集合
集合
集合的特点
- 可以动态保存任意多个对象,使用方便
- 集合提供了一系列方便操作对象的方法
- 使用集合操作代码简洁明了
集合体系
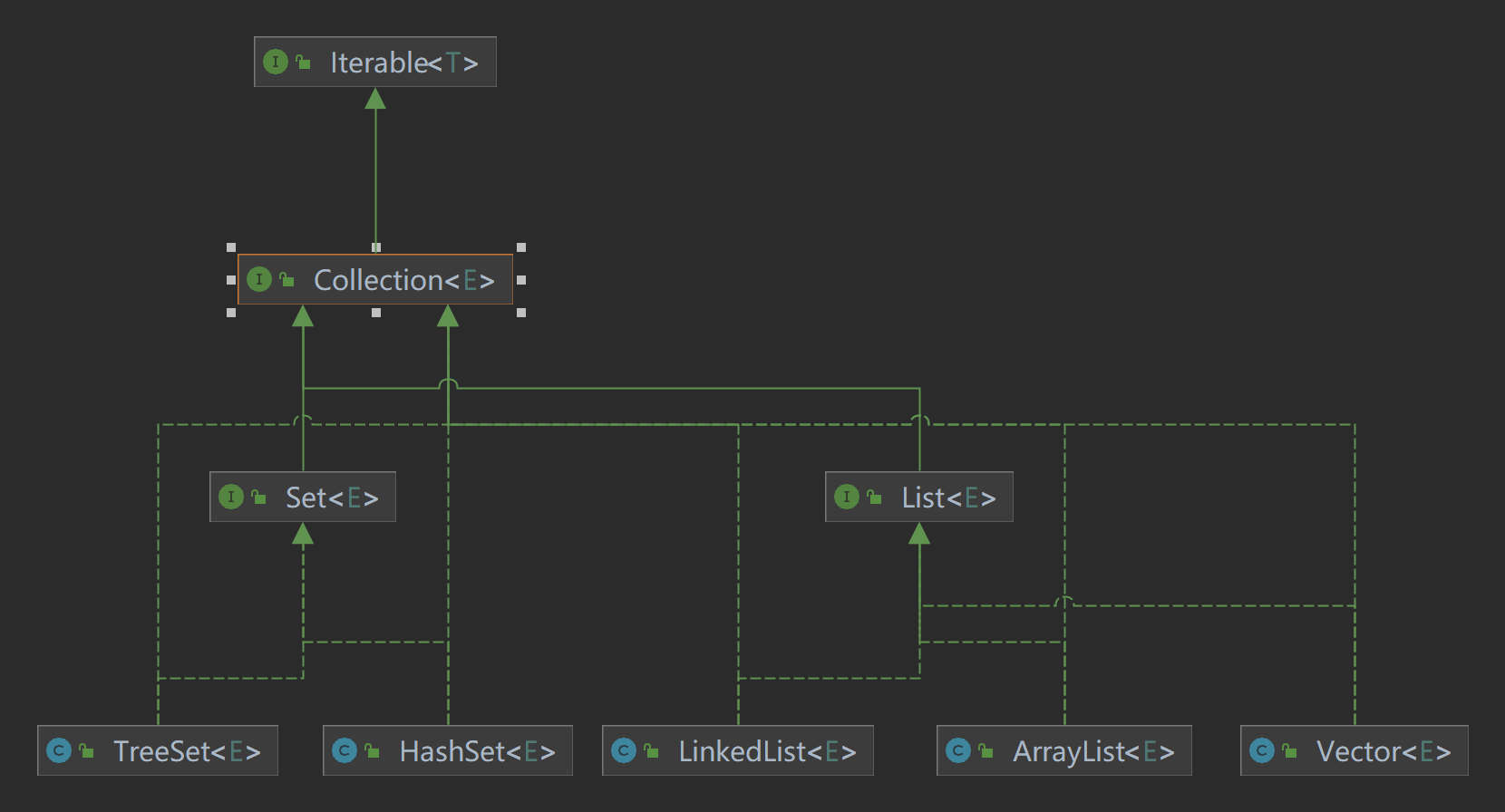
单列集合
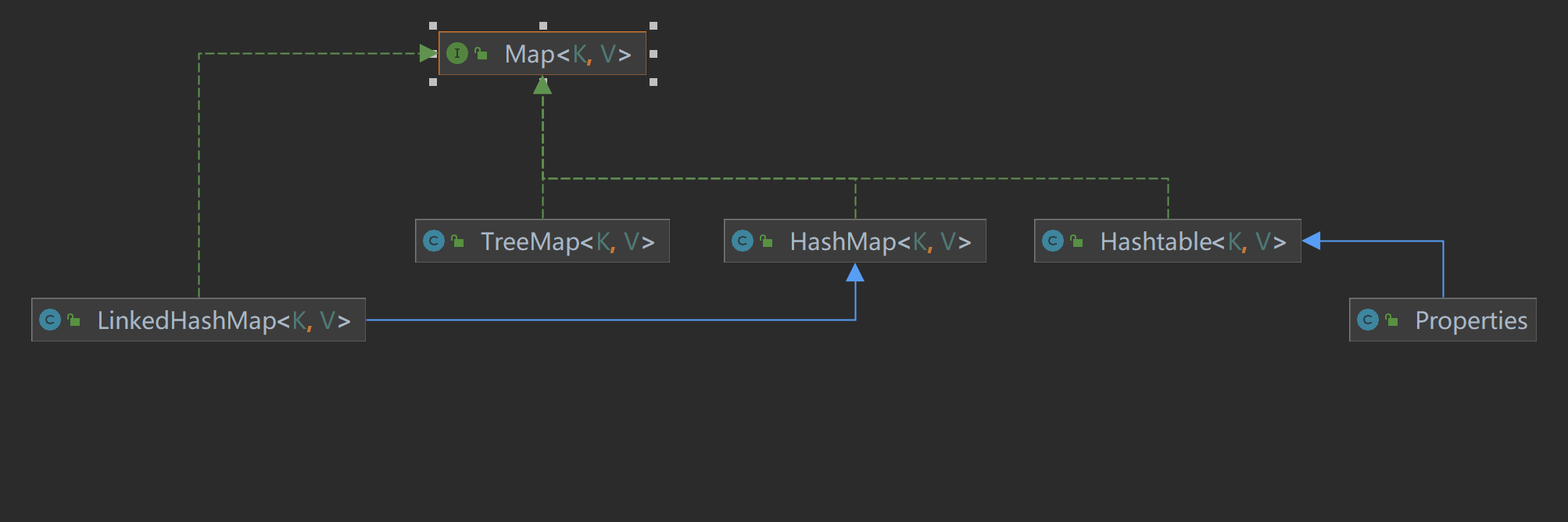
双列集合
集合迭代器
package com.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col = new ArrayList();
col.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 18.5));
col.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 22));
col.add(new Book("小李飞刀", "古龙", 9.9));
col.add("测试用例");
//System.out.println(col);
//遍历集合
//1、先得到集合对应的迭代器
Iterator iterator = col.iterator();
//2、使用while循环遍历集合(快捷键:itit+回车)
//Ctrl + J 查看快捷键设置
while (iterator.hasNext()) {//判断集合中是否还有数据
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
//3、当退出while循环的时候,这是我们的迭代器指向最后的元素,再继续取值操作会抛出异常
//4、如果需要再次遍历,需要重置我们的迭代器
iterator = col.iterator();//重置操作
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private double price;
public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
集合遍历的三种方式:
- 使用迭代器
- 使用增强for循环
- 使用普通佛瑞循环
ArrayList的扩容机制
- ArrayList中维护了一个Object类型的数组elementData,
- 当创建ArrayList对象时,如果使用的是无参构造器,则elementData容量为0,第一次添加,容量扩容为10,再次扩容,则为1.5倍
- 如果指定大小,后续扩容按1.5倍进行扩容
当对一个新建的为空的ArrayList进行add操作的时候,首先会检查内部容量
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
上方这个方法会将新建的ArrayList的minCapacity属性修改到10,因为在ArrayList类中的DEFAULT_CAPACITY默认为10
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
如果容量不足,就进行grow的扩容操作
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;//第一次扩容时minCapacity为10,后续才是1.5倍
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
按照1.5倍的大小进行扩容
Vector
-
Vector底层也是一个对象数组
-
Vector的操作方法有加synchronized,所以是线程安全的
Vector的扩容机制
Vector的初始默认容量大小为10
扩容倍数为2倍
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
扩容代码
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
LinkedList
- LinkedList底层实现了双向链表和双端队列
- 可以添加任意元素(重复或者null)
- 线程不安全
LinkedList底层机制
- 底层维护的是一个双向链表
- LinkedList中维护了两个属性first和last分别指向首节点和尾节点
- 每个节点维护了prev、next、item三个属性,其中prev指向前一个节点,next指向后一个节点
- LinkedList的元素的添加和删除,不是通过数组完成的,相对效率较高
LinkedList例子解析
package com.list;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedList01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟一个简单的双向链表
Node apple = new Node("apple");
Node huawei = new Node("huawei");
Node xiaomi = new Node("xiaomi");
//连接三个节点,形成链表
//apple -> huawei -> xiaomi
apple.next = huawei;
huawei.next = xiaomi;
xiaomi.pre = huawei;
huawei.pre = apple;
Node first = apple;//first指向头节点
Node last = xiaomi;//last指向尾节点
//对双向链表进行遍历,从头到尾
while (true) {
if (first == null) {
break;
} else {
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;
}
}
//添加数据方便
//例如,在apple和huawei中添加一个iPhone
//1、先创建一个iPhone节点
Node iPhone = new Node("iPhone");
//2、将创建的节点加入链表
apple.next = iPhone;
iPhone.next = huawei;
huawei.pre = iPhone;
iPhone.pre = apple;
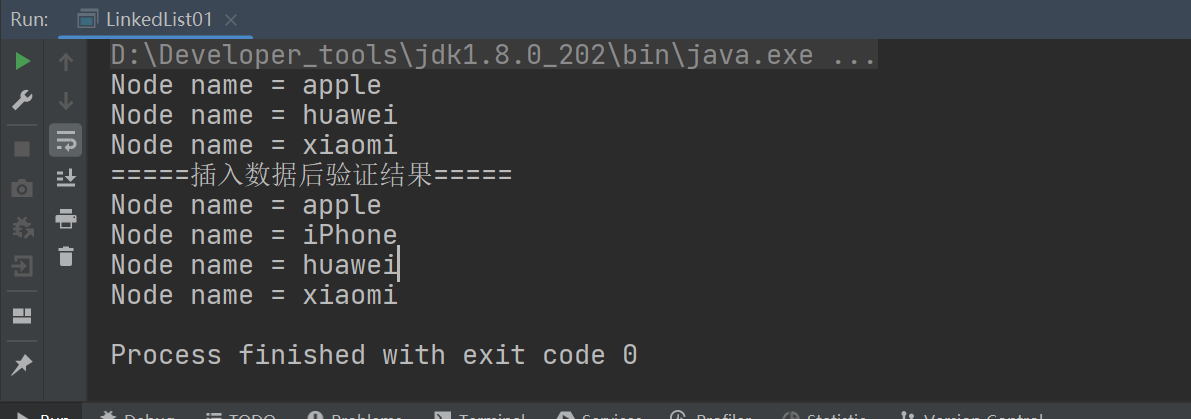
//进行遍历,验证结果
System.out.println("=====插入数据后验证结果=====");
first = apple;
while (true) {
if (first == null) {
break;
} else {
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;
}
}
}
}
//定义一个Node类,表示双向链表的节点
class Node {
public Object item;//真正存放数据的地方
public Node pre;//指向上一个节点
public Node next;//指向下一个节点
public Node(Object item) {
this.item = item;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node name = " + item;
}
}
LinkedList底层代码
package com.list;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListCRUD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.add(3);
System.out.println("LinkedList = " + linkedList);
//删除节点
linkedList.remove();//无参默认删除第一个节点
//使用迭代器对LinkedList进行遍历
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("LinkedList = " + next);
}
}
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
LinkedList增加节点方法
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
删除节点前判断是否为空链表,为空的话抛出异常
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
LinkedList删除节点方法
Set
- Set接口是无序的,没有索引
- Set集合的取出的顺序是固定的,但是与存入的顺序无关,因为底层保存是一个数组加链表的组合
- 不允许存在重复元素,所以最多包含一个null
- 遍历方式:可以使用迭代器和增强for,不能使用索引的方式来获取
package com.collection.set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashSet_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set hashSet = new HashSet();
System.out.println("set = " + hashSet);
System.out.println("=========测试1===========");
hashSet.add("apple");//成功
hashSet.add("apple");//失败
hashSet.add(new Phone("13"));//成功
hashSet.add(new Phone("13"));//成功
System.out.println("set = " + hashSet);
System.out.println("==========测试new String==========");
hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new String("test"));//成功
hashSet.add(new String("test"));//失败
System.out.println("set = " + hashSet);
}
}
class Phone{
private String name;
public Phone(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Phone{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
数组链表模拟
package com.collection.set;
import com.sun.corba.se.impl.oa.poa.AOMEntry;
public class HashSetStructure {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟一个HashMap底层结构
//1、创建一个数组,类型为Node[]
Node[] table = new Node[16];
System.out.println("table = " + table);
//2、创建节点
Node apple = new Node("apple", null);
table[2] = apple;
Node huawei = new Node("huawei", null);
apple.next = huawei;
Node xiaomi = new Node("xiaomi", null);
huawei.next = xiaomi;
System.out.println("table = " + table);
}
}
class Node {//节点,可以存储数据,指向下一个节点
Object item;//存储数据
Node next;//指向下一个节点
public Node(Object item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"item=" + item +
'}';
}
}
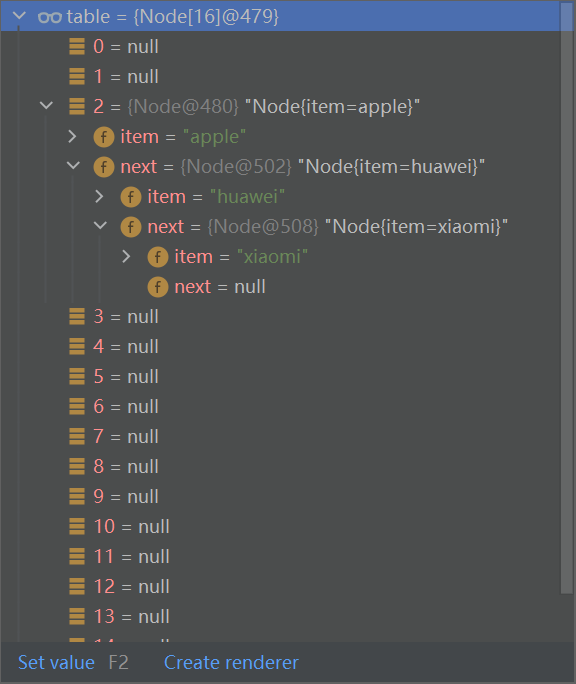
HashSet底层机制
结论:
- HashSet底层是HashMap
- 添加一个元素时,先得到hash值,再转成索引值
- 找到存储数据表,看这个索引的位置是否已经存放元素了
- 如果没有,直接添加元素
- 如果有,调用equals比较,如果相同,就放弃添加,如果不相同,就添加到最后
- 在java8中,如果一个链表的元素个数超过(大于等于)TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认值:8),并且table的大小>=MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认值:64 ),就会转化为红黑树
分析:
-
执行HashSet构造器
public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); } -
执行add方法
public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; } //private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); -
执行put方法,该方法会执行hash(key),得到key对应的hash值
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); }对hash值进行运算
static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); } -
执行putVal方法
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;//定义了辅助变量 //table就是HashMap的一个数组,类型是Node[] //if语句表示如果当前的table是null,或者大小=0 //就是第一次扩容,到16个空间 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; //(1)根据Key得到Hash,去计算Key该存到table表的哪个索引位置 //并把这个位置的对象,赋值给 p //(2)判断p是否为null //(2.1)如果 p 为null,表示还没有存放元素,就创建一个Node() //(2.2)就放在该位置 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null) if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { //在需要局部变量的时候再去创建 Node<K,V> e; K k;// //如果当前索引位置链表的第一个元素和准备添加的Key的hash值一样 //并且满足下面两个条件之一 //(1)准备加入的 Key 和 p 指向的Node节点的的Key是同一个对象 //(2)p 指向的Node节点的 Key 的equals()和准备加入的Key比较后相同 //就不能加入 if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; //再判断 p 是不是一颗红黑树 //如果是一棵红黑树,就调用 putTreeVal 来进行添加 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); //如果table对应的索引位置,已经是一个链表, //(1)依次和该链表的每一个元素比较后,都不相同的话,则加入该链表的最后 // 注意:在把元素添加到链表后,立即判断,这个链表是否已经达到8个节点 // 到达8个节点,就调用treeifyBin()对当前这个链表进行树化(转成红黑树) // 注意,在转成红黑树时,要进行判断,判断条件如下 // if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) // resize(); // 条件成立,先将table扩容 // 条件不成立,转化成红黑树 //(2)依次和该链表的每一个元素比较过程中,如果有相同的情况,就break推出 else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
HashSet扩容机制
HashSet底层是HashMap,第一次添加时,table数组扩容到16,临界值(threshold)是16 * 加载因子(loadFactor,0.75)=12,如果table数组的使用达到了临界值12,就会扩容到16 * 2 =32,新的临界值就是32 * 0.75 = 24
LinkedHashSet
- LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类
- LinkedHashSet底层是一个LinkedHashMap,底层维护的是一个数组+双向链表
- LinkedHashSet根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表维护元素的次序,这使元素看起来像是以插入顺序保存的
- LinkedHashSet不允许添加重复元素
TreeSet
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Map
package com.collection.map;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Map {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、Map 与 Collection 并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-Value
//2、Map 中的 Key 和 Value 可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到 HashMap$Node 对象中
//3、Map 中的 Key 不允许重复,原因和 HashSet 一样
//4、Map 中的 Value 可以重复
//5、Map 中的 Key 可以为 null,Value 也可以为 null,Key 为 null 只能有一个
//6、常用 String 类作为 Map 的 Key
//7、Key 和 Value 之间存在单向一对一关系,通过指定 Key 总能找到对应的 Value
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put(001, "apple");
hashMap.put(002, "xiaomi");
hashMap.put(001, "huawei");
System.out.println(hashMap.get(001));
System.out.println(hashMap);
}
}
package com.collection.map;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapSource {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put(001, "apple");
hashMap.put(002, "xiaomi");
//1、k-v 最后是HashMap$Node node = new Node(hash, key, value, null)
//2、k-v 为了方便程序员的遍历,还会创建EntrySet集合,该集合存放的元素类型为Entry,而
// 一个Entry对象就有k,v EntrySet$<Entry<k,v>>
//3、EntrySet中,定义的类型是Map.Entry,但实际上存放的还是HashMap$Node
// 这是因为static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V>
//4、当把 HashMap$Node 对象存放到 EntrySet 就方便我们的遍历,因为Map.Entry提供了重要方法
// K getKey(); V getValue()
Set set = hashMap.entrySet();
System.out.println(set.getClass());
for (Object obj : set) {
//为了从HashMap$Node 取出k-v
//先做一个向下的转型
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) obj;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "-" + entry.getValue());
}
Set set1 = hashMap.keySet();
System.out.println(set1.getClass());
Collection values = hashMap.values();
System.out.println(values.getClass());
}
}
Map接口的遍历方式
- containsKey:查找键是否存在
- keySet:获取所有的键
- entrySet:获取所有关系
- values:获取所有的值
package com.collection.map;
import java.util.*;
public class MapFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("邓超", "孙俪");
map.put("王宝强", "马蓉");
map.put("宋喆", "马蓉");
map.put("刘令博", null);
map.put(null, "刘亦菲");
map.put("鹿晗", "关晓彤");
//第一组,先取出所有的key,通过key取出对应的value
Set keySet = map.keySet();
//1、增强for循环
System.out.println("-----增强for循环-----");
for (Object key : keySet) {
System.out.println(key + "-" + map.get(key));
}
//2、迭代器
System.out.println("-----迭代器-----");
Iterator iterator = keySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next + "-" + map.get(next));
}
//第二组,把所有的value值取出来
Collection values = map.values();
System.out.println("=====取出所有的value=====");
//这里可以使用所有的Collections使用的遍历方法
//1、增强for
System.out.println("-----增强for-----");
for (Object obj : values) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
//2、迭代器
System.out.println("-----迭代器-----");
Iterator iterator1 = values.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator1.next());
}
//第三组,通过EntrySet来获取 k-v
System.out.println("=====通过EntrySet方式=====");
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
//1、增强for
System.out.println("-----增强for-----");
for (Object entry : entrySet) {
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "-" + m.getValue());
}
//2、迭代器
System.out.println("-----迭代器-----");
Iterator iterator2 = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator2.next();
//System.out.println(next.getClass());//class java.util.HashMap$Node
//转型成Entry类型,利用Entry类型里的getKey()和getValue()方法
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) next;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "-" + m.getValue());
}
}
}
Map接口小结
-
Map接口常用实现类:HashMap、HashTable和Properties
-
HashMap是Map接口使用频率最高的实现类
-
HashMap是以key-value对的方式来存储数据(HashMap$Node类型)
-
Key不能重复,但是Value可以重复,允许存在null
-
如果添加相同的Key,则会覆盖原来的Key-Value
-
与HashSet一样,不能保证映射的顺序,因为底层是以hash表的方式来存储的
-
HashMap没有实现同步,因此是线程不安全的,方法没有做同步互斥的操作
-
HashMap源码中
-
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next;存储数据节点的Node实现了Map.Entry接口
-
HashMap的扩容机制与HashSet一致
Hashtable
Hashtable的基本情况
- 存放的元素是键值对:k-v
- Hashtable的键和值都不能为null,否则会抛出NullPointerException
- Hashtable的使用方法基本上和HashMap一样
- Hashtable是线程安全的,HashMap是线程不安全的
- 底层有数组Hashtable$Entry[] 初始化大小为11
- 临界值 threshold 8 = 11 * 0.75
- 扩容:按照自己的扩容机制来扩容的:2 n + 1
Properties
- Properties可以用于从xxx.properties文件中,加载数据到Properties类对象。并进行读取和修改
- xxx.properties文件通常作为配置文件
TreeMap
package com.collection.map;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMap_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
//按传入的key的string的大小来排序
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o2).compareTo((String) o1);
}
});
treeMap.put("apple", "苹果");
treeMap.put("huawei", "华为");
treeMap.put("xiaomi", "小米");
treeMap.put("hotpot", "火锅");
System.out.println(treeMap);
//1、构造器把传入的比较器对象,赋值给了TreeSet底层的TreeMap的属性this.Comparator
// public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
// return comparator;
// }
//2、调用put方法
//2.1、第一次添加,把k-v封装到
/* TreeMap.Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new TreeMap.Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}*/
//2.2以后添加
/* Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {//遍历所有的Key,给当前的Key找位置
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}*/
}
}
集合选型
- 先判断存储的类型(一组对象(单列)或者一组键值对(双列))
- 一组对象(单列):Collections接口
- 允许重复:List
- 增删多:LinkedList(底层是一个双向链表)
- 改查多:ArrayList(底层是一个Object类型的数组)
- 不允许重复:Set
- 无序:HashSet(底层是HashMap,维护了一个Hash表)
- 排序:TreeSet
- 插入和取出顺序一致:LinkedHashSet,(底层是数组+双向链表)
- 允许重复:List
- 一组键值对(双列):Map接口
- 键无序:HashMap(底层是Hash表)
- 键排序:TreeMap
- 键插入和取出顺序一致:LinkedHashMap
- 读取文件:Properties


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号