实验4
实验任务1
GradeCalc.hpp
#pragma once #include <vector> #include <array> #include <string> class Gradecalc { public: Gradecalc(const std::string &cname); void input(int n); void output() const; void sort(bool ascending = false); int min() const; int max() const; double average() const; void info(); private: void compute(); std::string course_name; std::vector<int> grades; std::array<int, 5> counts{}; std::array<double, 5> rates{}; bool is_dirty; };
GradeCalc.cpp
#include "GradeCalc.hpp" #include <algorithm> #include <numeric> #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> Gradecalc::Gradecalc(const std::string &cname) : course_name(cname), is_dirty(true) { counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0.0); } void Gradecalc::input(int n) { if (n <= 0) return; grades.reserve(n); int g; for (int i = 0; i < n; ) { std::cin >> g; if (g < 0 || g > 100) continue; grades.push_back(g); ++i; } is_dirty = true; } void Gradecalc::output() const { for (int g : grades) std::cout << g << ' '; std::cout << '\n'; } void Gradecalc::sort(bool ascending) { std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end(), ascending ? std::less<int>(): std::greater<int>()); is_dirty = true; } int Gradecalc::min() const { return grades.empty() ? -1 : *std::min_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); } int Gradecalc::max() const { return grades.empty() ? -1 : *std::max_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); } double Gradecalc::average() const { return grades.empty() ? 0.0 : std::accumulate(grades.begin(), grades.end(), 0.0) / grades.size(); } void Gradecalc::compute() { if (grades.empty()) return; counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0.0); for (int g : grades) ++counts[g < 60 ? 0 : g < 70 ? 1 : g < 80 ? 2 : g < 90 ? 3 : 4]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / grades.size(); is_dirty = false; } void Gradecalc::info() { if (is_dirty) compute(); const std::array<std::string,5> R{"[0,60)","[60,70)","[70,80)","[80,90)","[90,100]"}; std::cout << "课程: " << course_name << '\n' << "平均分: " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << '\n' << "最高分: " << max() << '\n' << "最低分: " << min() << '\n'; for (int i = 4; i >= 0; --i) std::cout << R[i] << ' ' << counts[i] << "人 " << rates[i]*100 << "%\n"; }
demo1.cpp
#include "GradeCalc.hpp" int main(){ Gradecalc c("OOP"); std::cout << "录入5个成绩:\n"; c.input(5); std::cout << "输出:\n"; c.output(); std::cout << "降序:\n"; c.sort(); c.output(); std::cout << "统计:\n"; c.info(); }
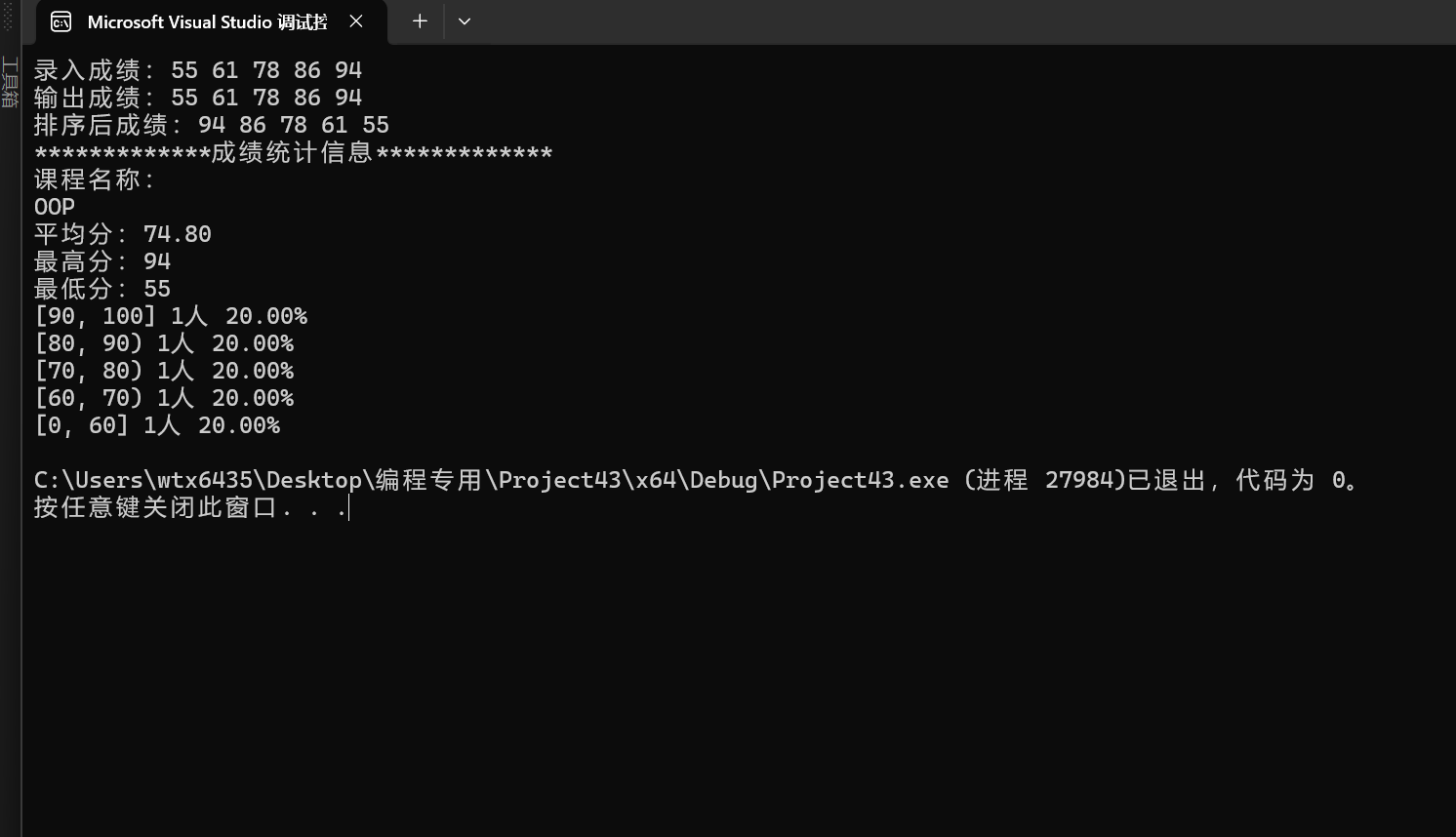
问题1:
std::vector<int> grades;:存储课程成绩; std::array<int,5> counts; :存储各分数段人数; std::array<double,5> rates; :存储各分数段比例
问题2:
不合法,grades是私有成员,类外无法直接访问
问题3(1):
只调用1次;避免重复计算
问题4:
不新增成员:在 info() 中加: auto tmp = grades; std::sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end()); double med = tmp[tmp.size()/2]; 。
问题5:
不能再次调用compute()时累加旧数据,导致错误
问题6:
无影响,性能上,导致多次扩容,降低效率
实验任务2
GradeCale.hpp
#pragma once #include <vector> #include <array> #include <string> class Gradecalc : private std::vector<int> { public: explicit Gradecalc(const std::string &cname); void input(int n); void output() const; void sort(bool ascending = false); int min() const; int max() const; double average() const; void info(); private: void compute(); std::string course_name; std::array<int,5> counts{}; std::array<double,5> rates{}; bool is_dirty; };
GradeCale.cpp
#include "GradeCalc.hpp" #include <algorithm> #include <numeric> #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> Gradecalc::Gradecalc(const std::string &cname) : course_name(cname), is_dirty(true) { counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0.0); } void Gradecalc::input(int n) { if (n <= 0) return; this->reserve(n); int g; for (int i = 0; i < n; ) { std::cin >> g; if (g < 0 || g > 100) continue; this->push_back(g); ++i; } is_dirty = true; } void Gradecalc::output() const { for (int g : *this) std::cout << g << ' '; std::cout << '\n'; } void Gradecalc::sort(bool ascending) { std::sort(this->begin(), this->end(), ascending ? std::less<int>(): std::greater<int>()); is_dirty = true; } int Gradecalc::min() const { return this->empty() ? -1 : *std::min_element(this->begin(), this->end()); } int Gradecalc::max() const { return this->empty() ? -1 : *std::max_element(this->begin(), this->end()); } double Gradecalc::average() const { return this->empty() ? 0.0 : std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0.0) / this->size(); } void Gradecalc::compute() { if (this->empty()) return; counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0.0); for (int g : *this) ++counts[g < 60 ? 0 : g < 70 ? 1 : g < 80 ? 2 : g < 90 ? 3 : 4]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / this->size(); is_dirty = false; } void Gradecalc::info() { if (is_dirty) compute(); const std::array<std::string,5> R{"[0,60)","[60,70)","[70,80)","[80,90)","[90,100]"}; std::cout << "课程: " << course_name << '\n' << "平均分: " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << '\n' << "最高分: " << max() << '\n' << "最低分: " << min() << '\n'; for (int i = 4; i >= 0; --i) std::cout << R[i] << ' ' << counts[i] << "人 " << rates[i]*100 << "%\n"; }
demo2.cpp
#include "GradeCalc.hpp" int main(){ Gradecalc c("OOP"); std::cout << "录入5个成绩:\n"; c.input(5); std::cout << "输出:\n"; c.output(); std::cout << "降序:\n"; c.sort(); c.output(); std::cout << "统计:\n"; c.info(); }

问题1:
class Gradecalc : private std::vector<int>
问题2:
合法,公有接口,类内可见
问题3:
第一个通过成员变量名访问
第二个通过自身作为容器访问
问题4:
组合更合适,成绩计算器是包含一个成绩容器,组合更清晰,封装性更强
实验任务3:
Graph.hpp
#pragma once #include <vector> #include <string> enum class GraphType { circle, triangle, rectangle }; class Graph { public: virtual void draw() const = 0; virtual ~Graph() = default; }; class Circle : public Graph { public: void draw() const override; }; class Triangle : public Graph { public: void draw() const override; }; class Rectangle : public Graph { public: void draw() const override; }; class Canvas { public: void add(const std::string& type); void paint() const; ~Canvas(); private: std::vector<Graph*> graphs; }; Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type);
Graph.cpp
#include "Graph.hpp" #include <algorithm> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> void Circle::draw() const { std::cout << "draw a circle\n"; } void Triangle::draw() const { std::cout << "draw a triangle\n"; } void Rectangle::draw() const{ std::cout << "draw a rectangle\n"; } void Canvas::add(const std::string& type) { Graph* g = make_graph(type); if (g) graphs.push_back(g); } void Canvas::paint() const { for (Graph* g : graphs) g->draw(); } Canvas::~Canvas() { for (Graph* g : graphs) delete g; } static GraphType str_to_type(const std::string& s) { std::string t = s; std::transform(t.begin(), t.end(), t.begin(), [](unsigned char c){ return std::tolower(c); }); if (t == "circle") return GraphType::circle; if (t == "triangle") return GraphType::triangle; if (t == "rectangle") return GraphType::rectangle; return GraphType::circle; // default } Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type) { switch (str_to_type(type)) { case GraphType::circle: return new Circle; case GraphType::triangle: return new Triangle; case GraphType::rectangle:return new Rectangle; } return nullptr; }
demo3.cpp
#include "Graph.hpp" int main(){ Canvas canvas; canvas.add("circle"); canvas.add("triangle"); canvas.add("rectangle"); canvas.paint(); }
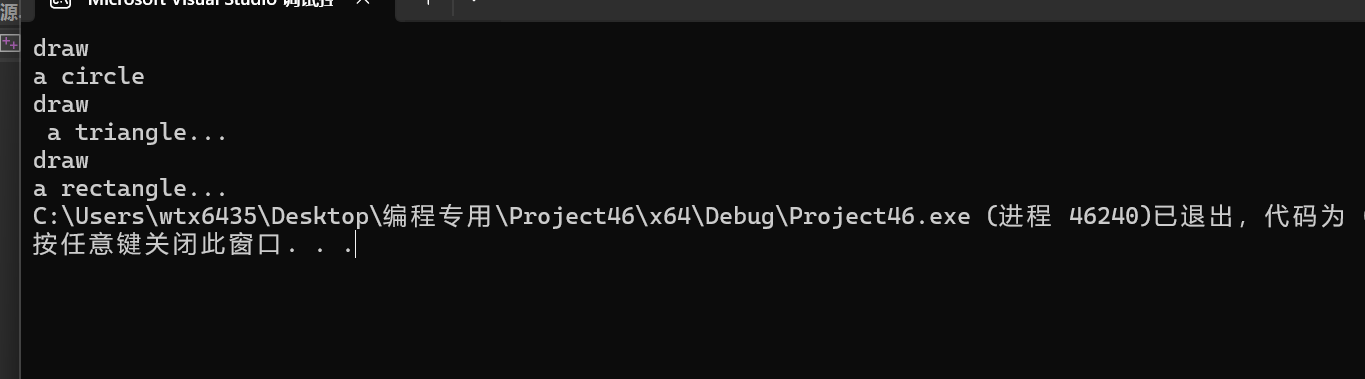
问题1(1):
std::vector<Graph*> graphs;:统一管理所有图形指针。
(2):
class Circle : public Graph
问题2(1):
无法多态,输出相同
(2):
会切片,丢失派生类信息
(3):
删除派生类对象时,派生类部分未析构,内存泄漏
问题3:
① Graph.hpp :新增 class Star : public Graph ;② Graph.cpp :实现 Star::draw() ;③ str_to_GraphType 加"star"分支;④ make_graph 中加case。
问题4(1):
在delete g;释放
(2):
灵活但是易漏删,写错
实验任务4:
Toy.hpp:
#pragma once #include <memory> #include <vector> #include <string> class Toy { public: explicit Toy(std::string name) : toy_name(std::move(name)) {} virtual void specialFunction() const = 0; virtual ~Toy() = default; const std::string& name() const { return toy_name; } private: std::string toy_name; }; class Bear : public Toy { public: Bear() : Toy("Bear") {} void specialFunction() const override; }; class Bunny : public Toy { public: Bunny() : Toy("Bunny") {} void specialFunction() const override; }; class ToyFactory { public: void add(std::unique_ptr<Toy> t) { toys.push_back(std::move(t)); } void showAll() const; private: std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Toy>> toys; };
Toy.cpp
#include "Toy.hpp" #include <iostream> void Bear::specialFunction() const { std::cout << name() << ": plays lullaby & glows in the dark\n"; } void Bunny::specialFunction() const { std::cout << name() << ": hops and plays Easter song\n"; } void ToyFactory::showAll() const { for (const auto& t : toys) t->specialFunction(); }
demo4:
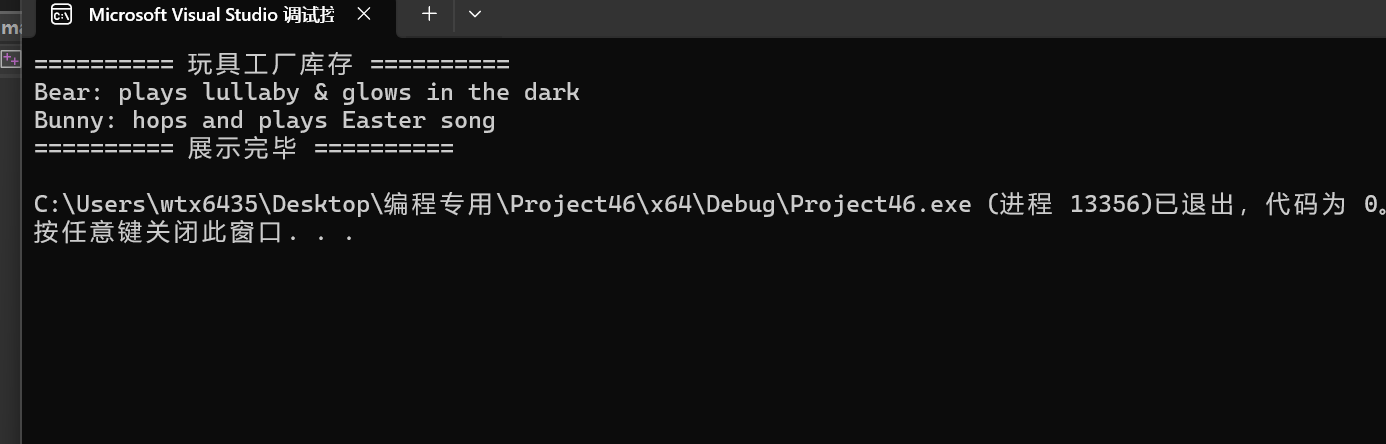
#include "Toy.hpp" int main(){ ToyFactory f; f.add(std::make_unique<Bear>()); f.add(std::make_unique<Bunny>()); f.showAll(); }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号