drf07 三大认证之 认证、权限、频率
一、认证
介绍:
认证是APIView提供的三大认证之一,使用它视图类必须继承APIView
作用:校验用户是否登录
注意:认证一般搭配权限使用
两个参数:
SessionAuthentication 通过session认证
BasicAuthentication 认证基类
1.内置认证Authentication
1.1 前提准备
# 新建一个app
python manage.py startapp app_auth
# 使用django内置admin站点创建一个管理员 - shell窗口
python manage.py createsuperuser
# 1.用户名
admin
# 2.邮箱 - 可回车跳过
admin@qq.com
# 3.密码
admin123
# 4.确认密码
admin123
# 在settings中配置修改如下内容
LANGUAGE_CODE = "zh-hans"
TIME_ZONE = "Asia/shanghai"
USE_TZ = False
# 最后可以登录
http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/
# 填写用户名密码
1.2 全局配置 -settings
可以在项目的配置文件中全局默认的认证方案:
(1) 查找默认配置
# 1.首先 三大认证是drf中实现的,所以先找到这个
# APIView是drf所有视图的基类
from rest_framework.views import APIView
# 2.点击 APIView 找到这个
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
# 3.点击api_settings
api_settings = APISettings(None, DEFAULTS, IMPORT_STRINGS)
# 4.点击DEFAULTS - 这个是rest_framwork的默认配置
DEFAULTS = {
# Authentication 认证
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
],}
(2) rest_framework 默认配置
DEFAULTS = {
# Authentication 认证
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
],
# 权限
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny',
],
# Throttling 频率
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'user': None,
'anon': None,
},
# Pagination 分页
'PAGE_SIZE': None,
# Filtering 过滤
'SEARCH_PARAM': 'search',
'ORDERING_PARAM': 'ordering',
# Exception handling 异常处理
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'rest_framework.views.exception_handler',
'NON_FIELD_ERRORS_KEY': 'non_field_errors',
}
(3) 在settings配置
# REST_FRAMEWORK,里面都是drf的配置信息
from rest_framework import settings
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# 配置认证
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
],
}
(4) 说明
因为默认使用Authentication默认配置,并没有修改默认系统,所以可能会显示你当前登录的用户,但是不会限制你登录后才能方访问,也就是说,游客也可以方法。
重要提示: 认证 需要和权限搭配使用才能产生效果
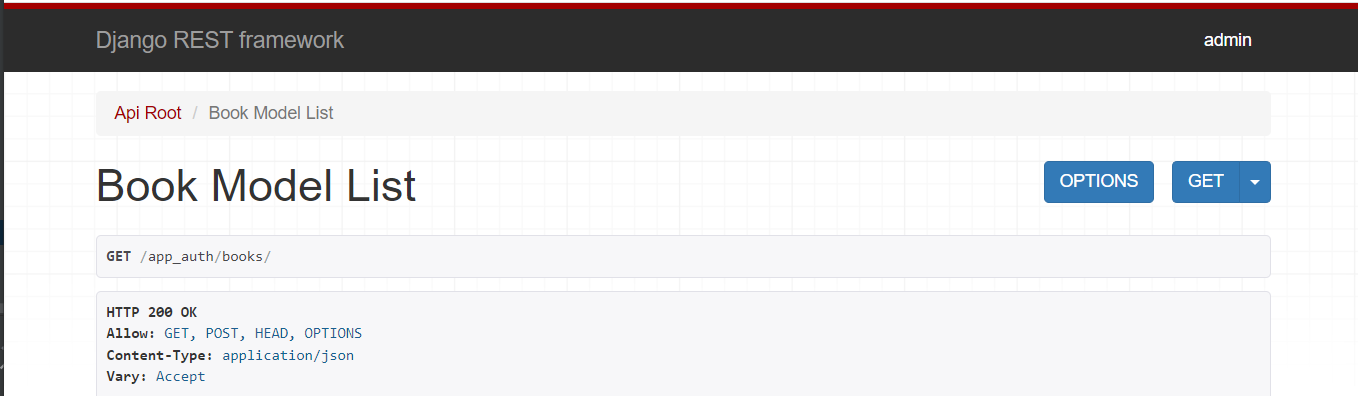
1.3 局部配置 - 视图类
# views.py
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from app05_api import models
from app05_api.ser import BookModelSerializer
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication
class BookModelViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = models.Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
authentication_classes =[SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication] # 局部配置
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated] # 判断是否登录,未登录则不给访问
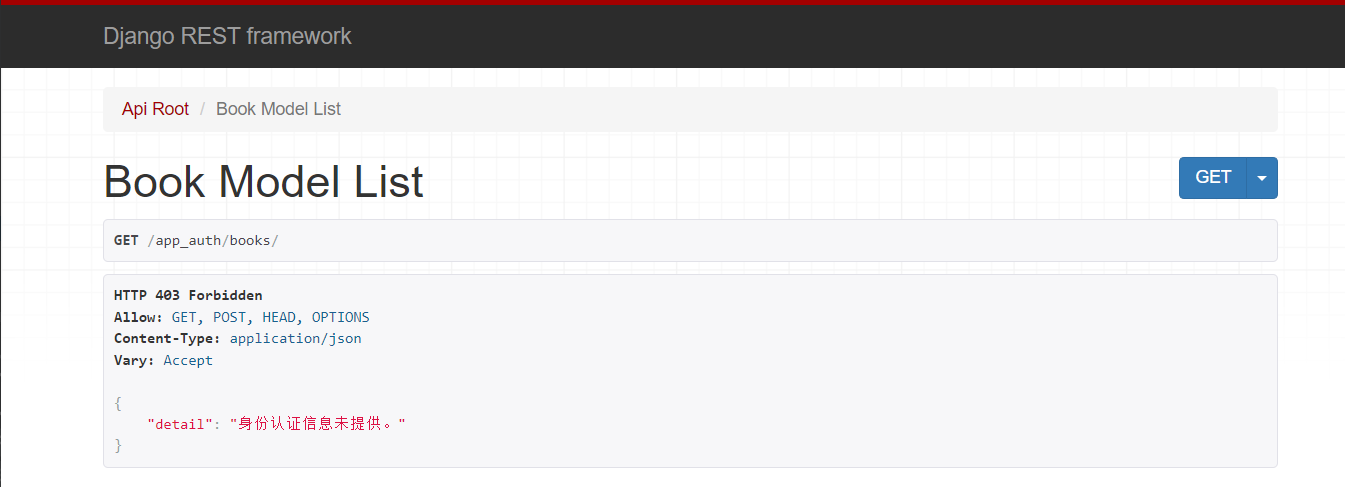
2.自定义认证
2.1 源码分析
#1 APIVIew----》dispatch方法---》self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)---->有认证,权限,频率
#2 只读认证源码: self.perform_authentication(request)
#3 self.perform_authentication(request)就一句话:request.user,需要去drf的Request对象中找user属性(方法)
#4 Request类中的user方法,刚开始来,没有_user,走 self._authenticate()
#5 核心,就是Request类的 _authenticate(self):
def _authenticate(self):
# 遍历拿到一个个认证器,进行认证
# self.authenticators配置的一堆认证类产生的认证类对象组成的 list
#self.authenticators 你在视图类中配置的一个个的认证类:authentication_classes=[认证类1,认证类2],对象的列表
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
# 认证器(对象)调用认证方法authenticate(认证类对象self, request请求对象)
# 返回值:登陆的用户与认证的信息组成的 tuple
# 该方法被try包裹,代表该方法会抛异常,抛异常就代表认证失败
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self) #注意这self是request对象
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise
# 返回值的处理
if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
# 如何有返回值,就将 登陆用户 与 登陆认证 分别保存到 request.user、request.auth
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple
return
# 如果返回值user_auth_tuple为空,代表认证通过,但是没有 登陆用户 与 登陆认证信息,代表游客
self._not_authenticated()
2.2 如何查找认证类
# 1. 找到这个 点击 BasicAuthentication
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication
# 2. 点击 BaseAuthentication
class BasicAuthentication(BaseAuthentication)
# 3. 找到这里,这里可以看到,基本的认证是要重写 authenticate
# 这里说明以下,这里规定了认证需要重写的方法,参照鸭子类型,可以不继承这个自己写一个
class BaseAuthentication:
def authenticate(self, request):
raise NotImplementedError(".authenticate() must be overridden.")
2.3 编写自定义认证类
前提准备 - 自定义类认证前提
# models.py
class User(models.Model):
username=models.CharField(max_length=32)
password=models.CharField(max_length=32)
user_type=models.IntegerField(choices=((1,'超级用户'),(2,'普通用户'),(3,'二笔用户')))
class UserToken(models.Model):
token=models.CharField(max_length=64)
user=models.OneToOneField(to=User,on_delete=models.CASCADE) #一对一关联到User表
# 别忘记在User表中添加数据
# views.py - 获取登录信息 - 并传如token 随机字符串
import uuid
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from app06_auth import models
class LoginView(APIView):
authentication_classes = []
def post(self,request):
username=request.data.get('username')
password=request.data.get('password')
user=models.User.objects.filter(username=username,password=password).first()
if user:
# 登陆成功,生成一个随机字符串
token=uuid.uuid4()
# 存到UserToken表中
# models.UserToken.objects.create(token=token,user=user)# 用它每次登陆都会记录一条,不好,如有有记录
# update_or_create有就更新,没有就新增
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(defaults={'token':token},user=user)
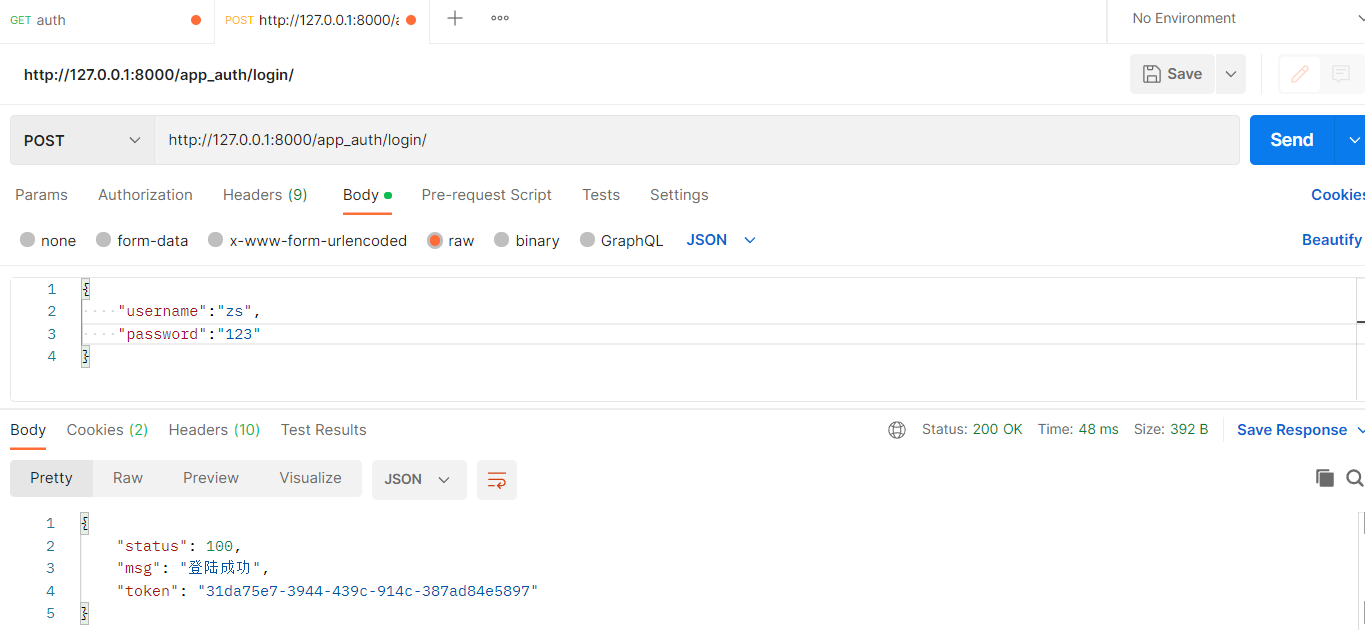
return Response({'status':100,'msg':'登陆成功','token':token})
else:
return Response({'status': 101, 'msg': '用户名或密码错误'})
# urls.py
from django.urls import path, re_path
from app06_auth import views
from rest_framework import routers
router = routers.SimpleRouter()
router.register('books', views.BookModelViewSet) # 不用加后缀
urlpatterns = [
path('login/', views.LoginView.as_view()),
]
urlpatterns += router.urls
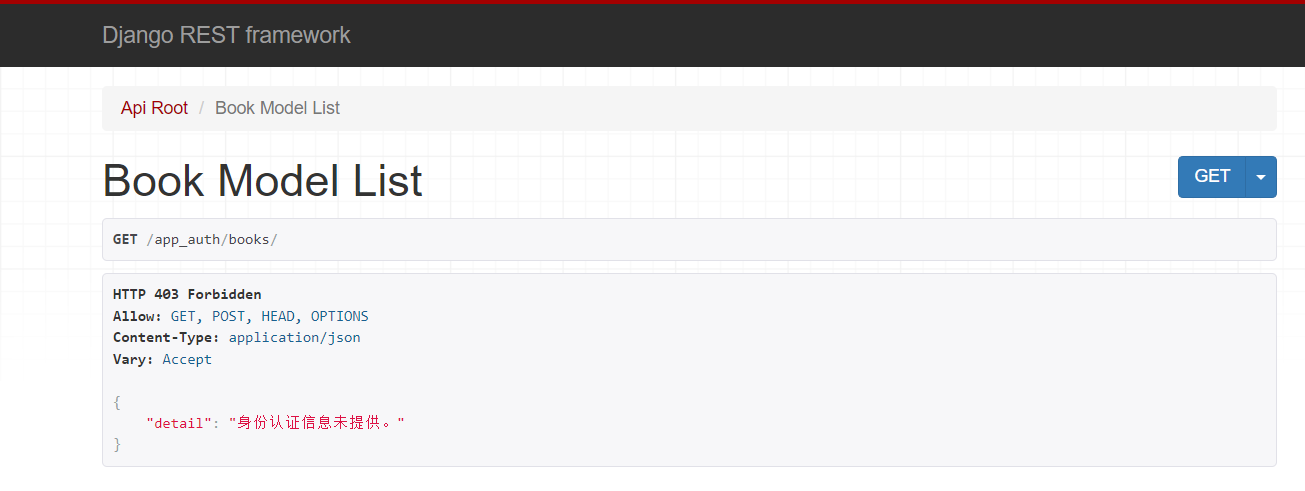
注意事项
1.需要先登录,才能获得token
2.访问必须要带token
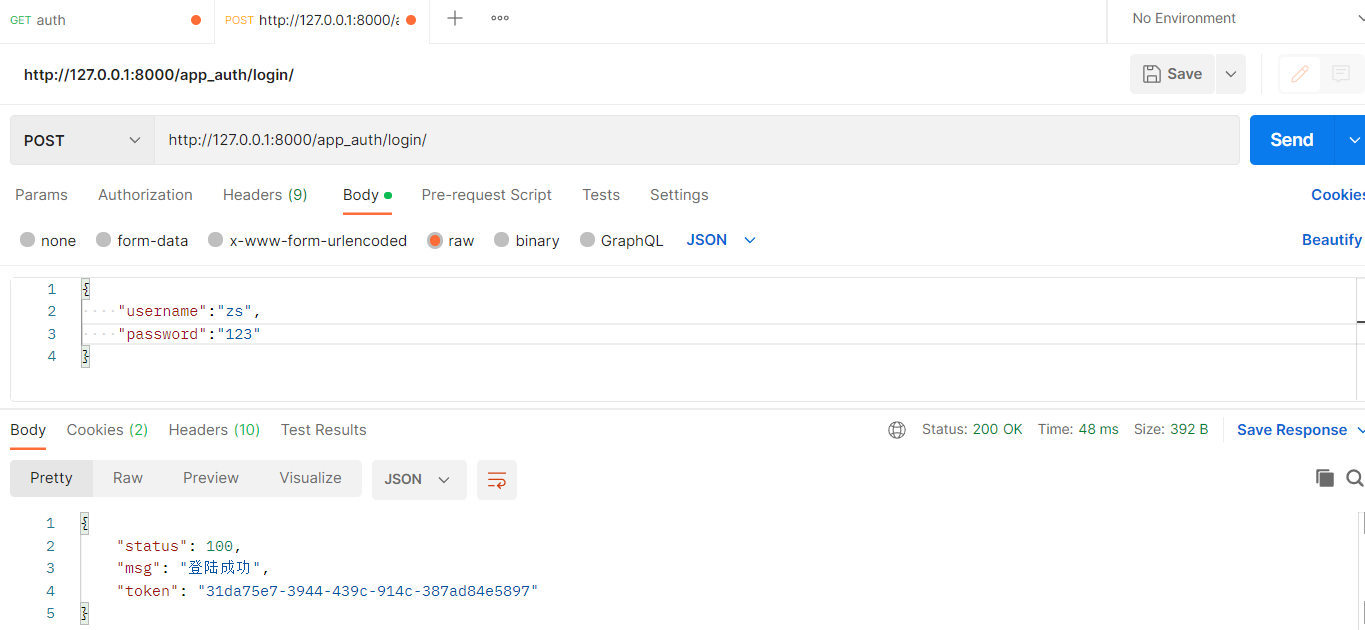
成功后拿到数据
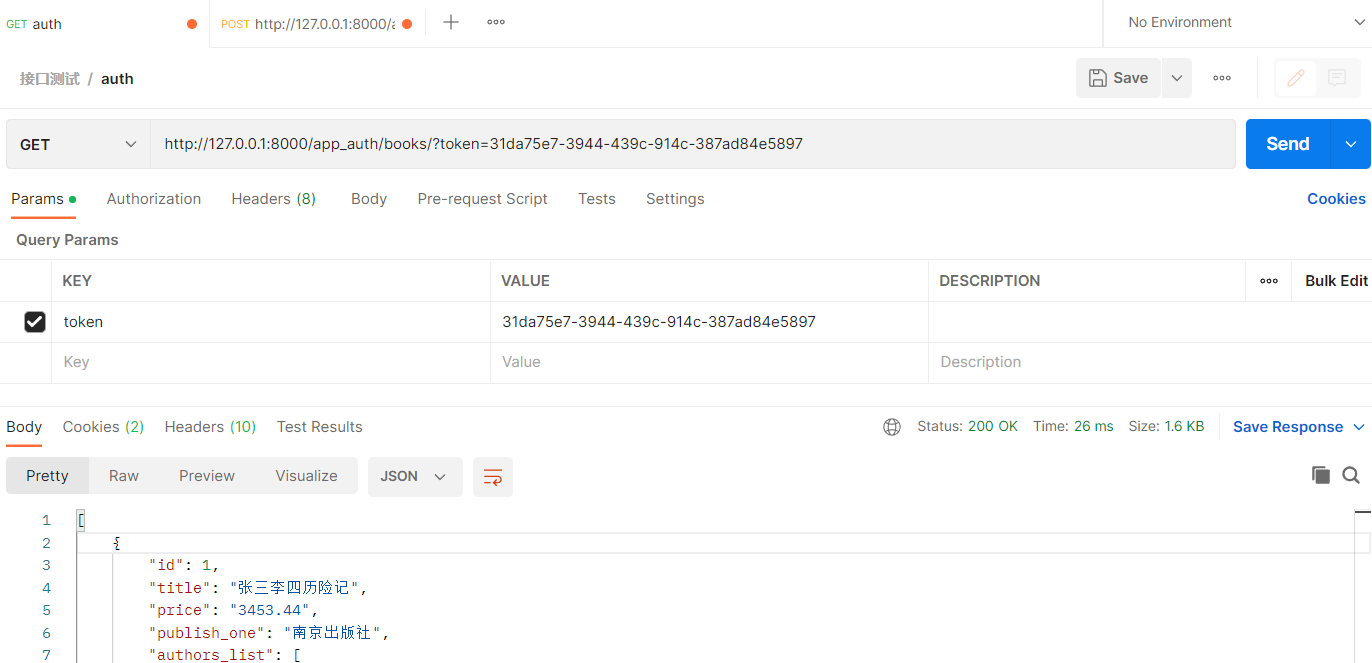
登录失败后,访问不了


认证逻辑
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
from app06_auth import models
class MyAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self,request):
# 认证逻辑,如果认证通过,返回以元组的形式返回两个值 (user, token)
token = request.GET.get('token')
if token:
user_token = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
# 认证通过
if user_token:
# print(user_token.user) # 解释 user_token.user 值得是user对象
return user_token.user,token
else:
raise AuthenticationFailed('认证失败')
else:
raise AuthenticationFailed('请求地址中需要携带token')
2.4 自定义认证类配置
2.4.1 全局配置 -settings
在项目的setting中配置如下
# 在项目的setting中配置如下
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
# 自定义认证类 - 类的路径
# from app06_auth.utils.app_auth_utils import MyAuthentication
'app06_auth.utils.app_auth_utils.MyAuthentication',
],
}
2.4.2 局部配置 - 视图类
# views.py
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from app05_api import models
from app05_api.ser import BookModelSerializer
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication
from app06_auth.utils.app_auth_utils import MyAuthentication
class BookModelViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
# authentication_classes =[SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication] # 局部配置
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication]
二、权限
介绍:
权限控制可以限制用户对于视图的访问和对于具体数据对象的访问。
- 在执行视图的dispatch()方法前,会先进行视图访问权限的判断
- 在通过get_object()获取具体对象时,会进行模型对象访问权限的判断
两个参数:
IsAuthenticated 是否登录
IsAdminUser 是否为管理员
1. 内置权限
用法在内置认证中已经写了,这里就不在补充。这里写下如何配置。并且权限之前需要有认证才行。
1.1 全局配置 -settings
在项目的settings中配置如下:
# 在项目的settings中配置如下:
# 登录用户 - 才能访问
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
# 管理员用户 - 管理员才能访问
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAdminUser
# settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
# 自定义认证类
# 'app06_auth.utils.app_auth_utils.MyAuthentication',
# 默认认证类
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication',
],
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
# 默认权限类
'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny',
# 是否登录
'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated',
# 是否 为管理员
'rest_framework.permissions.IsAdminUser',
],
}
1.2 局部配置 - 视图类
# views.py
# 可单个使用 最好搭配认证
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from app05_api.models import Book
from app05_api.ser import BookModelSerializer
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated,IsAdminUser
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication
from app06_auth.utils.app_auth_utils import MyAuthentication
# Create your views here.
class BookModelViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
# authentication_classes =[SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication] # 局部配置
# authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication]
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated,IsAdminUser]
2. 自定义权限
2.1 源码分析
# APIView---->dispatch---->initial--->self.check_permissions(request)(APIView的对象方法)
def check_permissions(self, request):
# 遍历权限对象列表得到一个个权限对象(权限器),进行权限认证
for permission in self.get_permissions():
# 权限类一定有一个has_permission权限方法,用来做权限认证的
# 参数:权限对象self、请求对象request、视图类对象
# 返回值:有权限返回True,无权限返回False
if not permission.has_permission(request, self):
self.permission_denied(
request, message=getattr(permission, 'message', None)
)
2.2 如何查找权限类
# 1. 找到这个 点击 IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated,IsAdminUser
# 2. 看到这个 点击 BasePermission
class IsAuthenticated(BasePermission):
# 3. 看到如下内容
class BasePermission(metaclass=BasePermissionMetaclass):
def has_permission(self, request, view):
return True
def has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj):
return True
# 注意:里面还继承了元类,这里就不再深入
2.3 编写自定义认证类
前提准备
准备同 认证类 -> 2.3 -> 前期准备
注意事项
1.需要先登录,才能获得token
2.访问必须要带token

权限逻辑
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
class MyPermission(BasePermission):
def has_permission(self, request, view):
user= request.user # 当前用户的user 是认证传过来的
# 由于经过认证后,request内就有user对象了,这个时候就能拿到登录用户的用户类型
# 如果该字段用了choice,别忘了用get_字段名_display()就能取出choice后面的中文
try:
if user.user_type == 1:
return True # 表示通过权限
else:
return False # 表示未通过权限,会报相应的错误信息
except:
return False
2.4 自定义权限类配置
前提准备 - 参考认证
# views.py
class LoginView(APIView):
authentication_classes = []
permission_classes = []
def post(self,request):
username=request.data.get('username')
password=request.data.get('password')
user=models.User.objects.filter(username=username,password=password).first()
if user:
# 登陆成功,生成一个随机字符串
token=uuid.uuid4()
# 存到UserToken表中
# models.UserToken.objects.create(token=token,user=user)# 用它每次登陆都会记录一条,不好,如有有记录
# update_or_create有就更新,没有就新增
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(defaults={'token':token},user=user)
return Response({'status':100,'msg':'登陆成功','token':token})
else:
return Response({'status': 101, 'msg': '用户名或密码错误'})
# urls.py
from django.urls import path, re_path
from app06_auth import views
from rest_framework import routers
router = routers.SimpleRouter()
# router.register('books/', views.BookModelViewSet)
router.register('books', views.BookModelViewSet) # 不用加后缀
urlpatterns = [
path('login/', views.LoginView.as_view()),
]
urlpatterns += router.urls
2.4.1 全局配置 - settings
from rest_framework import settings
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
# 自定义认证类
'app06_auth.utils.app_auth.MyAuthentication',
# 默认认证类
# 'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
# 'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication',
],
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
# 自定义权限类
'app06_auth.utils.app_permission.MyPermission'
# 默认权限类
# 'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny',
# 是否登录
# 'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated',
# 是否 为管理员
# 'rest_framework.permissions.IsAdminUser',
],
}
2.4.2 局部配置 - 视图类
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from app05_api.models import Book
from app05_api.ser import BookModelSerializer
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated,IsAdminUser
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication
from app06_auth.utils.app_auth import MyAuthentication
from app06_auth.utils.app_permission import MyPermission
class BookModelViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
# authentication_classes =[SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication] # 局部配置
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication]
# permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated,IsAdminUser] # 局部配置
permission_classes = [MyPermission]
三、限流(频率)Throttling
介绍:
用来限制用户的访问频率
两个参数:
AnonRateThrottle 游客 - 未登录
UserRateThrottle 用户 - 登录
1. 内置限流
1.1 全局使用 - settings
这里添加了默认认证类 和权限 不在settings中配置就会用默认的
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# Authentication
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
# 默认认证类
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
],
# Permission
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
# 是否登录
# 'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated',
],
# Throttling
# 配置角色
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': [
# 未登录 - 游客
'rest_framework.throttling.AnonRateThrottle',
# 登录 - 用户
'rest_framework.throttling.UserRateThrottle',
],
# 设置频率
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'user': '10/m',
'anon': '3/m',
},
}
1.2 局部使用 - 视图类
注意:无论全局还是局部,都要在settings中设置频率
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from app05_api.models import Book
from app05_api.ser import BookModelSerializer
from rest_framework.throttling import AnonRateThrottle,UserRateThrottle
# Create your views here.
class BookModelViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
# 认证
# authentication_classes =[SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication] # 局部配置
# authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication]
# 权限
# permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated,IsAdminUser]
# permission_classes = [MyPermission]
# 限流
# AnonRateThrottle 未登录
# UserRateThrottle 登录
throttle_classes = [AnonRateThrottle,UserRateThrottle]
2.自定义限流(频率)
2.1源码分析
# SimpleRateThrottle源码分析
def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None):
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
try:
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope] # scope:'user' => '3/min'
except KeyError:
msg = "No default throttle rate set for '%s' scope" % self.scope
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
def parse_rate(self, rate):
"""
Given the request rate string, return a two tuple of:
<allowed number of requests>, <period of time in seconds>
"""
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
#3 mmmmm
num, period = rate.split('/') # rate:'3/min'
num_requests = int(num)
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
return (num_requests, duration)
def allow_request(self, request, view):
if self.rate is None:
return True
#当前登录用户的ip地址
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view) # key:'throttle_user_1'
if self.key is None:
return True
# 初次访问缓存为空,self.history为[],是存放时间的列表
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
# 获取一下当前时间,存放到 self.now
self.now = self.timer()
# Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
# 当前访问与第一次访问时间间隔如果大于60s,第一次记录清除,不再算作一次计数
# 10 20 30 40
# self.history:[10:23,10:55]
# now:10:56
while self.history and self.now - self.history[-1] >= self.duration:
self.history.pop()
# history的长度与限制次数3进行比较
# history 长度第一次访问0,第二次访问1,第三次访问2,第四次访问3失败
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
# 直接返回False,代表频率限制了
return self.throttle_failure()
# history的长度未达到限制次数3,代表可以访问
# 将当前时间插入到history列表的开头,将history列表作为数据存到缓存中,key是throttle_user_1,过期时间60s
return self.throttle_success()
2.2 如何查找限流类
# 1.找到这个 然后点 SimpleRateThrottle - 其实这个已经够用了
from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle
# 2.看到这个 然后点 BaseThrottle
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
# 3.重写 allow_request 方法
class BaseThrottle:
def allow_request(self, request, view):
raise NotImplementedError('.allow_request() must be overridden')
def wait(self):
return None
2.3 编写自定义限流
(1)根据IP限流 - 难度版
import time
# 其实这个没必要自己去写,逻辑还没有别人写的好呢
class MyThrottle():
scope = 'test' # 设置这个后,需要与频率对应好
#定义成类属性,所有对象用的都是这个
VISIT_DIC = {}
def __init__(self):
self.history_list=[]
def allow_request(self, request, view):
'''
#(1)取出访问者ip
#(2)判断当前ip不在访问字典里,添加进去,并且直接返回True,表示第一次访问,在字典里,继续往下走
#(3)循环判断当前ip的列表,有值,并且当前时间减去列表的最后一个时间大于60s,把这种数据pop掉,这样列表中只有60s以内的访问时间,
#(4)判断,当列表小于3,说明一分钟以内访问不足三次,把当前时间插入到列表第一个位置,返回True,顺利通过
#(5)当大于等于3,说明一分钟内访问超过三次,返回False验证失败
'''
ip=request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
ctime=time.time()
if ip not in self.VISIT_DIC:
self.VISIT_DIC[ip]=[ctime,]
return True
self.history_list=self.VISIT_DIC[ip] #当前访问者时间列表拿出来
while True:
if ctime-self.history_list[-1]>60:
self.history_list.pop() # 把最后一个移除
else:
break
if len(self.history_list)<3:
self.history_list.insert(0,ctime)
return True
else:
return False
def wait(self):
# 当前时间,减去列表中最后一个时间
ctime=time.time()
return 60-(ctime-self.history_list[-1])
(2) 任意指标限流 - 简单版
from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle
class MyThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'sms'
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
telephone = request.query_params.get('telephone')
#'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'%{}
return self.cache_format%{'scope':self.scope,'ident':telephone}
2.4 自定义限流类配置
2.4.1 全局配置 - settings
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# Throttling
# 配置角色
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': [
# 自定义角色 - ip 限流
'app06_auth.utils.app_throttling.MyThrottle',
# 默认角色
# 未登录 - 游客
# 'rest_framework.throttling.AnonRateThrottle',
# 登录 - 用户
# 'rest_framework.throttling.UserRateThrottle',
],
# 设置频率
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
# 'user': '10/m',
# 'anon': '3/m',
'test':'3/m', # 自定义限流类 scope='test'
},
}
2.4.2 局部配置 - 视图类
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from app05_api.models import Book
from app05_api.ser import BookModelSerializer
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated,IsAdminUser
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication
from app06_auth.utils.app_auth import MyAuthentication
from app06_auth.utils.app_permission import MyPermission
from app06_auth.utils.app_throttling import MyThrottle
class BookModelViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
# authentication_classes =[SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication] # 局部配置
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication]
# permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated,IsAdminUser] # 局部配置
permission_classes = [MyPermission]
# 限流
# throttle_classes = [AnonRateThrottle,UserRateThrottle]
throttle_classes = [MyThrottle]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号