实现ls
学习目标
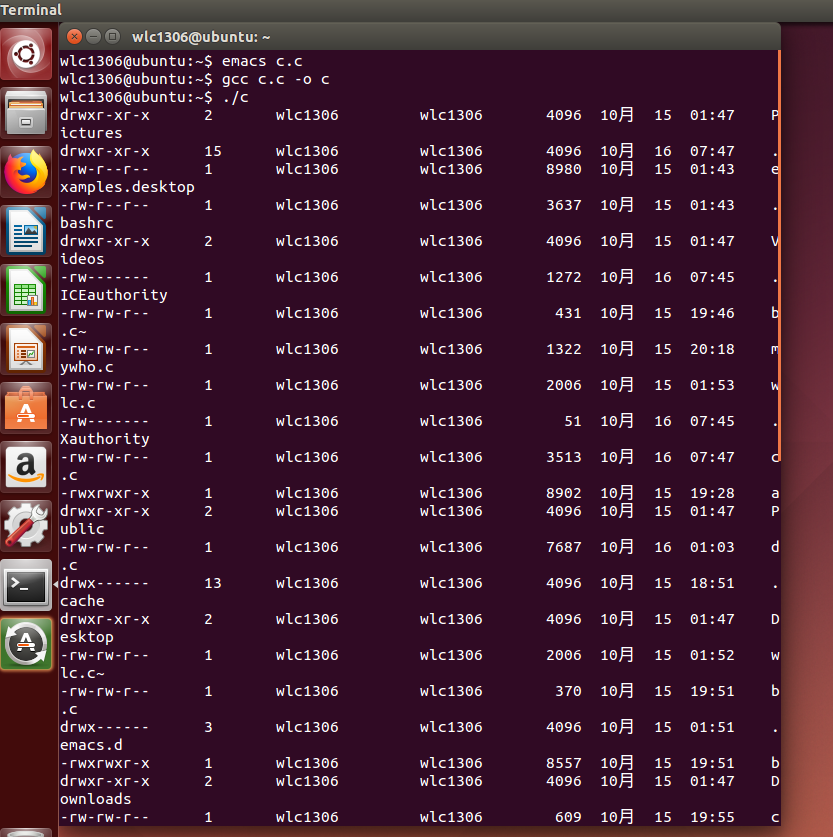
参考伪代码实现ls的功能,提交代码的编译,运行结果截图。
打开目录文件
针对目录文件
读取目录条目
显示文件名
关闭文件目录文件
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <time.h>
void do_ls( char [] );
void do_stat( char* filename );
void show_list( char* filename, struct stat* statinfo );
void mode_to_letters( mode_t filemode, char str[] );
void show_time( time_t filetime );
char* format_time( char* dsttime, const char* srctime );
//用户id转名称
char* uid_to_name( uid_t uid );
//组id转名称
char* gid_to_name( gid_t gid );
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if( argc == 1 ) {
do_ls( "." );
}else {
while( --argc ) {
printf( "arg=%s\n", * ++argv );
do_ls( *argv );
}
}
return 0;
}
void do_ls( char dir_entry[] ) {
DIR* pDir;
struct dirent* pCurDir;
if( ( pDir = opendir( dir_entry ) ) == NULL ){
perror( "read dir" );
exit( -1 );
}else {
while( ( pCurDir = readdir( pDir ) ) != NULL ) {
do_stat( pCurDir->d_name );
}
closedir( pDir );
}
}
//得到文件信息
void do_stat( char* filename ){
struct stat statinfo;
if ( stat( filename, &statinfo ) == -1 ) {
printf( "打开%s失败\n", filename );
exit( -1 );
}else {
show_list( filename, &statinfo );
}
}
//显示文件列表
void show_list( char* filename, struct stat* statinfo ) {
mode_t st_mode = statinfo->st_mode;
char str[10];
mode_to_letters( st_mode, str );
printf( "%s\t", str );
printf( "%ld\t", statinfo->st_nlink ); //符号链接
printf( "%s\t\t", uid_to_name( statinfo->st_uid ) ); //用户名
printf( "%s\t", gid_to_name( statinfo->st_gid ) ); //组名
printf( "%10ld", statinfo->st_size ); //文件大小
show_time( statinfo->st_mtime ); //最后一次修改时间
printf( "\t%s", filename );
printf( "\n" );
}
char* uid_to_name( uid_t uid ){
return getpwuid( uid )->pw_name;
}
char* gid_to_name( gid_t gid ){
return getgrgid( gid )->gr_name;
}
void mode_to_letters( mode_t filemode, char str[] ) {
strcpy( str, "----------" );
if( S_ISREG( filemode ) ) str[0] = '-';
if( S_ISDIR( filemode ) ) str[0] = 'd';
if( S_ISLNK( filemode ) ) str[0] = 'l';
//用户权限位
if( filemode & S_IRUSR ) str[1] = 'r';
if( filemode & S_IWUSR ) str[2] = 'w';
if( filemode & S_IXUSR ) str[3] = 'x';
//组权限位
if( filemode & S_IRGRP ) str[4] = 'r';
if( filemode & S_IWGRP ) str[5] = 'w';
if( filemode & S_IXGRP ) str[6] = 'x';
//其他组权限位
if( filemode & S_IROTH ) str[7] = 'r';
if( filemode & S_IWOTH ) str[8] = 'w';
if( filemode & S_IXOTH ) str[9] = 'x';
}
void show_time( time_t filetime ) {
struct tm* ptm;
ptm = localtime( &filetime );
int month = ptm->tm_mon + 1;
int day = ptm->tm_mday;
int hour = ptm->tm_hour;
int min = ptm->tm_min;
char srchour[3] = "0";
char srcmin[3] = "0";
char dsthour[3] = "0";
char dstmin[3] = "0";
sprintf( srchour, "%d", hour );
sprintf( srcmin, "%d", min );
format_time( dsthour, srchour );
format_time( dstmin, srcmin );
printf( "%4d月%4d%4s:%2s", month, day, dsthour, dstmin );
}
char* format_time( char* dsttime, const char* srctime ) {
if( strlen( srctime ) < 2 ) {
return strcat( dsttime, srctime );
}
return strcpy( dsttime, srctime );
}
截图


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号