Lambda表达式详解
简化了匿名委托的使用,让你让代码更加简洁,优雅。据说它是微软自c#1.0后新增的最重要的功能之一
lambda简介
lambda运算符:所有的lambda表达式都是用新的lambda运算符 " => ",可以叫他,“转到”或者 “成为”。运算符将表达式分为两部分,左边指定输入参数,右边是lambda的主体。
lambda表达式:
1.一个参数:param=>expr
2.多个参数:(param-list)=>expr
注:当输入参数为空是,Lambda表达式左边的()不能省略。例:
() => Console.WriteLine("Empty");
Func<DateTime> getDateTime = () => DateTime.Now;
当Lambda表达式的输入参数的数量为1时,输入参数的()可以省略。
x => x * x;
当Lambda表达式的输入参数的数量大于1时,输入参数的()是必须的,且参数之间使用逗号分隔。
(x, y) => x * y;
Lambda的delegate形式转换:
delegate(int x) { return x * x; };
上面这些东西,记着,下面我们开始应用并阐述lambda,让你乐在其中。
lambda应用阐述
阐述这技术,我先上一个例子,然后再慢慢深入分析。例子如下:
namespace 阐述lambda { public class Person { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get;set; } } class Program { public static List<Person> PersonsList() { List<Person> persons = new List<Person>(); for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) { Person p = new Person() { Name = i + "儿子", Age = 8 - i, }; persons.Add(p); } return persons; } static void Main(string[] args) { List<Person> persons = PersonsList(); persons = persons.Where(p => p.Age > 6).ToList(); //所有Age>6的Person的集合 Person per = persons.SingleOrDefault(p => p.Age == 1); //Age=1的单个people类 persons = persons.Where(p => p.Name.Contains("儿子")).ToList(); //所有Name包含儿子的Person的集合 } } }
看啦上面的例子,相信你能看出它确实是个甜枣,呵呵,下面我们来看下(p=>p.Age>6)这样的表达式,到底是怎么回事。。
首先我们看下委托
//委托 逛超市 delegate int GuangChaoshi(int a); static void Main(string[] args) { GuangChaoshi gwl = JieZhang; Console.WriteLine(gwl(10) + ""); //打印20,委托的应用 Console.ReadKey(); } //结账 public static int JieZhang(int a) { return a + 10; }
再看表达式
//委托 逛超市 delegate int GuangChaoshi(int a); static void Main(string[] args) { // GuangChaoshi gwl = JieZhang; GuangChaoshi gwl = p => p + 10; Console.WriteLine(gwl(10) + ""); //打印20,表达式的应用 Console.ReadKey(); }
委托跟表达式的两段代码,我们可以看出一些东东吧:其实表达式(p => p + 10;)中的 p 就代表委托方法中的参数,而表达式符号右边的 p+10,就是委托方法中的返回结果。 大侠绕道,小虾理解下。
下面再上两个稍微复杂点的理解理解。
1.多参数的
//委托 逛超市 delegate int GuangChaoshi(int a,int b); static void Main(string[] args) { GuangChaoshi gwl = (p,z) => z-(p + 10); Console.WriteLine(gwl(10,100) + ""); //打印80,z对应参数b,p对应参数a Console.ReadKey(); }
2. lambda主体运算复杂
/// <summary> /// 委托 逛超市 /// </summary> /// <param name="a">花费</param> /// <param name="b">付钱</param> /// <returns>找零</returns> delegate int GuangChaoshi(int a,int b); static void Main(string[] args) { GuangChaoshi gwl = (p, z) => { int zuidixiaofei = 10; if (p < zuidixiaofei) { return 100; } else { return z - p - 10; } }; Console.WriteLine(gwl(10,100) + ""); //打印80,z对应参数b,p对应参数a Console.ReadKey(); }
上面这些例子,好好理解下,下面我要介绍一个系统指定的 Fun<T>委托。
Func<T>委托
T 是参数类型,这是一个泛型类型的委托,用起来很方便的。
先上例子
static void Main(string[] args) { Func<int, string> gwl = p => p + 10 + "--返回类型为string"; Console.WriteLine(gwl(10) + ""); //打印‘20--返回类型为string’,z对应参数b,p对应参数a Console.ReadKey(); }
说明:我们可以看到,这里的p为int 类型参数, 然而lambda主体返回的是string类型的。
再上一个例子
static void Main(string[] args) { Func<int, int, bool> gwl = (p, j) => { if (p + j == 10) { return true; } return false; }; Console.WriteLine(gwl(5,5) + ""); //打印‘True’,z对应参数b,p对应参数a Console.ReadKey(); }
说明:从这个例子,我们能看到,p为int类型,j为int类型,返回值为bool类型。
看完上面两个例子,相信大家应该明白啦Func<T>的用法:多个参数,前面的为委托方法的参数,最后一个参数,为委托方法的返回类型。
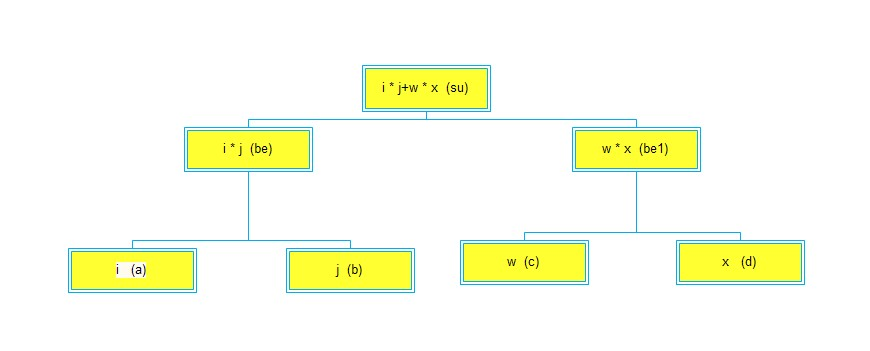
lambda表达式树动态创建方法
static void Main(string[] args) { //i*j+w*x ParameterExpression a = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int),"i"); //创建一个表达式树中的参数,作为一个节点,这里是最下层的节点 ParameterExpression b = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int),"j"); BinaryExpression be = Expression.Multiply(a,b); //这里i*j,生成表达式树中的一个节点,比上面节点高一级 ParameterExpression c = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "w"); ParameterExpression d = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "x"); BinaryExpression be1 = Expression.Multiply(c, d); BinaryExpression su = Expression.Add(be,be1); //运算两个中级节点,产生终结点 Expression<Func<int, int, int, int, int>> lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int, int, int>>(su,a,b,c,d); Console.WriteLine(lambda + ""); //打印‘(i,j,w,x)=>((i*j)+(w*x))’,z对应参数b,p对应参数a Func<int, int, int, int, int> f= lambda.Compile(); //将表达式树描述的lambda表达式,编译为可执行代码,并生成该lambda表达式的委托; Console.WriteLine(f(1, 1, 1, 1) + ""); //打印2 Console.ReadKey(); }
这段代码,放上来,仔细理解下,理解透彻啦,lambda表达式基本上也没什么啦。呵呵。。
算啦,我还是画个图算是结尾吧,以便于理解。
上段代码的lambda表达式树,图。
(转) Lambda表达式详解
.NET自带泛型委托方法Func、Action和Predicate (转)
Func、Action和Predicate是.NET自带的3个泛型委托方法,三个方法的区别其实并不大,要强行给混着用也是可以的,但是我们是有追求的人,把道理讲清楚总是好的。
一、Func是有返回值的方法(类似于Delphi里面的function),Func最多支持16个泛型参数和1个泛型返回值(最后一个固定为返回值),并且支持Lambda表达式;如果前面有泛型类型的参数,这个参数就是委托方法的形参类型,简单说func泛型委托就是一个带返回值的方法签名。
//无参数用法 Func<string> funcNone = delegate() { return "我是来打酱油的"; }; //无参数Lambda用法 Func<string> funcNoneLambda = () => "我是来打酱油的"; //一个参数用法 Func<string, bool> funcOne = delegate(string s) { return s.Contains("酱油"); }; //一个参数Lambda用法 Func<string, bool> funcOneLambda = s => s.Contains("酱油"); //两个参数用法 Func<int, int, int> funcTwo = delegate(int one, int two) { return one + two; }; //两个参数Lambda用法 Func<int, int, int> funcTwoLambda = (one, two) => one + two;
Func<int, int, int> objFun = (a, b) => { return a + b; }; Console.WriteLine("结果为:{0}",objFun(3, 4));
Func的优越性比较:
让我们看一下Func的复杂用法。现在提出一个需求,要求计算数组中任意指定开始位和结束位的“算数和” and 算数积。常规做法是

static int GetSum(int [] nums, int from, int to) { int result = 0; for (int i = from; i <= to; i++) { result += nums[i]; } return result; } static int GetMulti(int[] nums, int from, int to) { int result = 0; for (int i = from; i < to; i++) { result *= nums[i]; } return result; }
写两个方法,分别计算和与积,但是还有别的实现方法么,答案是肯定的:

static int CommonMethod(Func<int, int, int> com, int[] nums, int a, int b) { int result = nums[a]; for (int i = a+1; i < b; i++) { result = com(result, nums[i]); } return result; }
调用上面带泛型的方法:
int[] nums = { 1,2,10,4,5,6,7,8,9}; Console.WriteLine("数组前三个元素的和为:{0}",CommonMethod((a,b)=> { return a + b; },nums,0,3)); Console.WriteLine("数组前三个元素的积为:{0}", CommonMethod((a, b) => { return a * b; }, nums, 0, 3));
二、Action是无返回值的方法(类似于Delphi里面的procedure),Action也是最多支持16个泛型参数,并且支持Lambda表达式
//一个参数用法 Action<string> actionOne = delegate(string s) { Console.Write(s); }; //一个参数Lambda用法 Action<string> actionOneLambda = c => Console.Write(c);
三、 Predicate<T>委托定义如下:
public delegate bool Predicate<T>(T obj);
解释:此委托返回一个bool值的方法
在实际开发中,Predicate<T>委托变量引用一个“判断条件函数”,
在判断条件函数内部书写代码表明函数参数所引用的对象应该满足的条件,条件满足时返回true
Predicate比较特殊,它只有一个参数,而且只返回一个布尔值,并且支持Lambda表达式
//Predicate用法 Predicate<string[]> predicate = delegate(string[] s) { var result = from p in s where p.Contains("c") select p; return result.ToList().Count > 0 ? true : false; }; //Predicate Lambda用法 Predicate<string[]> predicateLambda = s => { var result = from p in s where p.Contains("c") select p; return result.ToList().Count > 0 ? true : false; };
static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> objList = new List<int> { 1,2,3,4,5,6}; List<int> resultList = objList.FindAll((s) => { return s > 2; });//predicate用法 foreach (var item in resultList) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey(); }
四:ForEach()用法
ForEach()方法的参数是一个参数类型是T的无返回值的Action委托,下面的示例中利用Action委托作为参数传递给ForEach()方法。
1、定义Student实体类
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ActionDemo { public class Student { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } public int Sex { get; set; } } }
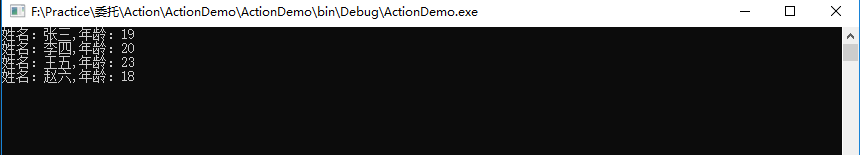
2、利用ForEach()方法输出集合内容
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ActionDemo { public class ActionTest { public static void Test() { List<Student> list = new List<Student>() { new Student(){Id=1,Name="张三",Age=19,Sex=1}, new Student(){Id=2,Name="李四",Age=20,Sex=2}, new Student(){Id=3,Name="王五",Age=23,Sex=1}, new Student(){Id=4,Name="赵六",Age=18,Sex=1} }; // Action<Student>委托作为参数传递给ForEach()方法 list.ForEach(student => { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{student.Name},年龄:{student.Age}"); }); } } }
======================================================================================================================
1. 普通绑定:
public void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { MessageBox.Show("ok"); } this.button1.Click += button1_Click;
2. 匿名委托:
this.button1.Click += delegate(object sender, EventArgs e) { MessageBox.Show("Click"); };
3. LAMDA表达式:
this.button1.Click += ((sender, e) => { MessageBox.Show("Click"); } );
编译器会自动推算出表达式中的类型。
4. 过滤条件:
List<User> users = new List<User>(); Func<User, bool> predicate = ( (user) => { return user.UserId > 100; } ); List<User> temps = users.Where(predicate).ToList();
等同于:
List<User> temps = users.Where(p => p.UserId > 100).ToList();
List<User> temps = (from p in users where p.UserId > 100 select p).ToList();
List<User> users = new List<User>(); Func<User, bool> predicate = ( (user) => user.UserId > 100 ); List<User> temps = users.Where(predicate).ToList();
单挑语句时不需要使用{},同时可以不使用return来返回结果。
5. 排序:
List<User> users = new List<User>(); List<User> temp1 = users.OrderBy(p=>p.UserId).ToList(); Func<User, int> orderby = (user => user.UserId); List<User> temp2 = users.OrderBy(orderby).ToList();
==========================================================================================================================
使用Func的5种写法:Lambda表达式的用法(第五种最简单)
1 namespace ConsoleApplication3 2 { 3 class Program 4 { 5 static void Main(string[] args) 6 { 7 //第一种写法,先实例化,再调用AddFunc方法,注意AddFunc是静态方法 8 Func<int, int, int> FuncDemo1 = new Func<int, int, int>(AddFunc); 9 Console.WriteLine(FuncDemo1(10, 11)); 10 11 //第二种写法,匿名方法 12 Func<int, int, int> FunDemo2 = delegate(int a, int b) { return a + b; }; 13 Console.WriteLine(FunDemo2(10, 12)); 14 15 //第三种写法,Lambda语句 16 Func<int, int, int> FunDemo3 = (int a, int b) => { return a + b; }; 17 Console.WriteLine(FunDemo3(10, 13)); 18 19 //第四种写法,Lambda表达式 20 Func<int, int, int> FunDemo4 = (a, b) => { return a + b; }; 21 Console.WriteLine(FunDemo4(10, 14)); 22 23 //第五种写法,Lambda表达式 简化 24 Func<int, int, int> FunDemo5 = (a, b) => a + b; 25 Console.WriteLine(FunDemo5(10, 15)); 26 27 Console.ReadKey(); 28 } 29 30 public static int AddFunc(int a,int b) 31 { 32 return a + b; 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 --------------------- 37 作者:sklzl1571 38 来源:CSDN 39 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/sklzl1571/article/details/80076532 40 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号