算法分析与设计第二次作业(最近点对)
题目:hdoj_1007
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 43000 Accepted Submission(s): 11172
Problem Description
Have you ever played quoit in a playground? Quoit is a game in which flat rings are pitched at some toys, with all the toys encircled awarded.
In the field of Cyberground, the position of each toy is fixed, and the ring is carefully designed so it can only encircle one toy at a time. On the other hand, to make the game look more attractive, the ring is designed to have the largest radius. Given a configuration of the field, you are supposed to find the radius of such a ring.
Assume that all the toys are points on a plane. A point is encircled by the ring if the distance between the point and the center of the ring is strictly less than the radius of the ring. If two toys are placed at the same point, the radius of the ring is considered to be 0.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. For each case, the first line contains an integer N (2 <= N <= 100,000), the total number of toys in the field. Then N lines follow, each contains a pair of (x, y) which are the coordinates of a toy. The input is terminated by N = 0.
Output
For each test case, print in one line the radius of the ring required by the Cyberground manager, accurate up to 2 decimal places.
Sample Input
2
0 0
1 1
2
1 1
1 1
3
-1.5 0
0 0
0 1.5
0
Sample Output
0.71
0.00
0.75
题目大意:平面上有好多点,让你找到一个最大的圆圈能把每个点都套进去同时圈不相交。其实就是找点与点之间最小距离
关于最近点对的问题在算法导论中计算几何学中有详细的解释,通过同学和我分享的算法思路以及对算法导论的研读,确定了我的解题思路,与算法书上的解法有点区别,但是没有很优化。
解法思路:
首先还是要用分治法将问题进行分解,用递归的方式进行解决。
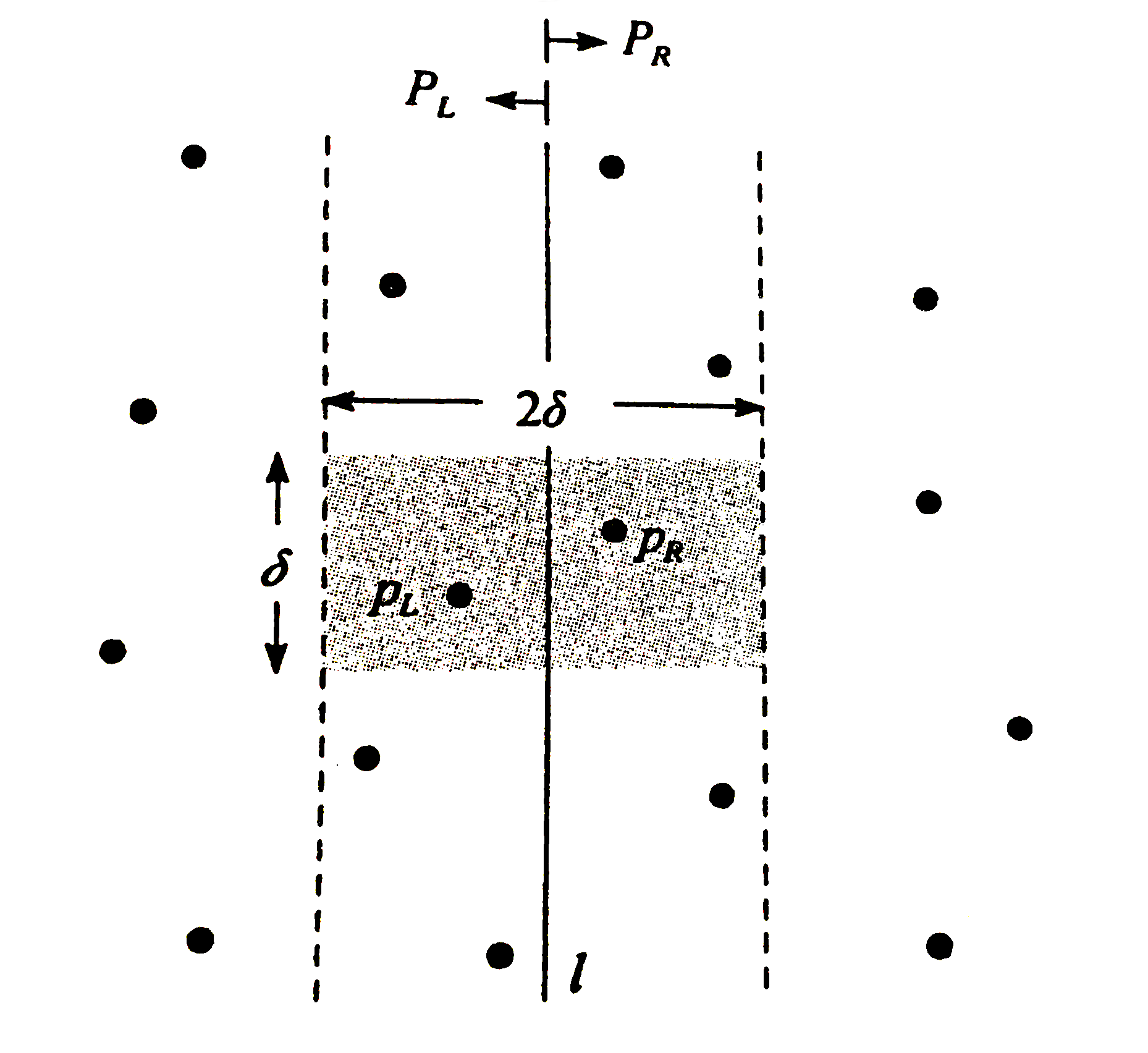
- 问题分解的策略:首先将坐标点根据x轴坐标排序,那么就可以通过一条垂直于x轴的直线l将坐标点分成左右两部分,用递归的思路,将分开的两部分继续按照此策略分解,并以此类推,就可以缩减问题的规模
- 递归边界:当被每一部分的点个数 \(n\leqslant 3\) 时,停止递归,并且分情况讨论:当 n = 2 时,返回两个点的点点间距离;当 n = 3 时,计算每个点的距离返回其中的最小值。
- 合并: 首先对比两部分的返回值,取其最小值为\(\sigma\),以划分这两部分的直线l为对称轴,将所以x坐标在[l+\(\sigma\),l+\(\sigma\)]区间上的点扫描出来,再求出这些点中的最小距离d如下图:
![]()
由于d再递归的过程中一直在减小,所以选取的点会越来越小,达到了优化的目的。
c++代码:
//hdoj_1007
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<cfloat>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
struct point{
double x;
double y;
};
bool cmp1(point a,point b){
return a.x< b.x;
}
bool cmp2(point a,point b){
return a.y<b.y;
}
double point_distance(point a,point b){
double ans = (a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y);
return sqrt(ans);
}
void print_pointsets(point temp[],int len){
for (int i=0;i<len;i++){
cout<<temp[i].x<<" "<<temp[i].y<<endl;
}
}
double hebin_distance(point temp[],int left ,int right){
double ans = DBL_MAX;
for(int i=left;i<right;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<=right;j++){
ans = min(ans,point_distance(temp[i],temp[j]));
}
}
return ans;
}
double min_Distance(point temp[],int left ,int right ){
double ans=DBL_MAX,a,b;
int mid=0,l,r;
if((right-left)<3){//设置递归边界
for(int i=left;i<right;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<=right;j++){
ans = min(ans,point_distance(temp[i],temp[j]));
}
}
return ans;
}
else{
mid = (left+right)/2;
a = min_Distance(temp,left,mid);
b = min_Distance(temp,mid+1,right);
ans = min(a,b);
l=left,r=right;
//寻找最小边界
while(temp[l].x <temp[mid].x -ans){
l++;
}
while(temp[r].x >temp[mid].x +ans){
r--;
}
//两个子类合并
ans = min(ans,hebin_distance(temp,l,r));
return ans;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
double ans;
while(cin>>n&&n){
point pp[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>pp[i].x>>pp[i].y;
}
//cout<<"排序前:"<<endl;
//print_pointsets(pp,n);
sort(pp,pp+n,cmp1);
ans = min_Distance(pp,0,n-1);
cout<<"最小距离为:"<<setprecision(2)<<ans/2<<endl;
//print_pointsets(pp,n);
}
return 0;
}
codeforce 刷题
刷到2B时看到tag是动态规划的题目,思考了很长时间没有头绪,先练习一些动态规划的例题:动态规划例题


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号