机器学习项目实战-新闻分类
任务简介与数据预处理
现在我们准备一份新闻数据,数据里面包含新闻的内容以及新闻的种类等等,我们要做的就是对新闻进行一个分类任务,比如说汽车类时尚类等等。数据集链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1fG_oagJT69bIgCZgasn_Ig 提取码:yzd0
导入相关的python库
import pandas as pd import jieba # 如果没有这个库可能需要手动安装
读取数据集并删除缺失的数据集(缺失的数据很少,所以可以删除)
# read_table()读取以‘/t’分割的文件到DataFrame # 在实际使用中可以通过对sep参数的控制来对任何文本文件读取 df_news = pd.read_table('./data/val.txt',names=['category','theme','URL','content'],encoding='utf-8') df_news = df_news.dropna() # 删除缺失数据 df_news.head()
content为新闻的主体
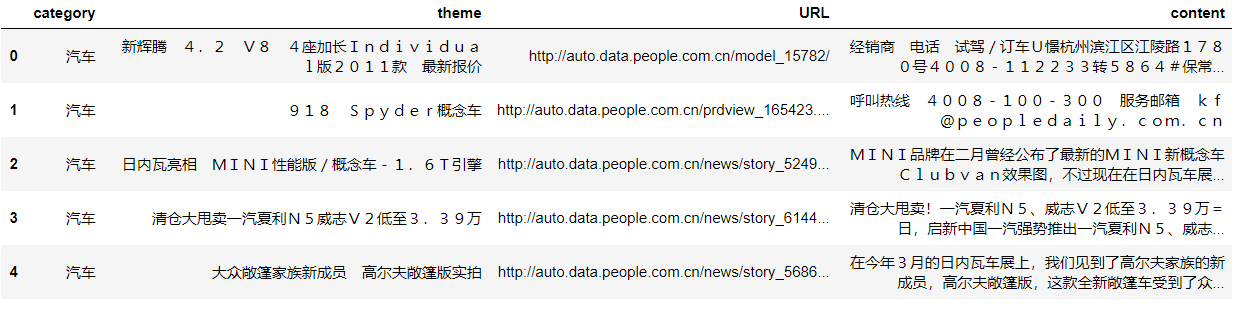
查看数据集纬度
df_news.shape
得到结果(5000,4)
将新闻内容转换为list方便进行分词并查看第1000条数据内容
content = df_news.content.values.tolist() # 转换为list 实际上是二维list print(content[1000])
内容为:
阿里巴巴集团昨日宣布,将在集团管理层面设立首席数据官岗位(Chief Data Officer),阿里巴巴B2B公
司CEO陆兆禧将会出任上述职务,向集团CEO马云直接汇报。>菹ぃ和6月初的首席风险官职务任命相同,首席数据官亦为阿
里巴巴集团在完成与雅虎股权谈判,推进“one company”目标后,在集团决策层面新增的管理岗位。0⒗锛团昨日表示
,“变成一家真正意义上的数据公司”已是战略共识。记者刘夏
下面使用python中的jieba库进行分词
content_S = []
for line in content:
# jieba分词 精确模式。返回一个列表类型,建议使用
current_segment = jieba.lcut(line)
if len(current_segment) > 1 and current_segment != '\r\n':
content_S.append(current_segment)
查看第1000条数据分词后的内容
content_S[1000]

转为pandas支持的DataFrame格式
df_content = pd.DataFrame({'content_S':content_S}) # 转换为DataFrame
df_content.head()
分完词后的结果为:
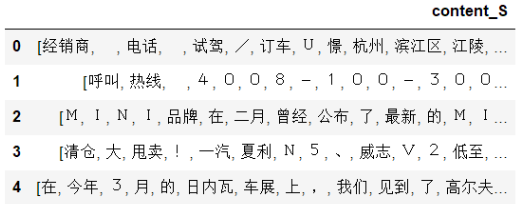
可以发现数据里面包含很多无用的词汇,所以我们需要对这些数据进行清洗,就是删除掉里面包含的停用词
删除停用词
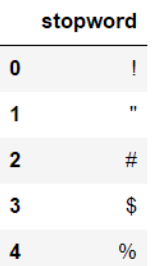
读取停用词表
# 读取停词表
stopwords = pd.read_csv('./data/stopwords.txt',index_col=False,sep='\t',quoting=3,names=['stopword'],encoding='utf-8')
stopwords.head()
结果为:
删除语料库中的停用词,这里面的all_words是为了后面的词云展示。
# 删除新闻中的停用词
def drop_stopwords(contents, stopwords):
contents_clean = [] # 删除后的新闻
all_words = [] # 构造词云所用的数据
for line in contents:
line_clean = []
for word in line:
if word in stopwords:
continue
line_clean.append(word)
all_words.append(str(word))
contents_clean.append(line_clean)
return contents_clean, all_words
contents = df_content.content_S.values.tolist()
stopwords = stopwords.stopword.values.tolist()
# 得到删除停用词后的新闻以及词云数据
contents_clean, all_words = drop_stopwords(contents, stopwords)
# df_content.content_S.isin(stopwords.stopword)
# df_content=df_content[~df_content.content_S.isin(stopwords.stopword)]
# df_content.head()
查看删除停用词后的新闻内容
df_content = pd.DataFrame({'contents_clean':contents_clean})
df_content.head()
从结果可以看出,这次的数据对比上面的数据来说质量提高了很多。

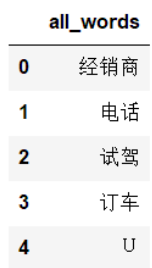
查看一下出现的所有的词汇,也就是删除停用词后的all_words。
df_all_words = pd.DataFrame({'all_words':all_words})
df_all_words.head()
结果为:
划分数据集
df_train=pd.DataFrame({'contents_clean':contents_clean,'label':df_news['category']})#生成DataFrame形式
df_train.tail()
df_train.label.unique()查看标签
array(['汽车', '财经', '科技', '健康', '体育', '教育', '文化', '军事', '娱乐', '时尚'], dtype=object)
label_mapping = {"汽车": 1, "财经": 2, "科技": 3, "健康": 4, "体育":5, "教育": 6,"文化": 7,"军事": 8,"娱乐": 9,"时尚": 0}#给标签编号
df_train['label'] = df_train['label'].map(label_mapping)
df_train.head()
调用sklearn库划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df_train['contents_clean'].values, df_train['label'].values, random_state=1)
查看x_train中的词
words = []
for line_index in range(len(x_train)):
try:
#x_train[line_index][word_index] = str(x_train[line_index][word_index])
words.append(' '.join(x_train[line_index]))
except:
print (line_index,word_index)
words[0]

调用CountVectorizer提取文本特征
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer vec = CountVectorizer(analyzer='word', max_features=4000, lowercase = False) vec.fit(words)
调用sklearn库函数MultinomialNB建立模型
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB classifier = MultinomialNB() classifier.fit(vec.transform(words), y_train)
测试
test_words = []
for line_index in range(len(x_test)):
try:
#x_train[line_index][word_index] = str(x_train[line_index][word_index])
test_words.append(' '.join(x_test[line_index]))
except:
print (line_index,word_index)
test_words[0]
测试结果
classifier.score(vec.transform(test_words), y_test) 0.80400000000000005
CountVectorizer只计算词频,统计有局限性,替换成TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer='word', max_features=4000, lowercase = False) vectorizer.fit(words)
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB classifier = MultinomialNB() classifier.fit(vectorizer.transform(words), y_train)
classifier.score(vectorizer.transform(test_words), y_test) 0.81520000000000004
准确率提高了1%
菜鸟的自我修养


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号