20232209实验二《Python程序设计》实验报告
20232209 2024-2025-2 《Python程序设计》实验二报告
课程:《Python程序设计》
班级: 2322
姓名: 吴易阳
学号:20232209
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2025年3月27日
必修/选修: 公选课
1.实验内容
(1)设计并完成一个完整的应用程序,完成加减乘除模等运算,功能多多益善。
(2)并灵活运用基本语法、判定语句、循环语句、逻辑运算等知识点。
2. 实验过程及结果
(1)实验源码
print("===============欢迎使用Best计算器==============")
print("-------作者:吴易阳-------")
print("-------功能强大 :一应俱全-------")
import math
# --------------------- 安全校验函数 ---------------------
def validate_positive(num, name="参数"):
"""校验数值是否为正数"""
if num <= 0:
print(f"错误:{name}必须大于0!")
return False
return True
def validate_log_base(a):
"""校验对数底数"""
if a <= 0:
print("错误:对数底数必须大于0!")
return False
if a == 1:
print("错误:对数底数不能为1!")
return False
return True
# --------------------- 数学函数 ---------------------
# 三角函数
def Pysin(a):
return math.sin(a)
def Pycos(a):
return math.cos(a)
def Pytan(a):
try:
return math.tan(a)
except:
print("错误:正切函数输入值不合法!")
return None
# 对数函数
def PyUg(a): # 自然对数
try:
if not validate_positive(a, "自然对数参数"):
return None
return math.log(a)
except Exception as e:
print("自然对数计算错误:", e)
return None
def Pylog(a, b): # 以a为底的对数
if not validate_log_base(a):
return None
if not validate_positive(b, "对数真数"):
return None
try:
return math.log(b) / math.log(a)
except Exception as e:
print("对数计算错误:", e)
return None
# 基础运算
def sum(a, b):
return a + b
def sub(a, b):
return a - b
def mul(a, b):
return a * b
def div(a, b):
if b == 0:
print("错误:除数不能为0!")
return None
return a / b
# 复数运算
def Pycomplex(a, b):
complexOper = input("请输入复数的运算(+,-,*,/): ")
if complexOper == "+":
result = a + b
elif complexOper == "-":
result = a - b
elif complexOper == "*":
result = a * b
elif complexOper == "/":
if b == 0:
print("错误:复数除法中除数不能为0!")
return None
result = a / b
else:
print("无效运算符!")
return None
print(f"结果:{result}")
return result
# --------------------- 主逻辑 ---------------------
flag = True
while flag:
try:
a = eval(input("请输入a: "))
b = eval(input("请输入b: "))
except:
print("输入格式错误,请重新输入!")
continue
operator = input("请输入运算符(+,-,*,/,com,sin,cos,tan,log): ")
if operator == "+":
print(f"{a} + {b} = {sum(a, b)}")
elif operator == "-":
print(f"{a} - {b} = {sub(a, b)}")
elif operator == "*":
print(f"{a} * {b} = {mul(a, b)}")
elif operator == "/":
result = div(a, b)
if result is not None:
print(f"{a} / {b} = {result}")
elif operator == "com":
Pycomplex(a, b)
elif operator == "sin":
print(f"sin({a}) = {Pysin(a)}")
print(f"sin({b}) = {Pysin(b)}")
elif operator == "cos":
print(f"cos({a}) = {Pycos(a)}")
print(f"cos({b}) = {Pycos(b)}")
elif operator == "tan":
res_a = Pytan(a)
res_b = Pytan(b)
if res_a is not None: print(f"tan({a}) = {res_a}")
if res_b is not None: print(f"tan({b}) = {res_b}")
elif operator == "log":
ln_a = PyUg(a)
ln_b = PyUg(b)
if ln_a is not None: print(f"ln({a}) = {ln_a}")
if ln_b is not None: print(f"ln({b}) = {ln_b}")
log_ab = Pylog(a, b)
if log_ab is not None:
print(f"以{a}为底{b}的对数 = {log_ab:.4f}")
else:
print("无效的运算符!")
# 循环控制
while True:
choice = input("继续计算吗?(y/n): ").lower()
if choice in ['y', 'n']:
flag = (choice == 'y')
break
print("请输入 y 或 n!")
(2) 代码解释
安全校验函数
validate_positive函数用于校验数值是否为正数,如果输入值为负则输出错误信息
def validate_positive(num, name="参数"):
"""校验数值是否为正数"""
if num <= 0:
print(f"错误:{name}必须大于0!")
return False
return True
validate_log_base函数校验对数底数,如果为1或者小于0则输出错误信息
def validate_log_base(a):
"""校验对数底数"""
if a <= 0:
print("错误:对数底数必须大于0!")
return False
if a == 1:
print("错误:对数底数不能为1!")
return False
return True
数学函数
三角函数根据所给的值进行计算sin、cos和tan
# 三角函数
def Pysin(a):
return math.sin(a)
def Pycos(a):
return math.cos(a)
def Pytan(a):
try:
return math.tan(a)
except:
print("错误:正切函数输入值不合法!")
return None
对数函数有两种情况,一种是根据所给的值计算自然对数,一种是给出底和值,进行计算,其中底要进行合法性判断
def PyUg(a): # 自然对数
try:
if not validate_positive(a, "自然对数参数"):
return None
return math.log(a)
except Exception as e:
print("自然对数计算错误:", e)
return None
def Pylog(a, b): # 以a为底的对数
if not validate_log_base(a):
return None
if not validate_positive(b, "对数真数"):
return None
try:
return math.log(b) / math.log(a)
except Exception as e:
print("对数计算错误:", e)
return None
基础运算中包含加减乘除,其中除要对除数进行合法性判断
def sum(a, b):
return a + b
def sub(a, b):
return a - b
def mul(a, b):
return a * b
def div(a, b):
if b == 0:
print("错误:除数不能为0!")
return None
return a / b
复数运算中也是计算加减乘除,除法也要进行合法性判断
def Pycomplex(a, b):
complexOper = input("请输入复数的运算(+,-,*,/): ")
if complexOper == "+":
result = a + b
elif complexOper == "-":
result = a - b
elif complexOper == "*":
result = a * b
elif complexOper == "/":
if b == 0:
print("错误:复数除法中除数不能为0!")
return None
result = a / b
else:
print("无效运算符!")
return None
print(f"结果:{result}")
return result
主逻辑
在主逻辑中用户循环输入a、b、所选择的操作数,并调用具体的函数进行解决
获取用户的输入值:
while flag:
try:
a = eval(input("请输入a: "))
b = eval(input("请输入b: "))
except:
print("输入格式错误,请重新输入!")
continue
operator = input("请输入运算符(+,-,*,/,com,sin,cos,tan,log): ")
根据所选择的操作符调用具体函数进行解决:
if operator == "+":
print(f"{a} + {b} = {sum(a, b)}")
elif operator == "-":
print(f"{a} - {b} = {sub(a, b)}")
elif operator == "*":
print(f"{a} * {b} = {mul(a, b)}")
elif operator == "/":
result = div(a, b)
if result is not None:
print(f"{a} / {b} = {result}")
elif operator == "com":
Pycomplex(a, b)
elif operator == "sin":
print(f"sin({a}) = {Pysin(a)}")
print(f"sin({b}) = {Pysin(b)}")
elif operator == "cos":
print(f"cos({a}) = {Pycos(a)}")
print(f"cos({b}) = {Pycos(b)}")
elif operator == "tan":
res_a = Pytan(a)
res_b = Pytan(b)
if res_a is not None: print(f"tan({a}) = {res_a}")
if res_b is not None: print(f"tan({b}) = {res_b}")
elif operator == "log":
ln_a = PyUg(a)
ln_b = PyUg(b)
if ln_a is not None: print(f"ln({a}) = {ln_a}")
if ln_b is not None: print(f"ln({b}) = {ln_b}")
log_ab = Pylog(a, b)
if log_ab is not None:
print(f"以{a}为底{b}的对数 = {log_ab:.4f}")
else:
print("无效的运算符!")
进行循环判断,当用户输入n时退出循环:
# 循环控制
while True:
choice = input("继续计算吗?(y/n): ").lower()
if choice in ['y', 'n']:
flag = (choice == 'y')
break
print("请输入 y 或 n!")
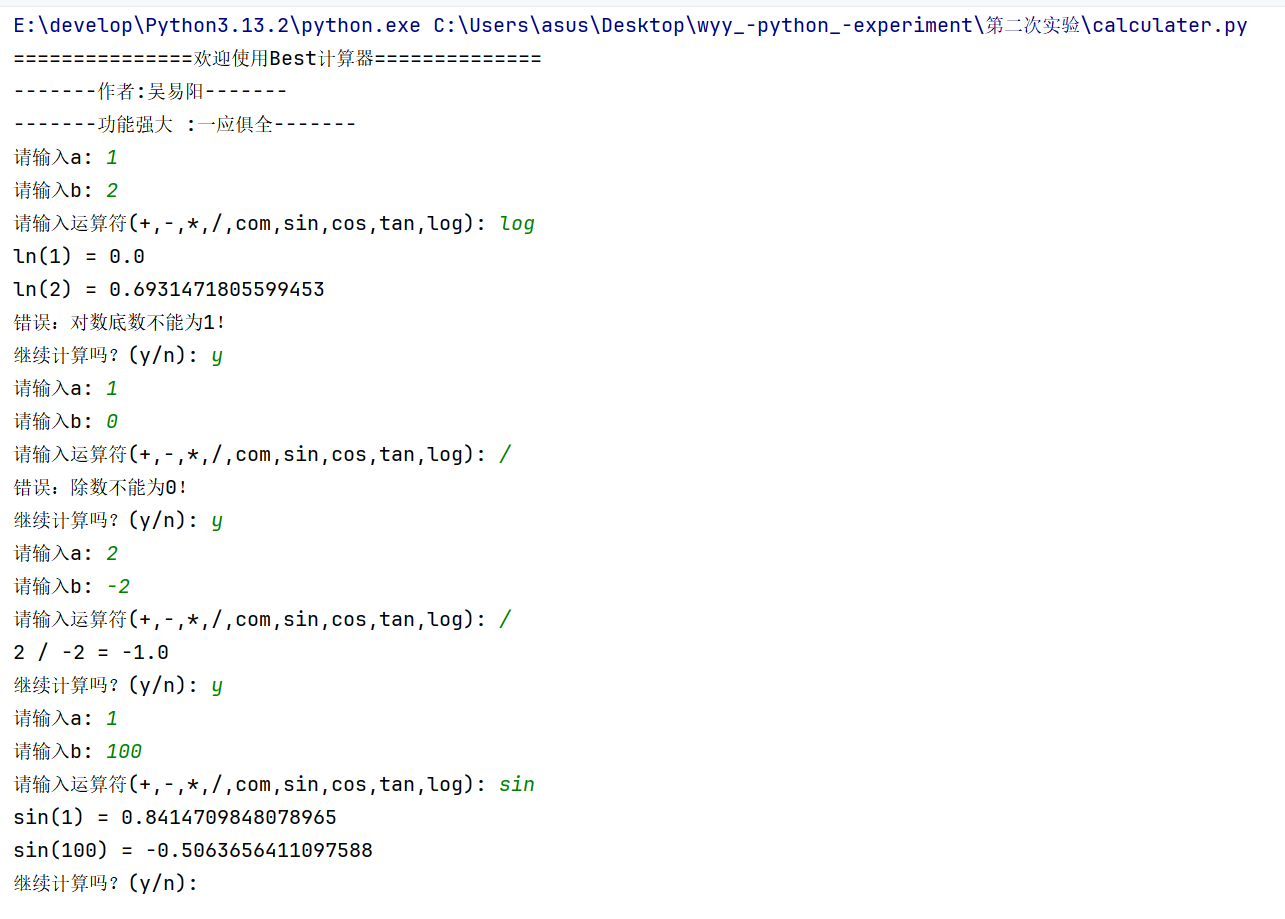
(3)实验结果
测试了除数不能为零,对数底不能为1,除负数,计算三角函数等情况,均正确
(4)上传gitee
3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:在开始的时候没有考虑安全性的问题,在底数输入为1的时候出现报错
![]()
- 问题1解决方案:增加安全性检测的部分,最终的代码可以检查安全性
![]()
其他(感悟、思考等)
程序中的if-else语句过于冗长,于是开始思考python中是否存在switch-case的结构,查询发现可以用字典来实现,更一目了然,易于修改,这也让我知道,程序需要不断进行修改,功能才能越完善,代码才能越简洁,不能怕麻烦。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号