线程的操作
线程操作
线程停止
package com.state;
//测试stop
//1、建议线程正常停止-->利用次数,不建议死循环
//2、建议使用标志为-->设置一个标志位
//3、不要使用stop或者destroy等过时的方法
public class StateTest01 implements Runnable {
//1、设置一个标志位
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (flag) {
System.out.println("run...Thread " + i++);
}
}
//2、设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志为
public void stop() {
this.flag = false;
}
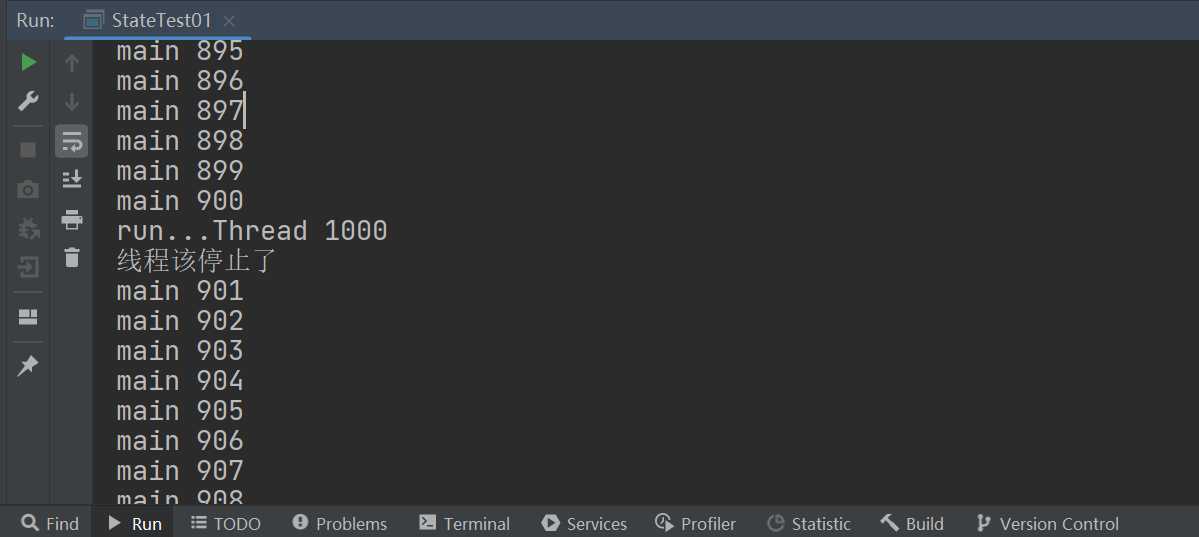
public static void main(String[] args) {
StateTest01 stateTest01 = new StateTest01();
new Thread(stateTest01).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main " + i);
if (i == 900) {
//调用stop方法切换标志位,停止线程
stateTest01.stop();
System.out.println("线程该停止了");
}
}
}
}
线程休眠
模拟网络延时
package com.state;
//模拟网络延时:放大问题的发生性
public class SleepTest01 implements Runnable {
private int ticketNum = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (ticketNum <= 0) {
break;
}
//模拟延时
try {
Thread.sleep(800);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->拿到了第 " + ticketNum-- + " 张票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SleepTest01 sleepTest01 = new SleepTest01();
new Thread(sleepTest01, "小明").start();
new Thread(sleepTest01, "老师").start();
new Thread(sleepTest01, "黄牛").start();
}
}
模拟倒计时
package com.state;
//模拟倒计时
public class SleepTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
tenDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException {
int num = 10;
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
if (num <= 0) break;
}
}
}
打印当前系统时间
package com.state;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
//打印当前系统时间
//每个对象都有一把锁,sleep不会释放锁
public class SleepTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//获取当前系统时间
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startTime));
startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//变更当前时间
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException {
int num = 10;
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
if (num <= 0) break;
}
}
}
线程礼让
代码:
package com.state;
//测试礼让线程
//礼让不一定能成功,需要看CPU的调度
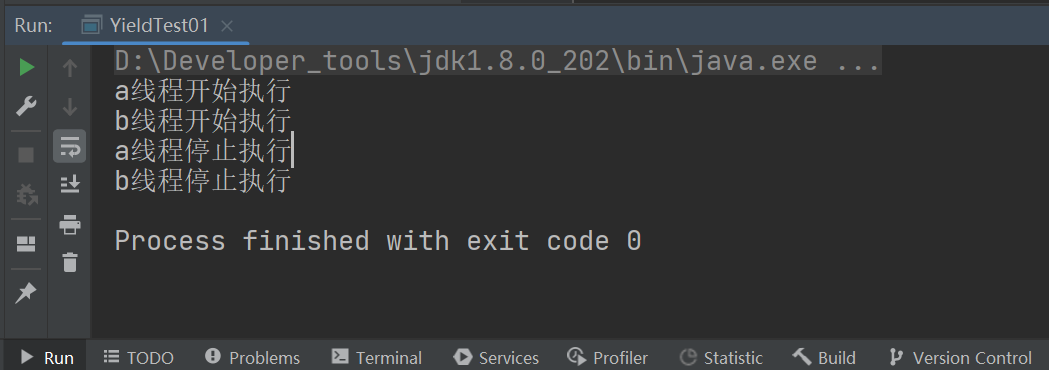
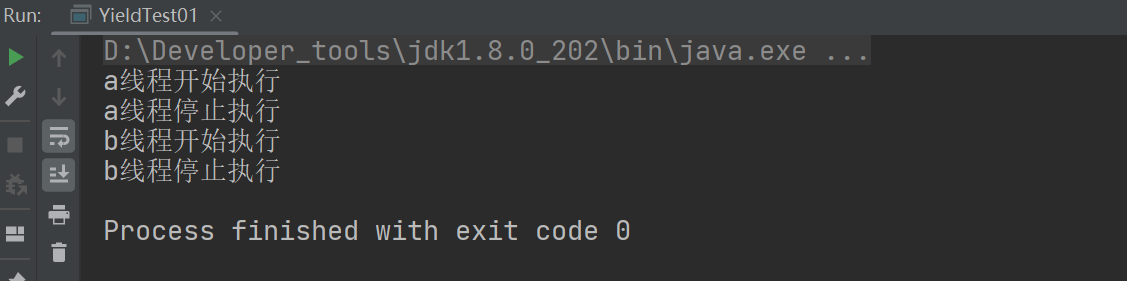
public class YieldTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYield myYield = new MyYield();
new Thread(myYield,"a").start();
new Thread(myYield,"b").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程开始执行");
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程停止执行");
}
}
礼让成功:
线程强制执行_join
join合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞
package com.state;
//测试join方法
public class JoinTest01 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("插队线程来了:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//启动我们的线程
JoinTest01 joinTest01 = new JoinTest01();
Thread thread = new Thread(joinTest01);
thread.start();
//主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
if (i == 200) {
thread.join();//插队
}
System.out.println("main:" + i);
}
}
}
线程状态
package com.state;
//观察测试线程的状态
public class StateTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(".....");
});
//观察状态
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
//观察启动后
thread.start();//启动线程
state=thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);//Run
while (state!= Thread.State.TERMINATED){
Thread.sleep(100);
state=thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
}
线程一旦死亡,就不能再次启动
线程的优先级
-
Java提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度器按照优先级决定应该调度哪个线程
-
线程的优先级用数字、表示,范围从1~10
- Thread.MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
- Thread.MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
- Thread.NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
-
使用以下方式改变或获取优先级
- getPriority().setPriority(int xxx)
package com.state;
public class PriorityTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 主线程默认优先级
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();
Thread t1 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t5 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t6 = new Thread(myPriority);
//先设置优先级,在再启动
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(1);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(3);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);//10
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(6);
t5.start();
t6.setPriority(8);
t6.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
优先级低并不意味着获得调度的概率低,并不是优先级低就不会被调用了,具体需要看CPU调度
守护线程(daemon)
- 线程分为守护线程和用户线程
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- 守护线程如:后台记录操作日志,监控内存,垃圾回收等待
package com.state;
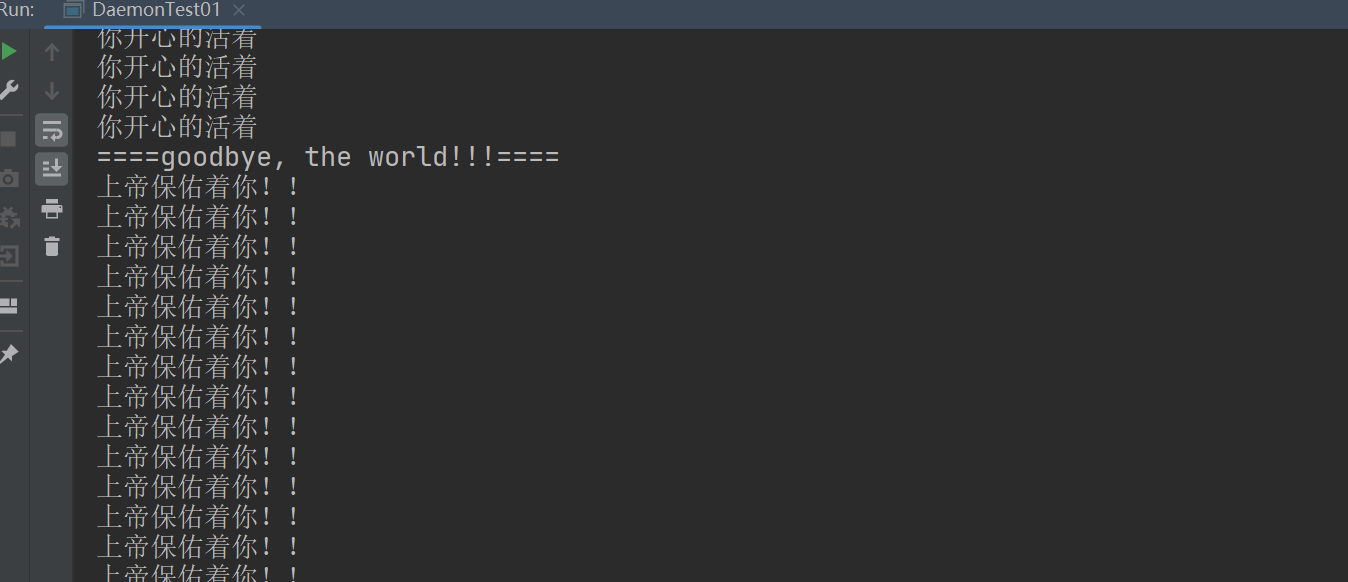
public class DaemonTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
god god = new god();
You you = new You();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true);//默认值false表示是用户线程,正常的线程都是用户线程
thread.start();//上帝守护线程启动
new Thread(you).start();//用户线程启动--你
}
}
//上帝
class god implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("上帝保佑着你!!");
}
}
}
//你
class You implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 36500; i++) {
System.out.println("你开心的活着");
}
System.out.println("====goodbye, the world!!!====");
}
}
线程同步机制
并发:多个线程访问同一个对象
线程不安全
1、
package com.syn;
//不安全的买票
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket();
new Thread(buyTicket, "小明").start();
new Thread(buyTicket, "小红").start();
new Thread(buyTicket, "黄牛").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable {
private int ticketNums = 10;
boolean flag = true;//外部停止方式
@Override
public void run() {
//买票
while (flag) {
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void buy() throws InterruptedException {
//判断是否有票
if (ticketNums <= 0) {
return;
}
//模拟延时
Thread.sleep(100);
//买票
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到了" + ticketNums--);
}
}
运行结果:
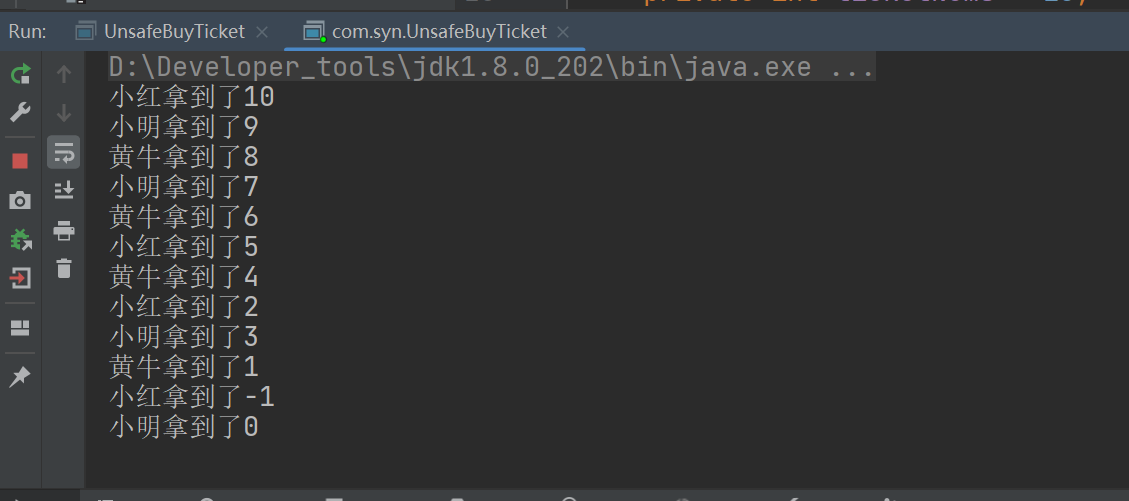
2、
package com.syn;
//不安全的取钱
public class UnsafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account(100, "结婚基金");
Drawing you = new Drawing(account, 50, "你");
Drawing girl = new Drawing(account, 100, "girl");
you.start();
girl.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account {
int money;
String name;
public Account(int money, String name) {
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
}
//银行
class Drawing extends Thread {
//账户
Account account;
//取钱金额
int drawingMoney;
//现在手里有多少钱
int nowMoney;
public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) {
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
//取钱
@Override
public void run() {
//判断有没有钱
if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "账户余额不足,无法取现!");
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//卡上余额更新
account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;
//手上现金更新
nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;
//输出
System.out.println("卡上余额为:" + account.money);
//Thread.currentThread().getName() = this.getName()
System.out.println(this.getName() + "手上的现金为:" + nowMoney);
}
}
运行结果:
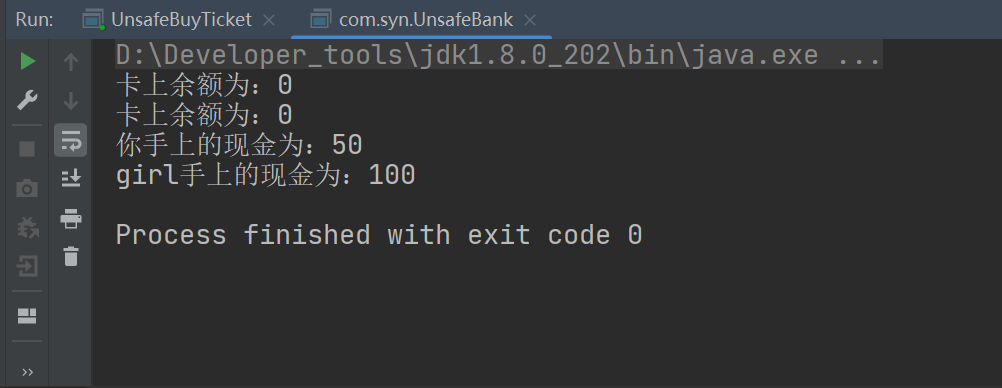
3、
package com.syn;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//线程不安全的集合
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
运行结果:
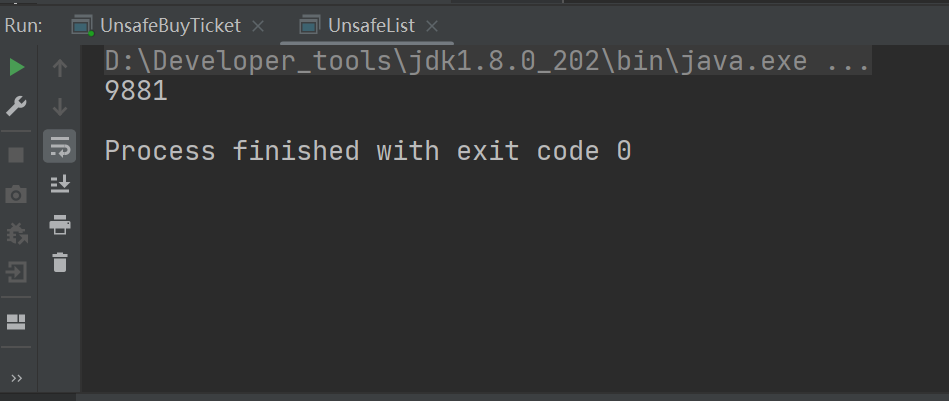
同步方法
synchronized同步方法
1、安全买票
package com.syn;
//不安全的买票
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket();
new Thread(buyTicket, "小明").start();
new Thread(buyTicket, "小红").start();
new Thread(buyTicket, "黄牛").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable {
private int ticketNums = 10;
boolean flag = true;//外部停止方式
@Override
public void run() {
//买票
while (flag) {
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//synchronized同步方法,锁的是this
private synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException {
//判断是否有票
if (ticketNums <= 0) {
return;
}
//模拟延时
Thread.sleep(100);
//买票
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到了" + ticketNums--);
}
}
运行结果:
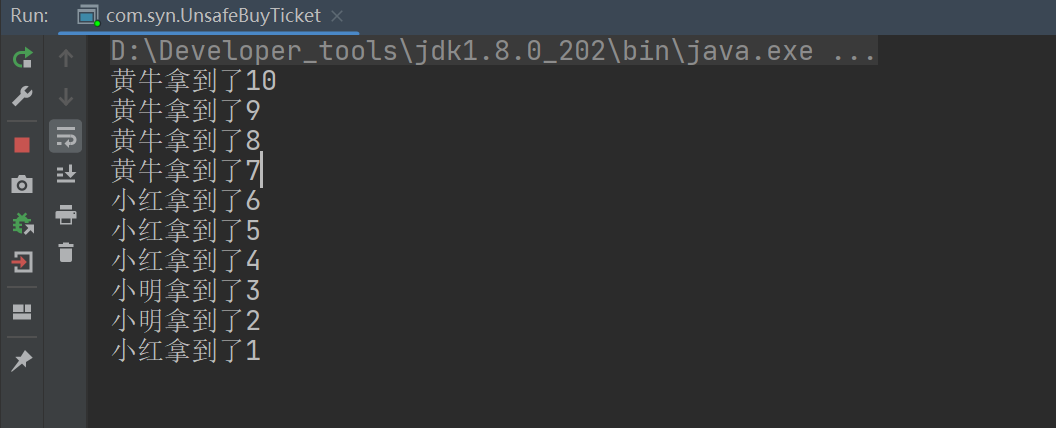
2、安全取钱
package com.syn;
//不安全的取钱
public class UnsafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account(100, "结婚基金");
Drawing you = new Drawing(account, 50, "你");
Drawing girl = new Drawing(account, 100, "girl");
you.start();
girl.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account {
int money;
String name;
public Account(int money, String name) {
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
}
//银行
class Drawing extends Thread {
//账户
Account account;
//取钱金额
int drawingMoney;
//现在手里有多少钱
int nowMoney;
public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) {
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
//取钱
//synchronized默认锁的是this本身
@Override
public void run() {
//锁的对象是变化的量,需要增删改的对象
synchronized (account) {
//判断有没有钱
if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "账户余额不足,无法取现!");
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//卡上余额更新
account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;
//手上现金更新
nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;
//输出
//Thread.currentThread().getName() = this.getName()
System.out.println(this.getName() + "手上取得的现金为:" + nowMoney);
System.out.println("卡上余额为:" + account.money);
}
}
}
运行结果:
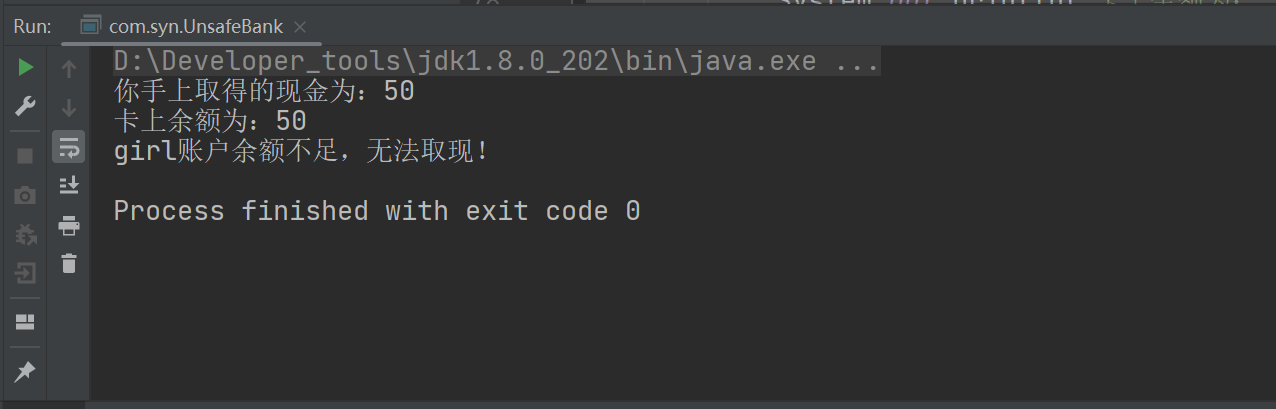
3、锁集合的线程
package com.syn;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//线程不安全的集合
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (list) {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
运行结果
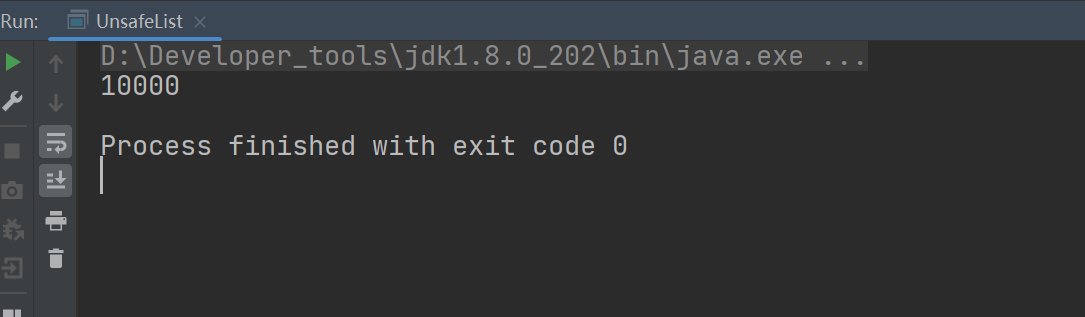
CopyOnWriteArrayList
一种线程安全的集合
package com.syn;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
//测试JUC安全类型的集合
public class TestJUC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(
() -> {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
死锁
两个或者多个线程都在等待对方释放资源,都停止执行的情形;
某一个同步块同时拥有“两个以上对象的锁”时,就可能会发生死锁的问题。
死锁代码:
package com.thread;
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Makeup girl1 = new Makeup(0, "灰姑凉");
Makeup girl2 = new Makeup(1, "白雪公主");
girl1.start();
girl2.start();
}
}
//口红
class LipStick {
}
//镜子
class Mirror {
}
class Makeup extends Thread {
//需要的资源自由一份,用static来修饰
static LipStick lipStick = new LipStick();
static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();
int choice;//选择
String name;//化妆的人
public Makeup(int choice, String name) {
this.choice = choice;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//化妆
try {
makeup();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//化妆,互相持有对方的锁,就是需要拿到对方的资源
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {
if (choice == 0) {
synchronized (lipStick) {//获得口红的锁
System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁");
Thread.sleep(1000);
synchronized (mirror) {//一秒钟后获得镜子的锁
System.out.println(this.name + "获得镜子的锁");
}
}
} else {
synchronized (mirror) {//获得镜子的锁
System.out.println(this.name + "获得镜子的锁");
Thread.sleep(2000);
synchronized (lipStick) {//一秒钟后获得口红的锁
System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁");
}
}
}
}
}
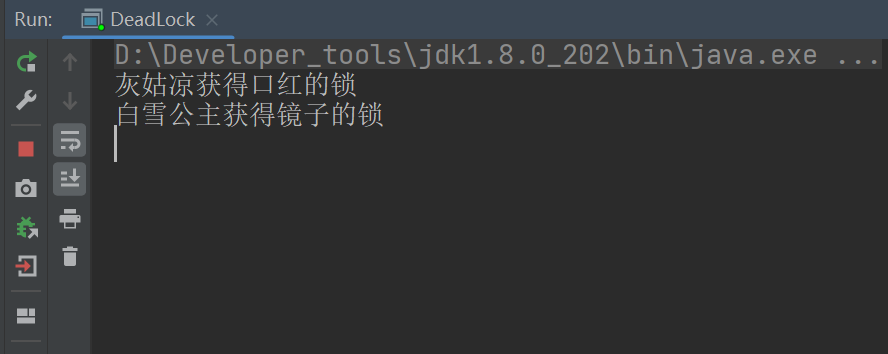
可以看见两个对象的锁都卡住了
优化代码:
package com.thread;
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Makeup girl1 = new Makeup(0, "灰姑凉");
Makeup girl2 = new Makeup(1, "白雪公主");
girl1.start();
girl2.start();
}
}
//口红
class LipStick {
}
//镜子
class Mirror {
}
class Makeup extends Thread {
//需要的资源自由一份,用static来修饰
static LipStick lipStick = new LipStick();
static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();
int choice;//选择
String name;//化妆的人
public Makeup(int choice, String name) {
this.choice = choice;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//化妆
try {
makeup();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//化妆,互相持有对方的锁,就是需要拿到对方的资源
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {
if (choice == 0) {
synchronized (lipStick) {//获得口红的锁
System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
synchronized (mirror) {//一秒钟后获得镜子的锁
System.out.println(this.name + "获得镜子的锁");
}
} else {
synchronized (mirror) {//获得镜子的锁
System.out.println(this.name + "获得镜子的锁");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
synchronized (lipStick) {//一秒钟后获得口红的锁
System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁");
}
}
}
}
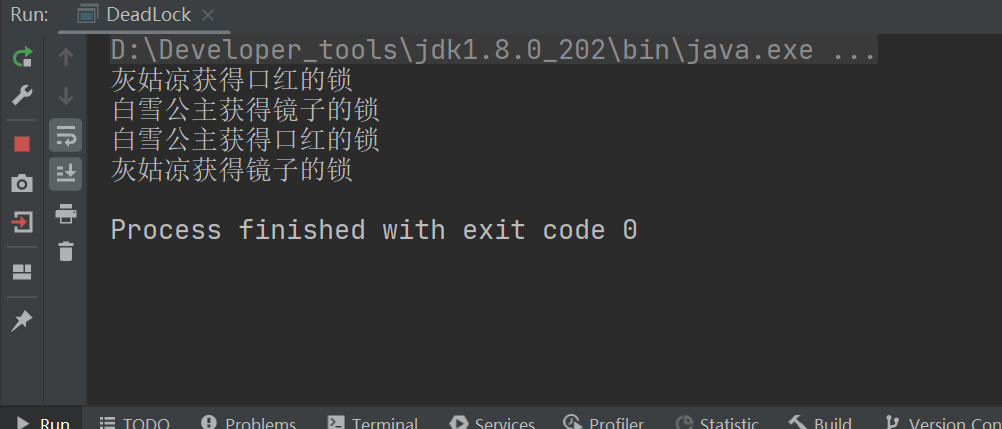
将包含的锁拿出来,用完了后释放
Lock锁
-
ReentrantLock锁是可重读锁
-
Lock是显式锁(手动开启和关闭锁),synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
-
Lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁
-
使用Lock锁,JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好。并且具有更好的扩展性
-
优先使用顺序:
- Lock > 同步代码块 > 同步方法
实现代码:
package com.syn;
import sun.util.resources.cldr.chr.TimeZoneNames_chr;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class LockTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LockTest02 lockTest02 = new LockTest02();
new Thread(lockTest02).start();
new Thread(lockTest02).start();
new Thread(lockTest02).start();
}
}
class LockTest02 implements Runnable {
int ticketNums = 10;
//定义Lock锁
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {//加锁
lock.lock();
if (ticketNums > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(ticketNums--);
} else {
break;
}
} finally {
//解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
运行结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号