python 装饰器和软件目录规范一
1、装饰器和迭代器的概念。
装饰器本质是一个函数,是为其他函数添加附加功能。
原则:不修改原函数源代码
不修改原函数的调用方式
2、装饰器的简单应用
# Author : xiajinqi
import time
def timmer(func):
def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
func()
stop_time =time.time()
print("执行时间为 %s" %(stop_time - start_time))
return wrapper
@timmer
def loggin():
time.sleep(1)
print("hello world")
loggin()
3、理解装饰器的知识需要储备 :
函数即为变量、高阶函数 、嵌套函数
4、 函数在内存中定义。深入理解函数即为变量的概念.
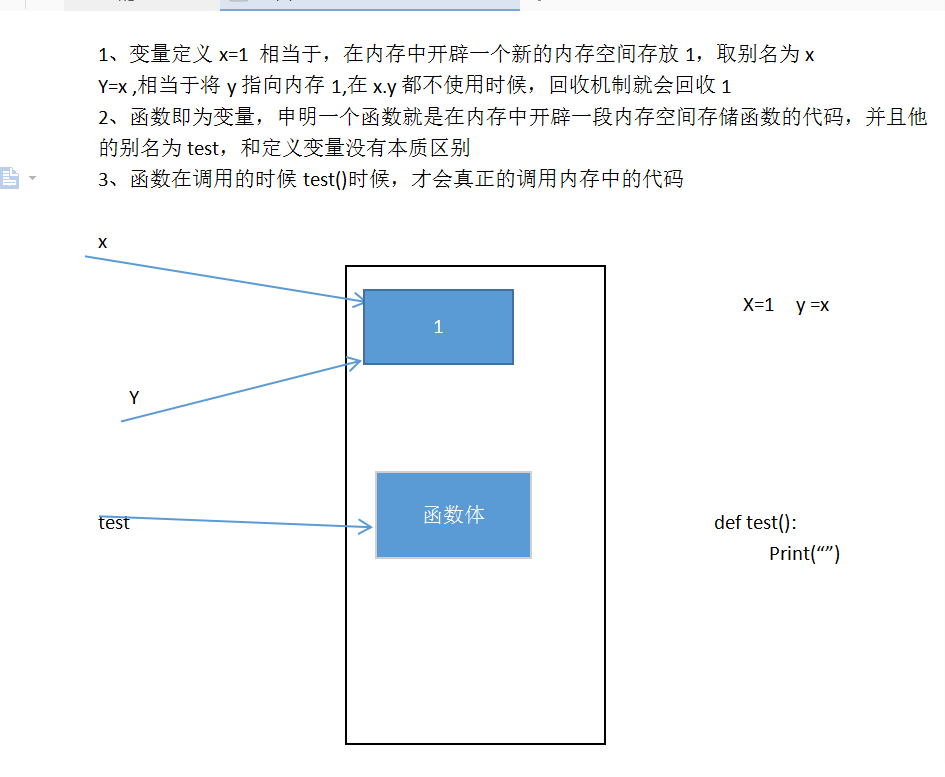
需要区分定义和调用是两步进行的。必须要先定义再调用
def foo(): print("foo") bar() def bar(): print("bar") foo() E:\Users\xiajinqi\PycharmProjects\Atm\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/Users/xiajinqi/PycharmProjects/Atm/bin/test2.py foo bar Process finished with exit code 0 # Author : xiajinqi def foo(): print("foo") bar() #foo 执行时候bar还没有定义所以执行会报错 foo() def bar(): print("bar") foo() bar() E:\Users\xiajinqi\PycharmProjects\Atm\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/Users/xiajinqi/PycharmProjects/Atm/bin/test2.py foo Traceback (most recent call last): File "E:/Users/xiajinqi/PycharmProjects/Atm/bin/test2.py", line 6, in <module> foo() File "E:/Users/xiajinqi/PycharmProjects/Atm/bin/test2.py", line 5, in foo bar() NameError: name 'bar' is not defined Process finished with exit code 1
5、函数即变量和高阶函数,高阶函数,将一个函数作为变量参数传递给另外一函数,返回值中包含函数。(可以实现装饰器的第一步,把改变代码添加功能,但是会改变调用方式还不是一个真正的装饰器)
#高阶函数
# Author : xiajinqi
import time
def foo():
time.sleep(1)
print("foo")
return 0
def test(func):
start_time = time.time()
func()
end_time = time.time()
print("tims is %s" %(end_time -start_time ))
test(foo) #相当于给foo加了一个附加功能 但是还是不符合装饰器规则。改变了调用规则
#高阶函数 传递 test(foo)
# Author : xiajinqi
import time
def foo():
time.sleep(1)
print("foo")
return 0
def test(func):
print(func)
func()
return func
foo=test(foo) # 在赋值时候,foo 作为地址传递给test函数,此处相当于同时调用了两个函数test和foo(test内部调用foo),所以会比foo更多的功能
foo() # 这时候的foo已经是新的foo了。
6、嵌套函数,在一个函数体内调用另外一个函数
#高阶函数 传递 test(foo)
# Author : xiajinqi
def test():
print('test')
def bar() :
print('bar')
return bar #bar()内部调用
# 外部调用
bar=test()
bar()
7、函数的作用域
# 全局变量和局部变量
def test1():
print("test1")
def test2():
print("test2")
def test3():
print("test3")
test3()
test1() #test2由于没有调用,所以test3也不会调用
8、装饰器的实现
# 装饰器,三个函数,要求实现统计三个函数的运行时间,在函数运行的时候,会自动统计函数的运行时间,要求不修源代码
import time
#装饰器
def deco(func):
start_time = time.time()
return func
end_time = time.time()
print("运行时间 %s" %(end_time-start_time))
def timeer(func):
def deco():
start_time = time.time()
func()
end_time = time.time()
print("运行时间 %s" % (end_time - start_time))
return deco
@timeer
def test1():
time.sleep(1)
print("test1")
@timeer
def test2():
time.sleep(1)
print("test2")
@timeer
def test3():
time.sleep(1)
print("test3")
#test1=timeer(test1) #思考timemer存在的含义 timmer调用什么也没有做,传递func给deco
#test1() #相当于执行deco,但是如果直接调用deco 就会改变调用方式。因此需用timmer可以达到
test2()
9 、高级装饰器:
# 装饰器,三个函数,要求实现统计三个函数的运行时间,在函数运行的时候,会自动统计函数的运行时间,要求不修源代码 import time #装饰器 def timeer(func): def deco(*args,**kwargs): start_time = time.time() func(*args,**kwargs) # 不定参数传递 end_time = time.time() print("运行时间 %s" % (end_time - start_time)) return deco @timeer def test1(): time.sleep(1) print("test1") @timeer def test2(name): time.sleep(1) print("test2 %s" %(name)) @timeer def test3(): time.sleep(1) print("test3") #test1=timeer(test1) #思考timemer存在的含义 timmer调用什么也没有做,传递func给deco #test1() #相当于执行deco,但是如果直接调用deco 就会改变调用方式。因此需用timmer可以达到 test1() test2("xiajinqi")
10、装饰器高潮,模拟网站登录,三个页面,其中两个需要加上验证功能
# Author : xiajinqi # 装饰器,三个函数,要求实现统计三个函数的运行时间,在函数运行的时候,会自动统计函数的运行时间,要求不修源代码 import time #装饰器 def auth(func): def deco(*args,**kwargs): print("func") username = input("name:") passwd = input("passwd:") if username == 'xiajinqi' and passwd == '123456': func(*args,**kwargs) else : print("认识失败") return deco def index(): print("index of xiajinqi") @auth def home(name): print("index of home %s" %(name)) @auth def bbs(): print("index of xiajinqi") index() home("xiajinqi") bbs()
良禽择木而栖 贤臣择主而侍



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号