ES6-ES11新语法之ES11
类的私有属性
// # 声明私有属性,私有属性只能出现在类里面,不能出现在类外面 class Person { name // 公有属性 #age // 私有属性 #weight constructor(name, age, weight) { this.name = name this.#age = age this.#weight = weight } intro() { console.log(this.name) console.log(this.#age) console.log(this.#weight) } } const girl = new Person('小红', 20, '45kg') console.log(girl) // Person {name: "小红", #age: 20, #weight: "45kg"} console.log(girl.name) // 小红 // console.log(girl.#age) // Uncaught SyntaxError: Private field '#age' must be declared in an enclosing class girl.intro() // 小红 20 45kg
Promise.allSettled()
如果想要得到每个异步任务的运行结果,用allSettled()
如果要求每个异步任务都成功才能继续往下执行,用all()
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('商品数据-1') }, 500); }) const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('商品数据-2') // reject('失败了') // 这里的状态只控制p2的状态,不影响 allSettled() 的状态 }, 500); }) // Promise.allSettled() 接收promise组成的数组,返回成功的promise对象,得到每个promise的status const result = Promise.allSettled([p1, p2]) console.log(result) // [[PromiseState]]: "fulfilled" [[PromiseResult]]: [{status: "fulfilled", value: "商品数据-1"}, {status: "fulfilled", value: "商品数据-2"}] // 有一个失败就返回失败,都成功才会返回成功,不返回每个promise的status因为都是fulfilled const res = Promise.all([p1, p2]) console.log(res) // // [[PromiseState]]: "fulfilled" [[PromiseResult]]: ["商品数据-1", "商品数据-2"]
matchAll()
适用于做页面内容提取,方便做爬虫类项目
// matchAll() 获取正则批量匹配的结果 let str = ` <ul> <li> <a>肖生克的救赎</a> <p>2020-01-01</p> </li> <li> <a>阿甘正传</a> <p>2021-01-01</p> </li> </ul> ` const reg = /<li>.*?<a>(.*?)<\/a>.*?<p>(.*?)<\/p>/sg const result = str.matchAll(reg) console.log(result) // 返回结果是一个可迭代对象 具有next() // 1、使用for...of遍历 // for (let item of result) { // console.log(item) // } // 2、使用扩展运算符展开 const arr = [...result] console.log(arr)
可选链操作符: ?.
// 接收对象类型的参数 function main(config) { // const dbHost = config && config.db && config.db.host // 原来的做法,写法比较麻烦 const dbHost = config?.db?.host // 如果config为true,就去判断db;如果db为true,就去判断host console.log(dbHost) } main({ db: { host: '1920.168.1.100', username: 'root' } })
动态 import 加载
定义 add.js:
export function add(a, b) { return a + b }
在入口文件中导入:
import { add } from './add.js' // 静态导入,不管用不用,先导入进来,相对于动态导入效率较低
console.log(add(3, 4)) // 静态引入时调用 add.js 中的 add()
// import() 方法动态导入,返回结果是一个promise,成功的值是所导入的模块
import('./add.js').then((module) => {
console.log(module.add(3, 5))
})
BigInt:进行大整数运算
// 声明BigInt:1、在数字后加上 n 2、用 BigInt() 将数字转为大整型 console.log(100n, typeof 100n) // 100n bigint console.log(BigInt(100), typeof BigInt(100)) // 100n bigint // BigInt和Number的区别 console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(100)) // [object Number] console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(100n)) // [object BigInt] console.log(100 == 100n) // true console.log(100 === BigInt(100)) // false // 不能对小数进行大整数转换 console.log(1n) // console.log(1.3n) // 报错 // 运算结果带小数会被自动取整 console.log(4n / 2n) // 2n console.log(5n / 2n) // 2n // 一个正整数后面加上n就转换成了大整型,在数组排序中认为4n大于4,但是在逻辑上4n==4 let arr = [4, 4n, 2, 2n, -10, -10n, -1, -1n, 0, 0n] console.log(fnSort(arr)) // [-10, -10n, -1, -1n, 0, 0n, 2, 2n, 4, 4n] // BigInt和String的比较 console.log(2n) // 2n console.log(2n + '') // '2' // 使用场景:进行大数字的运算,运算完了再使用Number()转为数字 let max = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER // js中最大安全数值 console.log(max) // 9007199254740991 console.log(max.toString().length) console.log(max + 1) // 9007199254740992 console.log(max + 2) // 9007199254740992 和 + 1 没有区别 console.log(BigInt(max)) // 9007199254740991n console.log(BigInt(max) + 1n) // 9007199254740992n console.log(BigInt(max) + 2n) // 9007199254740993n // 冒泡排序 function fnSort(arr) { for (var i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { for (var j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { var temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = temp; } } } return arr; }
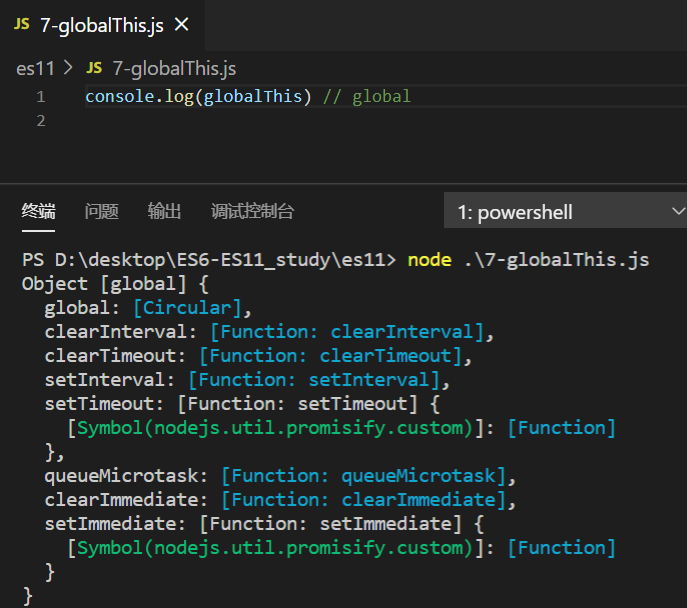
globalThis:指向全局对象
浏览器下指向window
console.log(globalThis) // Window console.log(globalThis === window) // true
nodejs(12+)下指向global
x


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号