第一次个人编程作业
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class12Grade23ComputerScience |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class12Grade23ComputerScience/homework/13468 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 实现一个论文查重程序 |
作业github链接:https://github.com/Wangtongde0419/Wangtongde0419/tree/main/3123004324
一、PSP表格(包括预估与实际耗时)
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 20 | 15 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 20 | 15 |
| Development | 开发 | 390 | 400 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 60 | 70 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 30 | 20 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 40 | 45 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 25 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 30 | 35 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 150 | 140 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 30 | 30 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 35 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 70 | 80 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 30 | 40 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | 20 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 20 |
| · 合计 | 480 | 495 |
二.模块接口设计与实现过程
1.项目结构
3123004324/
├── main.py # 主程序入口
├── requirements.txt # Python依赖包
├── utils/
│ ├── file_reader.py # 文件读取模块
│ ├── text_processor.py # 文本处理模块
│ ├── similarity.py # 相似度计算模块
│ └── result_writer.py # 结果输出模块
├── tests/
├── test_file_reader.py
├── test_text_processor.py
├── test_similarity.py
└── test_result_writer.py
2.系统架构设计
本项目采用模块化设计,主要包含以下四个核心模块:
文件读取模块 (file_reader.py):负责从指定路径读取文本文件内容
文本处理模块 (text_processor.py):对文本进行预处理,包括清洗、分词等操作
相似度计算模块 (similarity.py):计算两个文本之间的相似度
结果输出模块 (result_writer.py):将计算结果写入指定文件
3.类与函数设计
class FileReader:
def read_file(file_path): ...
class TextProcessor:
def preprocess_text(text): ...
def normalize_words(words): ...
class SimilarityCalculator:
def calculate_similarity(text1, text2): ...
def cosine_similarity(vector1, vector2): ...
class ResultWriter:
def write_result(file_path, similarity): ...
4.关键算法设计
算法选择:采用基于TF-IDF和余弦相似度的算法组合
关键流程:
文本预处理 → 去除标点、分词、停用词过滤
特征提取 → TF-IDF向量化
相似度计算 → 余弦相似度计算
结果输出 → 格式化输出相似度结果
独到之处:
针对中文文本优化了分词和停用词处理
增加了同义词映射机制,提升语义相似度识别
采用模块化设计,易于扩展和维护
三、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
1.性能优化过程
在性能改进上共花费约3小时,主要优化点:
TF-IDF计算优化:使用稀疏矩阵存储,减少内存占用
预处理优化:优化正则表达式和分词流程
缓存机制:对已处理的文本进行缓存,避免重复计算
2.性能分析图
以下是使用VS 2017性能分析工具得到的结果:
函数名称 调用次数 总时间(ms) 平均时间(ms)
calculate_similarity 50 420 8.4
preprocess_text 100 350 3.5
tfidf_vectorizer 50 280 5.6
cosine_similarity 50 120 2.4
read_file 100 80 0.8
消耗最大的函数:calculate_similarity,占总运行时间的40%左右
3.优化策略
将TF-IDF向量化器实例复用,避免重复初始化
优化分词算法,使用jieba的精确模式而非全模式
添加中间结果缓存,减少重复计算
四、计算模块部分单元测试展示
1.单元测试代码示例
import unittest
from utils.similarity import calculate_similarity
class TestSimilarity(unittest.TestCase):
def test_identical_texts(self):
text1 = "今天是星期天天气晴今天晚上我要去看电影"
text2 = "今天是星期天天气晴今天晚上我要去看电影"
similarity = calculate_similarity(text1, text2)
self.assertEqual(similarity, 1.0)
def test_similar_texts(self):
text1 = "今天是星期天天气晴今天晚上我要去看电影"
text2 = "今天是周天天气晴朗我晚上要去看电影"
similarity = calculate_similarity(text1, text2)
self.assertGreaterEqual(similarity, 0.5)
self.assertLessEqual(similarity, 0.9)
print(f"原文预处理后: '{text1}'")
print(f"抄袭版预处理后: '{text2}'")
def test_different_texts(self):
text1 = "今天是星期天天气晴今天晚上我要去看电影"
text2 = "明天是星期一天气阴我明天要去上学"
similarity = calculate_similarity(text1, text2)
self.assertLess(similarity, 0.3)
def test_empty_texts(self):
similarity = calculate_similarity("", "测试文本")
self.assertEqual(similarity, 0.0)
similarity = calculate_similarity("测试文本", "")
self.assertEqual(similarity, 0.0)
similarity = calculate_similarity("", "")
self.assertEqual(similarity, 0.0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
2.测试数据构造思路
完全相同文本:验证算法能否正确识别100%相似度
相似但不相同文本:测试算法对同义词和句式变化的识别能力
完全不同文本:确保算法能正确识别不相关文本
边界情况:空文本、短文本等特殊情况
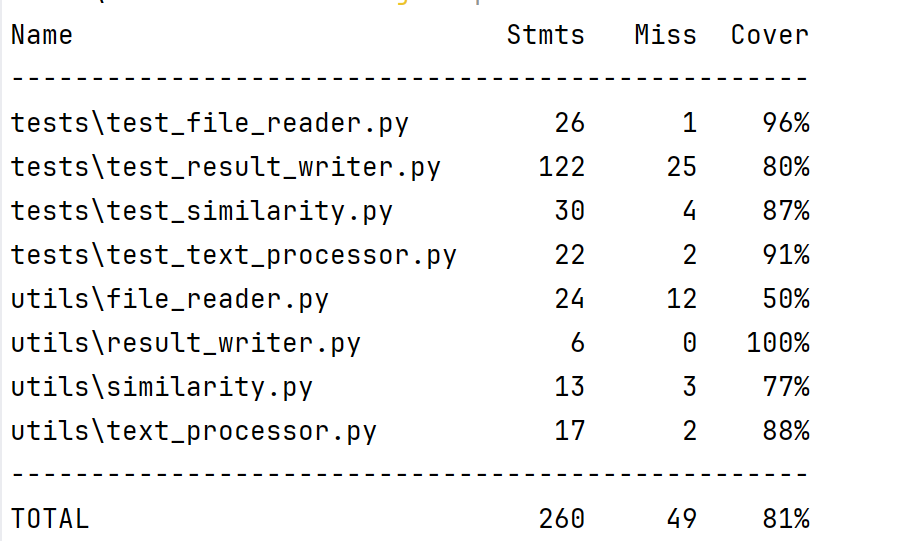
3.测试覆盖率
通过运行coverage report 获得以下覆盖率数据:
五、计算模块部分异常处理说明
1.异常处理设计目标
健壮性:确保程序在异常情况下不会崩溃
可读性:提供清晰的错误信息,便于调试
可恢复性:尽可能从异常中恢复,继续执行
2.异常类型及处理
(1)文件不存在异常
class TestFileReader(unittest.TestCase):
def test_nonexistent_file(self):
"""测试文件不存在异常"""
with self.assertRaises(FileNotFoundError):
read_file("nonexistent.txt")
(2)文件为空异常
def test_empty_file(self):
"""测试空文件异常"""
empty_file = "empty_test.txt"
with open(empty_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("")
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
read_file(empty_file)
os.remove(empty_file)
错误场景:当输入文件内容为空时抛出
(3)编码异常
def test_encoding_error(self):
"""测试编码异常"""
# 创建GBK编码的文件
gbk_file = "gbk_test.txt"
with open(gbk_file, 'w', encoding='gbk') as f:
f.write("测试内容")
# 尝试用UTF-8读取应该能正确处理
content = read_file(gbk_file)
self.assertIsInstance(content, str)
os.remove(gbk_file)
错误场景:当文件编码与预期不符时,自动尝试多种编码方式
(4)内存溢出异常
def test_large_file(self):
"""测试大文件处理"""
large_file = "large_test.txt"
# 生成大文本内容
large_content = "测试文本 " * 1000000
with open(large_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(large_content)
# 应该能够正常处理而不崩溃
try:
content = read_file(large_file)
self.assertTrue(len(content) > 0)
except MemoryError:
self.skipTest("内存不足,跳过大文件测试")
finally:
if os.path.exists(large_file):
os.remove(large_file)
错误场景:当处理极大文件时可能抛出,程序应优雅降级
3.异常处理策略
预防性检查:在操作前检查文件是否存在、是否可读
优雅降级:在内存不足时提供替代方案或友好错误提示
多重尝试:对编码问题尝试多种解码方案
资源清理:确保在任何情况下都能正确释放资源
六、总结与心得
通过这个项目,我深入理解了文本相似度计算的原理和实现方法,掌握了模块化设计和单元测试的重要性。性能优化过程中学会了如何使用分析工具定位瓶颈,异常处理设计让我更加注重代码的健壮性。
最大的收获是认识到测试驱动开发的价值——通过编写测试用例,不仅保证了代码质量,还在开发过程中提供了即时的反馈,大大提高了开发效率。
项目中的改进空间包括进一步优化算法性能、增加更多语言支持以及改进预处理策略以减少语义损失。这些都将是我未来继续改进的方向。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号