方法的重写(重点) 多态
重写:需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的方法!
1.方法名必须相同
2.参数列表必须系统
3.修饰符:范围可以扩大但不能缩小:public>protected>default>private
4.抛出的异常:范围,可以被缩小,但不能扩大:ClassNotFoundException-->Exception(大)
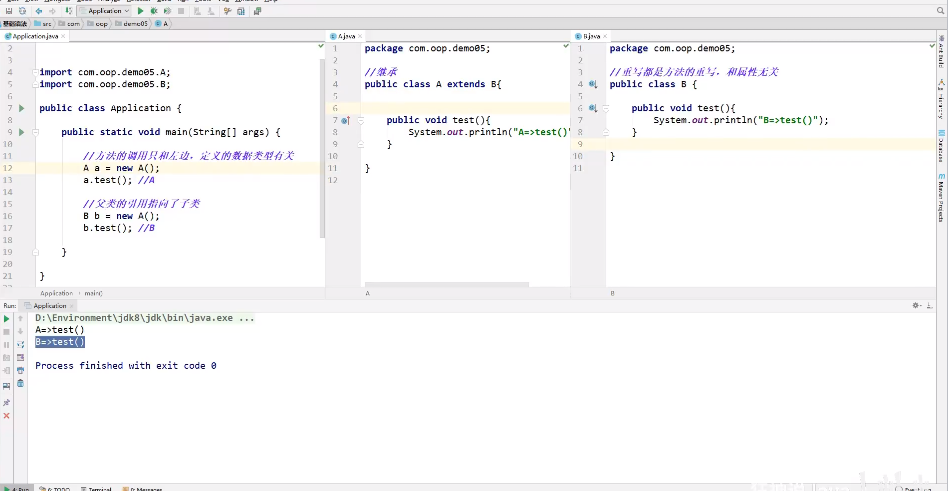
重写:子类的方法和父类必须要一致,方法体不同!
为什么需要重写:
1.父类的功能:子类不一定需要或不一定满足!
alt+ins:override
package oop.demo07; public class Person { public void run(){ System.out.println("run"); } }
package oop.demo07; public class Student extends Person { }
package oop.demo07; public class Teacher extends Person{ }
package oop; import oop.demo07.Person; import oop.demo07.Student; import oop.demo07.Teacher; public class Application { //静态方法和非静态方法区别很大! //静态方法: //方法的调用之和左边,定义的数据类型有关 //非静态:重写 public static void main(String[] args) { //Object>Person>Student //Object>Person>Teacher //Object>String Object object = new Student(); System.out.println(object instanceof Student);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Person);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Object);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher);//False System.out.println(object instanceof String);//False System.out.println("====================================="); Person person = new Student(); System.out.println(person instanceof Student);//true System.out.println(person instanceof Person);//true System.out.println(person instanceof Object);//true System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher);//False //System.out.println(person instanceof String);//编译报错 System.out.println("====================================="); Student student = new Student(); System.out.println(student instanceof Student);//true System.out.println(student instanceof Person);//true System.out.println(student instanceof Object);//true //System.out.println(student instanceof Teacher);//编译报错 //System.out.println(student instanceof String);//编译报错 } }
System.out,println(X instanceof Y);//能不能编译通过 取决于XY之间是否有父子关系
package oop.demo07; public class Person { public void run(){ System.out.println("run"); } }
package oop.demo07; public class Student extends Person { public void go(){ System.out.println("go"); } }
package oop.demo07; public class Teacher extends Person{ }
package oop; import oop.demo07.Person; import oop.demo07.Student; import oop.demo07.Teacher; public class Application { //静态方法和非静态方法区别很大! //静态方法: //方法的调用之和左边,定义的数据类型有关 //非静态:重写 public static void main(String[] args) { //类型之间的转化: 父 子 //高 低 Person obj = new Student(); //student将这个对象转换为Student类型,我们就可以使用Student类型的方法了 //子类转换为父类可能会丢失一些方法 Student student = new Student(); student.go(); Person person=student; person.run(); //低 高 //强制类型转换另一种写法((Student) obj).go(); } }
1.父类引用指向子类的对象
2.把子类转换为父类,向上转型
3.把父类转换为子类,向下转型,强制转换
4.方便方法的调用,减少重复的代码!
抽象三大特性:1.封装、继承、多态!static



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号