数据结构期末 树
树
基本概念
1.最多一个先驱 但可能有多个后继 表示具有层次的分支关系
2.Siblings(兄弟): nodes share the same parent
Degree(树的扇出) of a tree: the maximum number of its node.
3.深度为最大层数
第i层最多2^i个结点
4.完全二叉树:满二叉树去掉最下面一层最右边若干节点
完全二叉树深度 log2(n)向下取整
第i个结点 左孩子2i+1 右孩子2i+2
父结点(i-1)/2
5.preorder(TreeNode * root){
if(root!=NULL){
cout<<root->val<<endl;
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);}
inorder(TreeNode * root){
if(root!=NULL){
inorder(root->left);
cout<<root->value<<endl;
inorder(root->right);}
postorder
6.完全二叉树的数组存储
孩子与父亲节点的关系父亲i 左孩子2i+1 右孩子2i+2
7.完全二叉树插入、删除(3种情况)、查找、利用二叉查找树排序
插入
在二叉树末尾插入 只需要知道二叉树父节点的信息 即父节点的指针
当前插入节点temp=size();
判断是左节点还是右节点;将信息入栈
求出父节点的索引;
判断父节点是否为根节点,若不是重复上述操作;
查找到根节点后栈内保存从根节点到插入节点的信息,获取父节点指针;
将当前信息插入树中;
二叉搜索树
tree search
递归 TreeNode *search_for_node(TreeNode * root,int &target){ if(root==NULL||root->val==target) return root; else if(target>root->val) return search_for_node(root->right,target); else return search_for_node(root->left,target); } 非递归 TreeNode *search_for_node(TreeNode * root,int &target){ while(root!=NULL&&root->val!=target) { if(root->val>target) root=root->right; else root=root->left;} return root;} template <class Record> Error_code Search_tree<Record> :: tree_search(Record &target) const { Error_code result = success; Binary_node<Record> *found = search_for_node(root, target); if (found == NULL) result = not_present; else target = found->data; return result; }
二叉查找树insert
template <class Record> Error_code Search_tree<Record> :: insert( const Record &new_data) {//插入成功返回 success //插入失败返回 duplicate_error Error_code result=search_and_insert(root, new_data); if(result==success)count++; return result; } template <class Record> Error_code Search_tree<Record> :: search_and_insert( Binary_node<Record> * &sub_root , const Record &new_data) {if(sub_root==NULL) {sub_root=new Binary_node<Record>(new_data) ; return success;} else if(new_data>sub_root->val) return search_and_insert(sub_root->right,new_data); else if(new_data<sub_root->val) return search_and_insert(sub_root->left,new_data); else return duplicate_error;}
二叉查找树中序遍历即为有序序列
适用于无序序列 对基本有序序列排序效率较低 (较不平衡
二叉查找树的删除
1)删除节点为叶子节点 左右子树均为空
2)删除节点左右子树有一个非空 子树根节点与删除节点的父亲相连
3)删除节点左右子树均非空
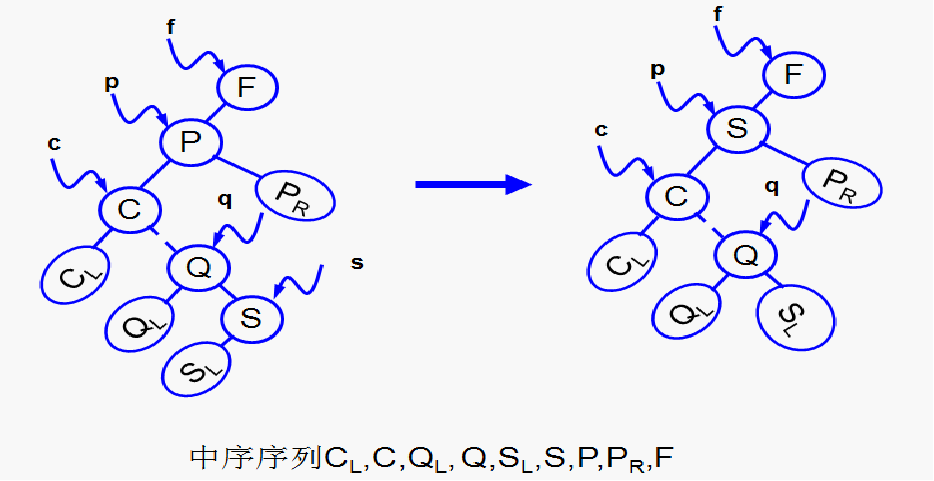
找到被删除节点中序遍历的前驱 用前驱代替被删除点
template <class Record> Error_code Search_tree<Record> :: remove(const Record &target) /* Post: If a Record with a key matching that of target belongs to the Search tree a code of success is returned and the corresponding node is removed from the tree. Otherwise, a code of not present is returned. Uses: Function search_and_destroy */ { Error_code result=search_and_destroy(root, target); if(result==success)count--; return result; } Error_code Search_tree<Record> :: search_and_destroy( Binary_node<Record>* &sub_root, const Record &target) {if(sub_root==NULL||sub_root->val==target) return remove_root(sub_root); else if(sub_root->val>target) return search_and_destroy(root->right); return search_and_destroy(root->left);} template <class Record> Error_code Search_tree<Record> :: remove_root(Binary_node<Record> * &sub_root) {if(sub_root==NULL) return not_present; Binary_node<Record> *to_delete=sub_root; else if(sub_root->right!=NULL) sub_root=sub_root->right); else if(sub_root->left!=NULL) sub_root=sub_root->left; else{
to_delete=sub_root->left;
Binary_node<Record> * parent=sub_root;
while(to_delete->right!=NULL){
parent=to_delete;
to_delete=to_delete->right;}
if(parent==sub_root)sub_root->left=to_delete->left;
else parent->right=to_delete->left;}
delete to_delete; // Remove to_delete from tree.
return success; }
8.堆
1)完全二叉树的存储 用数组存
2)堆和完全二叉树对应
3)堆的定义 大顶堆 父亲比孩子大的完全二叉树
4)堆的调整 先决条件 左右孩子都是堆
固定操作 取max 调整堆
5)Build-Heap(A) for i from n/2 downto 1 do Heapify(A, i)
从第一个非叶子节点开始从后往前依次进行对调整
6)堆排序 空间复杂度O(1) 因为将堆顶取出 将取出的数放到数组尾部 从后往前 堆不断变小 从第一个非叶子节点从后往前一次调整成堆 通过调整操作建成堆
第一步 构造初始堆 将给定无序序列构造成大顶堆(一般降序用小顶堆 升序用大顶堆)
第二步 将堆顶元素与末尾元素交换 使数组末尾元素最大
然后调整堆 再将堆顶元素和末尾元素交换 如此反复操作
思路总结
a.将无需序列构建成一个堆,根据升序降序需求选择大顶堆或小顶堆;
b.将堆顶元素与末尾元素交换,将最大元素"沉"到数组末端;
c.重新调整结构,使其满足堆定义,然后继续交换堆顶元素与当前末尾元素,反复执行调整+交换步骤,直到整个序列有序。
时间复杂度 O(nlogn)
它的最坏,最好,平均时间复杂度均为O(nlogn)
7)结合完全二叉树存储 堆排序在数组中怎么变
8)Topk算法 //往堆上想
若要时刻输出最大的K个数 维护一个小顶堆 每次弹出堆中最小的元素 保证堆内元素是最大的K 个
时间复杂度O(klogk)
9.AVL树
如何判断是否是一颗AVL树
先判断该树中序遍历后是否有序
在判断是否平衡
10.Trie树
Tries 应用 字符串匹配的相关算法, 如前缀匹配-type ahead
11.树上基本的递归操作 节点的存储
https://juejin.im/post/5b3b55c2e51d45195d7d8c20
最大深度
int depth(TreeNode * root) { if(root==NULL)return 0; return 1+max(depth(root->left),depth(root->right));}
111二叉树的最小深度
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL)return 0; if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)return 1; if(root->left==NULL&&root->right!=NULL)return minDepth(root->right)+1; if(root->right==NULL&&root->left!=NULL)return minDepth(root->left)+1; return min(minDepth(root->left),minDepth(root->right))+1; }
226翻转二叉树
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL)return NULL; swap(root->left,root->right); invertTree(root->left); invertTree(root->right); return root; }
110平衡二叉树
bool isBalanced(TreeNode * root){ if(root==NULL)return true; if(abs(depth(root->left)-depth(root->right))>1) return false; return isBalanced(root->left)&&isBalanced(root->right);}
100相同的树
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)return true; if(p==NULL&&q!=NULL)return false; if(p!=NULL&&q==NULL)return false; if(p->val!=q->val)return false; return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right); }
101对称二叉树
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL)return true; return ismirror(root->left,root->right); } bool ismirror(TreeNode * p,TreeNode * q) { if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)return true; if(p!=NULL&&q==NULL)return false; if(p==NULL&&q!=NULL)return false; if(p->val!=q->val)return false; return ismirror(p->left,q->right)&&ismirror(p->right,q->left); }
222完全二叉树结点个数
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL)return 0; return countNodes(root->left)+countNodes(root->right)+1; }
112路径总和
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { if(root==NULL)return false; if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)return root->val==sum; return hasPathSum(root->left,sum-root->val)||hasPathSum(root->right,sum-root->val); }
257二叉树的所有路径
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL)return res; binary(root,res,""); return res; } void binary(TreeNode * root,vector<string>&res,string path) { if(root==NULL)return; path+=to_string(root->val); if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL) res.push_back(path); if(root->left!=NULL)binary(root->left,res,path+"->"); if(root->right!=NULL)binary(root->right,res,path+"->"); }
129求根到叶子节点数之和
int result=0; int temp=0; int sumNumbers(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root); return result; } void dfs(TreeNode * root) { if(root==NULL)return ; temp=10*temp+root->val; if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL) result+=temp; if(root->left) {dfs(root->left); temp/=10; } if(root->right) {dfs(root->right); temp/=10; } }
437路径总和3
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { if(root==NULL)return 0; return path(root,sum)+pathSum(root->left,sum)+pathSum(root->right,sum); } int path(TreeNode * root,int sum) { if(root==NULL)return 0; return (root->val==sum)+path(root->left,sum-root->val)+path(root->right,sum-root->val); }
二叉树最大路径和
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL)return 0; int result=-1000; maxPath(root,result); return result; } int maxPath(TreeNode * root,int &val) { if(root==NULL)return 0; int left=max(0,maxPath(root->left,val)); int right=max(0,maxPath(root->right,val)); int ret=root->val+max(left,right); int lar=root->val+left+right; val=max(val,max(lar,ret)); return ret; }
113路径总和2
vector<vector<int>>result; vector<int>path; vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { if(root==NULL)return result; hasPath(root,sum,result,path); return result; } void hasPath(TreeNode * root,int sum,vector<vector<int>>&result,vector<int>&path) {path.push_back(root->val); if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL&&root->val==sum) {result.push_back(path); return;} if(root->left!=NULL) { hasPath(root->left,sum-root->val,result,path); path.pop_back(); } if(root->right!=NULL) { hasPath(root->right,sum-root->val,result,path); path.pop_back(); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号