1、Docker 的基本用法
1.1 镜像相关操作
1.1.1、#从 dockerhub 查找镜像
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker search centos
解释说明:
NAME: 镜像仓库源的名称
DESCRIPTION: 镜像的描述
OFFICIAL: 是否 docker 官方发布
stars: 类似 Github 里面的 star,表示点赞、喜欢的意思。
AUTOMATED: 自动构建。
1.1.2、#下载镜像
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker pull centos
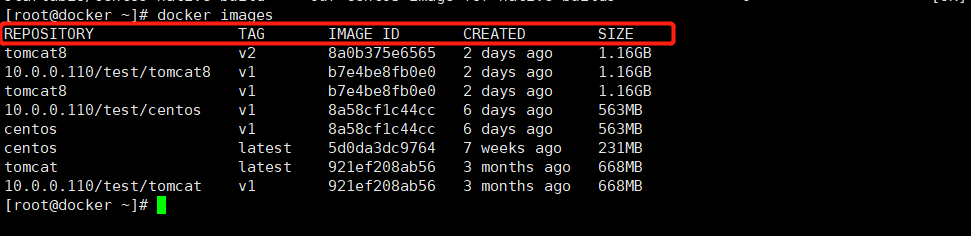
1.1.3、#查看本地镜像
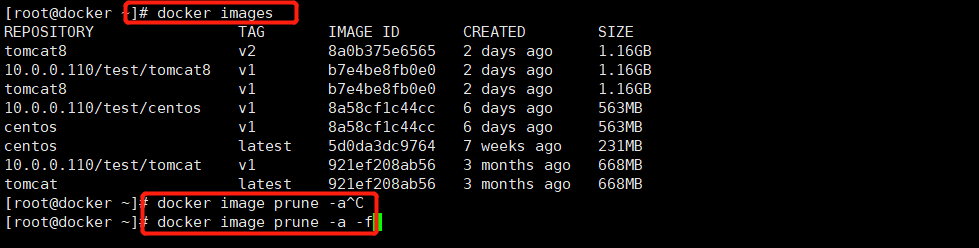
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker images
![]()
列举信息中,可以看到几个字段信息:
ü 镜像来源:来自哪个仓库,默认来自:hub.docker.com
ü 镜像标签:比喻1.17、1000-teach-2020-10-28-13-40-27
ü 镜像ID:例如22fdec3d9a6d
ü 镜像创建时间:例如:3 weeks ago
ü 镜像大小:127MB
image子命令主要支持如下选项:
-a : 列出所有(包括临时文件)镜像文件
--digests=true|false:列出镜像的数字摘要值
-q : 仅显示ID信息
1.1.4、为镜像添加tag
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker tag redis:latest myredis:latest
# 使用inspect命令查看详细信息
![]()
#使用history命令查看历史镜像
![]()
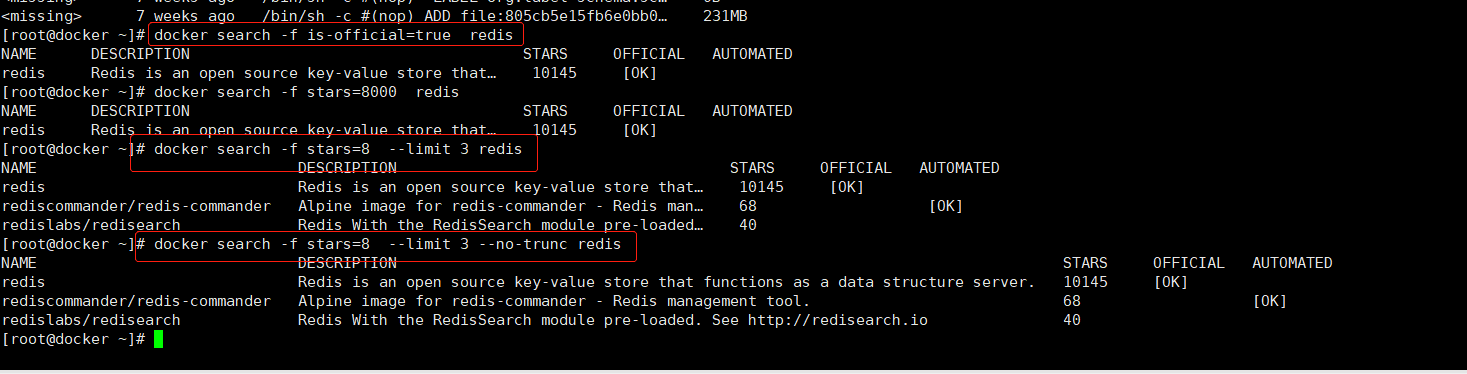
#搜索镜像
在docker中搜索镜像主要使用Search子命令,默认只搜索Docker Hub官方镜像仓库中的镜像。其语法为docker search [option] keyword。支持的命令选项主要包括:
![]()
-f : 过滤输出内容
--limit: 限制输出结果
--no-trunc: 不截断输出结果
#删除镜像
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker rmi -f centos:latest
-f:强制删除镜像
#清理镜像
使用一段时间之后,docker会产生很多临时文件,以及一些没有被使用的镜像, 我们可以通过docker image prune命令来进行清理
![]()
-a :删除所有无用的镜像,不光是临时镜像
-f :强制删除镜像,而不进行提示。
#保存镜像
使用 export 和 import
export 和 import的针对点是容器,将本机的容器导出为镜像包
使用export保存容器为镜像
[root@instance-gvpb80ao docs]# docker export daf9c3656be3 > nginx.tar
[root@instance-gvpb80ao docs]# ll | grep nginx.tar
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 135117824 9月 24 20:51 nginx.tar
使用import导入包为镜像
[root@instance-gvpb80ao docs]# docker import nginx.tar test/nginx:v1
sha256:02107323de1b074c5d2034b01eff855fec5922b45776c2721882d100ba6dd15b
[root@instance-gvpb80ao docs]# docker images | grep test
test/nginx v1 02107323de1b 22 seconds ago 131MB
#把镜像做成离线压缩包
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker save -o centos.tar.gz centos
#解压离线镜像包
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker load -i centos.tar.gz
1.2 容器相关操作
1.2.1 以交互式方式启动并进入容器
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker run --name=hello -it centos /bin/bash
[root@09c4933b5cd7 /]#
输入 exit,退出容器,退出之后容器也会停止,不会再前台运行
#docker run 运行并创建容器
--name 容器的名字
-i 交互式
-t 分配伪终端
centos: 启动 docker 需要的镜像
/bin/bash 说明你的 shell 类型为 bash,bash shell 是最常用的一种 shell, 是大多数 Linux 发行版默认的 shell。 此外还有 C shell 等其它 shell。
1.2.2 以守护进程方式启动容器
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker run --name=hello1 -td centos
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker ps |grep hello1
1a2b73ba0ac2 centos "/bin/bash" hello1
-d 在后台运行 docker
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker exec -it hello1 /bin/bash
1.2.3 查看正在运行的容器
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker ps
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker ps -a #查看所有容器,包括运行和退出的容器
1.2.4 停止容器
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker stop hello1
1.2.5 启动已经停止的容器
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker start hello1
1.2.6 进入容器
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker exec -it hello1 /bin/bash
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker rm -f hello1 #删除容器
[root@xianchaomaster1 ~]# docker --help
#查看 docker 帮助命令




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号