LinkedList: 13 #容器类,某种方式存储一个个节点 14 def __init__(self): 15 self.head = None 16 self.tail = None 17 18 def append(self,val): 19 node = SingleNode(val) 20 if self.head is None:# 0 21 self.head = node 22 else: 23 self.tail.next = node 24 node.prev = self.tail 25 self.tail = node 26 27 def pop(self): 28 if self.tail is None:#0 29 raise NotImplementedError('Empty') 30 tail = self.tail 31 prev= self.tail.prev 32 if prev is None:#1个节点 33 self.head = None 34 self.tail = None 35 else:#>1 36 self.tail = prev 37 prev.next = None 38 return tail.val 39 40 41 def insert(self,index,val):#1,7 42 if index < 0: 43 raise Exception('Error') 44 cur = None 45 for i,current in enumerate(self.iternodes()): 46 if i == index: 47 cur = current 48 break 49 50 if cur is None:#说明索引越界或空链表,直接末尾追加 51 self.append(val) 52 return 53 54 node = SingleNode(val) 55 prev = cur.prev 56 if prev is None:#1个节点,头部插入 57 self.head = node 58 node.next = cur 59 cur.prev = node 60 else:#>=2 61 node.next = cur 62 prev.next = node 63 cur.prev = node 64 node.prev = prev 65 66 def iternodes(self,reversed = False): 67 current = self.head 68 while current: 69 yield current 70 current = current.next 71 72 a = SingleNode(1) 73 b = SingleNode(2) 74 c = SingleNode(3) 75 d = SingleNode(4) 76 e = SingleNode(5) 77 f = SingleNode(6) 78 ll = LinkedList() 79 ll.append(a) 80 ll.append(b) 81 ll.append(c) 82 ll.append(d) 83 ll.append(e) 84 ll.append(f) 85 # ll.insert(1,0) 86 # ll.insert(0,0) 87 ll.insert(10,100) 88 print('pop元素:',ll.pop()) 89 print('pop元素:',ll.pop()) 90 print('pop元素:',ll.pop()) 91 ll.insert(0,10) 92 93 for node in ll.iternodes(): 94 print(node)
做一枚奔跑的老少年!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号