Linux用户登录超时设置
1、引言
在Linux系统中,用户登录超时设置通常用于增强系统的安全性,防止未经授权的长时间访问。合理的超时设置不仅可以提高系统的安全性,还可以优化用户体验。本文将探讨如何设置Linux用户登录超时,并提出一些优化策略,以确保系统资源得到有效利用,同时降低潜在的安全风险。
2、基础概念
Linux用户登录超时指的是在终端会话中,如果用户在指定的时间内没有任何操作(如按键、输入命令等),系统将自动断开该用户会话。
3、系统环境
系统环境:RedHat 8.0
主要配置文件:/etc/profile、~/.bashrc和/etc/ssh/sshd_config
4、超时类型
会话超时:用户在一定时间内没有任何操作,系统自动注销会话。
SSH超时:通过SSH登录时,如果在一定时间内没有活动,连接将被关闭。
屏幕超时:用户在一定时间内没有任何操作,屏幕会自动锁屏。
5、Linux用户登录超时设置
5.1、针对所有用户
执行命令: vi /etc/profile ,在文件末尾新增内容 export TMOUT=300 ,设置闲置时间为300秒,设置完成后使用命令: source /etc/profile ,使其配置生效。
1 [root@RedHat8 ~]# vi /etc/profile 2 # /etc/profile 3 4 # System wide environment and startup programs, for login setup 5 # Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc 6 7 # It's NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you 8 # are doing. It's much better to create a custom.sh shell script in 9 # /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this 10 # will prevent the need for merging in future updates. 11 12 pathmunge () { 13 case ":${PATH}:" in 14 *:"$1":*) 15 ;; 16 *) 17 if [ "$2" = "after" ] ; then 18 PATH=$PATH:$1 19 else 20 PATH=$1:$PATH 21 fi 22 esac 23 } 24 25 26 if [ -x /usr/bin/id ]; then 27 if [ -z "$EUID" ]; then 28 # ksh workaround 29 EUID=`id -u` 30 UID=`id -ru` 31 fi 32 USER="`id -un`" 33 LOGNAME=$USER 34 MAIL="/var/spool/mail/$USER" 35 fi 36 37 # Path manipulation 38 if [ "$EUID" = "0" ]; then 39 pathmunge /usr/sbin 40 pathmunge /usr/local/sbin 41 else 42 pathmunge /usr/local/sbin after 43 pathmunge /usr/sbin after 44 fi 45 46 HOSTNAME=`/usr/bin/hostname 2>/dev/null` 47 HISTSIZE=1000 48 if [ "$HISTCONTROL" = "ignorespace" ] ; then 49 export HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth 50 else 51 export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups 52 fi 53 54 export PATH USER LOGNAME MAIL HOSTNAME HISTSIZE HISTCONTROL 55 56 # By default, we want umask to get set. This sets it for login shell 57 # Current threshold for system reserved uid/gids is 200 58 # You could check uidgid reservation validity in 59 # /usr/share/doc/setup-*/uidgid file 60 if [ $UID -gt 199 ] && [ "`id -gn`" = "`id -un`" ]; then 61 umask 002 62 else 63 umask 022 64 fi 65 66 for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh /etc/profile.d/sh.local ; do 67 if [ -r "$i" ]; then 68 if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ]; then 69 . "$i" 70 else 71 . "$i" >/dev/null 72 fi 73 fi 74 done 75 76 unset i 77 unset -f pathmunge 78 79 if [ -n "${BASH_VERSION-}" ] ; then 80 if [ -f /etc/bashrc ] ; then 81 # Bash login shells run only /etc/profile 82 # Bash non-login shells run only /etc/bashrc 83 # Check for double sourcing is done in /etc/bashrc. 84 . /etc/bashrc 85 fi 86 fi 87 export TMOUT=300 # 设置闲置时间为5分钟,单位为秒;如果没有此行则直接添加进去
5.2、针对特定用户
执行命令: vi /home/test/.bashrc , 在文件末尾新增内容export TMOUT=60 ,设置test用户闲置时间为60秒,设置完成后使用命令: source /home/test/.bashrc ,使其配置生效。
1 [root@RedHat8 ~]# vi /home/test/.bashrc 2 # .bashrc 3 4 # Source global definitions 5 if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then 6 . /etc/bashrc 7 fi 8 9 # User specific environment 10 PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:$PATH" 11 export PATH 12 13 # Uncomment the following line if you don't like systemctl's auto-paging feature: 14 # export SYSTEMD_PAGER= 15 16 # User specific aliases and functions 17 18 export TMOUT=60 # 设置闲置时间为1分钟,单位为秒;如果没有此行则直接添加进去
5.3、SSH超时设置
执行命令: vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
找到以下参数,删除前面的“#”,并修改参数值
ClientAliveInterval 服务器向客户端发送空闲数据包的时间间隔
ClientAliveCountMax 在没有收到客户端响应的情况下,服务器发送空闲数据包的最大次数
设置完成后,使用命令: systemctl restart sshd.service ,重启服务使其配置生效。
1 [root@RedHat8 ~]# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config 2 # $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.103 2018/04/09 20:41:22 tj Exp $ 3 4 # This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See 5 # sshd_config(5) for more information. 6 7 # This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin 8 9 # The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with 10 # OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where 11 # possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options override the 12 # default value. 13 14 # If you want to change the port on a SELinux system, you have to tell 15 # SELinux about this change. 16 # semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp #PORTNUMBER 17 # 18 #Port 22 19 #AddressFamily any 20 #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 21 #ListenAddress :: 22 23 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key 24 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key 25 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key 26 27 # Ciphers and keying 28 #RekeyLimit default none 29 30 # System-wide Crypto policy: 31 # This system is following system-wide crypto policy. The changes to 32 # Ciphers, MACs, KexAlgoritms and GSSAPIKexAlgorithsm will not have any 33 # effect here. They will be overridden by command-line options passed on 34 # the server start up. 35 # To opt out, uncomment a line with redefinition of CRYPTO_POLICY= 36 # variable in /etc/sysconfig/sshd to overwrite the policy. 37 # For more information, see manual page for update-crypto-policies(8). 38 39 # Logging 40 #SyslogFacility AUTH 41 SyslogFacility AUTHPRIV 42 #LogLevel INFO 43 44 # Authentication: 45 46 #LoginGraceTime 2m 47 PermitRootLogin yes 48 #StrictModes yes 49 #MaxAuthTries 6 50 #MaxSessions 10 51 52 #PubkeyAuthentication yes 53 54 # The default is to check both .ssh/authorized_keys and .ssh/authorized_keys2 55 # but this is overridden so installations will only check .ssh/authorized_keys 56 AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys 57 58 #AuthorizedPrincipalsFile none 59 60 #AuthorizedKeysCommand none 61 #AuthorizedKeysCommandUser nobody 62 63 # For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts 64 #HostbasedAuthentication no 65 # Change to yes if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for 66 # HostbasedAuthentication 67 #IgnoreUserKnownHosts no 68 # Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files 69 #IgnoreRhosts yes 70 71 # To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here! 72 #PasswordAuthentication yes 73 #PermitEmptyPasswords no 74 PasswordAuthentication yes 75 76 # Change to no to disable s/key passwords 77 #ChallengeResponseAuthentication yes 78 ChallengeResponseAuthentication no 79 80 # Kerberos options 81 #KerberosAuthentication no 82 #KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes 83 #KerberosTicketCleanup yes 84 #KerberosGetAFSToken no 85 #KerberosUseKuserok yes 86 87 # GSSAPI options 88 GSSAPIAuthentication yes 89 GSSAPICleanupCredentials no 90 #GSSAPIStrictAcceptorCheck yes 91 #GSSAPIKeyExchange no 92 #GSSAPIEnablek5users no 93 94 # Set this to 'yes' to enable PAM authentication, account processing, 95 # and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will 96 # be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and 97 # PasswordAuthentication. Depending on your PAM configuration, 98 # PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass 99 # the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password". 100 # If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without 101 # PAM authentication, then enable this but set PasswordAuthentication 102 # and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to 'no'. 103 # WARNING: 'UsePAM no' is not supported in Fedora and may cause several 104 # problems. 105 UsePAM yes 106 107 #AllowAgentForwarding yes 108 #AllowTcpForwarding yes 109 #GatewayPorts no 110 X11Forwarding yes 111 #X11DisplayOffset 10 112 #X11UseLocalhost yes 113 #PermitTTY yes 114 115 # It is recommended to use pam_motd in /etc/pam.d/sshd instead of PrintMotd, 116 # as it is more configurable and versatile than the built-in version. 117 PrintMotd no 118 119 #PrintLastLog yes 120 #TCPKeepAlive yes 121 #PermitUserEnvironment no 122 #Compression delayed 123 ClientAliveInterval 60 #每60秒发送一次保持活动信号 124 ClientAliveCountMax 3 #如果连续3次没有收到响应,则断开连接 125 #ShowPatchLevel no 126 #UseDNS no 127 #PidFile /var/run/sshd.pid 128 #MaxStartups 10:30:100 129 #PermitTunnel no 130 #ChrootDirectory none 131 #VersionAddendum none 132 133 # no default banner path 134 #Banner none 135 136 # Accept locale-related environment variables 137 AcceptEnv LANG LC_CTYPE LC_NUMERIC LC_TIME LC_COLLATE LC_MONETARY LC_MESSAGES 138 AcceptEnv LC_PAPER LC_NAME LC_ADDRESS LC_TELEPHONE LC_MEASUREMENT 139 AcceptEnv LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_ALL LANGUAGE 140 AcceptEnv XMODIFIERS 141 142 # override default of no subsystems 143 Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server 144 145 # Example of overriding settings on a per-user basis 146 #Match User anoncvs 147 # X11Forwarding no 148 # AllowTcpForwarding no 149 # PermitTTY no 150 # ForceCommand cvs server
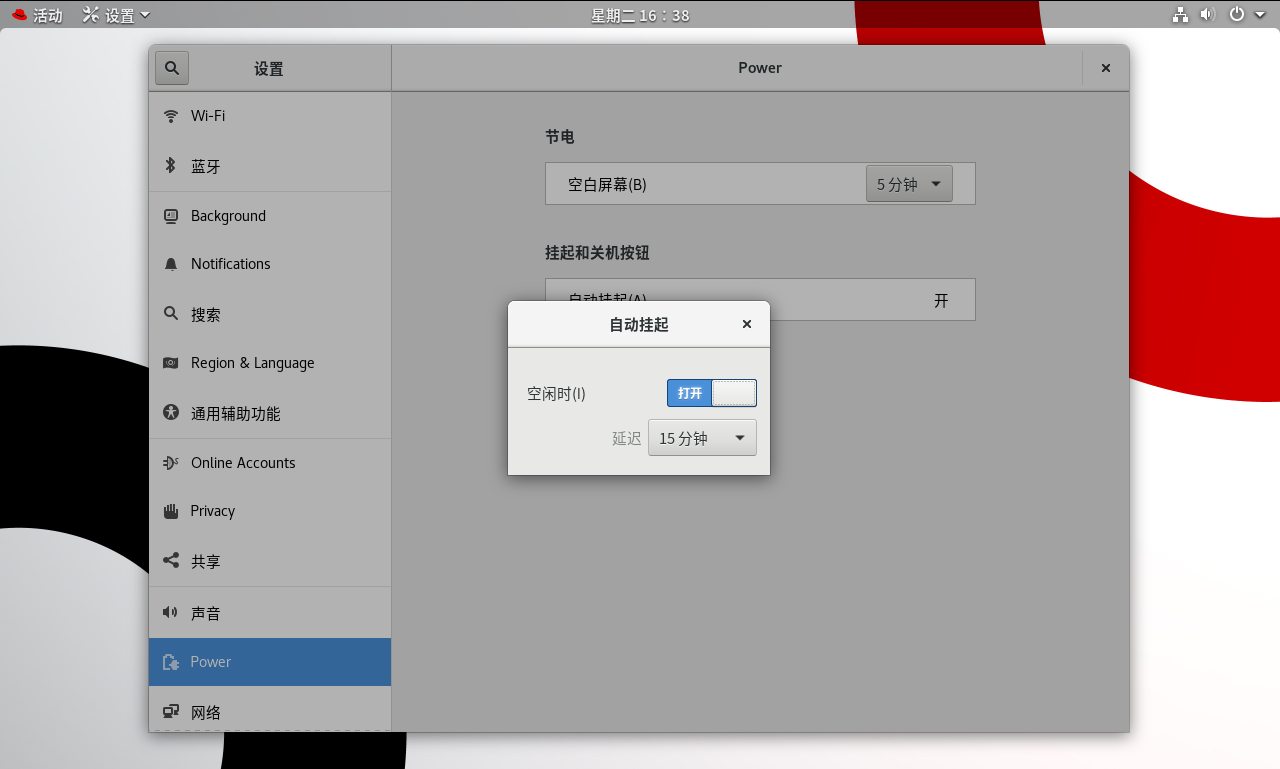
5.4、屏幕超时设置
进入图形化界面,右击桌面空白处,选择“设置”,在左侧导航栏中选择“电源”,然后在右侧窗口中点击“挂起和关机按钮”下的“自动挂起”,开启“空闲时”开关,设置延迟时间为15分钟。
 6、测试
6、测试
6.1、所有用户超时测试截图

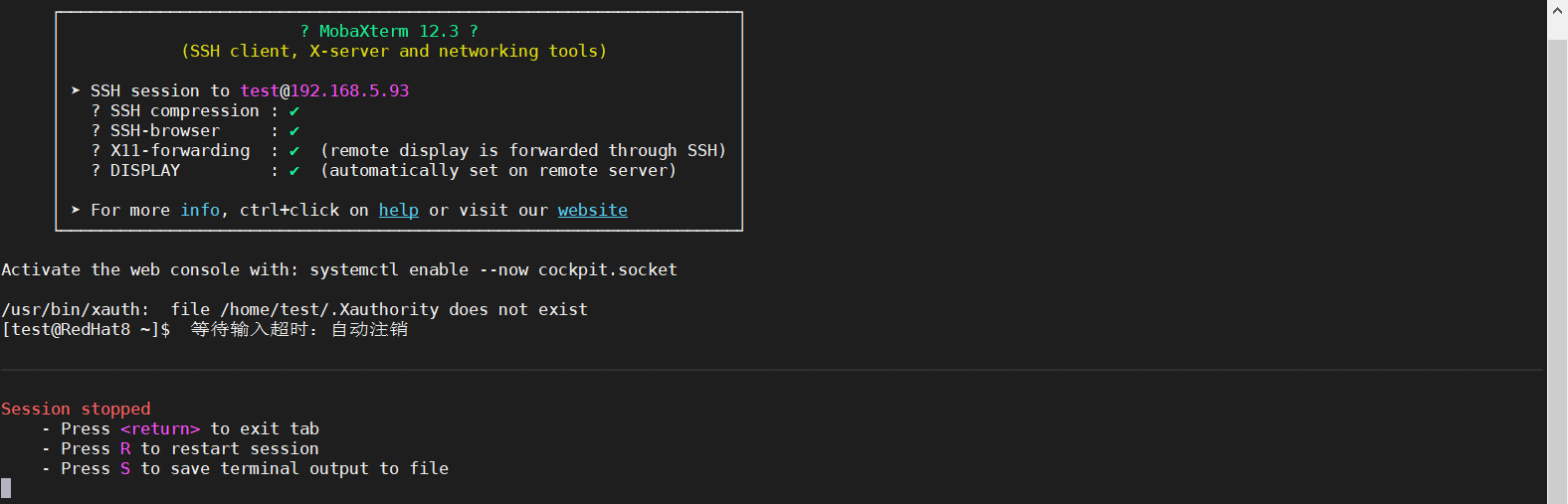
6.2、特定用户超时测试截图
前面设置的test用户超时退出为60秒,60秒未操作,会话自动注销。
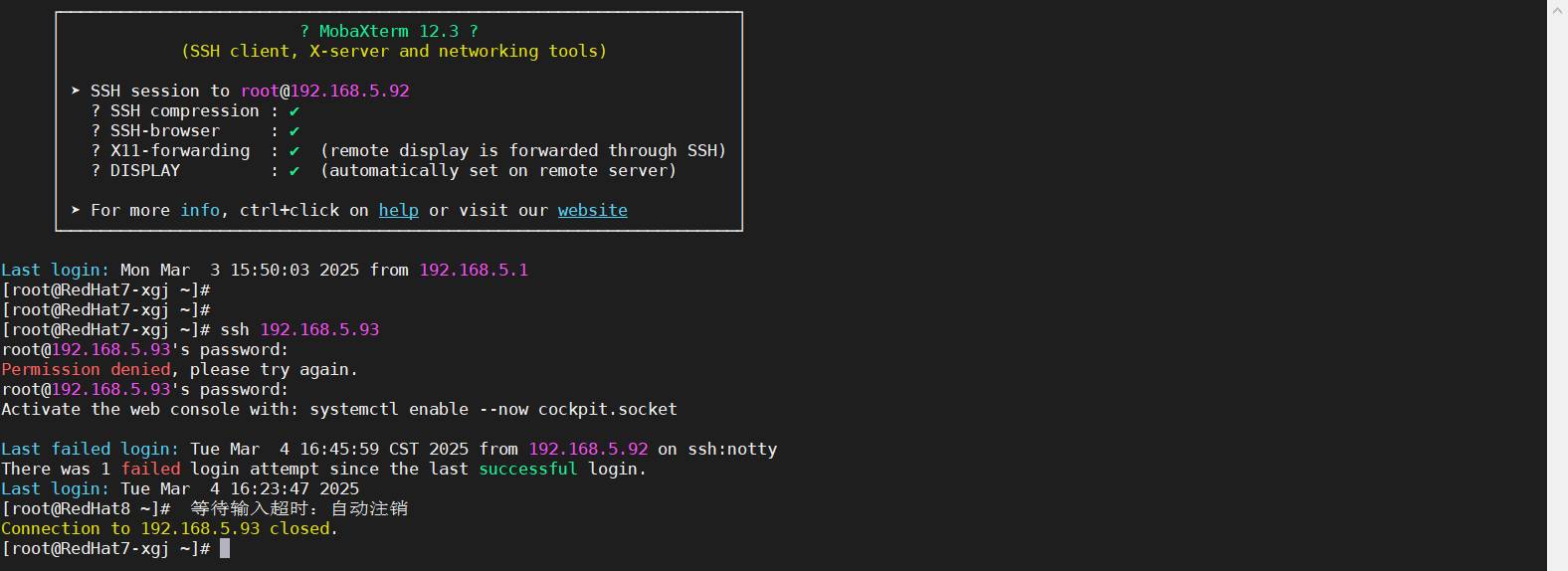
6.3、SSH超时测试截图
前面设置SSH参数,ClientAliveInterval 60 每60秒发送一次保持活动信号,ClientAliveCountMax 3 连续3次没有收到响应,则断开连接,也就是说3分钟过后自动超时,并注销其会话。
 6.4、屏幕超时测试截图
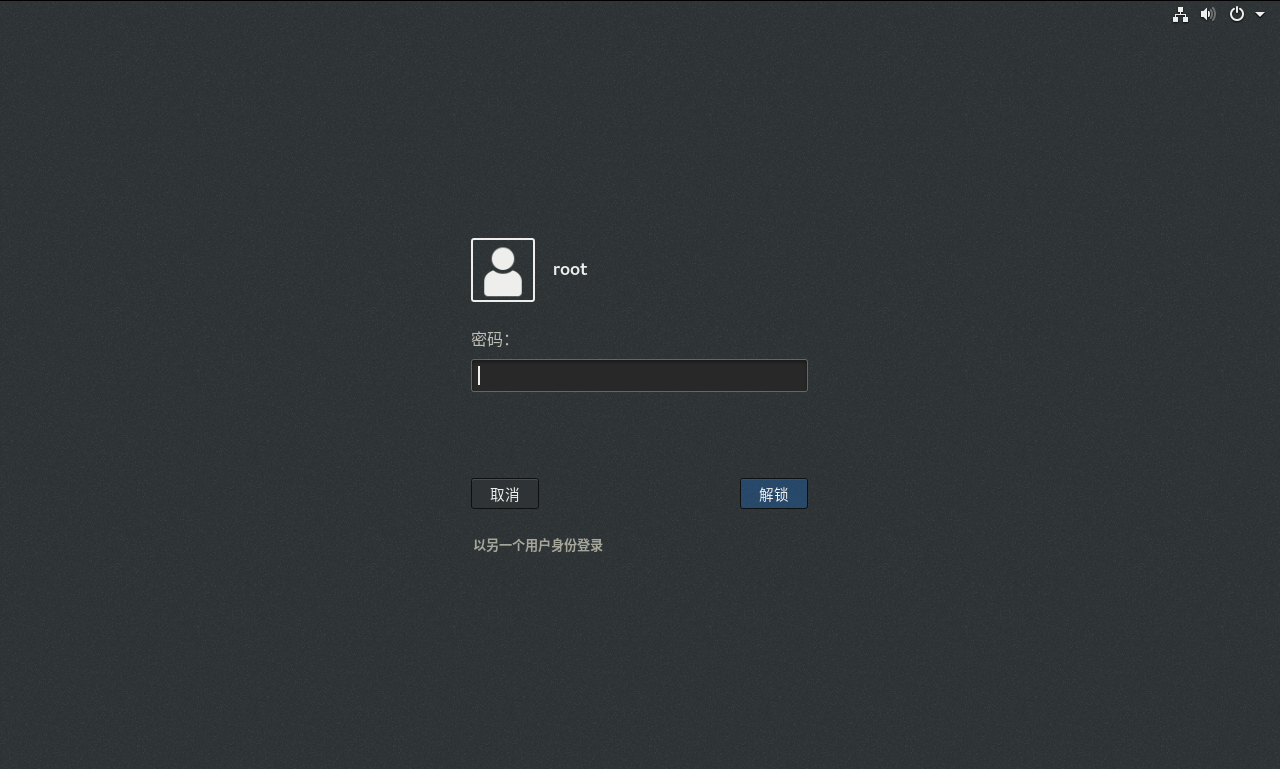
6.4、屏幕超时测试截图
15分钟内未进行任何操作,屏幕自动超时并锁定。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号