Spring ( 五 )Spring之数据访问与事务管理
个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有)
一、Spring之数据访问
1、Spring数据访问工程环境搭建
jdbc.properties配置文件:
applicationContext.xml配置文件:
测试代码:
2、Spring之JdbcTemplate使用
在Spring中提供了对jdbc的封装类叫JdbcTemplate。它可以很方便的帮我们执行sql语句,操作数据库。
先准备单表的数据库数据
创建一个与数据库表对应的javaBean类
3、将id=5的记录的salary字段更新为1300.00
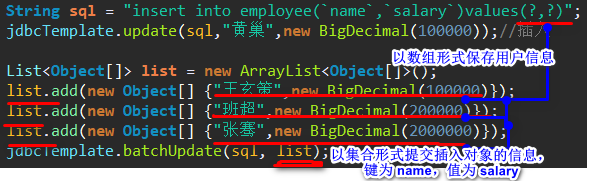
4、批量插入
分析图解:
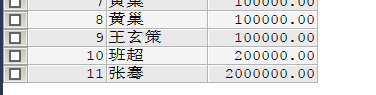
数据库结果:
5、查询id=5的数据库记录,封装为一个Java对象返回
6、查询salary>4000的数据库记录,封装为List集合返回
7、查询最大salary
8、使用带有具名参数的SQL语句插入一条员工记录,并以Map形式传入参数值
配置NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
Test中添加以下注解,用于注入xml中解析执行具名参数所用
Mysql 结果:
9、重复8,以SqlParameterSource形式传入参数值
10、创建Dao,自动装配JdbcTemplate对象
配置内容:
测试代码:
11、通过继承JdbcDaoSupport创建JdbcTemplate的Dao
源码分析方法实现与调用过程:
二、声明式事务
事务分为声明式和编程式两种:
声明式事务:声明式事务是指通过注解(和xml配置)的形式对事务的各种特性进行控制和管理。
编码式(编程式)事务:指的是通过编码的方式实现事务的声明。
1、编码方式实现事务:
2、声明式事务环境搭建
2.1、准备测试数据库
2.2、创建一个Java工程,导入Jar包
Service
3、测试Service的默认事务
【1】测试service服务层的默认事务
默认一个sql一个事务
异常的演示
Spring事务引入的分析------PlatformTransactionManager类简单介绍
4、使用Spring的注解声明事务管制
【1】测试Spring的声明式事务
TransactionService中的修改
配置文件中的内容:
5、noRollbackFor和noRollbackForClassName测试不回滚的异常
【1】noRollbackFor和noRollbackForClassName测试不回滚的异常
运行时异常回滚
编译异常:不回滚
6、自定义设置回滚异常
【1】rollbackFor和rollbackForClassName回滚的异常
7、事务的只读属性
实验4:测试readOnly只读属性
8、事务超时属性timeout(秒为单位)
10、事务的传播特性propagation
什么是事务的传播行为:
当事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,必须指定事务应该如何传播。例如:方法可能继续在现有事务中运行,也可能开启一个新事务,并在自己的事务中运行。
事务的传播行为可以由传播属性指定。Spring定义了7种类传播行为。
事务的传播特性,有以下几种类型:
11、注解演示事物传播特性
UserService
BookService
TransactionService
实验1:大小事务传播特性都是REQUIRED
实验2:大小事务传播特性都是REQUIRES_NEW
实验3:大事务是REQUIRED,小事务都是REQUIRES_NEW
实验3跟实验2一样。
实验4:大事务是REQUIRED,小1REQUIRED,小2REQUIRES_NEW
三、xml配置式事务声明
去掉。所有@Transactional的注解。
配置文件内容:
四、Spring整合Web
1、在web工程中添加Spring的jar包
- ServletContext在web工程启动的时候创建
- 在Web工程停止的时候销毁
整合Spring和Web容器分两个步骤:
1、导入spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
2、在web.xml配置文件中配置org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener监听器监听ServletContext的初始化
3、在web.xml配置文件中配置contextConfigLocation上下文参数。配置Spring配置文件的位置,以用于初始化Spring容器
在web.xml中配置
获取WebApplicationContext上下文对象的方法如下:
方法一(推荐):
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext())
方法二(不推荐):
getServletContext().getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);


























 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号