C++复习笔记
2021.3.4
很难体会第一次吃的美好。
C编译(检测语法 .o)->链接(.o .lib 产生可执行文件 .exe)
解释型文件HTML
结构体是C语言的封装
Everything is object.
self-defination
int通常占4个字节,char占1个字节
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct test {
int i;
int j;
char c;
};
int main() {
printf("%d",sizeof(test));
return 0;
}
//12 取大
#pragma pack(1)强制压缩单字节为1(输出9)(表示最多对齐到1个字节)
struct test1 {
int i;
int j;
char c;
char d;
};
//sizeof(test1) = 12
struct test2 {
int i;
char c;
int j;
char d;
};
//sizeof(test2) = 16
union共享内存:访问相同的内存段,进行不同的解释
极少单独使用,一般嵌套
union test1 {
double d;
unsigned long long u;
};
union test2 {
float d;
unsigned long long u;
};
union test1 un1;
union test2 un2;
int main() {
scanf("%lf %f", &un1.d, &un2.d);
printf("double : %.4f\n ull : %x\n", un1.d, un1.u);
printf(" float : %.4f\n ull : %x\n", un2.d, un2.u);
printf("%d\n",sizeof(un1));
printf("%d",sizeof(un2));
return 0;
}
/*
3.1415 3.1415
double : 3.1415
ull : c083126f
float : 3.1415
ull : 40490e56
8
8
*/
macro宏
表现形态共三种:常数宏、函数宏、控制宏
常数宏:define PI 3.1415消除神仙数,统一修改管理
函数宏:
控制宏:
Once the header is included, it checks if a unique value (in this case
HEADERFILE_H) is defined. Then if it's not defined, it defines it and continues to the rest of the page.
When the code is included again, the firstifndeffails, resulting in a blank file.
That prevents double declaration of any identifiers such astypes,enumsandstatic variables.
//在头文件开始处开始写
//TEST_H:不要和其他头文件重复,用文件名即可(文件名很少重复)
#ifndef TEST_H//if not define
#define TEST_H
struct A {
int i;
};
#endif
2021.3.11
喜欢就买,不合适就分,多喝热水,重启试试。
头文件:函数声明 方便被到处使用
| 声明 declaration | 定义definition |
|---|---|
| 多次声明 | 一次定义 |
| 未分配内存(存在于文件的符号表中) | 已分配内存 |
void fun(); //函数声明
void fun();
int main() {
//对于变量来说,声明即定义
int i; //没有初始化的定义
int j = 10; //有初始化的定义
fun();
return 0;
}
void fun() { //函数定义
printf("C++ yyds");
}
/*
[Error] redefinition
void fun() { //函数定义
printf("C++ yyds");
}
*/
add files for project
C与C++文件的融合
编译:源文件 a.c b.c c.c -> a.o b.o c.o (object)
链接:a.o b.o c.o libs -> x.exe
有时候link不到是代码修饰的问题,extern指示链接器用C/C++风格修饰
//指示链接器用C风格修饰
extern “C” void fun_c();
//指示链接器用C++风格修饰
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C++" {
#endif
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
//所有C++都有的,用于判断C++编译器,同时也是唯一小写宏
源文件和头文件成对出现
函数角度的A better C
overloading 重载:同名函数,不同参数(参数个数和参数类型)
(靠返回值不能也不允许用返回值区分同名函数)
default parameter 默认参数:
void fun(int a, int b, int c = 4);
int main() {
fun(1,2); //第三个参数由编译器默认传递
fun(1,2,3);
return 0;
}
void fun (int a, int b, int c) {
printf("a:%d b:%d c:%d\n", a, b, c);
}
/*
a:1 b:2 c:4
a:1 b:2 c:3
*/
- 减少终端程序员写的个数,但是并不减少传递过程,故不会提高性能
- 默认参数必须放在最后,否则编译器不清楚填了哪个
- 作为占位参数:
void fun(int) {}但不用这个int(初衷:高瞻远瞩的产品迭代,方便开发;实际:屁滚尿流的软件危机),大多只能用于同名、同参但希望是不同函数的情况
OO
struct Person {
int age;
char *name;
void init (int age, char *name); //用于解决命名爆炸的问题(封装)
};
void Person::init(int aage, char *aname) {
age = aage;
name = aname; //this->name(指向调用者) = aname;(指针变成了隐藏的this)
}
/*
void init_person(Person *p, int aage, char *aname) { //为了改值应该传指针(Person *p)而不是引用(Person p)
p->age = aage;
p->name = aname;
}
//address:-> value:.
*/
int main() {
Person p1,p2;
p1.init(20, "ZhangSan");
p2.init(21, "LiSi");
}
//进化
class Person {
private: //( [Error] p.age = 20;)隐藏属性,访问控制
//属性 data member
int age;
char *name;
public:
//行为 method function member
void init (int age, char *name);
};
/*
Person(抽象:类) p1,p2(实例:对象);
*/
C++类在内存中的空间分配
类本身不占有内存,可是如果类生成实例,将会在内存中分配一块内存来存储这个类。
- 一个类对象的地址就是类所包含的这一片内存空间的首地址
#pragma pack(1)
class Person {
public:
int age;
char *name;
void init (int age, char *name);
};
void Person::init(int aage, char *aname) {
age = aage;
name = aname;
}
int main()
{
Person p;
p.init(20, "ZhangSan");
printf("%d--%d--%d\n", &p, &p.age, &p.name);
printf("%d--%d--%d\n", sizeof(p), sizeof(p.age), sizeof(p.name));
int *age = (int*)(&(p.age));
char **name = (char **)(&(p.name));
printf("%d %s\n",*age, *name);
return 0;
}
/*
6487552--6487552--6487560
//&p :类对象的地址
//&p.age :Person对象的成员变量age的地址
//&p.name:Person对象的成员变量name的地址
12--4--8
//sizeof用于计算栈大小,不涉及全局区,故类的静态成员大小不参与计算
//sizeof(p) :类占用栈空间的大小(取决于类中成员变量的大小)
//sizeof(p.age) :int变量大小
//sizeof(p.name):char*变量大小(64位系统的地址总线是64位的,一个指针占用的空间是8个字节)
20 ZhangSan
//类内指针指向的值,说明类的地址对应类的某一个成员变量的值
*/
- 类的成员函数不占用栈空间
所有的函数都存放在代码区。
2020.3.18
我说不要死,但它不受控制。
私有属性不能直接访问error : p.age = 10
class Person {
int age;
char *name;
};
int main() {
Person p;
int *p = (int *)&p;
*p = 10;
}
//这样确实也可以访问,可以用smile隐藏
#pragma pack(1)
class Person {
private:
int age;
char *name;
public:
Person();
Person(int, char *);
int getAge();
char *getName();
};
//构造器:为了初始化赋初值
//Constructor should be overloaded.
Person::Person(int aage, char *aname) {
age = aage;
this->name = aname;
}
//default constructor:默认构造,一旦显示写出有参数的,默认构造就走了(可以补回)
Person::Person() {}
int Person::getAge() {
return age;
}
char* Person::getName() {
return name;
}
int main()
{
Person p1(20, "ZhangSan");
Person *p2 = new Person(20, "ZhangSan");
Person *p3 = new Person();
printf("%d--%s\n", (*p1).getAge(), (*p1).getName());
printf("%d--%s\n", (*p2).getAge(), (*p2).getName());
printf("%d--%s\n", (*p3).getAge(), (*p3).getName());
return 0;
}
/*
20--ZhangSan
20--ZhangSan
*/
class内部默认私有
struct内部默认公有
默认构造
class Test {
int ai;
int aj;
public:
Test(int ai, int aj); //(1)
Test(int ai); //(2)
Test(); //(3)
Test(int ai, int aj = 0); //(4) //默认参数传递,但还是会传的(理论上是overloading)
};
/*
t1.ai=3 //(2) Test t1(3);
t2->test //(3) Test *t2 = new Test();
t3.ai=2 t3.aj=3 //(1) Test t3(2,3);
t4() //this is a function
t4 //(3) Test t4();(这才是默认构造的对象)
t5->test.ai=3 //(2) Test *t5 = new Test(3);
*/
程序运行的空间划分问题
可执行代码->内存中->代码区(read only)
- 所有常数、常量
- 全局变量区:在main函数之前,最先创建,最后消失
- 运行期内存(memory runtime)
- 堆(heap):堆比栈慢,因为存在寻址问题(最早/优适应算法);但是堆比栈可控
- 栈(stack):保存局部变量;频繁定义函数有损性能,因为调用函数时需要用栈保存和回复现场;存在栈区限制,故预先不知道大小用堆区
int *fun() {
int a = 10;
return &a;
}
int main() {
int *p = fun();
cout << *p << endl;
}
/*
10
a是局部变量,用完就被释放,返回局部变量的地址埋下祸根
*/
/*
问题根源:返回了别人的指针,不要试图用函数的返回值,可以将自己的指针作为函数参数传入修改
或者:
*/
int *fun() {
int *p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*p = 10;
return p;
}
//可能会出现memory leak,使用者需要归还空间
class Test {
int i; //value
int *j; //address
};
/*
什么时候是value?什么时候是address?
看存在的必要性,有必要一直都在的最好以地址形式存在
*/
//嵌套循环错误 [Error] field 'p' has incomplete type 'Point'
class Point;
class Circle;
class Circle {
Point p;
//Point类的大小不能确定,故不能编译
};
class Point {
Circle c;
};
int main() {
return 0;
}
class Point;
class Circle;
class Circle {
Point *p;
//修改后Point *p指针大小确定,可以编译
};
class Point {
Circle c;
};
int main() {
return 0;
}
malloc申请不还存在内存泄漏的问题
//理论上是不同的地址(可能是相同的地址)
int main() {
int *p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
printf("%p\n",p);
free(p);
p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
printf("%p",p);
return 0;
}
free释放内存,指针不变,需要指空(避免二次free)
//将free(p);替换为
if (p != NULL) {
free(p);
p = NULL;
}
构造里面申请了内存,一定要在析构函数中释放(对:都是必然的调用)
析构函数应当只释放构造函数里申请的空间(错:析构函数释放类内一切函数申请的空间)
2021.3.25
越诡异就越愚蠢。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test {
public:
int i;
int *j;
Test(int, int);
~Test();
};
Test::Test(int ai, int aj) {
i = ai;
j = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*j = aj;
}
Test::~Test() {
cout << "destruct" << endl;
if (j != NULL) {
free(j);
j = NULL;
}
}
int main() {
Test test(1, 2);
//destructor析构函数:为了释放,完成空间回收,自动被系统调用
}
//destruct
/*
析构函数不需传参的原因:
Test::Test(int ai) {
i = ai;
j = NULL;
}
free(j);
free一个不存在的j程序可能会崩溃
析构不存在overloading(不存在参数,不能定义两次)
*/
指针的不安全性
int *p; //(1) fly pointer野指针
int i;
int j;
p = &i;
p = &j; //(2) 不安全,乱指
reference 引用(C++中的新指针)
int &r; //r declared as reference but not initialized
//(1) 一旦声明必须初始化
int &r = i;
int i = 10;
int &r = i;
cout << r << endl; //r = 10
int j = 20;
r = j;
cout << i << endl; //i = 20
//(2) r永远是i的引用
pass by value VS pass by address (pointer or reference)
void fun(int a) {
a++;
}
int main() {
int m = 10;
fun(m);
cout << m << endl;
return 0;
}
//10
//改为pointer指针
void fun(int *a) {
(*a)++;
}
int main() {
int m = 10;
fun(&m);
cout << m << endl;
return 0;
}
//11
//改为reference引用(看起来是值,实际上是指针)
void fun(int &a) {
a++;
}
int main() {
int m = 10;
fun(m);
cout << m << endl;
return 0;
}
//11
| pass by value | pass by address | |
|---|---|---|
| 效果 | read | read/write |
| 性能 | sizeof(object) | sizeof(int) |
| 麻烦 | copy-constructor | nothing |
| 结论 | never pass by value |
(函数参数不要是value:只要是类就不要pass by value,build-in-type除外)
危险的行为:
- fly pointer:永远赋初值,判空或者写断言函数
- memory leak
- return address of local variable:返回局部变量的地址
- multi-pointers for one object:如调用
memcpy函数时,若为address则出现此问题
拷贝构造
class Test {
int i; //value
int *j; //address
}
int main() {
Test t1(1, 2);
Test t2(t1); //复制:C++默认拷贝构造
}
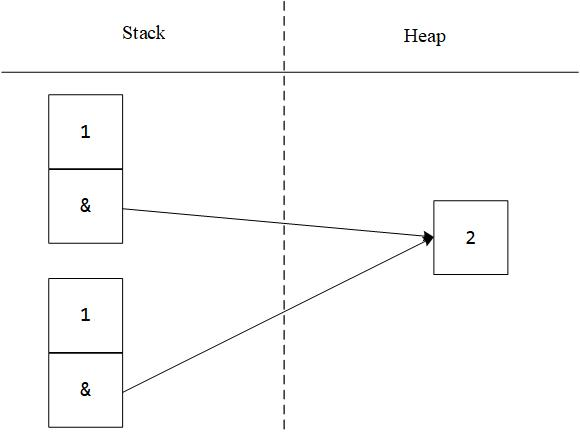
free(j);
free(j); //重复释放了
//改正 copy constructor 拷贝构造
Test(Test &t);
Test::Test(Test &t) {
this->i = t.i;
//this->j = t.j;改为
this->j = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*j = *t.j;
}
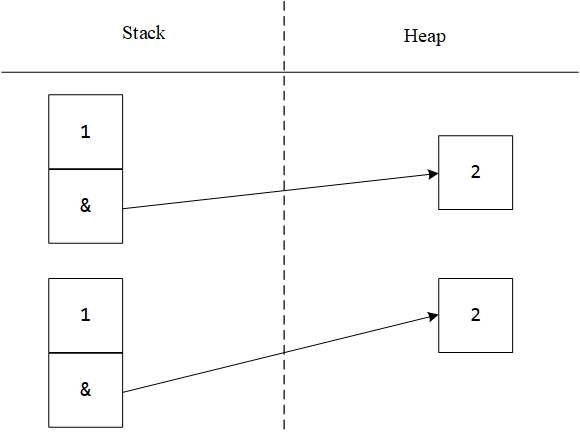
bitwise copy 浅拷贝(位拷贝/默认拷贝)VS logical copy 深拷贝
pass by value 就会拷贝构造
//可以在类内声明私有拷贝构造但不实现
private:
Test(Test &t);
//只要调用了拷贝构造就会先报错[Error]访问类内私有成员
new delete
new = malloc(void *) + constructor(this(Test *))
new是动态内存分配运算符
delete = destructor + free
先destructor再free
//有时需要补全默认构造方法
Test *p = new Test[10];
//delete p;删不掉,改为
delete []p;
const
-
//const pass by address (read only) void fun(const int *p) {} //p的内容只读,指针指向的内容不允许修改 //char* strcpy(char* des,const char* source) 后(带有const)拷贝给前 -
const double PI = 3.14; const Test t; //有类型 -
const Test t; //t.test_fun(); [Error] //认为调用函数是危险的,可能修改这一常量,如要调用: //(1) 需要在类中显式声明 void test_fun() const; //(2) 函数实现且函数内不能有任何修改操作 Test::test_fun() const {} -
int fun5(); Test fun5(); //写成 const Test fun5(); 编不过去,返回值本身没有意义 //[Warning] type qualifiers ignored on function return type [-Wignored-qualifiers] int main() { int m = fun5(); //fun5()++; [Error] lvalue required as increment operand(和const没关系,不合语法) fun5().test_fun();//能编过去 }
2021.4.1
错了错了都错了。
static
-
//被创建后永不释放直至程序结束,例如 static int i; //静态局部变量i,一次创建,最后释放,“保值” -
//将函数的可见性限制在本文件中,仅能在本文件中调用 static void fun(); /* int g_i; C2065:在另一file中使用了g_i,未声明的标识符 LNK2005:在另一file中声明/定义了int g_i; 在全局范围内重复定义 */ extern int g_i; //外链接:被file外的内容使用 //全局变量绝对不能定义在头文件中,外链接可以 void fun(); //fun()函数在外部,不用写extern,函数默认外链接 //可见性问题:函数默认全局可见,全局变量默认本文件可见 -
//修饰类中的属性 class Test { public: static int i; int j; public: Test(int ai, int aj); //一并修改Test(int j) } int Test::i = 100; //要求在下面的构造函数前一次性赋初值 Test::Test(int ai, int aj) { i = ai; j = aj; } int main() { Test t1(1, 2); Test t2(2, 2); } -
//类内的静态函数 class Test() { public: int i; int j; public: static void test_fun(); } //this指向调用者对象,而静态成员函数属于类、要用类来访问,故类内静态函数没有this指针,只能操作静态属性不能操作非静态属性 Test::test_fun(); //通过类名访问调用 -
总结:
- static local variable
- static global function
- static data member
- static function member
design pattern(如何组织一步到位)
分类:构建型、结构型、行为型(类与类中的调用关系)
facade单件模型(这个类只有一个对象)
class singletion {
private:
singletion(); //构造私有
static singletion* self;
public:
static singletion* get object();
};
singletion* singletion::self = NULL;
singletion* singletion::get_object() {
if (self == NULL) {
self = new singletion();
}
return self;
}
//还要写delete
operator overloading运算符重载
class Account {
int id;
int balance;
public:
Account();
void Deposit(int m);
Account& operator+(int m); //自身引用
};
Account::Account() { balance = 0; }
void Account::Deposit(int m) {
this->balance += m;
}
Account& Account::operator+(int m) {
this->balance += m;
return *this; //本质是addr 引用看起来永远是个值
}
int main() {
Account a;
a.Deposit(100);
a = a + 100; //(a = a +[函数] 100;)更符合存钱的认识
}
/*
其他运算符重载:
模拟数组//[]
模拟指针//*
长期运行,堆区不被搞碎//new(malloc + 构造)
//delete
*/
运算符重载:非必要,只是为了好用(不要超出常人理解的范围定义运算符)
- 不要被它迷惑
- 不改变本义
class Account {
public:
//++a
Account operater ++();
//a++
Account operater ++(int a);
};
//对比Account和Account&
//a++ 本次表达式不变,但+1了 返回对象(pass by value)
Account Account::operator++(int a) {
Account old = *this;
this->balance++;
return old; //局部变量 返回引用时会返回局部变量的地址,所以只能传值
}
//++a
Account& Account::operator++() {
this->balance++;
return *this;
}
2021.4.8
垃圾... 还是垃圾...
inheritance & composition
1 reuse重用
2 why inheritance
3 is a and is like a
函数(代码的重用)
继承(以物刻画关系)class derived-class: access-specifier base-class
class Student {
int card_id;
char *name; //等
public:
void borrow_book();
};
void Student::borrow_book() {
cout << "query DB how many books?" << endl;
cout << "if > 5 return" << endl;
}
class Teacher {
int card_id;
char *name; //等
public:
void borrow_book();
};
void Teacher::borrow_book() {
cout << "query DB how many books?" << endl;
}
//a student is a(是) borrower -> a student is like a(像) borrower
class Borrower {
int card_id;
char *name;
public:
void borrow_book();
};
void Borrower::borrow_book() {
cout << "query DB how many books?" << endl;
}
class Student:public Borrower { //子类 延伸类
Borrower::borrow_book();
cout << "if > 5 return" << endl;
}
/*
通常会在子类中用父类的方法,不能默认调用(因为调用位置不定)
彰显个性 1.重写父类方法 2.增加方法(void vertification() {})
*/
Java和C++的区别
- C++不纯粹:Java跨平台,C++不跨平台
- C++一堆语法,Java一堆语法和巨型类库
composition组成
组成与继承是不同的重用
class Engine {
int attr;
public:
void run();
}
class Car {
Engine e;
int other;
public:
void run();
}
void Car::run() {
e.run(); //组合关系下的reuse,重用Engine的run方法,两个run没关系
cout << "car is running" << endl;
}
构造顺序
//4 constructor initialization list
class Base {
int i;
public:
Base();
};
class Derived:public Base {
int j;
public:Derived();
}
/*
Derived::Derived() {
cout << "construct derived" << endl;
}
error > no watching function for call to "Base::Base()"
设有默认构造了(下面实现,上面被挤走了)
改为
*/
Base::Base() {
cout << "start" << endl;
}
Derived::Derived():Base() {
cout << "construct derived" << endl;
}
int main() {
Derived d;
cout << sizeof(Derived) << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
start
construct derived
8
必然会自动调用父类的构造方法,且先父类后子类
构造过程中可能会重用父类的方法
析构函数:先调子类析构,后调父类
*/
Derived::Derived(int ai, int aj):Base(ai) { //public Derived(int ai, int aj) 给两个(8字节)
j = aj;
}
//传参 ai base(ai)
int j = 10; //默认构造+拷贝
int j(10); //创建int对象;初始化为10;构造方法,效率更高
//传参 ai base(ai)
class Test {
public:
int j;
int i;
public:
Test();
};
Test::Test(int ai, int aj):i(ai),j(aj) {}
Test::Test(int aj):j(aj),i(j) {}
int main() {
Test t(3);
cout << t.i << endl; //未被初始化
cout << t.j << endl;
}
Test::Test(int aj):i(j),j(aj) {} //仍未被初始化
//原因:初始化顺序永远先i后j,参照不能在后面
protect
this->card_id = 10;
//父类声明为private,子类不能随便用
//父类对子类公有,对外私有:protected
private
class Student:public Borrow
//若为private,私有继承,父类的public方法对子类可见,对外不可见(不要削弱父类接口)
多重继承
class Base1 {
public:
void f();
};
void Base::f() {}
class Base2 {
public:
void h();
};
void Base::h() {}
class Derived:public Base1,public Base2 {
};
int main() {
Derived d;
d.f();
d.h();
return 0;
}
/*
多重继承:改为composition
形成菱形结构,会出现混淆(例:Base1和Base2都有f();)
*/
multiple inheritor
inheritor VS composition 优选组合
2021.4.15
精神图腾,孝庄皇太后!
upcasing 向上类型转化 (体现了reuse重用)
class Derived:public Base {};
void fun(Base base) {}
int main() {
Derived d;
fun(d);
}
/*
upcasting 是一定正确的
downcasting 不一定,可能出现越界
(父类 4字节 子类 8字节 强转后访问子类后四个字节可能会越界)
*/
class Pet {
char *name;
int age;
public:
virtual void speak(); //靠虚函数实现后绑定
}
void Pet::speak() {
cout << "pet speak" << endl;
}
class Cat:class Pet {
public:
void speak();
}
void Cat::speak() {
cout << "miao" << endl;
}
class Dog:class Pet {
public:
void speak();
}
void Dog::speak() {
cout << "wang" << endl;
}
void Neddle(&Pet pet) {
pet.speak //多态
}
/*
如果这里用void Needle(Pet pet)拷贝构造,会自动构造为pet的指针
never pass by value : 性能低下,能力低下,麻烦事多(各种混乱,应当声明私有拷贝函数),靠名(拷贝构造导致多态性失效)
*/
int main() {
Cat cat;
Dog dog;
Needle(cat);
Needle(dog);
}
//later binding
/*
if pet is a Cat
Cat::speak
if pet is a Dog
Dog::speak
*/
binding 绑定
绑定:将函数的一次调用与函数入口相映射的过程
- early binding 前绑定:函数调用前已经确定了调用什么
- later binding 后绑定:到调用时才确定调用什么
polymorphism 多态
无继承,不多态 (python无类型且是个诡异的多态)
不把子类当父类对待就没有所谓的多态
为解决类型混乱的问题引入了虚函数[实现]使得结果出现了多种可能[多态]
实现方式:
类 对象
虚函数表 v_table 虚指针 v_ptr(指向本类的虚函数表)
Pet Cat Cat cat
Pet.speak() Cat.speak()---------------------------xxx
Pet.sleep() Cat.sleep()
Dog Dog dog
Dog.speak()---------------------------xxx
Dog.sleep()
对象指向进虚函数的位置
对象调用者进行索引
//验证:造两个cat对象,前八字节相同,指向cat类
int main() {
Cat c1, c2;
int *p = (int *)&c1;
cout << *p << endl;
p = (int *)&c2;
cout << *p << endl;
}
//如何让猫,狗叫呢 只是相对绑定,全在前八字节
class Cat{
Dog dog;
memcpy(&pet, &dog, sizeof(int));
}
virtual constructor & destructor
构造函数不具有二义性,构造绝不多态;析构往往多态(should be)
void fun(Pet *p) { delete p;}
Cat *p = new Cat();
fun(p);//调用父类的析构,析不了
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Pet {
public:
virtual void speak();
virtual ~Pet();
};
void Pet::speak() {
cout << "pet speak" << endl;
}
Pet::~Pet() {
cout << "destructor" << endl;
}
class Cat:public Pet {
public:
void speak();
virtual ~Cat();
};
void Cat::speak() {
cout << "miao" << endl;
}
Cat::~Cat() {
cout << "destructor cat" << endl;
}
int main() {
Pet *p = new Pet;
p->speak();
Cat c;
c.speak();
p = &c;
p->speak();
return 0;
}
/*
pet speak
miao
miao
destructor cat
destructor
*/
多态影响性能 (对:占空间)
一旦类中有一个虚函数(意味着不在意性能),则应该把其他类能写成虚函数的函数都写成虚函数 (对)
- 构造绝不多态
- static不具有多态:没有this指针,不传对象,没有多态概念
/*删掉
void Pet::speak() {
cout << "pet speak" << endl;
}*/
//对应Pet类中 virtual void speak = 0;
class Pet {
public:
virtual void speak() = 0;
virtual ~Pet();
};
abstract class 抽象类 (interface in java & C#)
pure virtual function 纯虚函数
含至少一个纯虚函数类的为抽象类
被赋值为0的函数为纯虚函数
抽象类不能实例化,不能创建对象(因为行为不能确定,创建对象没有意义)
- 抽象类为整个类型家族规定了共性行为规范(
java中的abstract class)
| overloading | 同一作用域 |
|---|---|
| override | 父类的虚函数在子类中重写 |
| redefinition | 在子类中重新定义虚函数(暗指非虚函数) |
- 抽象类为行为角度抽象,行为串联(两个家庭因共性行为产生关联,定义抽象类关联共性行为)(
java中的interface)
class FlyObject { //无属性(行为角度共性)
public:
virtual void fly = 0;
};
class Machine {};
class Plane:public Machine, public FlyObject //多重继承(不搞多个实体类就行),可类比java中一个父类,多个接口
{
public:
void fly();
};
class Animal {};
class Bird:public Animal, public FlyObject
{
public:
void fly();
};
//对雷达来说两个fly的行为一致
void scan(FlyObject *ob) {
ob->fly();
}
2021.4.22
因为我就是管理员。
reuse
- 继承是最大的重用,处理行为角度的共性,多态并不是重用:
Pet例子中,speak重写了,Needle是重用
雷达例子中,fly重写了,scan是重用
(承载类型的函数是重用)
- overloading重用了函数名
- template模板类,用于处理行为完全一致但是类型不同的情况
class Stack {
int pool[100];
int top;
public:
stack:top(0) {
}
//inline function 内联函数:把函数体放在头文件中
void push(int v) {
pool[top++] = v;
}
int pop() {
return pool[--top];
}
};
int main() {
Stack s;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
s.push(i * i);
}
}
/*
int改为double型
代码复用先想继承,但是继承是行为角度的共性,push/pop无处可写
template模板类(泛型):用于处理行为完全一致,但是类型不同的情况
*/
template<class T> //template<class T1, class T2, ...>
class Stack {
T pool[100];
int pop;
public:
stack:top(0) {
}
void push(T v) {
pool[top++] = v;
}
T pop() {
return pool[--top];
}
};
int main() {
Stack<double> d;
Stack<int> i;
}
STL standard template library
C++不包含类库,但是包含STL,不能说是一门纯语言
STL中放的是动态增长(长度不定)的万能容器(模板类)
#include <vector>
int main() {
vector<int> v; //vector 不定长:动态数组
for (int i = 0;i < 10000;i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << v[9988] << endl;
}
/*
vector<void *> (任何对象的指针)
有多态保证:不管是父类还是子类,调speak就行(必须知道的时候自行查阅设计模式)
*/
#include <List>
int main() {
List<int> v;
for (int i = 0;i < 10000;i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
return 0;
}
//出现性能问题之前永远不考虑性能:vector和list选vector
class Test {
int a[100];
static int cnt;
public:
Test() {} //默认构造
Test(const Test &t) { //拷贝构造(传值=传地址)
cnt++;
cout << cnt << endl;
}
};
int Test::cnt = 0;
int main() {
Vector<Test> v;
for(int i = 0;i < 10000;i++) {
Test t;
v.push_back(t);
}
}
//26383
/*
要找一片连续的空间->先找一片空间->不够再找一片->搬家(性能不行)
*/
/*
vector可以用下标访问
list不能用下标访问
用一个统一的模式访问:iterator
*/
iterator 迭代器
list/vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while(it != v.end()/*[返回开始或结束]*/) {
cout << *it << endl;
it++;
}
迭代器自身也是一个设计模式
namespace 名空间(等价于package)
不要把类暴露成最顶级的分块,保证类名不冲突
Test类
namespace my_nsp {}
main:
#include "Test.h"
using namespace my_nsp; //using namespace stdin; C++自己定义的
int main() {
my_nsp::Test t;
Test t;
return 0;
}
exception 异常
不由程序员控制的错误
void fun(int v) throw (int) { //int为类型
if (v > 0) {
throw v; //v为对象
}
}
int main() {
fun(20);
}
//template called after throwing an instance of "int"
/*
异常处理若不处理,异常上诉至OS,OS会终止该程序
处理:
*/
try{
} catch(int e) { //类型需匹配
cout << "error, pls" << endl;
} catch() {
} catch() {
}
//catch不同的东西(处理不同类型的错误)
catch(...){} //catch所有的东西
//C语言:assert断言
void fun(int *p) {
assert(p != NULL);
if (p == NULL) {
return;
}
}
int main() {
fun(NULL); //assertion failed!
}
/*
#define NDEBUG
定义这个宏后所有的断言(assert)都失效
*/
friend 访问控制 public/private
class MyClass {
int i;
public:
friend void fun3(MyClass&); //友元函数:有缘人就可以访问我的私有成员
};
void fun3(MyClass &my) {
my.i = 10;
}
//函数或类都可以声明有缘



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号