实验六
实验任务1
源代码contestant.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include <iomanip> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <string> 5 struct Contestant { 6 long id; // 学号 7 std::string name; // 姓名 8 std::string major; // 专业 9 int solved; // 解题数 10 int penalty; // 总罚时 11 }; 12 // 重载<< 13 // 要求:姓名/专业里不含空白符 14 inline std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Contestant& c) { 15 out << std::left; 16 out << std::setw(15) << c.id 17 << std::setw(15) << c.name 18 << std::setw(15) << c.major 19 << std::setw(10) << c.solved 20 << std::setw(10) << c.penalty; 21 return out; 22 } 23 // 重载>> 24 inline std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, Contestant& c) { 25 in >> c.id >> c.name >> c.major >> c.solved >> c.penalty; 26 return in; 27 }
源代码utils.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include <fstream> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <stdexcept> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <vector> 7 #include "contestant.hpp" 8 // ACM 排序规则:先按解题数降序,再按罚时升序 9 inline bool cmp_by_solve(const Contestant& a, const Contestant& b) { 10 if (a.solved != b.solved) 11 return a.solved > b.solved; 12 return a.penalty < b.penalty; 13 } 14 // 将结果写至任意输出流 15 inline void write(std::ostream& os, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { 16 for (const auto& x : v) 17 os << x << '\n'; 18 } 19 // 将结果打印到屏幕 20 inline void print(const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { 21 write(std::cout, v); 22 } 23 // 将结果保存到文件 24 inline void save(const std::string& filename, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { 25 std::ofstream os(filename); 26 if (!os) 27 throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); 28 write(os, v); 29 } 30 // 从文件读取信息(跳过标题行) 31 inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) { 32 std::ifstream is(filename); 33 if (!is) 34 throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); 35 std::string line; 36 std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题 37 std::vector<Contestant> v; 38 Contestant t; 39 int seq; 40 while (is >> seq >> t) 41 v.push_back(t); 42 return v; 43 }
源代码task1.cpp
1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <stdexcept> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include "contestant.hpp" 6 #include "utils.hpp" 7 const std::string in_file = "./data.txt"; 8 const std::string out_file = "./ans.txt"; 9 void app() { 10 std::vector<Contestant> contestants; 11 try { 12 contestants = load(in_file); 13 std::sort(contestants.begin(), contestants.end(), cmp_by_solve); 14 print(contestants); 15 save(out_file, contestants); 16 } catch (const std::exception& e) { 17 std::cerr << e.what() << '\n'; 18 return; 19 } 20 } 21 int main() { 22 app(); 23 }
运行测试结果截图
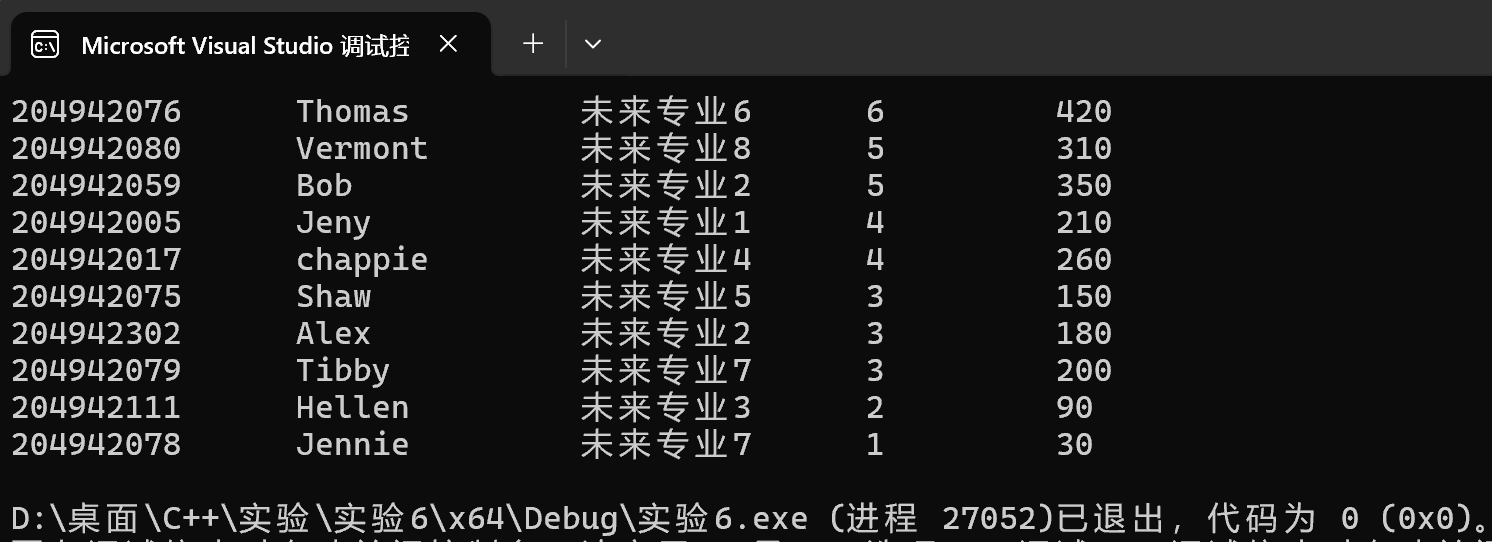
inline void save(const std::string& filename, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { std::ofstream os(filename); if (!os) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); // 第一处 throw write(os, v); }
inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) { std::ifstream is(filename); if (!is) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); // 第二处 throw // ... }
(2)这些异常在task1.cpp的app()函数中被统一捕获和处理。主程序使用try-catch块包裹了数据加载、排序和保存的整个流程,一旦捕获到任何异常,就会将异常信息输出到标准错误流std::cerr,然后安全地退出当前操作,避免了程序崩溃并给予用户明确的错误提示。
void app() { std::vector<Contestant> contestants; try { contestants = load(in_file); std::sort(contestants.begin(), contestants.end(), cmp_by_solve); print(contestants); save(out_file, contestants); } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cerr << e.what() << '\n'; return; } }
[](const Contestant& a, const Contestant& b) { return a.solved != b.solved ? a.solved > b.solved: a.penalty < b.penalty;}
答:可以。使用该 lambda 表达式在功能、性能和结果上都与原有的 cmp_by_solve 函数完全一致,因为它以相同的逻辑实现了先按解题数降序、再按罚时升序的排序规则;现代编译器能够将 lambda 内联优化,不会产生额外开销,因此两者在运行效率和排序结果上没有区别
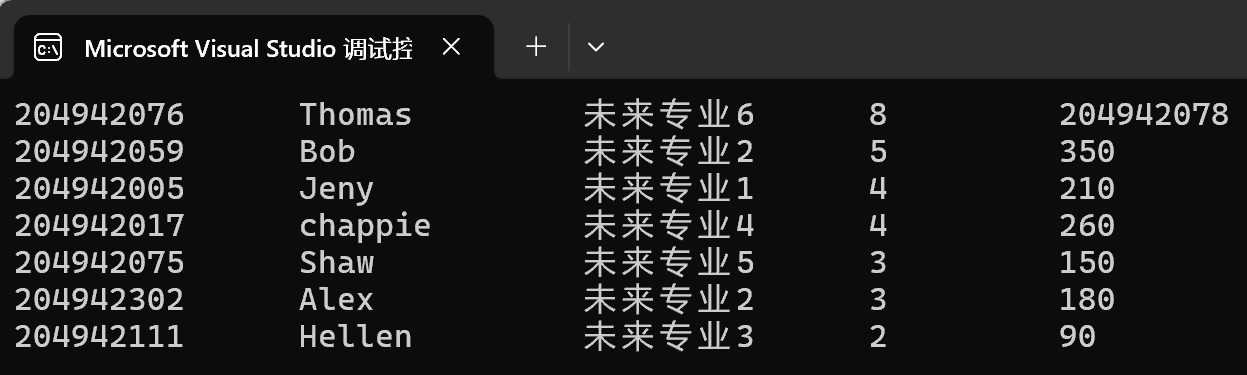
错误:图中第一行 Thomas 的解题数变成了 8,罚时变成了 204942078。这是因为 data_bad.txt 中 Thomas 这一行的解题数和罚时字段缺失 。在尝试读取时,会将下一行 Jennie 的学号 8 误当作 Thomas 的解题数,将 204942078 误当作罚时 。造成数据错位,这也间接导致了后面三个人Jennie、Tibby、Vermont的数据也都无法读取。最终显示只有7行
原因:原代码中的 is >> seq >> t 是基于格式化提取的 。一旦某个字段缺失,输入流(stream)会进入错误状态或开始“借用”后续行的内容来填充当前变量,导致整个数据链条崩溃。
(2)修改后的load函数
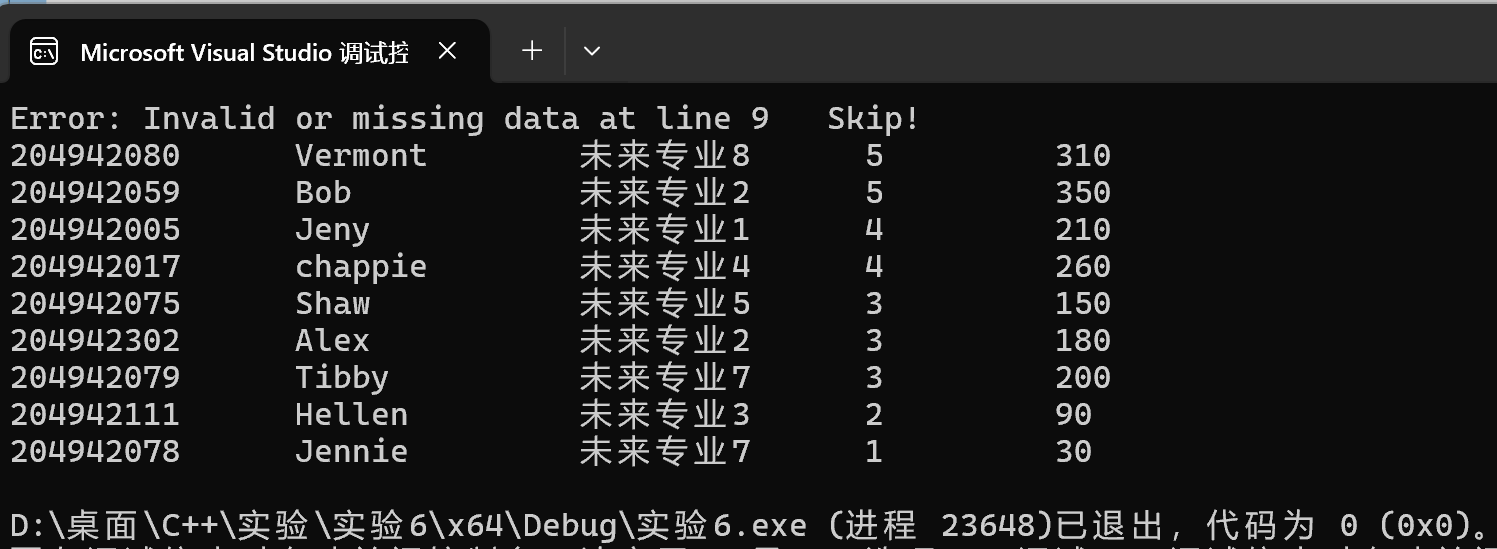
1 inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) { 2 std::ifstream is(filename); 3 if (!is) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); 4 5 std::vector<Contestant> v; 6 std::string line; 7 int line_num = 0; 8 9 // 1. 跳过第一行标题 10 if (std::getline(is, line)) { 11 line_num++; 12 } 13 14 // 2. 逐行读取,确保一行的问题不影响下一行 15 while (std::getline(is, line)) { 16 line_num++; 17 if (line.empty()) continue; // 跳过纯空白行 18 19 std::stringstream ss(line); // 将当前行放入独立的字符串流 20 Contestant t; 21 int seq; 22 23 // 3. 尝试解析。如果这一行字段缺失,ss >> t 会失败 24 if (ss >> seq >> t) { 25 v.push_back(t); 26 } 27 else { 28 // 4. 报错并继续处理下一行,不中断程序 29 std::cerr << "Error: Invalid or missing data at line " << line_num 30 << " Skip!\n"; 31 } 32 } 33 return v; 34 }
修改后的代码采用按行隔离机制,用 std::getline 保证每次处理都是独立的一行。即使某行少写了数据,stringstream 也只会在处理该行时报错,不会去“偷取”下一行的数据。同时引入 line_num 计数器,当发现数据不完整时,能准确告诉用户是哪一行出了问题。
运行结果:
实验任务2
源代码student.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 class Student { 5 public: 6 Student() = default; 7 ~Student() = default; 8 const std::string get_major() const; 9 int get_grade() const; 10 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Student& s); 11 friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Student& s); 12 private: 13 int id; 14 std::string name; 15 std::string major; 16 int grade; // 0-100 17 };
源代码student.cpp
1 #include"student.hpp" 2 #include<iomanip> 3 const std::string Student::get_major() const { 4 return major; 5 } 6 int Student::get_grade() const { 7 return grade; 8 } 9 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Student& s) { 10 os << std::left; 11 os << std::setw(15) << s.id 12 << std::setw(15) << s.name 13 << std::setw(15) << s.get_major() 14 << std::setw(15) << s.get_grade(); 15 return os; 16 } 17 std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Student& s) { 18 is >> s.id >> s.name >> s.major >> s.grade; 19 return is; 20 }
源代码stumgr.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include "student.hpp" 5 class StuMgr { 6 public: 7 void load(const std::string& file); // 加载数据文件(空格分隔) 8 void sort(); // 排序: 按专业字典序升序、同专业分数降序 9 void print() const; // 打印到屏幕 10 void save(const std::string& file) const; // 保存到文件 11 private: 12 void write(std::ostream& os) const; // 把数据写到任意输出流 13 private: 14 std::vector<Student> students; 15 };
源代码stumgr.cpp
1 #include"stumgr.hpp" 2 #include<fstream> 3 #include<sstream> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 6 void StuMgr::load(const std::string& file) { 7 std::ifstream is(file); 8 if (!is) 9 throw std::runtime_error("Error:cannot open file:" + file); 10 std::string line; 11 int line_num = 0; 12 13 if (std::getline(is, line)) {//跳过第一行标题 14 line_num++; 15 } 16 while (std::getline(is, line)) { 17 line_num++; 18 if (line.empty()) 19 continue; // 跳过纯空白行 20 std::istringstream iss(line); 21 Student stu; 22 23 if (iss >> stu) { 24 if (stu.get_grade() >= 0 && stu.get_grade() <= 100) 25 students.push_back(stu); 26 else { 27 // 显示具体的错误值 28 std::cout << "error: " << stu.get_grade() << std::endl; 29 // 捕获成绩范围异常 30 std::cout << "[Warning] line " << line_num << " grade invalid, skipped: " << line << std::endl; 31 } 32 } 33 else { 34 // 格式错误或字段缺失 35 std::cout << "[Warning] line " << line_num << " format error, skipped: " << line << std::endl; 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 40 void StuMgr::sort() { 41 std::sort(students.begin(), students.end(), [](Student& s1, Student& s2) { 42 return s1.get_major() != s2.get_major() ? s1.get_major() < s2.get_major() : s1.get_grade() > s2.get_grade(); }); 43 44 } 45 46 void StuMgr::print() const { 47 write(std::cout); 48 } 49 50 void StuMgr::save(const std::string& file) const { 51 std::ofstream os(file); 52 if (!os) { 53 throw std::runtime_error("Error:cannot open file:" + file); 54 } 55 56 write(os); 57 } 58 59 void StuMgr::write(std::ostream& os) const { 60 for (const auto& x : students) 61 os << x << "\n"; 62 }
源代码task2.cpp
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <limits> 3 #include <string> 4 #include "stumgr.hpp" 5 const std::string in_file = "./data_bad.txt"; 6 const std::string out_file = "./ans_bad.txt"; 7 void menu() { 8 std::cout << "\n**********简易应用**********\n" 9 "1. 加载文件\n" 10 "2. 排序\n" 11 "3. 打印到屏幕\n" 12 "4. 保存到文件\n" 13 "5. 退出\n" 14 "请选择:"; 15 } 16 void app() { 17 StuMgr mgr; 18 while (true) { 19 menu(); 20 int choice; 21 std::cin >> choice; 22 try { 23 switch (choice) { 24 case 1: mgr.load(in_file); 25 std::cout << "加载成功\n"; break; 26 case 2: mgr.sort(); 27 std::cout << "排序已完成\n"; break; 28 case 3: mgr.print(); 29 std::cout << "打印已完成\n"; break; 30 case 4: mgr.save(out_file); 31 std::cout << "导出成功\n"; break; 32 case 5: return; 33 default: std::cout << "不合法输入\n"; 34 } 35 } 36 catch (const std::exception& e) { 37 std::cout << "Error: " << e.what() << '\n'; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 int main() { 42 app(); 43 }
运行结果截图:
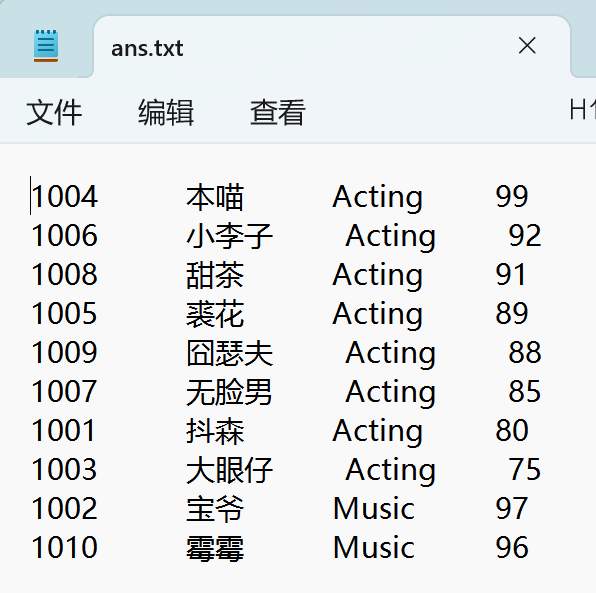
正常数据

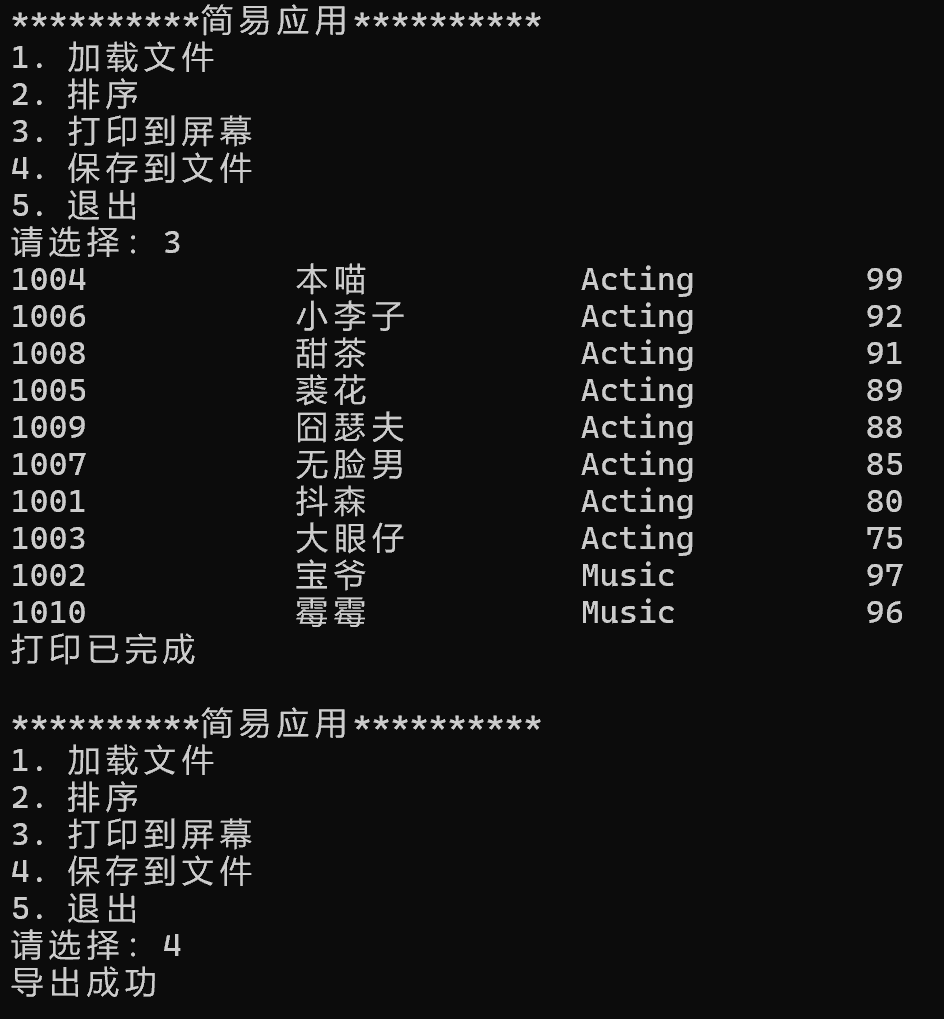
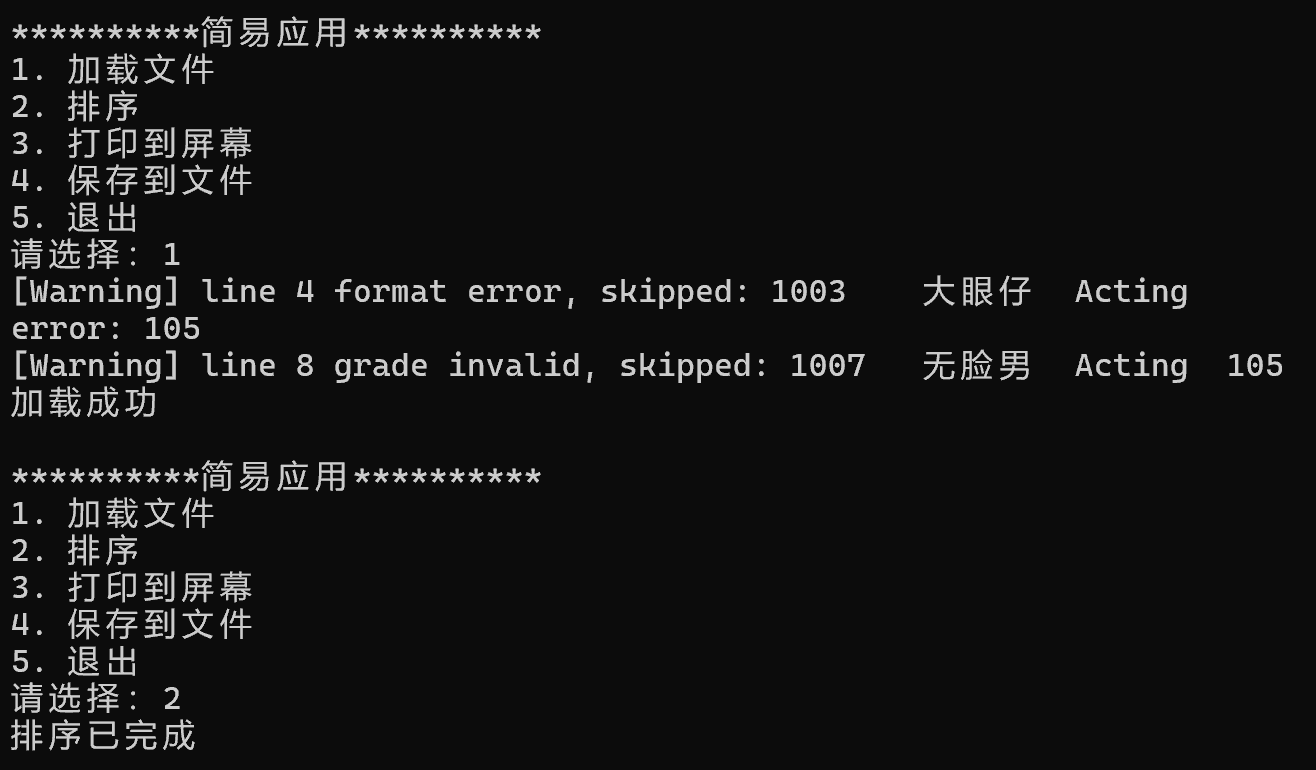
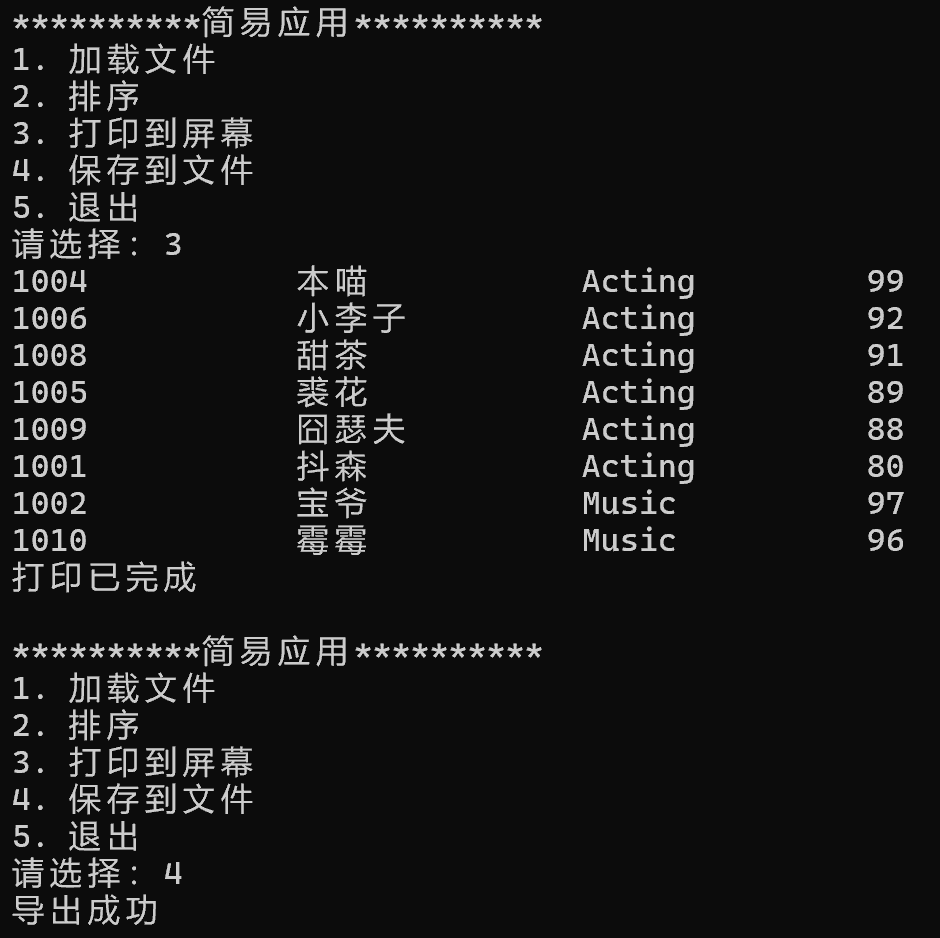
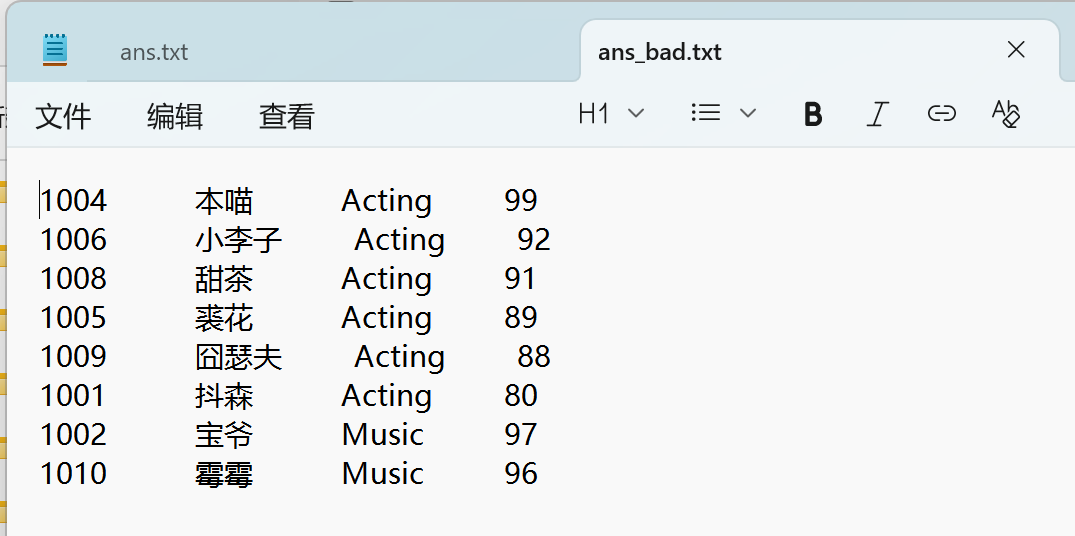
脏数据运行结果




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号