CS61A Fall 2020 Lab 4 Recursion, Tree Recursion, Python Lists 我的思路
Lab 4 Description: https://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61a/fa20/lab/lab04/#q1
我会把题目倒着放,因为通常后面的题能带给我的思考更多(也更可能做不出来),所以如果我revisit这个页面,希望先看到后面的题~
这个Lab关于list的题目都很简单,主要也是在做recursion,总体难度没有 Homework 2 那么大。
Q6: Add Characters
Given two words, w1 and w2, we say w1 is a subsequence of w2 if all the letters in w1 appear in w2 in the same order (but not necessarily all together). That is, you can add letters to any position in w1 to get w2. For example, "sing" is a substring of "absorbing" and "cat" is a substring of "contrast".
Implement add_chars, which takes in w1 and w2, where w1 is a substring of w2. This means that w1 is shorter than w2. It should return a string containing the characters you need to add to w1 to get w2. Your solution must use recursion.
In the example above, you need to add the characters "aborb" to "sing" to get "absorbing", and you need to add "ontrs" to "cat" to get "contrast".
The letters in the string you return should be in the order you have to add them from left to right. If there are multiple characters in the w2 that could correspond to characters in w1, use the leftmost one. For example, add_words("coy", "cacophony") should return "acphon", not "caphon" because the first "c" in "coy" corresponds to the first "c" in "cacophony".
思路:
以add_chars('resin', 'recursion')为例:
r == r
e == e
s != c (返回c)
i != u (返回u)
n != r (返回r)
s == s
i == i
n != o (返回o)
n == n
综上,recursion case应该有两种情况:
首字母相同时,返回add_chars(w1[1:], w2[1:])
首字母不同时,返回w2[0] + add_chars(w1, w2[1:])
然后,考虑base case的情况:
w2比w1更长,所以有可能出现w1已经没了但w2还在递归的情况(换句话说,只有w2的char全部都过了一遍,才是真正的结束)
先处理w2结束了的情况:return 0
再处理w1结束了(但w2没结束)的情况:return w2(剩下的字母都没有在w1出现)
代码:
def add_chars(w1, w2):
"""
Return a string containing the characters you need to add to w1 to get w2.
You may assume that w1 is a subsequence of w2.
>>> add_chars("owl", "howl")
'h'
>>> add_chars("want", "wanton")
'on'
>>> add_chars("rat", "radiate")
'diae'
>>> add_chars("a", "prepare")
'prepre'
>>> add_chars("resin", "recursion")
'curo'
>>> add_chars("fin", "effusion")
'efuso'
>>> add_chars("coy", "cacophony")
'acphon'
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if len(w2) == 0:
return ''
elif len(w1) == 0:
return w2
else:
return w2[0] + add_chars(w1, w2[1:]) if w1[0] != w2[0] else add_chars(w1[1:], w2[1:])Q5: Maximum Subsequence
A subsequence of a number is a series of (not necessarily contiguous) digits of the number. For example, 12345 has subsequences that include 123, 234, 124, 245, etc. Your task is to get the maximum subsequence below a certain length.
There are two key insights for this problem:
- You need to split into the cases where the ones digit is used and the one where it is not. In the case where it is, we want to reduce
tsince we used one of the digits, and in the case where it isn't we do not. - In the case where we are using the ones digit, you need to put the digit back onto the end, and the way to attach a digit
dto the end of a numbernis10 * n + d.
思路:
- 这个题感觉这个跟 Homework 2 Q4: Count coins 有点像,但不是简单count,是要算出具体的值
- Recursion case:每次只考虑最右边的一个digit,有用上这个digit的返回值是
max_subseq(n//10, t-1)*10 + n%10,没有用上这个digit的返回值是max_subseq(n//10, t) - Base case:如果
t为0,返回值为0;在此基础上,如果n只有1个digit,返回n。也就是说,比如(3, t)这种情况,不管t是1还是2还是3还是4还是5,只要t不是0,就返回n,这样可以得到位数比t小的组合(比如max_subseq(20215, 3)里的二位数和一位数),也可以处理t的位数比n的位数多的情况,比如max_subseq(20215, 6)这个test case
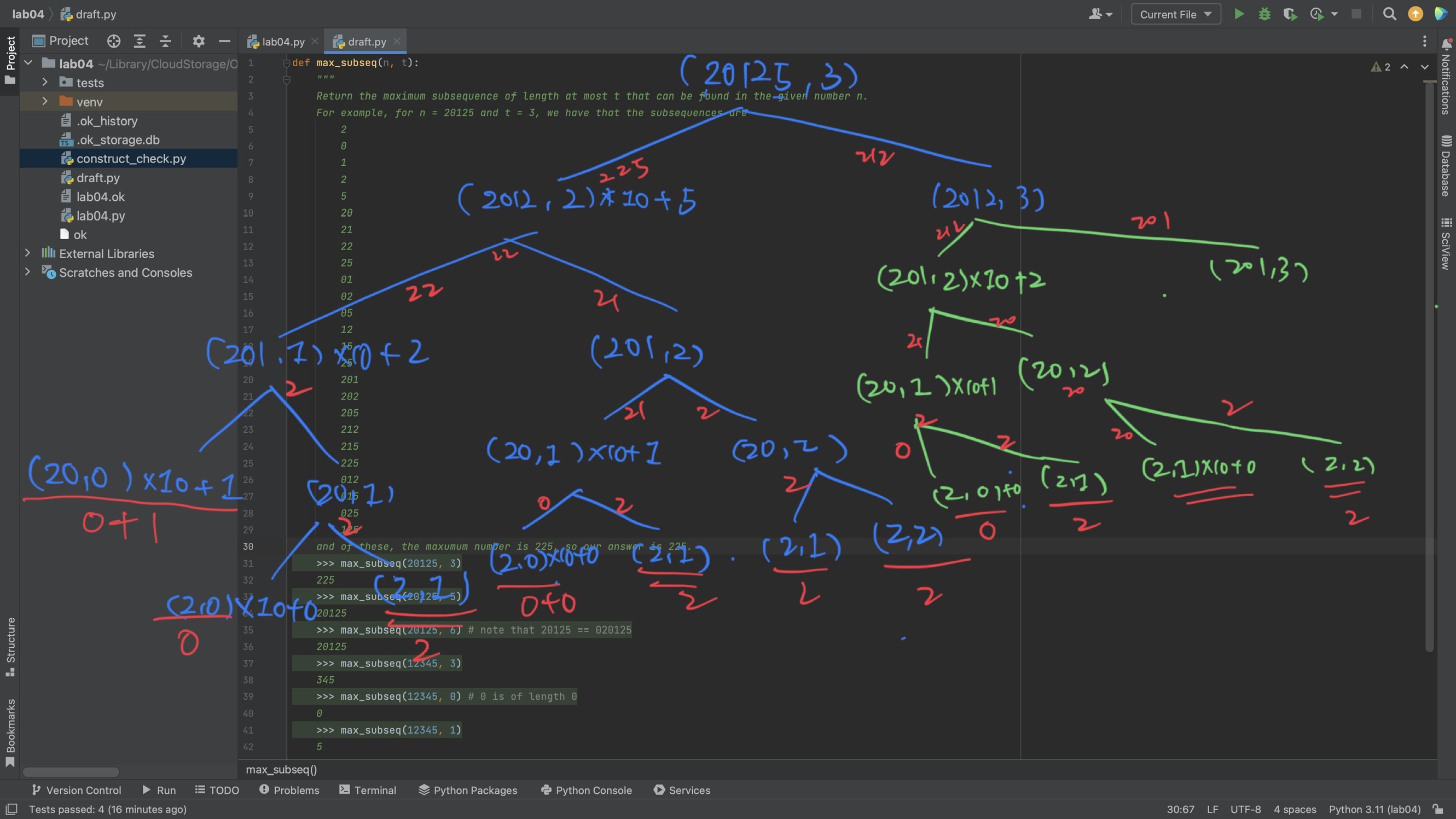
代码:
def max_subseq(n, t):
"""
Return the maximum subsequence of length at most t that can be found in the given number n.
For example, for n = 20125 and t = 3, we have that the subsequences are
2
0
1
2
5
20
21
22
25
01
02
05
12
15
25
201
202
205
212
215
225
012
015
025
125
and of these, the maxumum number is 225, so our answer is 225.
>>> max_subseq(20125, 3)
225
>>> max_subseq(20125, 5)
20125
>>> max_subseq(20125, 6) # note that 20125 == 020125
20125
>>> max_subseq(12345, 3)
345
>>> max_subseq(12345, 0) # 0 is of length 0
0
>>> max_subseq(12345, 1)
5
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if t == 0:
return 0
elif n < 10: # equivalent to (n < 10) and (t != 0)
return n
else:
return max(max_subseq(n // 10, t - 1) * 10 + n % 10, max_subseq(n // 10, t))Q4: Insect Combinatorics
Consider an insect in an M by N grid. The insect starts at the bottom left corner, (0, 0), and wants to end up at the top right corner, (M-1, N-1). The insect is only capable of moving right or up. Write a function paths that takes a grid length and width and returns the number of different paths the insect can take from the start to the goal. (There is a closed-form solution to this problem, but try to answer it procedurally using recursion.)
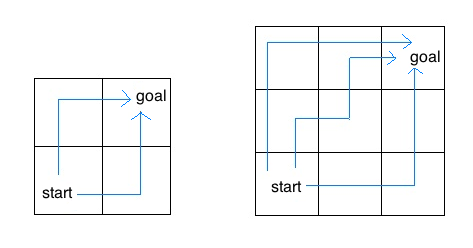
For example, the 2 by 2 grid has a total of two ways for the insect to move from the start to the goal. For the 3 by 3 grid, the insect has 6 diferent paths (only 3 are shown above).
思路:
目标是算从(1, 1)到(m, n)的可能路径。我们假设这个点目前在(x, y)这个位置上(1 < x ≤ m,1 < y ≤ n)。
根据规则(只能向右或者向上行动),对于在(x, y)的点来说,它只可能是由(x-1, y)向右移动,或者是(x, y-1)向上移动得到的。
这样一直往前追溯,直到x已经是1了(不能再往左推,换句话说就是只能一直往下推,或者是只有一直往下推这1种可能),
或者y已经是1了(不能再往下推,换句话说就是只能一直往左推,或者是只有一直往左推这1种可能),这就构成了base case。
代码:
def paths(m, n):
"""Return the number of paths from one corner of an
M by N grid to the opposite corner.
>>> paths(2, 2)
2
>>> paths(5, 7)
210
>>> paths(117, 1)
1
>>> paths(1, 157)
1
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if m == 1 or n == 1:
return 1
else:
return paths(m-1, n) + paths(m, n-1)Q3: Summation
Now, write a recursive implementation of summation, which takes a positive integer n and a function term. It applies term to every number from 1 to n including n and returns the sum of the results.
Requirement: Ban iteration. Do not use while/for loops!
代码:
def summation(n, term):
"""Return the sum of the first n terms in the sequence defined by term.
Implement using recursion!
>>> summation(5, lambda x: x * x * x) # 1^3 + 2^3 + 3^3 + 4^3 + 5^3
225
>>> summation(9, lambda x: x + 1) # 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10
54
>>> summation(5, lambda x: 2**x) # 2^1 + 2^2 + 2^3 + 2^4 + 2^5
62
"""
assert n >= 1
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if n == 1:
return term(n)
else:
return term(n) + summation(n - 1, term)Q2: Skip Add
Write a function skip_add that takes a single argument n and computes the sum of every other integer between 0 and n. Assume n is non-negative.
Requirement: Ban iteration. Do not use while/for loops!
代码:
def skip_add(n):
""" Takes a number n and returns n + n-2 + n-4 + n-6 + ... + 0.
>>> skip_add(5) # 5 + 3 + 1 + 0
9
>>> skip_add(10) # 10 + 8 + 6 + 4 + 2 + 0
30
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if n <= 0:
return 0
else:
return n + skip_add(n-2)Q1: List Indexing
Use Ok to test your knowledge with the following "List Indexing" questions: python3 ok -q list-indexing -u --local
加上--local的话不会发送至服务器!
比较简单,没有什么需要highlight的题目。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号