Oracle Day5
本节内容
1.数据库中常用的函数
2.分组查询
3.过滤查询
4.伪列 rownum ,rowid,分组排序函数 row_number() over()
5.set操作符
6.多表联接查询
7.子查询
一、数据库常用函数
函数:通过给定参数输出结果。
数据库中的函数分类:
单行函数:一条数据返回一个结果。
数值函数:关于数值的一些操作。
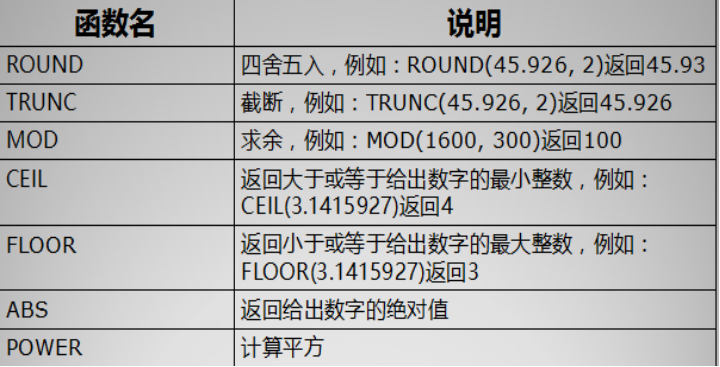
--数值函数的操作 --四舍五入 round(数值,保留的小数点位数) select round(45.965,2) from dual; --截断 保留几位小数,直接截断不进行四舍五入 select trunc(45.965,2) from dual; --求余数 select mod(16,5) from dual; --向上取整 只要小数点后有1-9就会向上取整 select ceil(3.01) from dual; --整数不管向上还是向下取整都是整数本身 --向下取整:不管小数点后是多少数值都会向下取整 select floor(3.99999) from dual --绝对值 select abs(-10) from dual; --求次方 power(数值,次方数); select power(2,4) from dual;
字符函数:关于字符的一些操作


--字符函数的操作
--大小写转换
--大写转小写
select lower('Drango Wal') from dual;
--小写转大写
select upper('Drango Wal') from dual;
--首字母转大写,其余转小写
select initcap('Drango wal') from dual;
--字符联接: 只能2个字符联接,可以嵌套使用
select concat('Drango','Wal') from dual;
select concat('Drango',concat('Wal','欢迎学习Oracle')) from dual;
--字符串截取 :从开始截到最后
select substr('Drango War',2) from dual;
--从2开始截取共截取5位
select substr('Drango War',2,5)from dual;
--字符串长度
select length('Drango War') from dual;
--查找字符串在字符串中的下标位置:存在返回下标,不存在返回0
select instr('Drango War','an')from dual;
--使用字符补齐字符串的位数
--左补齐
select lpad('Drango War',20,'*') from dual;
--右补齐
select rpad('Drango War',20,'*') from dual;
--去掉字符:去掉2端的字符
select trim('D'from 'Drango WarD') from dual;
--去掉右边的
select rtrim('Drango WarD' , 'D') from dual;
--去掉左边的
select ltrim('Drango WarD' , 'D') from dual;
运行结果:
drango wal
DRANGO WAL
Drango Wal
DrangoWal
DrangoWal欢迎学习Oracle
rango War
rango
10
3
**********Drango War
Drango War**********
rango War
Drango War
rango WarD
日期函数:关于日期的一些操作
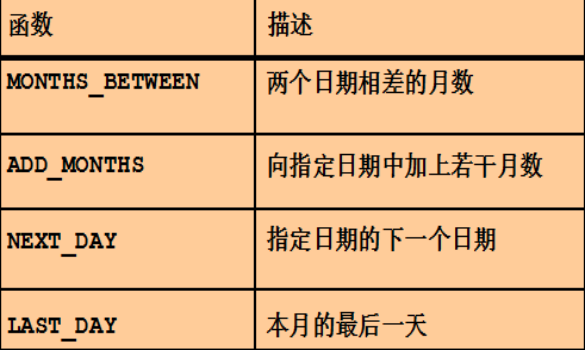
--日期函数的操作
--2个日期相差的月份数:不是整月数,就会产生小数
select months_between(sysdate,to_date('2017/10-13','yyyy/mm/dd')) from dual
--向月份上加上月份数
select add_months(sysdate,3) from dual;
--指定日期的下一个星期几是那一天
select next_day(sysdate,7) from dual;
--返回本月的最后一天
select last_day(sysdate) from dual
运算结果:
10
2018/11/13 15:25:15
2018/8/18 15:25:26
2018/8/31 15:25:35
转换函数:字符、数值、日期之间的转换

--转换函数
--字符串与数值可以直接转换
select '10'+20 from dual
--数值与字符转可以直接转
select concat(10,'20')from dual;
--字符串转日期
select to_date('2018-8-13','yyyy-mm-dd') from dual
--字符转数值
select to_number('10000.00','99999.99')from dual
--日期转字符
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd') from dual;
函数可以嵌套使用:函数的执行是由内到外执行。
通用函数: nvl 逻辑判断函数
nvl(参数1,参数2);
第一个参数为空那么显示第二个参数的值,如果第一个参数的值不为空,则显示第一个参数本来 的值
select nvl('',sysdate) from dual;
decode函数:
逻辑判断函数
select salary, decode(employees.employee_id,
101 ,salary*0.5,
130,salary*10,
salary) from employees
使用decode自定义排序:
select salary, decode(employees.employee_id,
101 ,salary*0.5,
130,salary*10,
salary) from employees
多行函数(组函数):多条数据返回一个结果。
avg 平均值 count 统计 max最大值 min 最小值 sum求和
select avg(salary) from employees select max(salary),min(salary) from employees select sum(salary) from employees --count() * 不会忽略空值 字段:会忽略空值 select count(*) from employees; 108 select count(employees.commission_pct) from employees 35
在查询中 where之后不能使用组函数。
二、分组查询
使用的关键词: group by
使用 group by 出现在where之后,如果没有where 条件,则直接出现在表名之后 。
使用group by注意:
在SELECT 列表中所有未包含在组函数中的列都应该包含在 GROUP BY 子句中。
包含在 GROUP BY 子句中的列不必包含在SELECT 列表中
group by后不能使用组函数,可以出现单行函数。
--分组查询 --分组查询员工表中有多少个部门 select department_id from employees group by department_id --查询每个部门的平均工资 select department_id,avg(salary) from employees group by department_id; --分组查询每个部门的员工的姓名: select last_name from employees group by department_id,last_name;
三、过滤查询
过滤查询关键词:having
注意:
使用having过滤查询,过滤指:是在分组查询的基础上进行过滤,有分组查询,才能有过滤查询
使用having查询语句必须有group by ,使用group by 不一定有having出现,
having后跟的是过滤条件:可以出现组函数。
--过滤查询 --查询各部门人数超过4人的部门,按照部门升序排序 select department_id,count(department_id) from employees group by department_id having count(department_id)>4 order by department_id --按照职位分组,工资大于10000的职位显示 select job_id,salary from employees group by job_id,salary having salary>10000 order by salary desc
四、伪列、分组统计函数
伪列:就像表中的一个列一样,每个表创建号之后就存在了,只不过不显示,我们使用时需要手动显示出来。 例如:rownum、以及rowid
rownum : 行号,他会随着数据显示的位置而改变。从1开始的
rowid:每一条数据的唯一标识,数据添加后系统会产生一个rowid,永久性的不会改变。
例如我现在要查询前10条员工信息
select rownum,employees.* from employees where rownum<10
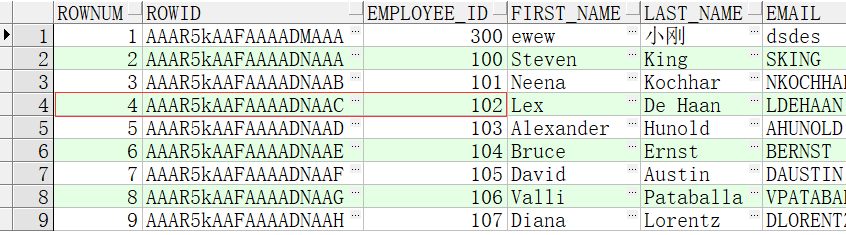
现在我单独查询102号员工
select rownum,rowid,employees.* from employees where employee_id=102
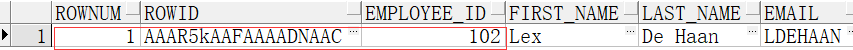
你会发现:rownum在随着查询数据显示的位置而发生改变,但是rowid不会改变。
伪列我们会在我们讲解Orcale分页的时侯来讲解,他的使用..........
分组排序函数:
select employees.*,row_number() over(partition by department_id order by salary
desc) from employees
这样就可以看到每一组的排序。
五、set操作符
set操作符:并集 交集 差集
并集: UNION / UNION ALL 取并集
UNION 会去掉重复元素
UNION ALL 不会去掉重复元素
交集:INTERSECT
差集: MINUS
--员工表与部门表部门编号的并集 select department_id from employees union --去重 select department_id from departments select department_id from employees union all --不去重 select department_id from departments --交集 select department_id from employees INTERSECT --不去重 select department_id from departments
六、多表联接查询
我们前面学习的都是单表查询,今天我们学习多表查询,也就是多张表关联查询:主要在与找主外键关系
笛卡儿积
select employees.*,departments.* from employees inner join departments on 1=1;
关联条件无效
select employees.*,departments.* from employees,departments ;
没有关联条件
这种情况就会出现笛卡尔积,数据会全部交叉。
避免笛卡儿积就需要关联查询的条件。
等值联接查询
使用“=”来进行左关联条件的操作符
select employees.*,departments.* from employees,departments ; 等值关联查询 select employees.*,departments.* from employees inner join departments on employees.department_id=departments.department_id;
--查询 90号部门的员工以及部门信息 select employees.*,departments.* from employees,departments where departments.department_id=employees.department_id and employees.department_id=90;
不等值联接查询(了解)
select e.last_name,e.salary,j.job_id,j.job_title,j.min_salary,j.max_salary from employees e,jobs j where e.salary between j.min_salary and j.max_salary order by e.last_name
外连接查询:
主要是为了找到不符合条件的数据
左外联查询
--查询的是员工信息,不管员工有没有部门,都展示出来 select e.employee_id,e.department_id,d.department_name from employees e,departments d where e.department_id = d.department_id(+)
右外联查询
--查询的是部门信息,不管部门有没有员工,都展示出来 select e.employee_id,e.department_id,d.department_name from employees e,departments d where e.department_id(+) = d.department_id
自联接查询
--自连接(难点) --from后面写2个相同的表,需要同别名区别开 select worker.employee_id,worker.first_name,manager.employee_id,manager.last_name from employees worker,employees manager where worker.manager_id = manager.employee_id order by worker.employee_id
注意:在多表联接查询中:关联查询的条件个数不能少于 表数-1个,只能多不能少。
七、子查询
子查询:就是在一个查询中嵌套另一个查询。也即通过SELECT语句的嵌套使用形成子查询。当我们不知道特定的查询条件时,可以用子查询来为父查询提供查询条件以获得查询结果
常见的子查询: 单列子查询 :单列单行子查询、单列多行子查询、
多列子查询
在书写子查询时需要注意:
子查询必须放在括号内
子查询也必须放在比较操作符号的右边
子查询最多可以嵌套到255级
子查询中不能使用ORDER BY子句,即ORDER BY必须位于查询的最外层
子查询的运行原理: 先执行子查询,后执行父查询。(由内向外执行)
单列单行子查询:
行子查询并不是最后输出的结果只能返回一行,而是指子查询只能返回一行
当我们用“等于”比较操作符把子查询和父查询嵌套在一起时,父查询期望从子查询那里只得到一行返回值。
单行子查询:子查询只能返回一行数据,否则会出错。
单行操作符:= 、> 、< 、>= 、<= 、 <>
--子查询 --单行子查询 --查询比Abel工资高的员工信息 select * from employees where salary> (select salary from employees where last_name='Abel')
注意:如果子查询没有结果,那么整个查询都不会有结果。
--每个部门哪些员工工资比本部门平均工资高,同时显示员工工资,和
--部门平均工资
--子查询出现在from子句后,相当于一张虚拟的表
select e.employee_id,e.last_name,e.salary,e.department_id,avgsal.sal
from employees e,(select department_id,avg(salary) sal
from employees
group by department_id) avgsal
where e.department_id = avgsal.department_id
and e.salary > avgsal.sal
order by e.department_id
--子查询可以出现在select后面,相当于一个列
select employee_id,last_name,salary,(select avg(salary) from employees) sal
from employees
where salary > (select avg(salary)
from employees)
多行子查询:
子查询返回多行数据
多行操作符:in any all

--2.多行子查询
select employee_id,salary
from employees
where salary <any(
select salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG')
and job_id<>'IT_PROG'
select employee_id,salary
from employees
where salary >any(
select salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG')
and job_id<>'IT_PROG'
select employee_id,salary
from employees
where salary in(
select salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG')
and job_id<>'IT_PROG'
select employee_id,salary
from employees
where salary >all(
select salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG')
and job_id<>'IT_PROG'
select employee_id,salary
from employees
where salary <all(
select salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG')
and job_id<>'IT_PROG'
--2.选择工资大于所有JOB_ID = 'SA_MAN'的员工的
--工资的员工的last_name, job_id, salary
select last_name, job_id, salary
from employees
where salary>all(
select salary
from employees
where JOB_ID = 'SA_MAN')
使用多行子查询时:不能使用单行子查询操作符。单行子查询可以使用多行子查询操作符,但是子查询只能返回一行数据。
多列子查询:子查询返回多个列
在使用多列子查询时必须注意:
主查询中,必须把WHERE子句中需要的多个列用括号括起来,否则发生错误
主查询WHERE子句中的列与子查询中返回的列必须匹配
--多列子查询 --查询与150号员工工资相同,部门相同的员工 select * from employees where (salary,department_id)= (select salary,department_id from employees where employee_id=150) and employee_id<>150;
Oracle中的分页查询:
Oracle中分页查询使用子查询来完成。借助伪列 rownum。
就是从查询中截取出我们需要的每页的数据
select * from (select rownum rn,employees.* from employees where rownum<=20) where rn>10 10每页开始的下标 20每页结束的下标



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号