实验结论
1.实验内容 2
(1)先求出每行的字符数,再通过比较位置下标的大小关系,判断输出空格还是符号
(2)源码
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "graph.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Graph graph1('*',5), graph2('$',7) ; // 定义Graph类对象graph1, graph2
graph1.draw(); // 通过对象graph1调用公共接口draw()在屏幕上绘制图形
graph2.draw(); // 通过对象graph2调用公共接口draw()在屏幕上绘制图形
return 0;
}
graph.h
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H
// 类Graph的声明
class Graph {
public:
Graph(char ch, int n); // 带有参数的构造函数
void draw(); // 绘制图形
private:
char symbol;
int size;
};
#endif
graph.cpp
// 类graph的实现
#include "graph.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 带参数的构造函数的实现
Graph::Graph(char ch, int n): symbol(ch), size(n) {
}
// 成员函数draw()的实现
// 功能:绘制size行,显示字符为symbol的指定图形样式
// size和symbol是类Graph的私有成员数据
void Graph::draw() {
int i,j,n;
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
n=2*size-1;//n为每行输出的字符数
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(j<size-i||j>size+i)
cout<<" ";
else
cout<<symbol;
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
(3)程序运行环境:Dev-C++ 5.10
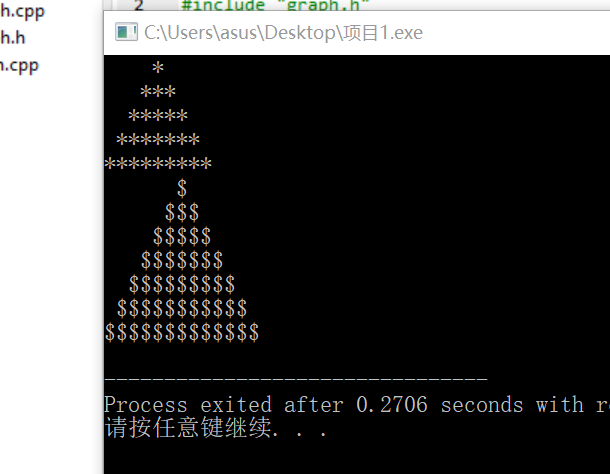
运行测试截图
2.实验内容 3
(1)类Fraction的类图

(2)源码
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include"fraction.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Fraction a;
Fraction b(3,4);
Fraction c(5);
cout<<"a:",a.show();
cout<<"b:",b.show();
cout<<"c:",c.show();
int x1,y1,x2,y2;
cout<<"输入第一个分数的分子分母" <<endl;
cin>>x1>>y1;
Fraction a1(x1,y1);
cout<<"输入第二个分数的分子分母" <<endl;
cin>>x2>>y2;
Fraction a2(x2,y2);
a.add(a1,a2);
cout<<"和:",a.show();
a.sub(a1,a2);
cout<<"差:",a.show();
a.mul(a1,a2);
cout<<"积:",a.show();
a.div(a1,a2);
cout<<"商:",a.show();
a.compare(a1,a2);
return 0;
}
fraction.h
//Fraction类的声明
class Fraction{
public:
Fraction(int t0,int b0);
Fraction();
Fraction(int t0);
void add(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2);
void sub(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2);
void mul(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2);
void div(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2);
void compare(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2);
void show();
private:
int top;
int bottom;
};
fraction.cpp
#include"fraction.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int gys(int x,int y)//求最大公约数
{
int m=1,a=x,b=y;
for(;m!=0;)
{
m=a%b;a=b;b=m;
}
return a;
}
//Fraction类的实现
int m;//m为分子分母最大公约数
Fraction::Fraction():top(0),bottom(1){}
Fraction::Fraction(int t0):top(t0),bottom(1){}
Fraction::Fraction(int t0,int b0):top(t0),bottom(b0){}//构造函数重载
void Fraction::add(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2){
bottom=p1.bottom*p2.bottom;
top=p1.top*p2.bottom+p1.bottom*p2.top;
m=gys(fabs(top),fabs(bottom));
top/=m,bottom/=m;
}
void Fraction::sub(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2){
bottom=p1.bottom*p2.bottom;
top=p1.top*p2.bottom-p1.bottom*p2.top;
m=gys(fabs(top),fabs(bottom));
top/=m,bottom/=m;
}
void Fraction::mul(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2){
top=p1.top*p2.top,bottom=p1.bottom*p2.bottom;
m=gys(fabs(top),fabs(bottom));
top/=m,bottom/=m;
}
void Fraction::div(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2){
top=p1.top*p2.bottom,bottom=p1.bottom*p2.top;
m=gys(fabs(top),fabs(bottom));
top/=m,bottom/=m;
}
void Fraction::compare(Fraction &p1,Fraction &p2){
if(p1.top*p2.bottom>p2.top*p1.bottom)
cout<<"大小关系:"<<p1.top<<"/"<<p1.bottom<<">"<<p2.top<<"/"<<p2.bottom<<endl;
if(p1.top*p2.bottom<p2.top*p1.bottom)
cout<<"大小关系:"<<p1.top<<"/"<<p1.bottom<<"<"<<p2.top<<"/"<<p2.bottom<<endl;
else
cout<<"大小关系:"<<p1.top<<"/"<<p1.bottom<<"="<<p2.top<<"/"<<p2.bottom<<endl;
}
void Fraction::show(){
cout<<top<<"/"<<bottom<<endl;
}
(3)程序运行环境:Dev-C++ 5.10
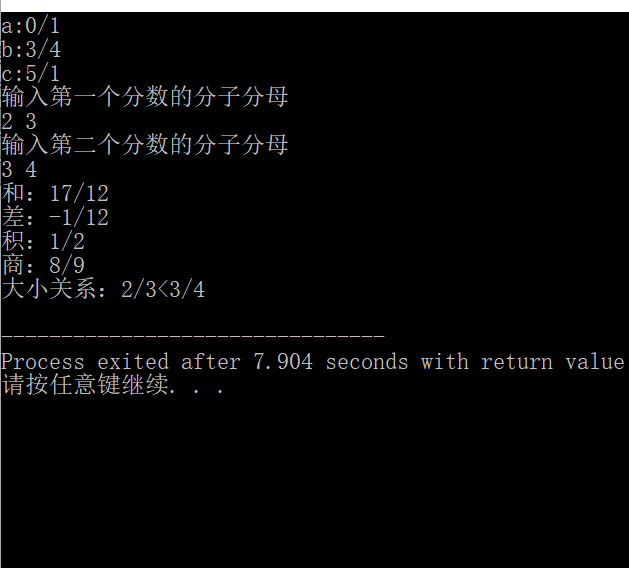
运行测试截图
实验总结和体会
本次实验基本掌握了如何将C++程序以项目文件组织的多文件结构方式编写,通过这样的方式来写一个程序,能够使程序的各个部分的功能更加清晰的表现出来,适合用于两个人或者多个人合作写一个程序时使用,毕竟以后工作中要写的程序可能都比较长,更多的时候可能还是几个人合作写,所以觉得将C++程序以项目文件组织的多文件结构方式编写很实用



 posted on
posted on

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号