automake_autotools 工具集
学习blog:https://www.cnblogs.com/liwanliangblog/p/9289247.html
autotools 工具集自动生成符合 Linux 规范的 Makefile 文件。
安装 autotools 工具集,安装命令如下,
$ sudo apt-get install automake
安装完成之后,会有如下工具可用,
aclocal
autoscan
autoconf
autoheader
automake
一般大型项目,代码组织结构分为两种,一种是所有文件都在同一个目录下的 flat 结构,另一种是按层次组织的多文件夹形式。
flat 结构的项目使用 autotools 工具集
本篇测试代码如下,
入口代码 int_arithmetic.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include "sum.h" #include "sub.h" #include "mul.h" #include "div.h" int main() { printf("======== < Integer Arithmethic > ========\n"); int x, y; printf("Enter two integer: "); scanf("%d%d", &x, &y); int sm = sum(x, y); printf("sum is: %d\n", sm); int sb = sub(x, y); printf("sub is: %d\n", sb); int ml = mul(x, y); printf("mul is: %d\n", ml); int dv = divide(x, y); printf("div is: %d\n", dv); return 0; }
辅助代码,头文件,
sum.h
#ifndef SUM_H_ #define SUM_H_ int sum(int x, int y); #endif
sub.h
#ifndef SUB_H_ #define SUB_H_ int sub(int x, int y); #endif
mul.h
#ifndef MUL_H_ #define MUL_H_ int mul(int x, int y); #endif
div.h
#ifndef DIV_H_ #define DIV_H_ int divide(int x, int y); #endif
辅助代码,实现文件,
sum.c
#include "sum.h"
int sum(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
sub.c
#include "sub.h"
int sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
mul.c
#include "mul.h"
int mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
div.c
#include "div.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int divide(int x, int y)
{
if(x % y != 0)
printf("\nWarning: Integer Division May Have Accuracy Loss.\n");
return x / y;
}
1) 在项目目录下,运行 autoscan 命令,生成 configure.scan 文件,内容如下,
# -*- Autoconf -*- # Process this file with autoconf to produce a configure script. AC_PREREQ([2.69]) AC_INIT([FULL-PACKAGE-NAME], [VERSION], [BUG-REPORT-ADDRESS]) AC_CONFIG_SRCDIR([int_arithmetic.c]) AC_CONFIG_HEADERS([config.h]) # Checks for programs. AC_PROG_CC # Checks for libraries. # Checks for header files. AC_CHECK_HEADERS([stdlib.h unistd.h]) # Checks for typedefs, structures, and compiler characteristics. # Checks for library functions. AC_OUTPUT
重命名 configure.scan 为 configure.ac ,并修改其内容为,
# -*- Autoconf -*- # Process this file with autoconf to produce a configure script. AC_PREREQ([2.69]) #AC_INIT([FULL-PACKAGE-NAME], [VERSION], [BUG-REPORT-ADDRESS]) AC_INIT(int_arithmetic, 0.1, ggao@micron.com) AM_INIT_AUTOMAKE(int_arithmetic, 0.1) AC_CONFIG_SRCDIR([int_arithmetic.c]) AC_CONFIG_HEADERS([config.h]) # Checks for programs. AC_PROG_CC # Checks for libraries. # Checks for header files. AC_CHECK_HEADERS([stdlib.h unistd.h]) # Checks for typedefs, structures, and compiler characteristics. # Checks for library functions. AC_CONFIG_FILES([Makefile]) AC_OUTPUT
上述 configure.ac 中宏定义意义如下,
AC_PREREQ : 声明 autoconf 的版本号
AC_INIT : 声明软件名称,版本号及 bug report 地址
AM_INIT_AUTOMAKE : automake 需要的信息,参数为软件名和版本号
AC_CONFIG_SRCDIR : autoscan 侦测的源文件名,用来确定目录的有效性
AC_CONFIG_HEADERS : autoscan 定义要生成的头文件,后续 autoheader 要使用
AC_PROG_CC : 指定编译器,默认为 gcc
AC_CHECK_HEADERS : autoscan 侦测到的头文件
AC_CONFIG_FILES : 指定生成 Makefile,如果是多目录结构,可指定生成多个Makefile,以空格分隔,例如,AC_CONFIG_FILES([Makefile src/Makefile])
AC_OUTPUT : autoscan 输出
2) 运行 aclocal,根据 configure.ac 生成 aclocal.m4 文件,该文件主要处理各种宏定义
3) 运行 autoconf,将 configure.ac 中的宏展开,生成 configure 脚本,这过程中可能会用到 aclocal.m4
4) 执行 autoheader,生成 config.h.in 文件,该命令通常会从 "acconfig.h” 文件中复制用户附加的符号定义。该例子中没有附加的符号定义, 所以不需要创建 "acconfig.h” 文件
5) 创建 Makefile.am 文件,automake工具会根据 configure.in 中的参量把 Makefile.am 转换成 Makefile.in 文件,最终通过 Makefile.in 生成 Makefile
AUTOMAKE_OPTIONS=foreign bin_PROGRAMS=int_arithmetic int_arithmetic_SOURCES=int_arithmetic.c sum.c sub.c mul.c div.c
include_HEADERS=sum.h sub.h mul.h div.h
对上述 makefile.am 中各标签的解释,
AUTOMAKE_OPTIONS : 由于 GNU 对自己发布的软件有严格的规范, 比如必须附带许可证声明文件 COPYING 等,否则 automake 执行时会报错。
automake 提供了3中软件等级: foreign, gnu, gnits, 默认级别是gnu, 在本例中,使用 foreign 等级,它只检测必须的文件。
bin_PROGRAMS : 要生成的可执行文件名称,如果要生成多个可执行文件,用空格隔开。
int_arithmetic_SOURCES : 可执行文件依赖的所有源文件。
6) 手动添加必要的文件 NEWS,README,AUTHORS,ChangeLog
7) 执行 automake --add-missing ,该命令生成 Makefile.in 文件。使用选项 "--add-missing" 可以让 automake 自动添加一些必需的脚本文件。
8) 执行 ./configure 生成 Makefile
====>>> 至此 Makefile 生成完毕。
如果要继续安装,
9) $ make
10) $ sudo make install 即可将可执行文件安装在 /usr/local/bin/ 目录下,以后就可以直接使用啦
11) $ sudo make uninstall 即可将安装的可执行文件从 /usr/local/bin 目录下移除
如果要发布你的软件,
12) $ make dist 即可打包生成 xxx-version.tar.gz 文件
如果要清理中间文件,
13) make clean
14) make distclean
层次结构的项目使用 autotools 工具集
当前项目层次结构如下图,
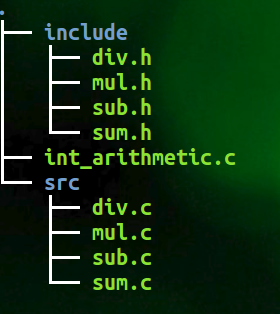
主入口函数 int_arithmetic.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "include/sum.h"
#include "include/sub.h"
#include "include/mul.h"
#include "include/div.h"
int main()
{
printf("======== < Integer Arithmethic > ========\n");
int x, y;
printf("Enter two integer: ");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
int sm = sum(x, y);
printf("sum is: %d\n", sm);
int sb = sub(x, y);
printf("sub is: %d\n", sb);
int ml = mul(x, y);
printf("mul is: %d\n", ml);
int dv = divide(x, y);
printf("div is: %d\n", dv);
return 0;
}
头文件,
sum.h
#ifndef SUM_H_ #define SUM_H_ int sum(int x, int y); #endif
sub.h
#ifndef SUB_H_ #define SUB_H_ int sub(int x, int y); #endif
mul.h
#ifndef MUL_H_ #define MUL_H_ int mul(int x, int y); #endif
div.h
#ifndef DIV_H_ #define DIV_H_ int divide(int x, int y); #endif
实现文件,
sum.c
#include "../include/sum.h"
int sum(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
sub.c
#include "../include/sub.h"
int sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
mul.c
#include "../include/mul.h"
int mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
div.c
#include "../include/div.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int divide(int x, int y)
{
if(x % y != 0)
printf("\nWarning: Integer Division May Have Accuracy Loss.\n");
return x / y;
}
1) 在项目顶层目录,建立文件 Makefile.am, 内容如下,
AUTOMAKE_OPTIONS=foreign # 软件等级 SUBDIRS=src # 先扫描子目录 bin_PROGRAMS=int_arithmetic # 软件生成后的可执行文件名称 int_arithmetic_SOURCES=int_arithmetic.c # 当前目录源文件 int_arithmetic_LDADD=src/libsrc.a # 静态连接方式,连接 src 下生成的 libsrc.a 文件 #LIBS = -l xxx -l xxx # 添加必要的库
在 src 目录,建立文件 Makefile.am,内容如下,
noinst_LIBRARIES=libsrc.a # 生成的静态库文件名称,noinst加上之后是只编译,不安装到系统中 libsrc_a_SOURCES=sum.c sub.c mul.c div.c # 这个静态库文件需要用到的依赖 include_HEADERS=../include/sum.h ../include/sub.h ../include/mul.h ../include/div.h # 导入需要依赖的头文件
2) 执行 autoscan 生成 configure.scan 文件, 如下,
# -*- Autoconf -*-
# Process this file with autoconf to produce a configure script.
AC_PREREQ([2.69])
AC_INIT([FULL-PACKAGE-NAME], [VERSION], [BUG-REPORT-ADDRESS])
AC_CONFIG_SRCDIR([int_arithmetic.c])
AC_CONFIG_HEADERS([config.h])
# Checks for programs.
AC_PROG_CC
# Checks for libraries.
# Checks for header files.
AC_CHECK_HEADERS([stdlib.h unistd.h])
# Checks for typedefs, structures, and compiler characteristics.
# Checks for library functions.
AC_CONFIG_FILES([Makefile
src/Makefile])
AC_OUTPUT
重命名 configure.scan 为 configure.ac 并修改如下,
# -*- Autoconf -*-
# Process this file with autoconf to produce a configure script.
AC_PREREQ([2.69])
#AC_INIT([FULL-PACKAGE-NAME], [VERSION], [BUG-REPORT-ADDRESS])
AC_INIT(int_arithmetic, 0.1, ggao@micron.com)
AM_INIT_AUTOMAKE(int_arithmetic, 0.1)
# Generate static lib
AC_PROG_RANLIB
AC_CONFIG_SRCDIR([int_arithmetic.c])
AC_CONFIG_HEADERS([config.h])
# Checks for programs.
AC_PROG_CC
# Checks for libraries.
# Checks for header files.
AC_CHECK_HEADERS([stdlib.h unistd.h])
# Checks for typedefs, structures, and compiler characteristics.
# Checks for library functions.
AC_CONFIG_FILES([Makefile
src/Makefile])
AC_OUTPUT
3) 执行 aclocal
4) 运行 autoconf
5) 运行 autoheader
6) 手动添加必要的文件 NEWS,README,AUTHORS,ChangeLog
7) 执行 automake --add-missing
8) 执行 ./configure 生存 Makefile
====>>> 至此 Makefile 生成完毕。
如果要继续安装,
9) $ make
10) $ sudo make install 即可将可执行文件安装在 /usr/local/bin/ 目录下,以后就可以直接使用啦
11) $ sudo make uninstall 即可将安装的可执行文件从 /usr/local/bin 目录下移除
如果要发布你的软件,
12) $ make dist 即可打包生成 xxx-version.tar.gz 文件
如果要清理中间文件,
13) make clean
14) make distclean
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gaowengang/p/6170098.html
注:本篇博客是阅读文末【参考博客】的讲解所写,内容非原创,仅是学习笔记
1. 概述
GNU构建系统,是利用脚本和make程序在特定的平台上构建软件的过程。一般过程是configure,make,make install 三部曲。这种方式成为一种习惯,被广泛使用。
为了简化可移植构建的难度,早期有一套AutoTools的工具帮助程序员构建软件。configure,make,make install三部曲,大多都是基于Auto Tools来构建的。Auto Tools是GNU程序的标准构建系统。
注:有些程序虽然也是这三部曲,但是却不是Auto Tools实现的,如Nginx
2. 不同视角的程序构建
2.1 用户视角
configure脚本是由软件开发者维护并发布的给用户使用的shell脚本。该脚本的作用是检测系统环境,最终目的是生成Make file和configure.h。
make通过读取Make file文件,开始构建软件。
make install可以将软件安装到默认或者指定的系统路径 
在上图中,开发者在分发源码包时,除了源代码中的头文件(.h)和程序源文件(.c),还有许多支持软件构建的文件和工具。
最重要的就是Makefile.in和config.h。
configure脚本执行时,将为每一个.i文件处理成对应的非.in文件,即生成:Makefile,src/Makefile,config.h
大部分情况下,只有Makefile和config.h。
Makefile用于被make程序识别并构建软件,而config.h中定义的宏,有助于软件通过预编译来改变自身代码,来适应目标平台某些特殊性。
有些软件在configure阶段,还可以生成其他文件,这完全取决于软件本身。
configure
一般而言,configure主要检查当前目标平台的程序,库,头文件,函数等的兼容性。这些结果将作用于config.h和Makefile文件的生成,从而影响最终的编译。
用户可以通过configure配置参数,来定制需要包含或者不需要包含的组件,安装路径等。大概可以分为五组:
- 安装路径相关
- 程序名配置
- 跨平台编译
- 动静态库选项
- 程序组件
configure在执行过程中,除了生成Makefile外,还会生成,但是不限于以下文件:
- config.log日志文件
- config.cache缓存文件。提高下一次configure的速度,-C指定
- config.status实际调用编译工具构建软件的shell脚本
如果软件通过libtool构建,还会生成libtool脚本。
2.2 开发者视角
开发者除了编写软件本身的代码外,还需要负责生成构建软件所需要的文件和工具。因此对于开发者而言,要么自己编写构建用的脚本,要么选择部分依赖工具。Auto tools就是这样的工具。
Autotools包括了autoconf和automake等命令
autoreconf
为了生成configure脚本和Makefile.in等文件,开发者需要创建并维护一个configure.ac文件,以及一些列的Makefile.am
autoreconf程序能够自动按照合理的顺序调用autoconf,automake,aclocal程序 
configure.ac
configure.ac用于生成configure脚本,autoconf工具用来完成这一步。如一个简单的configure.ac例子:
AC_PREREQ
AC_PREREQ([2.63])
AC_INIT([st], [1.0], [zhoupingtkbjb@163.com])
AC_CONFIG_SRCDIR([src/main.c])
AC_CONFIG_HEADERS([src/config.h])
AM_INIT_AUTOMAKE([foreign])
# Checks for programs.
AC_PROG_CC
AC_PROG_LIBTOOL
# Checks for libraries.
# Checks for header files.
# Checks for typedefs, structures, and compiler characteristics.
# Checks for library functions.
AC_CONFIG_FILES([Makefile
src/Makefile
src/a/Makefile
src/b/Makefile])
AC_OUTPUT 其中以AC_开头的类似函数调用一样的代码,实际上时被称为“宏”的调用。
这里的宏,与C语言中的宏概念类似,会被替换展开。
configure.ac文件的一般布局是:
AC_INIT
测试程序
测试函数库
测试头文件
测试类型定义
测试结构
测试编译器特性
测试库函数
测试系统调用
AC_OUTPUTconfigure.ac标签说明
| 标签 | 说明 |
| AC_PREREQ | 声明autoconf要求的版本号 |
| AC_INIT | 定义软件名称,版本号,联系方式 |
| AM_INIT_AUTOMAKE | 必须要的,参数为软件名和版本号 |
| AC_CONFIG_SCRDIR | 该宏用来侦测所指定的源码文件是否存在,来确定源码有效性。 |
| AC_CONFIG_HEADER | 该宏用来生成config.h文件,以便autoheader命令使用 |
| AC_PROG_CC | 指定编译器,默认GCC |
| AC_CONFIG_FILE | 生成相应的Makefile文件,不同目录下通过空格分隔 |
| AC_OUTPUT | 用来设定configure所要产生的文件,如果是makefile,config会把它检查出来的结果带入makefile.in文件,产生合适的makefile |
m4是一个经典的宏工具。autoconf正是构建在m4之上,可以理解为autoconf预先定义了大量的,用户检查系统可移植性的宏,这些宏在展开就是大量的shell脚本。
所以编写configure.ac就需要对这些宏掌握熟练,并且合理调用。
autoscan和configure.scan
可以通过调用autoscan命令,得到一个初始化的configure.scan文件。然后重命名为configure.ac后,在此基础上编辑configure.ac。
autoscan会扫描源码,并生成一些通用的宏调用,输入的声明,以及输出的声明。尽管autoscan十分方便,但是没人能够在构建之前,就把源码完全写好。
因此,autoscan通常用于初始化configure.ac,即生成configure.ac的雏形文件configure.scan
autoheader和configure.h
autoheader命令扫描configure.ac文件,并确定如何生成config.h.in。每当configure.ac变化时,都可以通过执行autoheader更新config.h.in。
在configure.ac通过AC_CONFIG_HEADERS([config.h])告诉autoheader应当生成config.h.in的路径
config.h包含了大量的宏定义,其中包括软件包的名字等信息,程序可以直接使用这些宏。更重要的是,程序可以根据其中的对目标平台的可移植相关的宏,通过条件编译,动态的调整编译行为。
automake和Makefil.am
手工编写Makefile是一件相当繁琐的事情,并且随着项目的复杂程序变大,编写难度越来越大。automake工具应运而生。
可以编辑Makefile.am文件,并依靠automake来生成Makefile.in
aclocal
configure.ac实际是依靠宏展开来得到configure。因此,能否成功生成,取决于宏定义是否能够找打。
autoconf会从自身安装路径下寻找事先定义好的宏。然而对于像automake,libtool,gettex等第三方扩展宏,autoconf便无从知晓。
因此,aclocal将在configure.ac同一个目录下生成aclocal.m4,在扫描configure.ac过程中,将第三方扩展和开发者自己编写的宏定义复制进去。
如此一来,autoconf遇到不认识的宏时,就会从aclocal.m4中查找 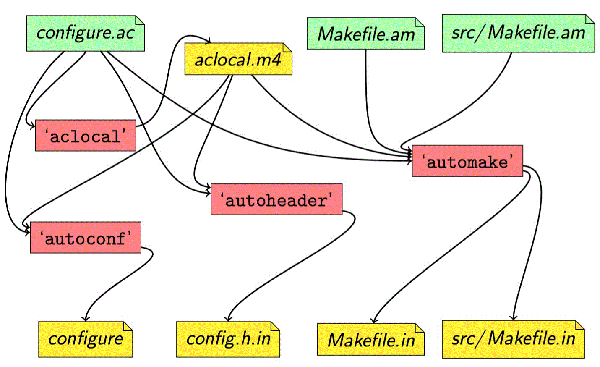
libtool
libtool试图解决不同平台下,库文件的差异。libtool实际是一个shell脚本,实际工作中,调用了目标平台的cc编译器和链接器,以及给予合适的命令行参数。
libtool可以单独使用,也可以跟autotools集成使用。
辅助文件
aclocal.m4 该宏定义文件包含了第三方宏定义,用于autoconf展开configure.ac
NEWS,README,AUTHORS,ChangeLog GNU软件标配
config.guess,config.sub 由automake产生,两个用于目标平台检查的脚本
depcomp install-sh 由automake产生,用于完成编译和安装的脚本
missing 由automake产生
ltmain.sh 由libtoolize产生,用于在configure阶段,配置生成可运行于目标平台的libtool脚本
ylwrap 由automake产生
autogen.sh 早期autoreconf并不存在,软件开发者就自己编写脚本,按照顺序调用autoconf,autoheader,automake等工具。这个文件就是这样的脚本。
3. 导图图片

4. configure选项
`configure' configures hello 1.0 to adapt to many kinds of systems.
Usage: ./configure [OPTION]... [VAR=VALUE]...
To assign environment variables (e.g., CC, CFLAGS...), specify them as
VAR=VALUE. See below for descriptions of some of the useful variables.
Defaults for the options are specified in brackets.
Configuration:
-h, --help display this help and exit
--help=short display options specific to this package
--help=recursive display the short help of all the included packages
-V, --version display version information and exit
-q, --quiet, --silent do not print `checking ...' messages
--cache-file=FILE cache test results in FILE [disabled]
-C, --config-cache alias for `--cache-file=config.cache'
-n, --no-create do not create output files
--srcdir=DIR find the sources in DIR [configure dir or `..']
Installation directories:
--prefix=PREFIX install architecture-independent files in PREFIX
[/usr/local]
--exec-prefix=EPREFIX install architecture-dependent files in EPREFIX
[PREFIX]
By default, `make install' will install all the files in
`/usr/local/bin', `/usr/local/lib' etc. You can specify
an installation prefix other than `/usr/local' using `--prefix',
for instance `--prefix=$HOME'.
For better control, use the options below.
Fine tuning of the installation directories:
--bindir=DIR user executables [EPREFIX/bin]
--sbindir=DIR system admin executables [EPREFIX/sbin]
--libexecdir=DIR program executables [EPREFIX/libexec]
--sysconfdir=DIR read-only single-machine data [PREFIX/etc]
--sharedstatedir=DIR modifiable architecture-independent data [PREFIX/com]
--localstatedir=DIR modifiable single-machine data [PREFIX/var]
--libdir=DIR object code libraries [EPREFIX/lib]
--includedir=DIR C header files [PREFIX/include]
--oldincludedir=DIR C header files for non-gcc [/usr/include]
--datarootdir=DIR read-only arch.-independent data root [PREFIX/share]
--datadir=DIR read-only architecture-independent data [DATAROOTDIR]
--infodir=DIR info documentation [DATAROOTDIR/info]
--localedir=DIR locale-dependent data [DATAROOTDIR/locale]
--mandir=DIR man documentation [DATAROOTDIR/man]
--docdir=DIR documentation root [DATAROOTDIR/doc/hello]
--htmldir=DIR html documentation [DOCDIR]
--dvidir=DIR dvi documentation [DOCDIR]
--pdfdir=DIR pdf documentation [DOCDIR]
--psdir=DIR ps documentation [DOCDIR]
Some influential environment variables:
CC C compiler command
CFLAGS C compiler flags
LDFLAGS linker flags, e.g. -L<lib dir> if you have libraries in a
nonstandard directory <lib dir>
LIBS libraries to pass to the linker, e.g. -l<library>
CPPFLAGS (Objective) C/C++ preprocessor flags, e.g. -I<include dir> if
you have headers in a nonstandard directory <include dir>
CPP C preprocessor
Use these variables to override the choices made by `configure' or to help
it to find libraries and programs with nonstandard names/locations.
Report bugs to <yunweinote@126.com>.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号