MySQL 的基本知识和常用语句
一、sql介绍
数据库介绍
1、什么是数据库?
定义:数据库是存放数据的电子仓库。
2、是以某种方式存储百万条,上亿条数据,提供多个用户访问共享。
3、每个数据有一个或多个api用于创建,访问,管理和复制所保存的数据。(api接口)
4、系统中很多动态数据都存储在数据库中,需要通过访问数据库才能显示;
二、数据库的类型
1、关系型数据库
定义:数据库中表与表之间存在某种关系,数据存储在不同的表中
常见的关系型数据库:
(1)db2 IBM 公司
(2)oracle oracle 公司
(3)mysql oracle公司收购 (我们学习的mysql)
(4)sql server
特点:
a、安全
b、保持数据的一致性
c、实现对表与表进行复杂的数据查询
2、非关系型数据库
定义:通常数据是以对象的形式存储在数据库中
常见的非关系性数据库:
1、hbase (列模型)
2、redis (键值对存储)缓存数据
3、mongodb (文档类型)
特点:
a、效率高
b、容易扩展
c、使用更加灵活
如:淘宝搜索,添加商品购物车,存在缓存
三、mysql介绍定
1、mysql的定义
mysql是关系型数据库管理系统,我们常说的xxx数据库就是指xx数据库管理系统。
2、mysq数据库是有瑞典mysql db公司开发,目前属于oracle 公司,
3、在web应用方面(bs架构上),mysql是最好的关系型数据管理系统
4、特点:
a.体积小
b.开源,免费
c、使用c++编写
d、支持多系统
e、支持多引擎
f、msyql与其他工具组合可以搭建免费的网站系统
lamp=linux+apache+mysql+php 多有米
lnmp=linux+nginx+mysql+php 论坛
5、mysql的应用结构:
(1)单点数据库:使用于小规模应用(我们现在学的)
(2)复制:适用于中小规模的应用
(3)数据库集群,适合大规模的应用
比如:mgr集群,三主三从,一主三从;
6、数据库中术语:
(1)数据库
(2)数据表
(3)列
(4)行
(5)值
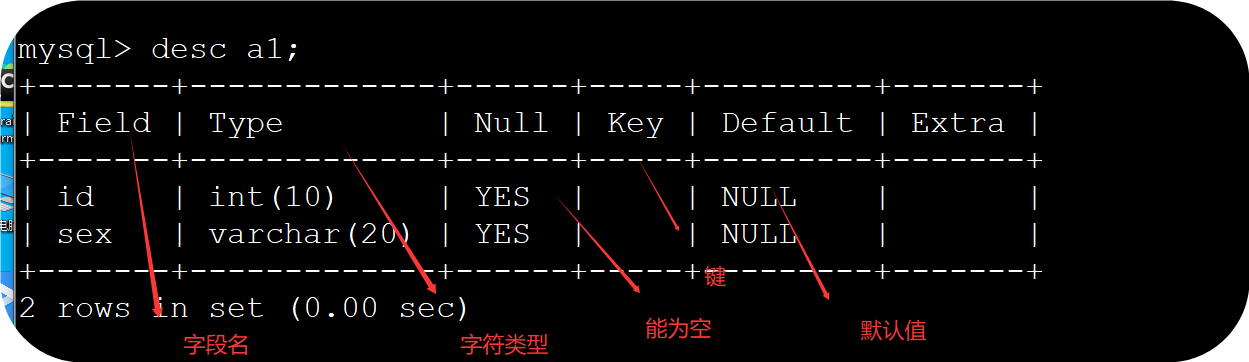
(6)字段名
(7)字符类型
(8)冗余
(9)主键
(10)外键
(11)视图
(12)索引
(13)单表
(14)多表
(15)存储

(一)数据库的操作流程
1、mysql -u root -p 进入数据库
2、show databases; 显示所有的仓库
3、create database 仓库名称; 创建仓库
如:create database h1;
4、use 库名 使用库
如:use ck1
5、show tables 查看数据库中的所有表
6、create table 表名(字段名1 字符类型(字符长度),字段名2 字符类型2(字符长度)); 创建一个表
如:create table a1(id int(10),sex varchar(20));
(二)
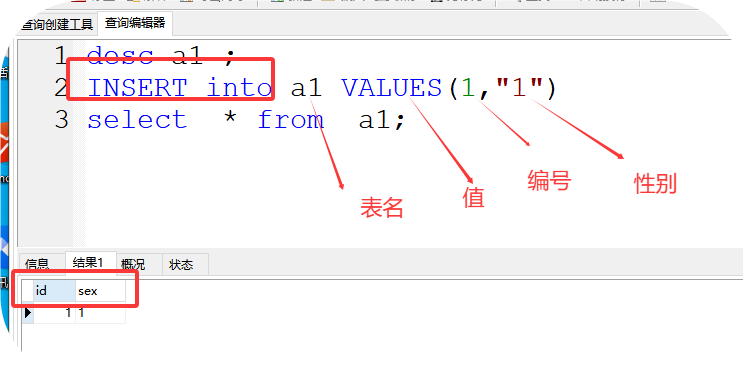
1、desc 表名 查看表结构
如:desc a1
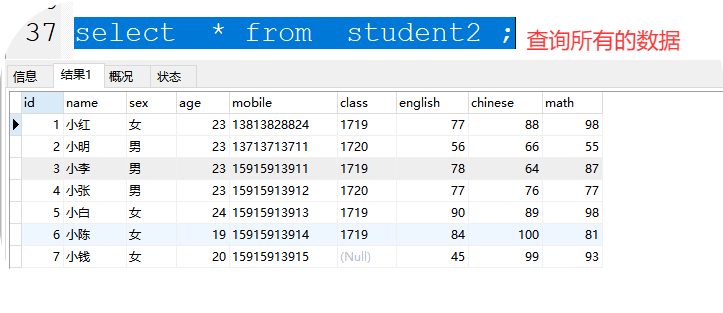
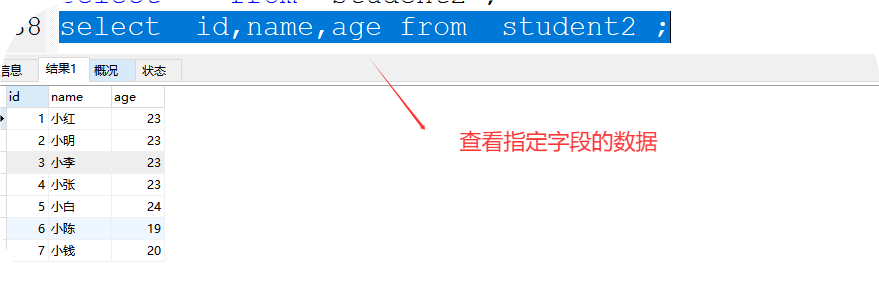
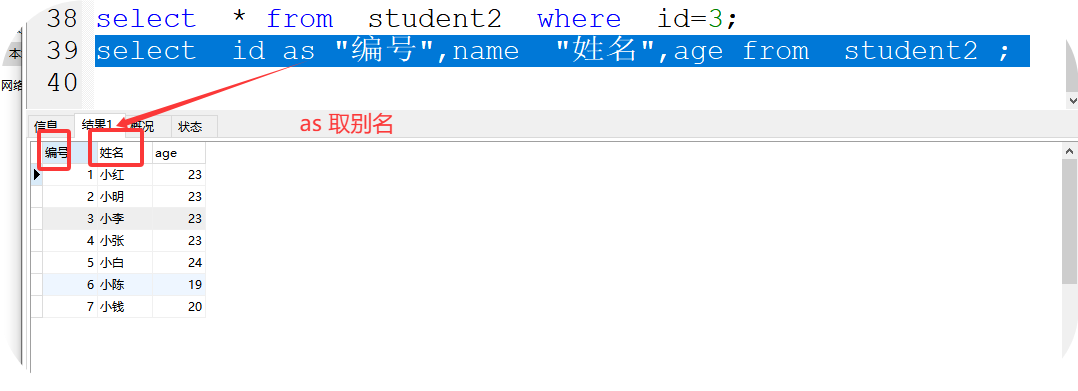
2、select * from 表名; 查看表中所有的数据 * 代表所有信息
如:select * from a1;
3、插入数据
(1)插入所有的信息
备注:插入的数值,可以直接写;插入的是字符类型,加上单引号或双引号
格式:INSERT into 表名 VALUES(值1,值2)
如:INSERT into a1 VALUES(1,"1")
(2)插入部分信息
INSERT into 表名(字段m名) VALUES(值)
如:
INSERT into a1(id) VALUES(3)
(3)解决插入中文变成?号
建表语句后面接:DEFAULT charset=utf8;
如:create table a2(id int(10),sex varchar(20)) DEFAULT charset=utf8;
4、sql字符类型
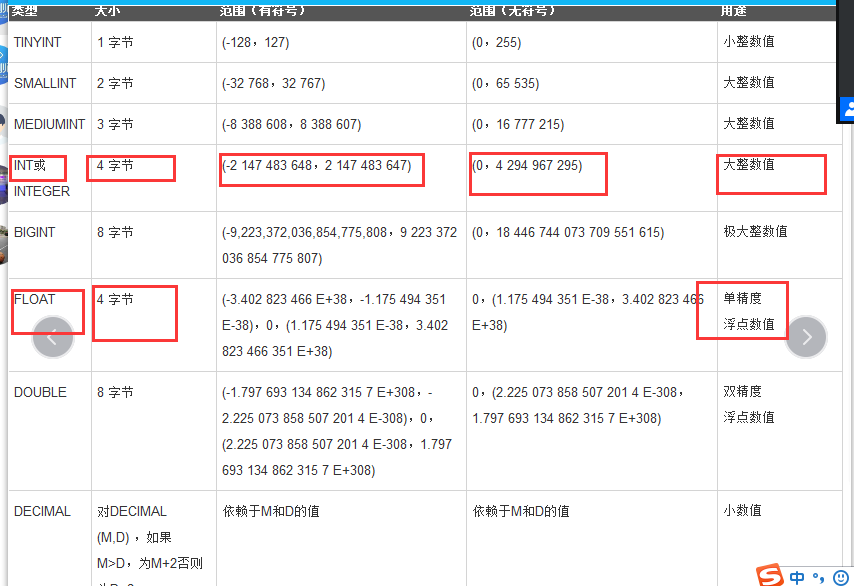
(1)数值类型
int 类型 大整数值(常用)
bugint 类型 极大整数
fliat 浮点数
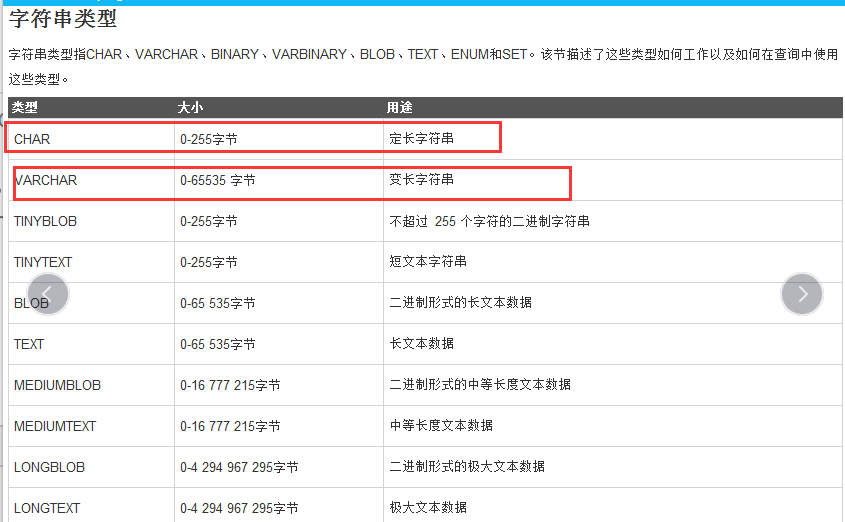
(2)字符类型
char 定长字符类型
varchar 变长字符类型
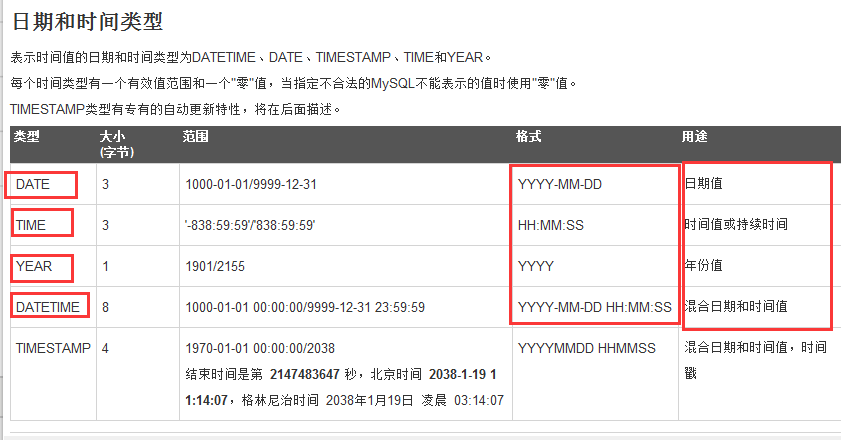
(3)时间类型
date 日期值 年月日
time 时间值 时分秒
year 年
datatime 年月日 时分秒
timestamp 混合日期 年月日 时分秒
案例:建表
5、删除
(1)drop table 表名 删除表
如:drop table a3;
(2)
a、删除表中所有数据
delete from 表名
如:delete from a2
b、删除表中指定条件的数据
格式:delete from 表名 where 条件
如:delete from a2 where id=4
(3)truncate 表名
如:truncate a2
drop >truncate>delete from 删除数据的速度
(三)对表字段操作
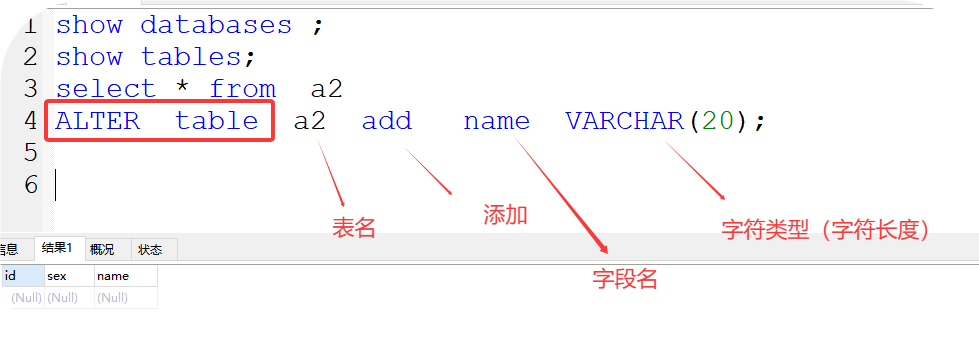
1、通过add 添加表字段
格式:ALTER table 表名 add 字段名 字符类型(字符长度);
如:
ALTER table a2 add name VARCHAR(20);
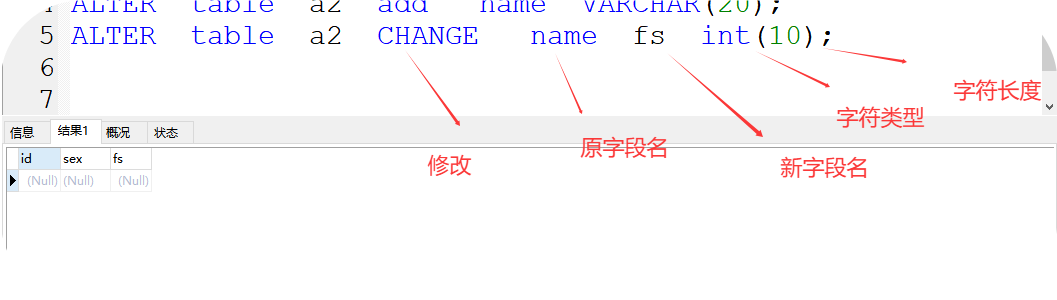
2、change 修改字段
格式:ALTER table 表名 CHANGE 原字段名 新字段名 字符类型(字符长度);
如:ALTER table a2 CHANGE name fs int(10);
3、drop 删除字段
格式:ALTER table 表名 drop 字段名;
如:ALTER table a2 drop name ;
4、rename 修改表名
格式:
ALTER table 表名 RENAME 新名
如:
ALTER table a2 RENAME hz
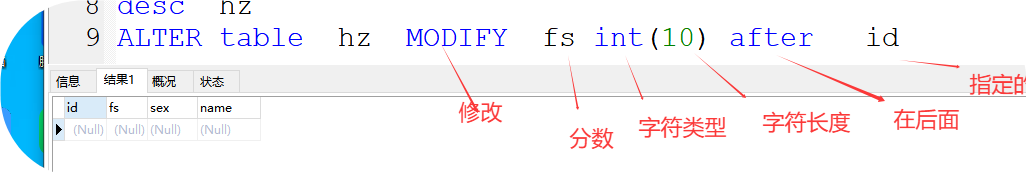
5、modify ..... after 字段调换
格式:
ALTER table 表名 MODIFY 移动的字段名 字符类型(字符长度) after 指定字段
如:
ALTER table hz MODIFY fs int(10) after id
6、first 添加字段到第一位
格式:alter table 表名 add 字段名 字符类型(字符长度) first ;
如:alter table hz add tz int(20) first ;
例题:
创建一个班级表:
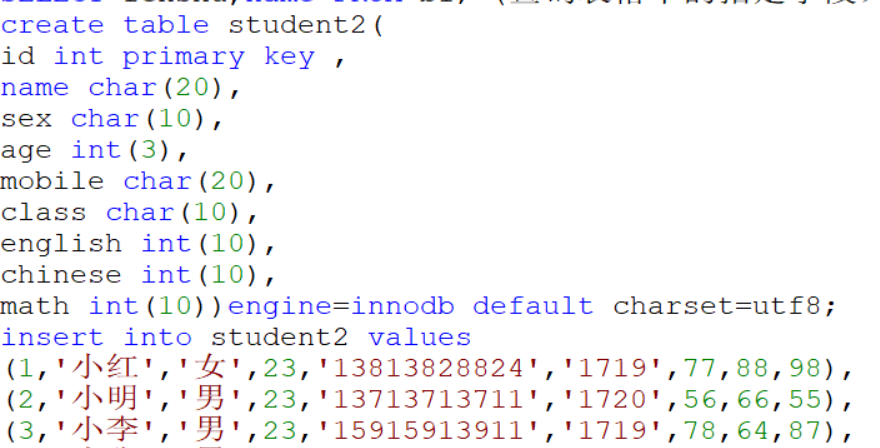
select * from student2 where id>3;
select * from student2 where id<3;
select * from student2 where id=3;
select * from student2 where id!=3;
select * from student2 where id<>3;
select * from student2 where id>=3;
select * from student2 where id<=3;
6、order by 排序
(1)order by desc 降序(从大到小)
如:select * from student2 order by math desc ;
(2)order by asc 升序(从小到大)
asc可以省略
如:select * from student2 order by math asc ;
select * from student2 order by math
(3)二次排序
select * from student2 order by math desc,chinese desc ;
(2)
and,or,between...and ,in,not in、 is not null,is null
a、and 同时满足所有的条件
select * from student2 where id>=3 and math>90
b、or 满足其中一个条件,或多个条件
select * from student2 where id>=3 or math>90
c、between...and 在范围之间 包含开始值,也包含结束值
select * from student2 where id BETWEEN 3 and 5 ;
d、 in 在一个范围匹配
select * from student2 where id in (1,4,9)
e、not in 不在这个范围 去范围
select * from student2 where id not in (1,4,9)
f、is not null 不为空
select * from student2 where class is not null ;
g、 null 为空
select * from student2 where class is null ;
7、like 模糊查询
% :匹配1个字符或多个字符
: 表示是一个字符
如:
select * from student2 where math like "8%" 匹配8开头的数据
select * from student2 where math like "%8" 匹配8 结尾的数据
select * from student2 where math like "%8%" 匹配包含8的数据
select * from student2 where math like "8" 匹配8开头的具体位数
8、limit 显示指定行数
limit (索引位,步长)
索引是从0开始,第一行的索引是0,
如:
select * from student2 LIMIT 1,2; 1表示索引0,1第二行,2表示显示2行
select * from student2 LIMIT 2; 2表示几行,默认从索引0开始
select * from student2 LIMIT 4,3


10、group by ....having
分组
group by 和函数使用
如:
select class,sum(math) from student2 group by class
分组接条件having
如:
select class,sum(math)s from student2 group by class
HAVING s>300
注意:having 一般接在group by 后面
11、改 update ....set...
格式:
UPDATE 表名 set 字段名=值 where 条件
如:
UPDATE student2 set math=60 where id=2
11、改 update ....set...
格式:
UPDATE 表名 set 字段名=值 where 条件
如:
UPDATE student2 set math=60 where id=2
12、快捷键:
(1)选择内容,右键执行
(2)注释单行# ,多行注释:ctrl+/ 选择区域
取消多行注释:ctrl+shift+/
13、linux中备份,还原
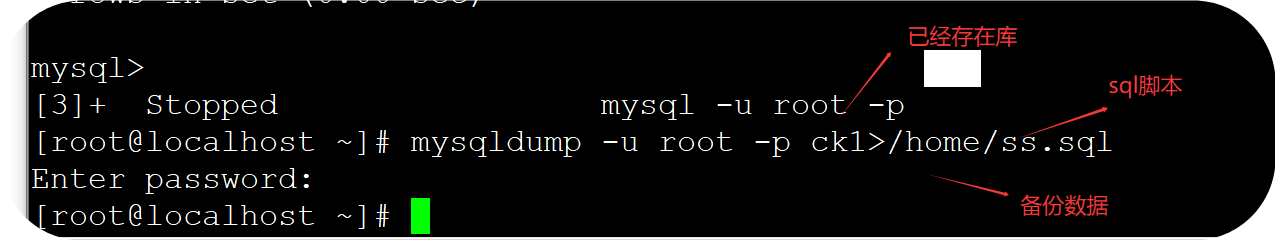
(1)备份
格式:
mysqldump -u root -p 仓库>路径/sql脚本.sql
如:mysqldump -u root -p ck1>/home/ss.sql
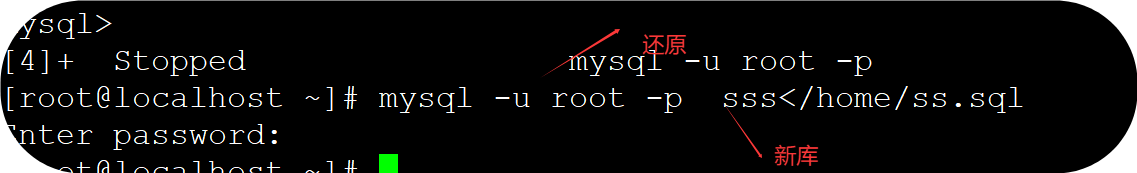
(2)还原
格式:
mysql -u root -p 新库<路径/备份好的sql语句
如:
mysql -u root -p sss</home/ss.sql


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号