Spark内核源码解析十:task原理解析和源码解析
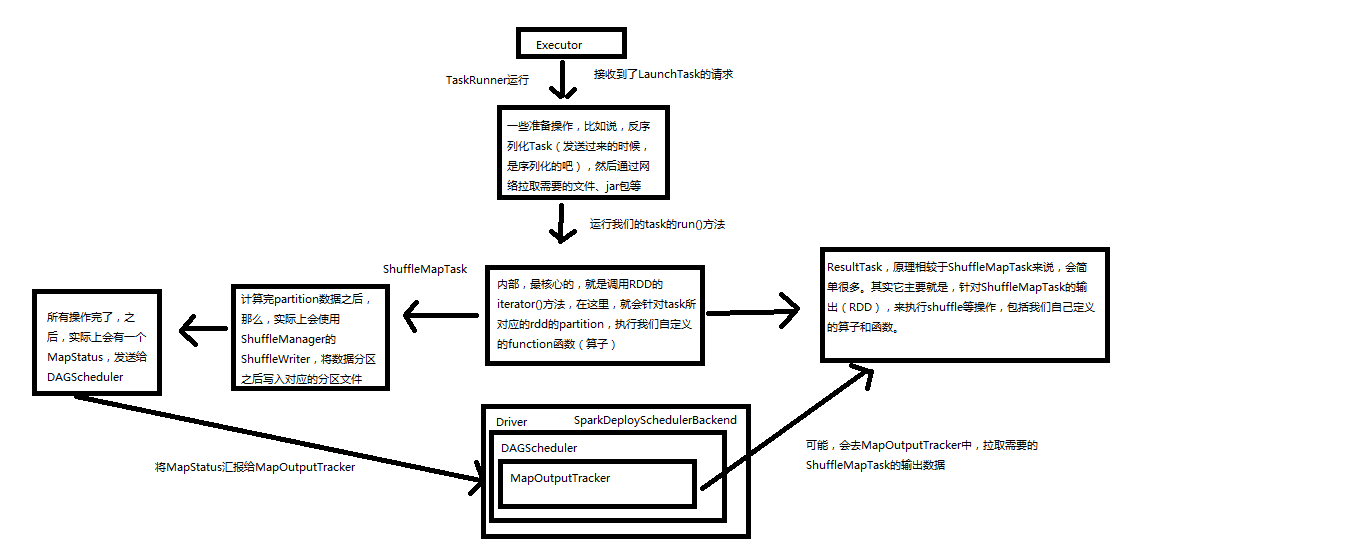
入口函数如下,Executor
// 对于每一个task都会创建一个taskRunner,继承了java的Runnable接口可以作为一个线程任务进行调用,后面会放入线程池中进行执行 def launchTask( context: ExecutorBackend, taskId: Long, attemptNumber: Int, taskName: String, serializedTask: ByteBuffer) { val tr = new TaskRunner(context, taskId = taskId, attemptNumber = attemptNumber, taskName, serializedTask) // 放入内存缓存 runningTasks.put(taskId, tr) threadPool.execute(tr) }
override def run() { val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis() // 设置了当前类的加载器, Thread.currentThread.setContextClassLoader(replClassLoader) val ser = env.closureSerializer.newInstance() logInfo(s"Running $taskName (TID $taskId)") execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.RUNNING, EMPTY_BYTE_BUFFER) var taskStart: Long = 0 startGCTime = gcTime try { // 对task采用反序列化, val (taskFiles, taskJars, taskBytes) = Task.deserializeWithDependencies(serializedTask) // 将需要的jar包和依赖拷贝过来 updateDependencies(taskFiles, taskJars) // 将数据反序列化成为task,因为java的类加载可以利用反射动态加载一个类,然后创建这个类的对象, // 可以指定相关资源进行加载 task = ser.deserialize[Task[Any]](taskBytes, Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) // If this task has been killed before we deserialized it, let's quit now. Otherwise, // continue executing the task. if (killed) { // Throw an exception rather than returning, because returning within a try{} block // causes a NonLocalReturnControl exception to be thrown. The NonLocalReturnControl // exception will be caught by the catch block, leading to an incorrect ExceptionFailure // for the task. throw new TaskKilledException } attemptedTask = Some(task) logDebug("Task " + taskId + "'s epoch is " + task.epoch) env.mapOutputTracker.updateEpoch(task.epoch) // Run the actual task and measure its runtime. taskStart = System.currentTimeMillis() // 计算task执行时间,执行task。就是mapstatus,封装了ShuffleMapTask计算数据,输出位置, // 如果后面有一个shuffleMapTask,就会去联系MapOutPutTracker,来获取上一个ShuffleMapTask位置,通过网络获取数据 // ResultTask也是一样处理 val value = task.run(taskAttemptId = taskId, attemptNumber = attemptNumber) val taskFinish = System.currentTimeMillis() // If the task has been killed, let's fail it. if (task.killed) { throw new TaskKilledException } val resultSer = env.serializer.newInstance() val beforeSerialization = System.currentTimeMillis() val valueBytes = resultSer.serialize(value) val afterSerialization = System.currentTimeMillis() // 计算跟task的一些相关统计信息,序列化,gc时间,反序列化时间 for (m <- task.metrics) { m.setExecutorDeserializeTime(taskStart - deserializeStartTime) m.setExecutorRunTime(taskFinish - taskStart) m.setJvmGCTime(gcTime - startGCTime) m.setResultSerializationTime(afterSerialization - beforeSerialization) } val accumUpdates = Accumulators.values val directResult = new DirectTaskResult(valueBytes, accumUpdates, task.metrics.orNull) val serializedDirectResult = ser.serialize(directResult) val resultSize = serializedDirectResult.limit // directSend = sending directly back to the driver val serializedResult = { if (maxResultSize > 0 && resultSize > maxResultSize) { logWarning(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). Result is larger than maxResultSize " + s"(${Utils.bytesToString(resultSize)} > ${Utils.bytesToString(maxResultSize)}), " + s"dropping it.") ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](TaskResultBlockId(taskId), resultSize)) } else if (resultSize >= akkaFrameSize - AkkaUtils.reservedSizeBytes) { val blockId = TaskResultBlockId(taskId) env.blockManager.putBytes( blockId, serializedDirectResult, StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER) logInfo( s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent via BlockManager)") ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](blockId, resultSize)) } else { logInfo(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent to driver") serializedDirectResult } } // 调用CoarseGrainedExecutor的statusUpdate方法,发送任务的执行结束的消息,向driver发送 execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FINISHED, serializedResult) } catch { case ffe: FetchFailedException => { val reason = ffe.toTaskEndReason execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FAILED, ser.serialize(reason)) } case _: TaskKilledException | _: InterruptedException if task.killed => { logInfo(s"Executor killed $taskName (TID $taskId)") execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.KILLED, ser.serialize(TaskKilled)) } case cDE: CommitDeniedException => { val reason = cDE.toTaskEndReason execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FAILED, ser.serialize(reason)) } case t: Throwable => { // Attempt to exit cleanly by informing the driver of our failure. // If anything goes wrong (or this was a fatal exception), we will delegate to // the default uncaught exception handler, which will terminate the Executor. logError(s"Exception in $taskName (TID $taskId)", t) val serviceTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - taskStart val metrics = attemptedTask.flatMap(t => t.metrics) for (m <- metrics) { m.setExecutorRunTime(serviceTime) m.setJvmGCTime(gcTime - startGCTime) } val reason = new ExceptionFailure(t, metrics) execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FAILED, ser.serialize(reason)) // Don't forcibly exit unless the exception was inherently fatal, to avoid // stopping other tasks unnecessarily. if (Utils.isFatalError(t)) { SparkUncaughtExceptionHandler.uncaughtException(t) } } } finally { // Release memory used by this thread for shuffles env.shuffleMemoryManager.releaseMemoryForThisThread() // Release memory used by this thread for unrolling blocks env.blockManager.memoryStore.releaseUnrollMemoryForThisThread() // Release memory used by this thread for accumulators Accumulators.clear() runningTasks.remove(taskId) } } }
final def run(taskAttemptId: Long, attemptNumber: Int): T = { // 创建task执行上线问,记录全局性的东西,例如重试了几次,处于那个stage,要处理那个partition的rdd context = new TaskContextImpl(stageId = stageId, partitionId = partitionId, taskAttemptId = taskAttemptId, attemptNumber = attemptNumber, runningLocally = false) TaskContextHelper.setTaskContext(context) context.taskMetrics.setHostname(Utils.localHostName()) taskThread = Thread.currentThread() if (_killed) { kill(interruptThread = false) } try { // 只封装了子类的通用操作,task子类有ShuffleMapTask,ResultTask runTask(context) } finally { context.markTaskCompleted() TaskContextHelper.unset() } }
shuffleMapTask
// 有mapstatus返回值, override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = { // Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable. // 对要处理的rdd相关数据,做一些反序列化的,这个rdd是怎么拿到的,多个task运行在executor里面,并行运行或者并发运行 // 可能不在一个地方,但是一个stage的task,要处理的rdd都是一样的,通过broadcast variable拿到 val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance() val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])]( ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) metrics = Some(context.taskMetrics) var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null try { // 获取shuffleManager val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context) // 调用rdd的iterator方法,并且传入当前task要处理哪个partition,核心逻辑就在rdd的iterator // 方法中在这里实现了针对某个partition执行算子和函数,针对rdd的partition进行处理,有返回数据通过shuffleWriter经过 // HashPartition写入自己的分区,mapstatus封装了shufflemaptask计算后的数据,存储在那里,就是blockmanager信息 // blockmanager就是spark底层内存、数据、磁盘管理组件 writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]]) return writer.stop(success = true).get } catch { case e: Exception => try { if (writer != null) { writer.stop(success = false) } } catch { case e: Exception => log.debug("Could not stop writer", e) } throw e } }
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend,调用taskscheduler更新任务的状态
case StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) => scheduler.statusUpdate(taskId, state, data.value) if (TaskState.isFinished(state)) { executorDataMap.get(executorId) match { case Some(executorInfo) => executorInfo.freeCores += scheduler.CPUS_PER_TASK makeOffers(executorId) case None => // Ignoring the update since we don't know about the executor. logWarning(s"Ignored task status update ($taskId state $state) " + "from unknown executor $sender with ID $executorId") } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号