Java 关键字
目录
assert
断言,用来进行程序调试
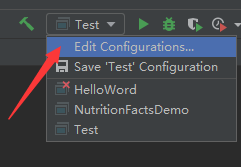
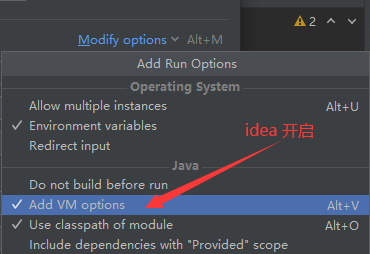
找到 VM options 输入-ea
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
// false时会报异常 java.lang.AssertionError: 结果不正确
assert 11+10 == 20:"结果不正确";
}
}
我没用到过
基本类型
byte、short、int、long、float、double、char、boolean
作用域
| 关键字 | 当前类 | 同一包 | 子类 | 其他包 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| private | √ | × | × | × |
| default | √ | √ | × | × |
| protected | √ | √ | √ | × |
| public | √ | √ | √ | √ |
private:表明该方法或者变量只有当前类才可以进行访问
default:表明只有同一类,或者同一包中的类有访问权限,(默认为不写,在作用范围如此,同一包下的子类可以访问,其他包下的都不能访问)
protected:表明该变量或者变量不能被其他包中的类或者对象调用,子类具有访问父类的权限,(不同包中的子类可以访问)
public: 表明该方法或者变量对所以得类是可见的,所有的类或者对象都可以进行访问。
if和else
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//生成一个随机数给n
int n = (int) (Math.random()*10);
//if 判断 ()中表达式结果运算要么为true,要么为false
if (i == 1){
System.out.println("n==1");
}else if (i == 2){//i!=1时,再判断i 等不等于 2
System.out.println("n==2");
}else {//前面if、else if都不成立,执行else(只有一个)
System.out.println("n== 其他");
}
}
}
switch和case
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//生成一个随机数给n
int n = (int) (Math.random()*3);
switch (n){
case 1:
System.out.println("n等于1打印此语句");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("n等于2打印此语句");
break;
default:
System.out.println("n不满足上面要求时打印此语句");
}
}
}
default:默认,例如,用在switch语句中,表明一个默认的分支(即case所有条件不成立)
try、catch和finally
异常处理
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//ArithmeticException: / by zero 除数不能为0
int i = 10/0;
}catch (Exception e){
//catch 中进行语句处理
System.out.println(e);
}finally {
//finally里的语句一定会执行(除开程序终止)
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}
continue和break
continue:跳过
break:结束
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//for循环打印0~9
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i == 3){
//i等于3时跳过,不执行for此后面的代码
continue;
}else if (i == 8){
//i等于8时,结束for循环,不会打印9
break;
}
//打印i
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
do、while和for(循环)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
//do{执行语句}while(布尔表达式);
do {
//执行语句
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}while(i<10);//布尔表达式
//先执行do{}代码块中的语句,在对while中的布尔表达式判断true还是false
//while(布尔表达式){执行语句};
while(i<15){
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
//先判断布尔表达式结果,再执行{}代码块中的语句
//for(变量初始化; 布尔表达式; 更新){//代码语句}
for(int j = 0; j<5; j++){
System.out.println(j);
}
/* 先 j=0(变量赋值), j<5判断 , 执行语句 , j++ , j<5 , 执行语句 , j++ , j<5 , 执行语句 ......
*/
}
}
return
从成员方法中返回数据
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = method(1, 2);
System.out.println(sum);
}
private static int method(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
}
void
声明当前成员方法没有返回值
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
print("你好");
print("嘻嘻");
}
//方法
private static void print(String str) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
static
表明具有静态属性
静态的可直接调用
详解(更新中......)
class(类)
声明一个类
public class Main {
class NeiMain{
}
}
new
用来创建新实例对象
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// new 一个当前 Main类的实例对象,调用print方法
Main main = new Main();
main.print();
}
void print(){
System.out.println("方法");
}
}
enum(枚举)
//枚举类
public enum WeekDay {
//常量
SUN, MON, TUE, WED, THT, FRI, SAT
}
final
用来说明最终属性,表明一个类不能派生出子类,或者成员方法不能被覆盖,或者成员域的值不能被改变,用来定义常量
public class Main {
//sb引用不可被改变(str可以改变其内容)
static final StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("你好");
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(sb);
str.append("我变了");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
interface(接口)
public interface A{
}
extends(继承)
表明一个类型是另一个类型的子类型。对于类,可以是另一个类或者抽象类;对于接口,可以是另一个接口
public class A {
}
class FA extends A{//FA类继承A类,(抽象类也一样)
}
interface B{
}
interface FB extends B{//FB接口继承B接口
}
abstract
抽象:定义在类上表明该类是抽象类,成员方法具有抽象属性
//抽象类
public abstract class MyAbstract {
//抽象方法
abstract void method();
}
import(导包)
//import 需要导入util下的Scanner
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//此处使用Scanner控制台扫描输入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//从控制台读入一行数据赋值给str
String str = sc.nextLine();
}
}
instanceof
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
//判断该对象是A的实例化(new的对象,A的子类实例也可以)
System.out.println(b instanceof A);
}
}
class A{
}
class B extends A{
}
implements(实现)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new B();
a.eat();
}
}
interface A{
void eat();
}
class B implements A{
//实现A接口
//重写方法
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃大份的");
}
}
native
用来声明一个方法是由与计算机相关的语言(如C/C++/FORTRAN语言)实现的
java底层就有一些是调用的C++的代码
this和super
this:指向当前实例对象的引用
super:表明当前对象的父类型的引用或者父类型的构造方法
synchronized
表明一段代码需要同步执行(多个线程,只有一个能执行该段代码块)
throw和throws
throw:抛出一个异常
throws:声明在当前定义的成员方法中所有需要抛出的异常


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号