数据结构与算法
| 软件需求分析与系统设计 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE/homework/11406 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 排序算法与二叉树遍历 |
| 参考资料 | 尚硅谷 Java数据结构与Java算法 |
基本学习:
尚硅谷 Java数据结构与Java算法
冒泡排序算法:
- 基本思想:
通过对待排序序列从前向后(从小标较小的元素开始),依次比较相邻的值,若发现逆序则交换,使较大的元素逐渐从前向后移。
因为排序的过程中,各元素不断接近自己的位置,如果一趟比较下来没有进行过交换,就说明序列有序,
因此在排序过程中设置一个flag判断是否交换。从而减少不必要的比较
小结:(1)一共进行数组的大小-1次大的循环
(2) 每一趟排序的次数在逐渐的减少
(3)如果发现某一趟排序中,没有发生一次交换,可以提前结束冒泡排序。
题一、寻找数组中第K大是数 考察算法:排序算法
1.1实现:冒泡排序算法
1.2基本思路:
1、分析题意
2、调用Scanner()方法实现序列的输入
3、遍历输入的序列,存入数组
4、确定输入次数,使用循环确定序列首尾和第K大数
5、使用冒泡排序算法实现找到对应的第K大数
6、输出结果
1.3代码实现:
'''java
package com.company;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 给定一个序列,每次询问序列中第i个数到第r个数中的第K大的数是那个
*/
public class ButtShort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("输入数组的长度:");
int n = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("给定的序列分别为:");
int[] arr1 = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //遍历数组各元素
arr1[i] = input.nextInt();
/*检查遍历序列
System.out.print(arr[i]);
*/
}
System.out.print("输入你要查询的次数:");
int m = input.nextInt();
int[] arr2 = new int[n + 1];
int temp; //临时变量
boolean flag = false; // 标识变量,表示是否进行过交换
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
System.out.print("\n你要输入的序列和第K大的数分别为:");
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
arr2[j] = arr1[j];
}
int l = input.nextInt(); //序列首
int r = input.nextInt(); //序列位
int k = input.nextInt(); // 第K大的数
//冒泡排序,时间复杂度O(N²)
for (int a = 1; a <= r; a++) {
for (int b = a; b <= r; b++) {
if (arr2[b] > arr2[a]) {
// flag = true;
temp = arr2[b];
arr2[b] = arr2[a];
arr2[a] = temp;
}
}
/*
if (!flag) { //如果没有交换,就退出
break;
} else {
flag = false; //重置flag,进行下次交换。
}
*/
}
System.out.print("第" + k + "大的数为:" + arr2[1 + k - 1]);
}
}
}
'''
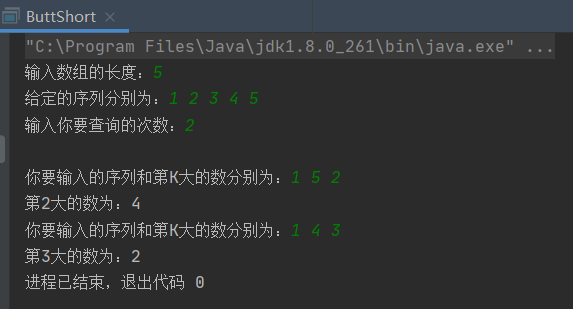
1.4运行结果
题二、二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历 考察算法: dfs + bfs搜索算法
1.1实现:递归算法
1.2基本思路:
- 创建一颗二叉树
- 前序遍历:先输出父节点,在遍历左子树和右子树
- 先输出当前节点(初始root节点);
- 如果左子节点不为空则递归继续前序遍历;
- 如果右子节点不为空则递归继续前序遍历
- 中序遍历:先遍历左子树,在输出父节点,再遍历右子树
- 先输出当前节点左子节点不为空,则递归中序遍历;
- 输出当前结点;
- 如果当前右子节点不为空,则递归继续中序遍
- 后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
- 如果当前节点左子节点不为空,则递归后序遍历;
- 如果当前右子节点不为空,则递归继续后序遍历;
- 输出当前结点
- 层级遍历:每一层从左到右遍历,借助队列实现。
1.3代码实现:
'''java
package com.company;
/**
作业要求:叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
自己实现四个方法,main方法中调用,将结果打印到控制台
*/
import java.util.LinkedList;
/** 二叉树的结构
A
/ \
T 6
/
D
/ \
N 5
/ \ /
B 4 1
\
9
*/
public class MainDemp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Info info = new Info();
Node root = new Node("A");
Node node1 = new Node("T");
Node node2 = new Node("D");
Node node3 = new Node("N");
Node node4 = new Node("B");
Node node5 = new Node("6");
Node node6 = new Node("5");
Node node7 = new Node("4");
Node node8 = new Node("9");
Node node9 = new Node("1");
//说明,手动创建二叉树
root.setL(node1);
node1.setL(node2);
node2.setL(node3);
node2.setR(node6);
node3.setR(node7);
node7.setR(node8);
node6.setL(node9);
node3.setL(node4);
root.setR(node5);
info.setRoot(root);
//测试,前序遍历
System.out.print("前序遍历:");
info.A();
//中序遍历
System.out.print("\n中序遍历:");
info.B();
//后序遍历
System.out.print("\n后序遍历:");
info.C();
//层级序列
System.out.print("\n层级遍历:");
info.D();
}
}
class Info{
private Node root;
public void setRoot(Node root) {
this.root = root;
}
//前序遍历
public void A(){
if (this.root != null){
this.root.A();
}else {
System.out.print("当前二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//中序遍历
public void B(){
if (this.root != null){
this.root.B();
}else{
System.out.print("当前二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//后序遍历
public void C(){
if (this.root != null){
this.root.C();
}else{
System.out.print("当前二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
public void D(){
if (this.root != null){
this.root.D();
}else{
System.out.print("当前二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
}
// 节点
class Node {
// 数据
private String data;
// 左孩子
private Node l;
// 右孩子
private Node r;
public Node(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getL() {
return l;
}
public void setL(Node l) {
this.l = l;
}
public Node getR() {
return r;
}
public void setR(Node r) {
this.r = r;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data ;
}
public void A() {
// TODO 先序遍历
System.out.print(this + "\t"); //先输出父节点
//递归前序左子树前序遍历
if (this.l != null) {
this.l.A();
}
//递归右子树遍历
if (this.r != null) {
this.r.A();
}
}
public void B() {
// TODO 中序遍历
//递归向左子树中序遍历
if (this.l != null) {
this.l.B();
}
//输出父节点
System.out.print(this + "\t");
//递归右子树中序遍历
if (this.r != null) {
this.r.B();
}
}
public void C() {
// TODO 后续遍历
if (this.l != null) {
this.l.C();
}
if (this.r != null) {
this.r.C();
}
System.out.print(this + "\t");
}
public void D() {
// TODO 层级遍历
if (this == null){
return;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Node current = null;
queue.offer(this);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
current = queue.poll();
System.out.print(current.data + "\t");
if (current.l != null){
queue.offer(current.l);
}
if(current.r != null) {//如果当前节点的右节点不为空,把右节点入队
queue.offer(current.r);
}
}
}
}
'''
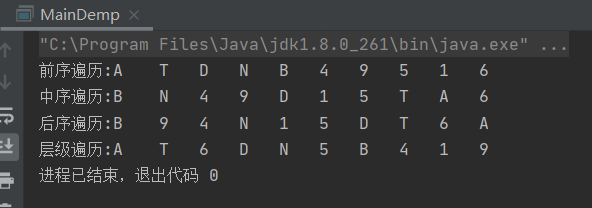
2.4运行结果

 程序的灵魂---算法
程序的灵魂---算法


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号