实验1

#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> int main() { using namespace std; string s1; // 创建一个string对象 string s2{"c plus plus"}; // 创建一个string对象,并初始化 string s3{s2}; // 创建一个string对象,并用s2对其进行初始化 string s4 = s2; // 创建一个string对象,并用s2对其进行初始化 s1 = "oop"; vector<string> v1; // 创建一个vector对象 v1.push_back(s1); // 向v1末尾添加数据项s1 v1.push_back(s2 + "1"); v1.push_back(s3 + "2"); v1.push_back(s4 + "3"); // 输出方式1:使用自动类型推导、范围for cout << "output1: " << endl; for(auto item: v1) cout << item << endl; // 输出方式2:使用自动类型推导、迭代器 cout << "ouput2: "; for(auto p = v1.begin(); p != v1.end(); ++p) cout << *p << endl; // 输出方式3:使用自动类型推导、索引 cout << "output3: " << endl; for(auto i = 0; i < v1.size(); ++i) cout << v1[i] << endl; vector<string> v2{v1.rbegin(), v1.rend()}; // 使用vector对象v1极其迭代器, //构造对象v2 cout << "v2: " << endl; for(auto item: v2) cout << item << endl; }

#include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; // 定义Point类 class Point { public: Point(int x0 = 0, int y0 = 0); Point(const Point&p ); ~Point() = default; int get_x() const { return x; } // 内联成员函数 int get_y() const { return y; } // 内联成员函数 void show() const; private: int x, y; }; // Point类的实现 // 构造函数(带有默认形参值) Point::Point(int x0, int y0): x{x0}, y{y0} { cout << "constructor called." << endl; } // 复制构造函数 // 参数必须是自身对象的引用类型 Point::Point(const Point& p): x{p.x}, y{p.y} { cout << "copy constructor called." << endl; } void Point::show() const { cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl; } int main() { Point p1(4, 5); // 构造函数被调用 p1.show(); Point p2 = p1; // 复制构造函数被调用 p2.show(); Point p3{p2}; // 复制构造函数被调用 p3.show(); cout << p3.get_x() << endl; }
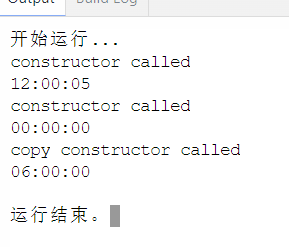
// 时钟类Clock // 相较于教材,做了以下微调整: // 1. 在构造函数的写法上,采用了业界更通用的初始化列表方式 // 2. 对于时钟显示的格式,使用操控符函数,控制其输出格式 #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using std::cout; using std::endl; // 定义时钟类Clock class Clock { public: Clock(int h = 0, int m = 0, int s = 0); Clock(const Clock& t); ~Clock() = default; void set_time(int h, int m = 0, int s = 0); void show_time() const; private: int hour, minute, second; }; // 类Clock实现 Clock::Clock(int h, int m, int s): hour{h}, minute{m}, second{s} { cout << "constructor called" << endl; } Clock::Clock(const Clock& t): hour{t.hour}, minute{t.minute}, second{t.second} { cout << "copy constructor called" << endl; } void Clock::set_time(int h, int m, int s) { hour = h; minute = m; second = s; } void Clock::show_time() const { using std::setw; using std::setfill; cout << setfill('0') << setw(2) << hour << ":" << setw(2) << minute << ":" << setw(2) << second << endl; } // 普通函数定义 Clock reset() { return Clock(0, 0, 0); // 构造函数被调用 } int main() { Clock c1(12, 0, 5); // 构造函数被调用 c1.show_time(); c1 = reset(); // 理论上:复制构造函数被调用 c1.show_time(); Clock c2(c1); // 复制构造函数被调用 c2.set_time(6); c2.show_time(); }
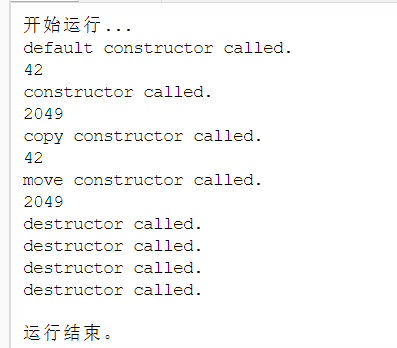
#include <iostream> // 定义一个简单抽象类 class X{ public: X(); // 默认构造函数 ~X(); // 析构函数 X(int m); // 构造函数 X(const X& obj); // 复制构造函数 X(X&& obj) noexcept; // 移动构造函数 void show() const; // 显示数据 private: int data; }; X::X(): data{42} { std::cout << "default constructor called.\n"; } X::~X() { std::cout << "destructor called.\n"; } X::X(int m): data{m} { std::cout << "constructor called.\n"; } X::X(const X& obj): data{obj.data} { std::cout << "copy constructor called.\n"; } X::X(X&& obj) noexcept: data{obj.data} { std::cout << "move constructor called.\n"; } void X::show() const { std::cout << data << std::endl; } int main() { X x1; //默认构造函数被编译器自动调用 x1.show(); X x2{2049}; x2.show(); // 构造函数被编译器自动调用 X x3{x1}; // 复制构造函数被编译器自动调用 x3.show(); X x4{ std::move(x2) }; // 移动构造函数被编译器调用 x4.show(); }
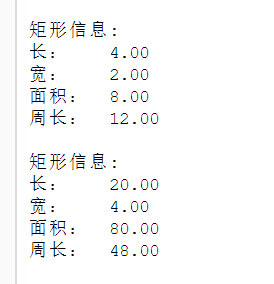
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> using namespace std; class Rectangle { public: Rectangle(double length = 2.0, double width = 1.0); Rectangle(const Rectangle& r); ~Rectangle(); double len() { return length; }; double wide() { return width; }; double area() { return length*width; }; double circumference() { return(width + length) * 2; }; void resize(int m); void resize(int m,int n); private: double length, width; }; Rectangle::Rectangle(double l, double w) :length(l), width(w) {}; Rectangle::Rectangle(const Rectangle& r) :length(r.length), width(r.width) {}; Rectangle:: ~Rectangle() {}; void Rectangle::resize(int m) { length *= m; width *= m; }; void Rectangle::resize(int m,int n) { length *= m; width *= n; }; void output(Rectangle& rect) { cout << "矩形信息: \n"; cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << "长: " << rect.len() << endl << "宽: " << rect.wide() << endl << "面积: " << rect.area() << endl << "周长: " << rect.circumference() << endl << endl; } int main(){ Rectangle rect1; output(rect1); Rectangle rect2(10, 5); output(rect2); Rectangle rect3(rect1); rect3.resize(2); output(rect3); rect3.resize(5, 2); output(rect3); }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号