学习C#
day1
① 什么是 .NET ?
.NET 包含两部分 .NET 平台 和 .NET FrameWork 框架
.NET FrameWork 框架包含于 .NET 平台 , .NET FrameWork 框架提供环境和支撑保证 .NET 平台运行
② 什么是 C# ?
C# 是一种面向对象、运行于 .NET Framework 上的高级程序设计语言 , 而 Java 既是语言又是平台
③配置 Visual Studio 2019 Community环境
④C#的项目构造 : 解决方案
----项目文件夹
----类文件(.cs)
⑤类文件构造
//导入命名空间 , 类似 Java 中的 import using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; //命名空间 , 类似 Java 中的 package namespace day01_MyFirstDemo{ //声明类 , 跟 Java 不同的是 , C# 的类名不用跟文件名一致 class Program{ //声明方法 , 与 Java 一样 static void Main(string[] args){ Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); //把 Hello World 打印在控制台中 , 类似 Java 的 System.out.println(); Console.ReadKey(); //将用户此后第一次按下的按键 , 显示在控制台中 , 暂时用来暂停程序 , 不知道有没有别的用处 } } }
④ 启动项目
右键解决方案 → 属性 → 通用属性 → 启动项目 , 选中当前选定内容 , 然后点击正上方的  或按下 F5 启动项目
或按下 F5 启动项目
day2
① 注释
//单行注释
/*多行注释*/
///文档注释 类似 Java 的 /**
② 常用快捷键
代码格式化 Ctrl + K + D , 被我改成了 Ctrl + Alt + L
快速注释代码 Ctrl + Shift + /
快速移动光标 Shift + Home / Shift + End
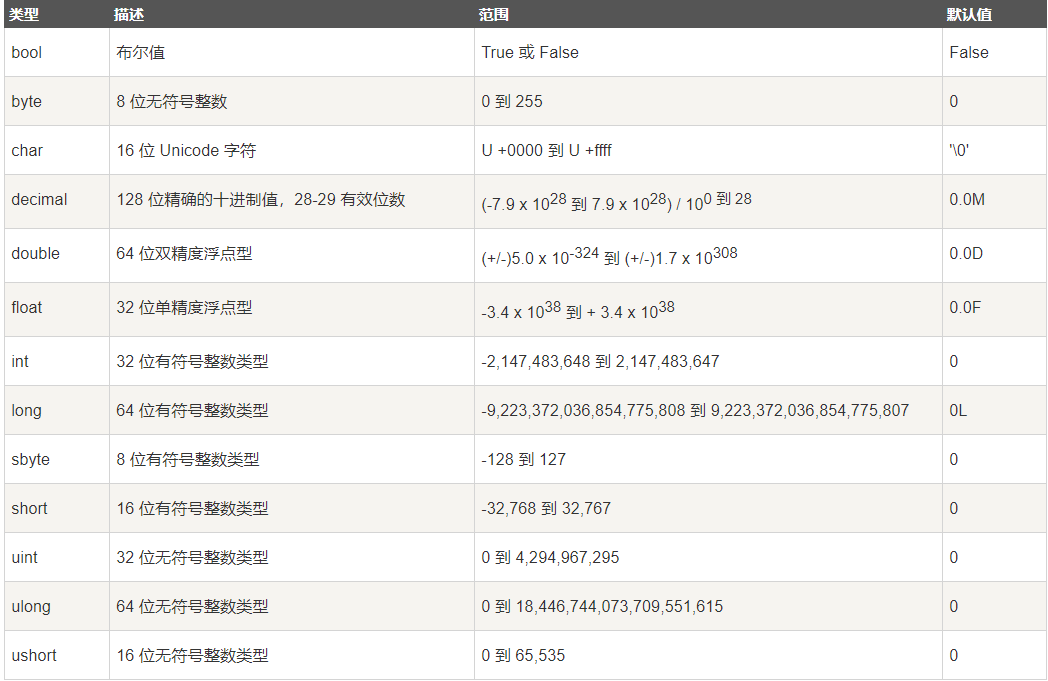
③ 基本数据类型
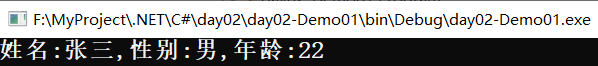
④ 使用占位符方式打印字符串
string name = "张三"; char sex = '男'; int age = 22; Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0},性别:{1},年龄:{2}",name,sex,age); Console.ReadKey();
⑤ 定义一个字符串接收用户的输入
string input = Console.ReadLine();
⑥ 转义符
" \ " + 字符 , 和 Java 用法一样
string 字符串的前面可以加 " @ " 将字符串里所有的 " \ " 当作普通字符对待 , 并且按照原格式输出 , 常用来表示路径
day3
① 结构体
struct xxx{}
和 class 类似,但是有以下不同
类是引用类型,结构是值类型
结构不支持继承
结构不能声明默认的构造函数
day4
① delegate 委托
委托是存有对某个方法的引用的一种引用类型变量。引用可在运行时被改变。
声明 :
delegate <return type> <delegate-name> <parameter list>
实例化 :
public delegate void MyDelegate(string s);
......
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(show);
触发 :
myDelegate("Hello World");
② event 事件
事件在类中声明且生成,且通过使用同一个类或其他类中的委托与事件处理程序关联。包含事件的类用于发布事件。这被称为 发布器 类。其他接受该事件的类被称为 订阅器 类。
事件使用 发布-订阅(publisher-subscriber) 模型。
发布器(publisher) 是一个包含事件和委托定义的对象。事件和委托之间的联系也定义在这个对象中。发布器(publisher)类的对象调用这个事件,并通知其他的对象。
订阅器(subscriber) 是一个接受事件并提供事件处理程序的对象。在发布器(publisher)类中的委托调用订阅器(subscriber)类中的方法(事件处理程序)。
声明 :
public event MyDelegate myEvent;
绑定 :
a.myEvent += new A.MyDelegate(show);
触发 :
TransfEvent("Hello World");
③ out 和 ref
使用 :
static void doFirst(out string msg) { msg = "信息"; } static void doSecond(ref int num) { num = 10; } static void Main(string[] args) { string msg; doFirst(out msg); int num = 0; doSecond(ref num); }
相同 : 都按地址传递参数,使用后都将改变原来参数的数值。
不同 : out 在传递参数前不需要将参数初始化 , ref 需要
④ parmas 可变参数
public void doSome(parmas int[] nums){
}
和 Java 的 int... nums 一样
day5
① 封装 , 快捷键 Alt + Enter
public class User {
private String name;
public string Name { get => name; set => name = value; }
}
......
User user = new User();
user.Name="张三";
Console.WriteLine("NAME: {0} " , user.Name);
② static class 静态类
静态类只允许有静态成员 , 不允许出现实例成员 ,并且不能被实例化
public static class{ private static int num; public static int Num{ set{num = value;} get{return num;} } }
③ ~ 析构函数
当程序结束的时候自动执行
~ ClassName() {
......
}
day6
① FileStream 文件流
//1. 读文件 FileStream fs = new FileStream(@"路径",FileMode.OpenOrCreate,FileAccess.Read); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*1024]; int num = fs.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length); //返回读取到的有效字节数 fs.Close(); //关闭流 fs.Dispose(); //释放流的资源 string bufferStr = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer,0,num); Console.WriteLine(bufferStr); */ //2. 写文件 /*string str = "这是一条测试语句"; byte[] buffer = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(str); //覆盖文本 //使用using自动关闭流和释放流的资源 using ( FileStream fs = new FileStream(@"路径", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write)) { fs.Write(buffer,0,buffer.Length); }*/ //追加文本 using ( FileStream fs = new FileStream(@"路径", FileMode.Append, FileAccess.Write) ) { fs.Position = fs.Length; fs.Write(buffer, 0, buffer.Length); } //3. 复制文件 using ( FileStream fsRead = new FileStream(@"源文件路径", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read) ) { using ( FileStream fsWrite = new FileStream(@"目标文件路径", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write) ) { byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024]; while ( true ) { int num = fsRead.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length); if ( num == 0 ) { break; } Console.WriteLine("进行复制中"); fsWrite.Write(buffer, 0, num); } } }
② Stream 流
using ( StreamReader read = new StreamReader(@"路径") ) { while ( !read.EndOfStream ) { Console.WriteLine(read.ReadLine()); } } //true追加,false覆盖,默认是false using ( StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(@"路径", true) ) { writer.WriteLine("这是一条测试语句"); }
③ virtual 虚方法
和 JAVA 不同的是 , C# 默认是不使用多态的 , 需要在父类的方法上添加 virtual 关键字 , 并且在子类的方法上添加 override 关键字才可以使用
namespace VirtualTest { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Person person = new Person(); Chinese chinese = new Chinese(); Japanese japanese = new Japanese(); Person[] persons = { person , chinese , japanese }; foreach ( var item in persons ) { item.sayHello(); } Console.ReadKey(); } } class Person { public virtual void sayHello() { Console.WriteLine("你好,我是人"); } } class Chinese:Person { public override void sayHello() { Console.WriteLine("你好,我是中国人"); } } class Japanese:Person { public override void sayHello() { Console.WriteLine("八嘎,我是傻逼"); } } }
使用 virtual 和override之前 :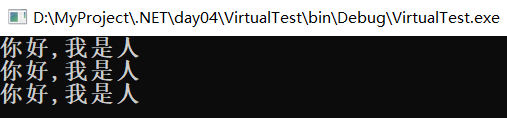
使用 virtual 和override之后 :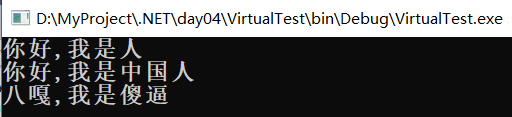
④ abstract 抽象类
子类实现抽象方法需要加上 override 关键字, 其他语法和 Java 一样
namespace AbstractTest { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Bird bird = new Bird(); Fish fish = new Fish(); Horse horse = new Horse(); Animal[] animals = { bird, fish, horse }; foreach ( var item in animals ) { item.move(); } Console.ReadKey(); } } abstract class Animal { public abstract void move(); } class Bird : Animal { public override void move() { Console.WriteLine("鸟儿在飞"); } } class Fish : Animal { public override void move() { Console.WriteLine("鱼儿在游"); } } class Horse : Animal { public override void move() { Console.WriteLine("马儿在奔跑"); } } }

⑤ 访问修饰符
和 Java 不同的是 , C# 类默认的修饰符是 internal , 属性和方法默认是 private , 并且 C# 要求子类的访问权限不能高于父类 , 重写方法的访问权限必须一致
⑥ 工厂设计模式
namespace FactoryPatternTest { public class Program { // 简单工厂的核心 : 根据用户输入把对象赋值给父类 public static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Clear(); Console.WriteLine("请输入你需要的笔记本品牌"); GetNotebook(Console.ReadLine()).sayHello(); Console.ReadKey(false); } public static Notebook GetNotebook(string name) { Notebook notebook = null; switch ( name ) { case "戴尔": notebook = new DaiEr(); break; case "联想": notebook = new LianXiang(); break; case "华硕": notebook = new HuaShuo(); break; } return notebook; } } public abstract class Notebook { public abstract void sayHello(); } public class DaiEr : Notebook { public override void sayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是戴尔,我的价格是10000"); } } public class LianXiang : Notebook { public override void sayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是联想,我的价格是8000"); } } public class HuaShuo : Notebook { public override void sayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是华硕,我的价格是99999"); } } }
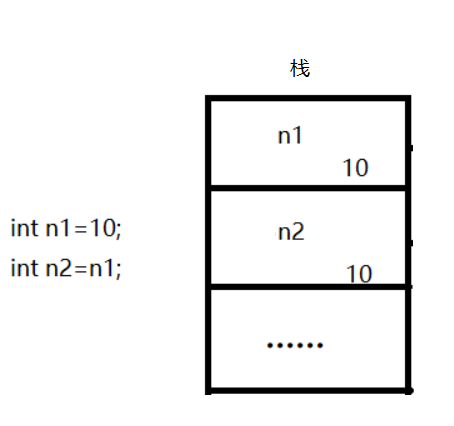
⑦ 值传递和引用传递
值传递是一种复制传递 , 传递过程中对对象的值进行修改不影响对象本身的值
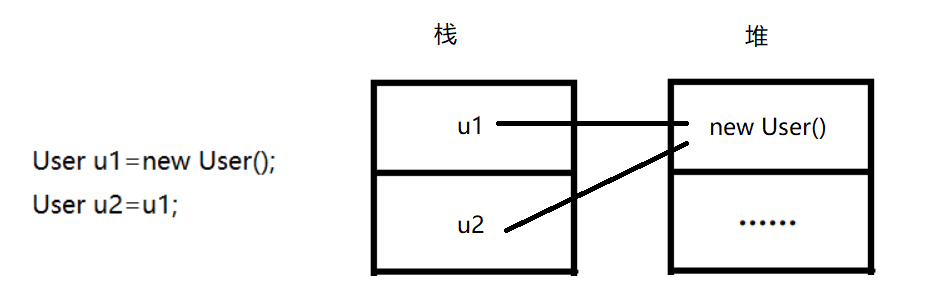
引用传递是传递的对象本身 , 传递过程中对对象的值进行修改影响对象本身的值
day7
① 序列化和反序列化
/* * 序列化 : 把对象转为二进制 * 反序列化 : 把二进制转为对象 * 作用 : 传输数据 * tips : ① 只有被[Serializable]修饰的类的对象才可以被序列化 */ namespace 序列化和反序列化 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //序列化 using ( FileStream fs = new FileStream(@"D:\test\序列化.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write) ) { BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter(); bf.Serialize(fs, new User("1", "张三", "男")); } //反序列化 using ( FileStream fs = new FileStream(@"D:\test\序列化.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read) ) { BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter(); object obj= bf.Deserialize(fs); Console.WriteLine((User)obj); } Console.WriteLine("成功"); Console.ReadKey(); } } [Serializable] class User { private string id; private string name; private string sex; public User(string id, string name, string sex) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; } public override string ToString() { return "ID:" + id + ", NAME:" + name + ", SEX:" + sex; } } }
② pertial 部分类
同一个命名空间下 , 被 pertial 修饰的类可以被允许重复 , 部分类顾名思义就是每个部分类都是类的一部分
③ sealed 密封类
被 sealed 修饰的类不能被继承
④ interface 接口类
命名规范 : public interface I...able
实现接口类 : 和继承的语法一致 , className : interfaceName
实现方法的访问权限默认是 private 并且不能被修改 , 其他和 Java 一致
⑤ 普通属性和自动属性
class A { private string name; //普通属性, 需要手动声明字段 public string Name { get => name; set => name = value; } //自动属性, 会自动生成一个私有的字段 public string Age { get; set; } }
⑥ MD5 加密
namespace MD5Test { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string psw = "123"; MD5 md5 = MD5.Create(); byte[] pswByte = Encoding.Default.GetBytes(psw); byte[] md5Byte = md5.ComputeHash(pswByte); string md5Str = ""; foreach ( byte b in md5Byte ) { md5Str+=b.ToString("x"); //转为16进制的字符串 } Console.WriteLine(md5Str); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
day8
① Process 线程类
namespace ProcessTest { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { /* * 打开计算器 */ Process.Start("calc"); } private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { /* * 打开test.tet */ ProcessStartInfo psi = new ProcessStartInfo(@"D:\test\txt\test.txt"); Process process = new Process(); process.StartInfo = psi; process.Start(); } } }
② Thread 进程类
namespace ThreadTest { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //doSome(); //不启用线程的话要等doSome()执行完毕才能关闭窗口 Thread t = new Thread(doSome); t.IsBackground = true; //设置这个进程为后台进程(等同于Java中的守护进程) t.Start(); /* t.Abort(); //终止线程 t.Start(); //报错,线程终止后不能被重新开启 */ } private void doSome() { //textBox1.Text = "button1被点击了!"; //报错,只能在主线程才能访问到Form控件 Thread.Sleep(10000); } private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { //Control.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false; //设置不捕获错误线程的调用,这样其他线程访问Form控件就不会报错 } } }
③ Socket 网络编程
/* * Socket 服务端 */ namespace SocketTest1 { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } Socket socketSend; List<Socket> sockets = new List<Socket>(); private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { try { //创建一个Socket对象 Socket socketListen = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); //创建一个IP和端口号对象 IPEndPoint point = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text)); //让负责监听的Socket绑定IP和端口号 socketListen.Bind(point); //设置监听队列(同一时间最大连接数) socketListen.Listen(3); showMsg("监听成功"); Thread t = new Thread(listen); t.IsBackground = true; t.Start(socketListen); } catch { showMsg("监听失败"); } //开启一个线程等待客户端连接 } private void showMsg(string msg) { textBox3.AppendText(msg + "\r\n"); } private void listen(object obj) { while ( true ) { try { Socket socketListen = obj as Socket; socketSend = socketListen.Accept(); showMsg(socketSend.RemoteEndPoint.ToString() + "连接成功"); sockets.Add(socketSend); comboBox1.Items.Add(socketSend.RemoteEndPoint.ToString()); //开启一个线程接收客户端发送的数据 Thread t = new Thread(receive); t.IsBackground = true; t.Start(socketSend); } catch { } } } //可以不用传参,因为socketSend已经是全局变量了,这里主要是演示一下怎么把有参方法用多线程启动 private void receive(object obj) { while ( true ) { try { socketSend = obj as Socket; byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024]; int r = (socketSend as Socket).Receive(buffer); if ( r == 0 ) { break; } string str = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer, 0, r); showMsg(socketSend.RemoteEndPoint.ToString() + ":" + str); } catch { showMsg("数据接收失败"); break; } } } private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { Control.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false; } private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if ( comboBox1.SelectedIndex == -1 ) { MessageBox.Show("请选择发送目标"); } else { byte[] buffer = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(textBox4.Text); List<byte> bufferList = new List<byte>(); bufferList.Add(0); bufferList.AddRange(buffer); try { sockets[comboBox1.SelectedIndex].Send(bufferList.ToArray()); showMsg("我:" + textBox4.Text); } catch { showMsg("数据发送失败"); } } } string path; private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { OpenFileDialog ofd = new OpenFileDialog(); ofd.InitialDirectory = @"D:\test"; ofd.Title = "选择你要发送的文件"; ofd.Filter = "全部文件|*.*"; ofd.ShowDialog(); path = ofd.FileName; if ( path != null && path != "" ) { textBox5.Text = path; } } private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if ( comboBox1.SelectedIndex == -1 ) { MessageBox.Show("请选择发送目标"); } else if ( path != null && path != "" ) { using ( FileStream fsRead = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read) ) { byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024]; int r = fsRead.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length); List<byte> bufferList = new List<byte>(); bufferList.Add(1); bufferList.AddRange(buffer); try { sockets[comboBox1.SelectedIndex].Send(bufferList.ToArray(), 0, r + 1, SocketFlags.None); showMsg("文件发送成功"); } catch { showMsg("文件发送失败"); } } } } private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if ( comboBox1.SelectedIndex == -1 ) { MessageBox.Show("请选择发送目标"); } else { byte[] buffer = new byte[]{ 2 }; try { sockets[comboBox1.SelectedIndex].Send(buffer); showMsg("震动发送成功"); } catch { showMsg("震动发送失败"); } } } } }
/* * Socket客户端 */ namespace SocketTest2 { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } Socket socketSend; private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { try { socketSend = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); IPAddress ip = IPAddress.Parse(textBox1.Text); IPEndPoint point = new IPEndPoint(ip, Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text)); socketSend.Connect(point); showMsg("连接成功"); } catch { showMsg("连接失败"); } //开启一个线程接收服务器发送的数据 Thread t = new Thread(receive); t.IsBackground = true; t.Start(); } void showMsg(string msg) { textBox3.AppendText(msg + "\r\n"); } private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { byte[] buffer = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(textBox4.Text); try { socketSend.Send(buffer); showMsg("我:" + textBox4.Text); } catch { showMsg("消息发送失败"); } } private void receive(object obj) { while ( true ) { byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024]; try { int r = socketSend.Receive(buffer); if ( r == 0 ) { break; } if ( buffer[0] == 0 ) { string str = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer, 1, r - 1); showMsg(socketSend.RemoteEndPoint.ToString() + ":" + str); } else if ( buffer[0] == 1 ) { SaveFileDialog sfd = new SaveFileDialog(); sfd.InitialDirectory = @"D:\test"; sfd.Title = "请选择你要保存的路径"; sfd.Filter = "所有文件|*.*"; sfd.ShowDialog(this); string path = sfd.FileName; if ( path != null && path != "" ) { using ( FileStream fsWrite = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write) ) { fsWrite.Write(buffer, 1, r - 1); showMsg("文件接收成功"); } } } else if ( buffer[0] == 2 ) { for(int i=0;i<500;i++ ) { this.Location = new Point(250, 250); this.Location = new Point(280, 280); } } } catch { showMsg("数据接收失败"); break; } } } private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { Control.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false; } } }
④ GDI+ 图形设备接口
namespace GDI_Test { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //绘制一条直线 Pen pen = new Pen(Brushes.Red); Point p1 = new Point(30, 50); Point p2 = new Point(250, 250); Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics(); g.DrawLine(pen, p1, p2); } private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e) { //在这里可以当图形被拖出屏幕时,重新绘制图形 } private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //绘制一个矩形 Pen pen = new Pen(Brushes.Red); Rectangle rec = new Rectangle(new Point(50, 50), new Size(80, 80)); Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics(); g.DrawRectangle(pen, rec); } private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //绘制一个扇形 Pen pen = new Pen(Brushes.Red); Rectangle rec = new Rectangle(new Point(50, 50), new Size(80, 80)); Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics(); g.DrawPie(pen, rec, 60, 60); } private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //绘制一个文本 Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics(); g.DrawString("文本", new Font("宋体", 20, FontStyle.Underline), Brushes.Black, new Point(200, 200)); } private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //绘制一张验证码 Random r = new Random(); Bitmap bitmap = new Bitmap(120, 40); Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(bitmap); string[] fonts = { "宋体", "微软雅黑", "黑体", "隶书", "仿宋" }; Color[] colors = { Color.Blue, Color.Black, Color.Red, Color.Green, Color.Gray }; //字 for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ ) { Point p = new Point(i * 30, r.Next(0, 10)); g.DrawString(Convert.ToString(r.Next(0, 10)), new Font(fonts[r.Next(0, 5)], 20, FontStyle.Bold), new SolidBrush(colors[r.Next(0, 5)]), p); } //线 for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) { Point p1 = new Point(r.Next(0, bitmap.Width), r.Next(0, bitmap.Height)); Point p2 = new Point(r.Next(0, bitmap.Width), r.Next(0, bitmap.Height)); g.DrawLine(new Pen(Brushes.Green), p1, p2); } //点 for ( int i = 0; i < 500; i++ ) { Point p = new Point(r.Next(0, bitmap.Width), r.Next(0, bitmap.Height)); bitmap.SetPixel(p.X, p.Y,Color.Black); } pictureBox1.Image = bitmap; } } }
day8
① 单例模式
步骤 : 将构造函数私有化 → 创建一个静态方法返回一个对象 → 创建一个单例对象
public partial class Form1 : Form { private static Form1 form1 = null; private Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } public Form1 getForm1() { if ( form1 == null ) { form1 = new Form1(); } return form1; } }
② XML
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //1.创建Xml文档对象 XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument(); //2.创建行描述信息 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> XmlDeclaration dec = doc.CreateXmlDeclaration("1.0", "utf-8", null); doc.AppendChild(dec); //3.创建根节点Books XmlElement books = doc.CreateElement("Books"); doc.AppendChild(books); //4.创建Books的子节点Book XmlElement book1 = doc.CreateElement("Book"); books.AppendChild(book1); //4.创建Book的子节点Name、Price XmlElement name1 = doc.CreateElement("Name"); name1.InnerText = "三国演义"; book1.AppendChild(name1); XmlElement price1 = doc.CreateElement("Price"); price1.InnerText = "20"; book1.AppendChild(price1); //5.保存Xml文档 doc.Save("Books.xml"); Console.WriteLine("保存成功"); Console.ReadKey(); } }
③ 泛型委托
class Program { delegate int DelMax<T>(T t1, T t2); static void Main(string[] args) { int[] nums = { 1, 564, 8741, 545, 3, 9, 444 }; int max=Max<int>(nums, compare); //string[] strs = { "abc", "defg", "hi", "jklmnopq", "r" }; //string max = Max<string>(strs, compare); Console.WriteLine(max); Console.ReadKey(); } static T Max<T>(T[] ts, DelMax<T> dm) { T max = ts[0]; for ( int i = 0; i < ts.Length; i++ ) { if ( dm(ts[i], max) > 0 ) { max = ts[i]; } } return max; } static int compare(int num1, int num2) { return num1 - num2; } static int compare(string str1,string str2) { return str1.Length - str2.Length; } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号