NCHU 第四第五次大作业 + 期中考试心得
1. 前言
对于图形类的构建实在是不了解,走了很多弯路,一开始使用了triangle,quadrilateral,pentagon三个类来进行计算,后来发现很多函数都是统一的像求面积边长、判断能否构成多边形、多边形的凹凸性、点是否在多边形内、判断边与多边形的关系,判断多边形与多边形的关系,于是将这些函数都放到了一个polygon类里,然后再将一些独有的函数放入了子类中,代码一下简洁了并且各个函数使用起来非常舒服。期中考试则没什么难度,但是踩了一个很无语的坑,接收int或double类型再接收String类型就只能接收到一个回车...刚学c语言的时候碰到的老问题了,想了老一会才想到。
2. 设计与分析
2.1. practice 4
2.1.1. sdut-String-2 识蛟龙号载人深潜,立科技报国志(II)(正则表达式)
-
思路
个人认为用了Pattern和Matcher类后变成了输入输出题(因为题目里没出现小数),一直匹配"\d+"然后转为int型累加即可
-
实现
//sdut-String-2 识蛟龙号载人深潜,立科技报国志(II)(正则表达式)
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String s=input.nextLine();
Pattern a=Pattern.compile("\\d+");
while(s!="end")
{
int sum=0;
Matcher m=a.matcher(s);
while(m.find())
sum+=Integer.parseInt(m.group(0));
System.out.println(sum);
s=input.nextLine();
}
}
}
2.1.2. 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
-
思路:
这题靠着triangle和quadrilateral两个类硬写过去了,代码实在惨不忍睹,各种冗余老长一大堆但是过去了所以也没再改(甚至比我第五次两题加起来还长,难绷),具体思路放在五边形的题目中讲 -
实现:
//点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
point[] p=new point[10];
int[] o={0,4,4,4,6,5};
int i=0,flag=0,op=0;
String s=input.nextLine();
String pt="[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)$";
String pt2="[1-5]:[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)$";
for(String te:s.split(" "))
{
if(i==0)
{
if(te.matches(pt2))
{
p[i] = new point();
op=(te.charAt(0)-'0');
p[i].setxy(te.substring(2,te.length()));
i++;
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
else{
if(te.matches(pt))
{
p[i] = new point();
p[i].setxy(te);
i++;
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
}
input.close();
if(flag==1)
return ;
if(flag==0&&i!=o[op])
{
System.out.printf("wrong number of points");
return ;
}
if(op==1)
{
quadrilateral q=new quadrilateral();
int te=q.create_quadrilateral(p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3]);
if(te<=1)
System.out.print("false false");
else System.out.print("true "+q.pan());
}
else if(op==2)
{
quadrilateral q=new quadrilateral();
int te=q.create_quadrilateral(p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3]);
if(te<=1)
System.out.print("not a quadrilateral");
else {
int te1=q.pantype();
if(te1==0)
System.out.print("false false false");
else if(te1==1)
System.out.print("true false false");
else if(te1==2)
System.out.print("false true false");
else System.out.print("true true true");
}
}
else if(op==3)
{
quadrilateral q=new quadrilateral();
int te=q.create_quadrilateral(p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3]);
if(te<=1)
System.out.print("not a quadrilateral");
else System.out.print(q.aotu()+" "+Main.zh(q.zhouchang())+" "+Main.zh(q.mianji));
}
else if(op==4)
{
line l=new line();
if(!l.get(p[0],p[1]))
{
System.out.print("point coincide");
return ;
}
quadrilateral q=new quadrilateral();
int te=q.create_quadrilateral(p[2], p[3], p[4], p[5]);
if(te==2)
{
q.aotu();
q.lqjiaodian(l);
return ;
}
line tl=new line();
triangle tt=new triangle();
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
if(!tl.get(p[(j+3)%4+2], p[(j+1)%4+2]))
{
if(tt.get(p[(j+3)%4+2], p[j+2],p[(j+2)%4+2]))
{
tt.ltjiaodian(l);
return ;
}
continue;
}
if((tl.shangxia(p[j+2])==1&&tl.panduan(p[j+2])||point.sample(p[(j+3)%4+2], p[j+2])||point.sample(p[(j+1)%4+2], p[j+2])))
{
if(tt.get(p[(j+3)%4+2], p[(j+1)%4+2],p[(j+2)%4+2]))
tt.ltjiaodian(l);
return ;
}
}
System.out.print("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
}
else
{
quadrilateral q=new quadrilateral();
int te=q.create_quadrilateral(p[1], p[2], p[3], p[4]);
if(te==2)
{
q.aotu();
q.pqpanduan(p[0]);
return ;
}
line tl=new line();
triangle tt=new triangle();
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
if(!tl.get(p[(j+3)%4+1], p[(j+1)%4+1]))
{
if(tt.get(p[(j+3)%4+1], p[j+2],p[(j+2)%4+1]))
{
tt.ptpanduan(p[0]);
return ;
}
continue;
}
if((tl.gongxian(p[j+1])&&(tl.panduan(p[j+1]))||point.sample(p[(j+3)%4+1], p[j+1])||point.sample(p[(j+1)%4+1], p[j+1])))
{
if(tt.get(p[(j+3)%4+1], p[(j+1)%4+1],p[(j+2)%4+1]))
tt.ptpanduan(p[0]);
return ;
}
}
System.out.print("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
}
}
public static String zh(double a){
String res = String.format("%.3f",a);
res = res.replaceAll("0+?$", "");
if(res.charAt(res.length()-1) == '.') res+='0';
return res;
}
}
class quadrilateral{
point[] qp=new point[4];
line[] ql=new line[4];
double mianji;
int create_quadrilateral(point p1,point p2,point p3,point p4)
{
ql[0]=new line();
ql[1]=new line();
ql[2]=new line();
ql[3]=new line();
if(point.sample(p1, p2)||point.sample(p3, p2)||point.sample(p3, p4)||point.sample(p1, p4)||point.sample(p1, p3)||point.sample(p4, p2))
return 0;
ql[0].get(p1,p2);
ql[1].get(p2, p3);
ql[2].get(p3, p4);
ql[3].get(p1, p4);
if(line.pingxing(ql[0], ql[1])||line.pingxing(ql[2], ql[1])||line.pingxing(ql[3], ql[2])||line.pingxing(ql[0], ql[3]))
return 1;
if((!line.pingxing(ql[1],ql[3])&&ql[3].panduan(line.jiaodian(ql[1], ql[3]))&&ql[1].panduan(line.jiaodian(ql[1], ql[3])))||(!line.pingxing(ql[0],ql[2])&&ql[0].panduan(line.jiaodian(ql[0], ql[2]))&&ql[2].panduan(line.jiaodian(ql[0], ql[2]))))
return 1;
else {
qp[0]=p1;
qp[1]=p2;
qp[2]=p3;
qp[3]=p4;
return 2;
}
}
boolean pan()
{
if(line.pingxing(ql[0], ql[2])&&line.pingxing(ql[1], ql[3]))
return true;
return false;
}
int pantype()
{
line tel=new line();
tel.get(qp[0],qp[2]);
double tmp = line.changdu(ql[0])*line.changdu(ql[0])+line.changdu(ql[1])*line.changdu(ql[1])-line.changdu(tel)*line.changdu(tel);
if(pan()&&line.changdu(ql[0])==line.changdu(ql[1]))
{
if(Math.abs(tmp)<0.0000001)
return 3;
else return 1;
}
if(Math.abs(tmp)<0.0000001)
return 2;
return 0;
}
boolean aotu()
{
triangle te1=new triangle();
triangle te2=new triangle();
triangle te3=new triangle();
triangle te4=new triangle();
te1.get(qp[0],qp[1],qp[2]);
te2.get(qp[0],qp[3],qp[2]);
te3.get(qp[0],qp[1],qp[3]);
te4.get(qp[3],qp[1],qp[2]);
double temp=te1.mianji()+te2.mianji()-te3.mianji()-te4.mianji();
if(Math.abs(temp)<0.0000001)
{
mianji=te1.mianji()+te2.mianji();
return true;
}
mianji=Math.min(te1.mianji()+te2.mianji(),te3.mianji()+te4.mianji());
return false;
}
double zhouchang ()
{
return line.changdu(ql[0])+line.changdu(ql[1])+line.changdu(ql[2])+line.changdu(ql[3]);
}
void lqjiaodian(line l)
{
point[] pt1=new point[4];
point[] pt2=new point[4];
point[] pt3=new point[4];
int cnt1=0,cnt2=0,cnt3=0;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
if(line.chonghe(l, ql[i]))
{
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
System.exit(0);
}
if(!line.pingxing(ql[i], l)&&ql[i].panduan(line.jiaodian(l, ql[i])))
pt2[cnt2++]=line.jiaodian(l, ql[i]);
if(l.shangxia(qp[i])==1)
pt2[cnt2++]=qp[i];
else if(l.shangxia(qp[i])==0)
pt1[cnt1++]=qp[i];
else pt3[cnt3++]=qp[i];
}
System.out.print(cnt2);
if(cnt2==2)
{
if(cnt1==0)
System.out.print(" 0.0 "+Main.zh(mianji));
else if(cnt1==1)
{
triangle te=new triangle();
te.get(pt1[0],pt2[0],pt2[1]);
System.out.print(" "+Main.zh(Math.min(Math.abs(mianji-te.mianji()),te.mianji()))+" "+Main.zh(Math.max(Math.abs(mianji-te.mianji()),te.mianji())));
}
else if(cnt1==2)
{
quadrilateral te=new quadrilateral();
int i;
i=te.create_quadrilateral(pt1[0],pt1[1],pt2[0],pt2[1]);
if(i==1)
te.create_quadrilateral(pt1[1],pt1[0],pt2[0],pt2[1]);
te.aotu();
System.out.print(" "+Main.zh(Math.min(Math.abs(mianji-te.mianji),te.mianji))+" "+Main.zh(Math.max(Math.abs(mianji-te.mianji),te.mianji)));
}
else
{
triangle te=new triangle();
te.get(pt3[0],pt2[0],pt2[1]);
System.out.print(" "+Main.zh(Math.min(mianji-te.mianji(),te.mianji()))+" "+Main.zh(Math.max(mianji-te.mianji(),te.mianji())));
}
}
}
void pqpanduan(point p)
{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
if(point.sample(p,qp[i])||(ql[i].gongxian(p)&&ql[i].panduan(p)))
{
System.out.print("on the quadrilateral");
return ;
}
triangle t1=new triangle();
triangle t2=new triangle();
triangle t3=new triangle();
triangle t4=new triangle();
t1.get(qp[0],qp[1],p);
t2.get(qp[1],qp[2],p);
t3.get(qp[2],qp[3],p);
t4.get(qp[3],qp[0],p);
if(Math.abs(t1.mianji()+t2.mianji()+t3.mianji()+t4.mianji()-mianji)<=0.000001)
System.out.print("in the quadrilateral");
else System.out.print("outof the quadrilateral");
}
}
class triangle{
point[] tp=new point[3];
line[] tl=new line[3];
double[] tlc=new double[3];
boolean get(point d,point e,point f)
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
tl[i]=new line();
if(tl[0].get(d,e)&&tl[1].get(f,e)&&tl[2].get(d,f))
{
if(line.pingxing(tl[0],tl[1]))
{
//System.out.printf("data error");
return false;
}
tp[0]=d;
tp[1]=e;
tp[2]=f;
tlc[0]=Math.sqrt((d.x-e.x)*(d.x-e.x)+(d.y-e.y)*(d.y-e.y));
tlc[1]=Math.sqrt((f.x-e.x)*(f.x-e.x)+(f.y-e.y)*(f.y-e.y));
tlc[2]=Math.sqrt((f.x-d.x)*(f.x-d.x)+(f.y-d.y)*(f.y-d.y));
return true;
}
//System.out.printf("data error");
return false;
}
boolean dengyao()
{
if(tlc[0]==tlc[1]||tlc[0]==tlc[2]||tlc[1]==tlc[2])
return true;
return false;
}
boolean dengbian()
{
if(tlc[0]==tlc[1]&&tlc[0]==tlc[2])
return true;
return false;
}
double zhouchang()
{
return tlc[0]+tlc[1]+tlc[2];
}
double mianji()
{
double p=(tlc[0]+tlc[1]+tlc[2])/2;
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-tlc[0])*(p-tlc[1])*(p-tlc[2]));
}
point zhongxin()
{
point te=new point();
te.x=(tp[0].x+tp[1].x+tp[2].x)/3;
te.y=(tp[0].y+tp[1].y+tp[2].y)/3;
return te;
}
void pdtype(){
Arrays.sort(tlc);
double tmp = tlc[0]*tlc[0]+tlc[1]*tlc[1]-tlc[2]*tlc[2];
if(Math.abs(tmp) < 0.0000001)
System.out.print("false true false");
else if(tmp < 0) System.out.print("true false false");
else System.out.print("false false true");
}
void ltjiaodian(line l)
{
point[] pt1=new point[3];
point[] pt2=new point[3];
point[] pt3=new point[3];
int cnt1=0,cnt2=0,cnt3=0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
if(line.chonghe(l, tl[i]))
{
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
System.exit(0);
}
if(!line.pingxing(tl[i], l)&&tl[i].panduan(line.jiaodian(l, tl[i])))
pt2[cnt2++]=line.jiaodian(l,tl[i]);
if(l.shangxia(tp[i])==1)
pt2[cnt2++]=tp[i];
else if(l.shangxia(tp[i])==0)
pt1[cnt1++]=tp[i];
else pt3[cnt3++]=tp[i];
}
System.out.print(cnt2);
if(cnt2==2)
{
if(cnt1==1)
{
triangle te=new triangle();
te.get(pt1[0],pt2[0],pt2[1]);
System.out.print(" "+Main.zh(Math.min(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji()))+" "+Main.zh(Math.max(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji())));
}
else
{
triangle te=new triangle();
te.get(pt3[0],pt2[0],pt2[1]);
System.out.print(" "+Main.zh(Math.min(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji()))+" "+Main.zh(Math.max(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji())));
}
}
}
void ptpanduan(point p)
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
if(point.sample(p,tp[i])||(tl[i].gongxian(p)&&tl[i].panduan(p)))
{
System.out.print("on the triangle");
return ;
}
triangle t1=new triangle();
triangle t2=new triangle();
triangle t3=new triangle();
t1.get(tp[0],tp[1],p);
t2.get(tp[0],tp[2],p);
t3.get(tp[1],tp[2],p);
if(Math.abs(t1.mianji()+t2.mianji()+t3.mianji()-this.mianji())<=0.000001)
System.out.print("in the triangle");
else System.out.print("outof the triangle");
}
}
class line {
double a,b,c;
point p1,p2;
public void prk()
{
if(this.b!=0)
System.out.print(-this.a/this.b);
else System.out.printf("Slope does not exist");
}
public void dislp(point d)
{
double ans=Math.abs(this.a*d.x+this.b*d.y+this.c)/Math.sqrt(this.a*this.a+this.b*this.b);
System.out.print(ans);
}
public boolean gongxian(point d)
{
double ans=Math.abs(this.a*d.x+this.b*d.y+this.c)/Math.sqrt(this.a*this.a+this.b*this.b);
if(Math.abs(ans)<=0.000001)
return true;
else return false;
}
public static boolean pingxing(line d,line e)
{
if(d.a==0)
{
if(e.a==0)
return true;
return false;
}
if(d.b==0)
{
if(e.b==0)
return true;
return false;
}
if(d.a*e.b==e.a*d.b)
return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean chonghe(line d,line e)
{
if(!line.pingxing(d,e))
return false;
if(d.a==0&&d.b*e.c==e.b*d.c)
return true;
if(d.a*e.c==e.a*d.c)
return true;
return false;
}
public static point jiaodian(line d,line e)
{
point te=new point();
te.x=(d.c*e.b-e.c*d.b)/(e.a*d.b-d.a*e.b);
if(d.b!=0)
te.y=-(d.a*te.x+d.c)/d.b;
else if(e.b!=0)
te.y=-(e.a*te.x+e.c)/e.b;
return te;
}
boolean panduan(point e)
{
double te=(p1.x-e.x)*(p2.x-e.x)+(p1.y-e.y)*(p2.y-e.y);
if(te<0)
return true;
return false;
}
boolean get(point d,point e)
{
if(point.sample(d,e))
{
//System.out.printf("points coincide");
return false;
}
a=d.y-e.y;
b=e.x-d.x;
c=-(a*d.x+b*d.y);
p1=d;
p2=e;
return true;
}
static double changdu(line e)
{
return Math.sqrt((e.p1.x-e.p2.x)*(e.p1.x-e.p2.x)+(e.p1.y-e.p2.y)*(e.p1.y-e.p2.y));
}
int shangxia (point e)
{
if(Math.abs(a*e.x+b*e.y+c)==0)
return 1;
if(a*e.x+b*e.y+c<0)
return 0;
return 2;
}
}
class point{
double x,y;
void setxy(String t)
{
int tmp=0;
for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++)
if(t.charAt(i)==',')
{
tmp=i;
break;
}
this.x=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(0,tmp));
this.y=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(tmp+1,t.length()));
}
public static void dis(point a,point b)
{
double te=Math.sqrt((b.x-a.x)*(b.x-a.x)+(b.y-a.y)*(b.y-a.y));
System.out.print(te);
}
public static boolean sample(point d,point e)
{
if(d.x==e.x&&d.y==e.y)
return true;
return false;
}
}
2.1.3. 设计一个银行业务类
-
思路:
照着题目要求编写即可
-
实现:
//奇数求和
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
BankBusiness.welcome();
BankBusiness account=new BankBusiness();
String a,b;
a=input.next();
b=input.next();
account.kaihu(a,b);
double x;
a=input.next();
x=input.nextDouble();
account.deposit(a, x);
a=input.next();
x=input.nextDouble();
account.withdraw(a, x);
a=input.next();
x=input.nextDouble();
account.withdraw(a, x);
a=input.next();
x=input.nextDouble();
account.withdraw(a, x);
BankBusiness.welcomeNext();
}
}
class BankBusiness{
public static String bankName="中国银行";
private String name;
private String password;
private double balance=0;
static void welcome()
{
System.out.println(bankName+"欢迎您的到来!");
}
static void welcomeNext()
{
System.out.println("请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!");
}
void kaihu(String a,String b)
{
this.name=a;
this.password=b;
}
void deposit(String a,double x)
{
if(a.equals(this.password))
{
this.balance+=x;
System.out.println("您的余额有"+this.balance+"元。");
}
else System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
}
void withdraw(String a,double x)
{
if(a.equals(this.password))
{
if(this.balance>=x)
{
this.balance-=x;
System.out.println("请取走钞票,您的余额还有"+this.balance+"元。");
}
else System.out.println("您的余额不足!");
}
else System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
}
}
复杂度分析
本次练习只分析第二题,一片飘红,惨不忍睹...
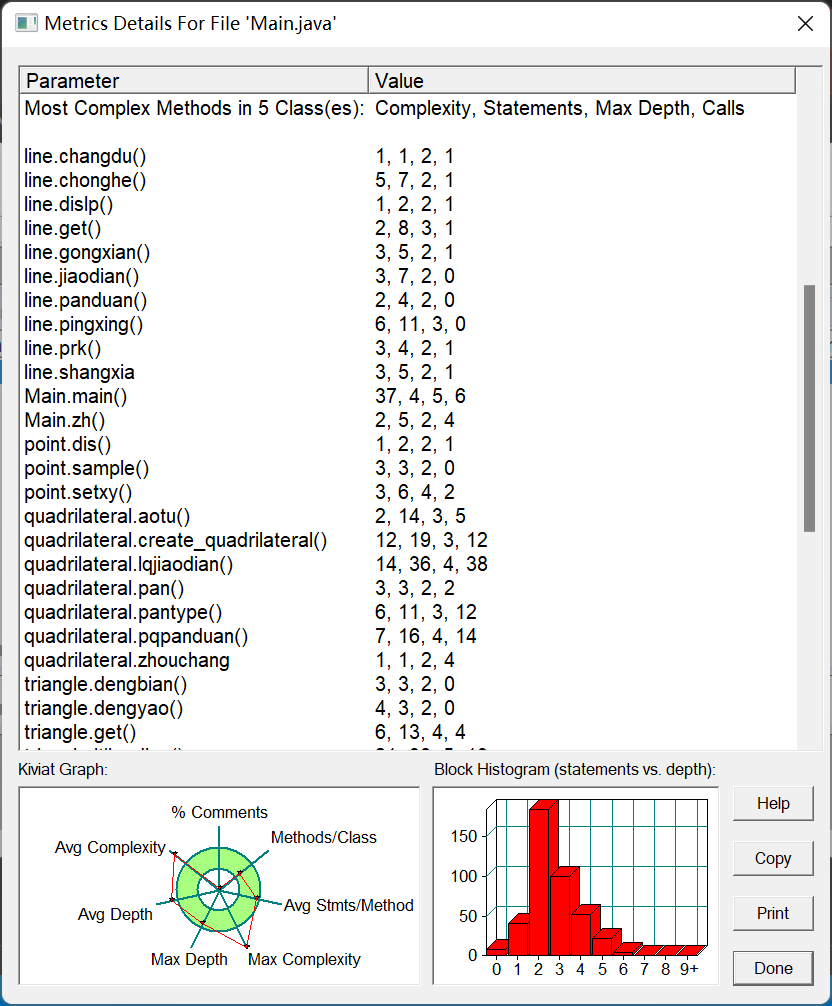
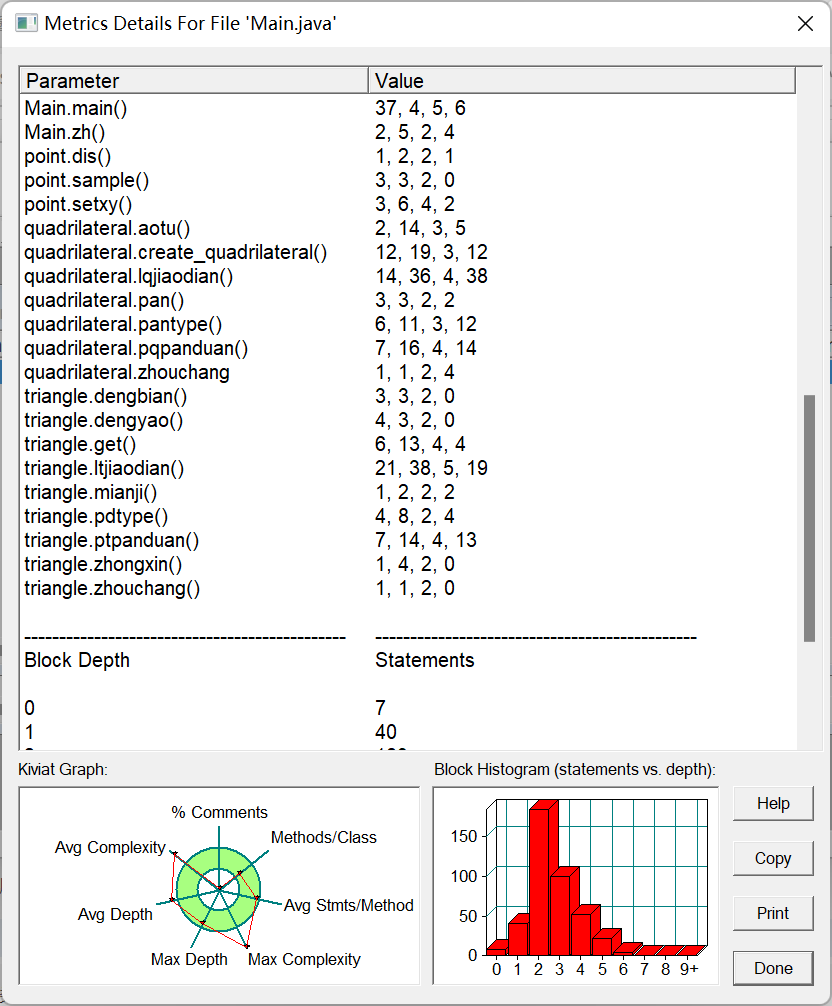
2.2. practice 5
2.2.1. 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算
-
思路:
(我第二道题的代码是沿用第一道题的代码,所以就放在一起没有分成两道题,每一个选项前都会去掉错误的输入,所以后面不再赘述了)第一个功能判断是否为五边形,循环判断是否有两点相交,相邻的边是否平行,不相邻的边是否有交点,都没有则返回true,一旦有则立马返回false
第二个功能判断凹凸,输出周长面积,判断凹凸用的是向量点乘,相邻两条边的向量点乘出现负数则为凹多边形,反之则为凸多边形,算面积用的是多边形通用的面积公式,具体百度"多边形面积公式"即可,讲的很详尽,周长就没啥好讲的,有多少条边把边长全加起来就行
第三个功能判断直线和多边形的关系,到这里前面函数的作用就有很大的体现了,直接循环判断交点,并且将直线上方或者下方的点塞入一个点集内,然后直接暴力生成多边形求面积,再用该多边形面积减生成的多边形面积得到另一块面积,最后输出一大一小两个面积(只有两个交点的情况需要后面这些操作,如不是直接输出交点数)
第四个功能判断多边形与多边形的位置关系,我这里先判的是重合,如果两个点集经过循环对比可以得到相同的多边形则判定为重合
再判两个多边形是否在对方内部,即一个多边形所有点都在另一个多边形上或者里面(因为已经判过重合所以不会出现重合判为包含的情况)
再判两个多边形是否相离,即没有交点,两个多边形都没有点在对方上面或者里面
再判两个多边形是否链接,即两个多边形都没有点在对方里面,在对方上面的点加起来不超过两个(去掉重复的),两个多边形边与边之间没交点
剩下的情况就是交错了第五个功能计算两个多边形重叠面积,由于一个多边形只会被分成两块,所以用了一个很邪教的方法,直接将两个多边形在对方上面和里面的点和边与边之间的交点放入一个点集内(经过了去重),再将点集排序成一个多边形计算面积。
排序方面就是找到这些点的重心,然后选一个点当标准的向量,通过向量点乘除以向量长度算向量夹角的余弦值再用acos算出弧度制的夹角值再进行排序(在标准向量所在直线下方的点计算夹角时需要加个3.14)第六个功能判断点是否在多边形内,先判断点是否在多边形边上或者与顶点重合,如果是则在多边形上,然后直接连接点与多边形的所有相邻两顶点构成三角形,计算这些三角形的面积和判断是否与多边形的面积相等,相等则在内部,不相等则在外部(前面用了很多次这个方法,封装好了确实省很多事,而且调用起来也舒服)
本身Main函数中还放了个对于点是否有效的判断,具体就是判断是否有点重复,是否有点在相邻两点构成的线段上,有就去掉这些点
-
实现:
//点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
point[] p=new point[10];
int[] o={0,5,5,7,10,10,6};
int i=0,flag=0,op=0;
String[] pr1={"triangle","quadrilateral","pentagon"};
String[] pr2={"in the ","on the ","outof the "};
String[] pr3={" is connected to the following "," coincides with the following "," is inside the following "," is interlaced with the following "," contains the following "};
String s=input.nextLine();
String pt="[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)$";
String pt2="[1-6]:[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)$";
for(String te:s.split(" "))
{
if(i==0)
{
if(te.matches(pt2))
{
p[i] = new point();
op=(te.charAt(0)-'0');
p[i].setxy(te.substring(2,te.length()));
i++;
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
else{
if(te.matches(pt))
{
p[i] = new point();
p[i].setxy(te);
i++;
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
}
input.close();
if(flag==1)
return ;
if(flag==0&&i!=o[op])
{
System.out.printf("wrong number of points");
return ;
}
if(op==1)
{
polygon q=new polygon();
System.out.print(q.create_polygon(p,5));
}
if(op==2)
{
polygon q=new polygon();
if(!q.create_polygon(p,5))
{
System.out.print("not a pentagon");
return ;
}
System.out.print(q.aotu());
if(q.aotu())
System.out.print(" "+Main.zh(q.zhouchang())+" "+Main.zh(q.mianji()));
}
if(op==3)
{
line l=new line();
if(!l.get(p[0],p[1])){
System.out.print("point coincide");
return ;
}
point[] tp=new point[10];
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
tp[j]=p[j+2];
tp=judge(tp);
int cnt=5;
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
if(tp[j]==null)
{
cnt=j;
break;
}
if(cnt<=2)
{
System.out.print("not a polygon");
return ;
}
polygon te=new polygon();
if(!te.create_polygon(tp,cnt))
System.out.print("not a polygon");
else te.judge_line(l);
}
if(op==4)
{
point[] tp=new point[10];
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
tp[j]=p[j];
tp=judge(tp);
int cnt=5;
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
if(tp[j]==null)
{
cnt=j;
break;
}
polygon p1=new polygon();
if(cnt<=2||!p1.create_polygon(tp,cnt))
{
System.out.print("not a polygon");
return ;
}
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
tp[j]=p[j+5];
tp=judge(tp);
cnt=5;
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
if(tp[j]==null)
{
cnt=j;
break;
}
polygon p2=new polygon();
if(cnt<=2||!p2.create_polygon(tp,cnt))
{
System.out.print("not a polygon");
return ;
}
if(polygon.judge_relationship(p1, p2)==0)
System.out.print("no overlapping area between the previous "+pr1[p1.line_cnt-3]+" and the following "+pr1[p2.line_cnt-3]);
else System.out.print("the previous "+pr1[p1.line_cnt-3]+pr3[polygon.judge_relationship(p1, p2)-1]+pr1[p2.line_cnt-3]);
}
if(op==5)
{
point[] tp=new point[10];
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
tp[j]=p[j];
tp=judge(tp);
int cnt=5;
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
if(tp[j]==null)
{
cnt=j;
break;
}
polygon p1=new polygon();
if(cnt<=2||!p1.create_polygon(tp,cnt))
{
System.out.print("not a polygon");
return ;
}
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
tp[j]=p[j+5];
tp=judge(tp);
cnt=5;
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
if(tp[j]==null)
{
cnt=j;
break;
}
polygon p2=new polygon();
if(cnt<=2||!p2.create_polygon(tp,cnt))
{
System.out.print("not a polygon");
return ;
}
System.out.print(Main.zh(polygon.chmianji(p1, p2)));
}
if(op==6)
{
point[] tp=new point[10];
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
tp[j]=p[j+1];
tp=judge(tp);
int cnt=5;
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
if(tp[j]==null)
{
cnt=j;
break;
}
if(cnt<=2)
{
System.out.print("not a polygon");
return ;
}
polygon te=new polygon();
if(!te.create_polygon(tp,cnt))
System.out.print("not a polygon");
else System.out.print(pr2[te.judge_point(p[0])]+pr1[cnt-3]);
}
}
public static String zh(double a){
String res = String.format("%.3f",a);
res = res.replaceAll("0+?$", "");
if(res.charAt(res.length()-1) == '.') res+='0';
return res;
}
public static point[] judge(point[] p)
{
point[] tp=new point[5];
point[] ttp=new point[5];
int cn=0,jj;
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
{
for(jj=0;jj<j;jj++)
if(point.sample(p[j],p[jj]))
break;
if(jj==j)
tp[cn++]=p[j];
}
for(int j=0;j<cn;j++)
{
line tl=new line();
tl.get(tp[(j-1+cn)%cn], tp[(j+1+cn)%cn]);
if(tl.gongxian(tp[j])&&tl.panduan(tp[j]))
{
for(jj=j;jj<cn-1;jj++)
tp[jj]=tp[jj+1];
j--;
cn--;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<cn;j++)
ttp[j]=tp[j];
return ttp;
}
}
class polygon{
point[] pp=new point[10];
line[] pl=new line[10];
int line_cnt;
boolean create_polygon(point[] p,int cnt)
{
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<cnt;j++)
if(point.sample(p[i], p[j]))
return false;
pp[i]=p[i];
pl[i]=new line();
pl[i].get(p[i],p[(i+1)%cnt]);
}
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++)
{
if(line.pingxing(pl[i], pl[(i+1)%cnt]))
return false;
for(int j=2;j<=cnt-2;j++)
if((!line.pingxing(pl[i],pl[(i+j)%cnt])&&pl[(i+j)%cnt].panduan(line.jiaodian(pl[i], pl[(i+j)%cnt]))&&pl[i].panduan(line.jiaodian(pl[i], pl[(i+j)%cnt]))))
return false;
}
line_cnt=cnt;
return true;
}
boolean aotu()
{
double[] x=new double[10];
double[] y=new double[10];
for(int i=0;i<line_cnt;i++)
{
x[i]=pp[i].x-pp[(i+line_cnt-1)%line_cnt].x;
y[i]=pp[i].y-pp[(i+line_cnt-1)%line_cnt].y;
}
for(int i=0;i<line_cnt;i++)
if(x[i]*x[(i+1)%line_cnt]+y[i]*y[(i+1)%line_cnt]<0)
return false;
return true;
}
double mianji()
{
double s=0;
for(int i=0;i<line_cnt;i++)
s+=pp[i].x*pp[(i+1)%line_cnt].y-pp[(i+1)%line_cnt].x*pp[i].y;
return Math.abs(s)/2;
}
double zhouchang()
{
double s=0;
for(int i=0;i<line_cnt;i++)
s+=line.changdu(pl[i]);
return s;
}
void judge_line(line l)
{
point[] pt1=new point[10];
int cnt1=0,cnt2=0;
for(int i=0;i<line_cnt;i++)
{
if(line.chonghe(l, pl[i]))
{
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
System.exit(0);
}
if(l.shangxia(pp[i])==1)
cnt2++;
if(l.shangxia(pp[i])<=1)
pt1[cnt1++]=pp[i];
if(!line.pingxing(pl[i], l)&&pl[i].panduan(line.jiaodian(l, pl[i])))
{
pt1[cnt1++]=line.jiaodian(l, pl[i]);
cnt2++;
}
}
System.out.print(cnt2);
if(cnt2==2)
{
System.out.print(" ");
polygon te=new polygon();
te.create_polygon(pt1, cnt1);
System.out.print(Main.zh(Math.min(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji()))+" "+Main.zh(Math.max(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji())));
}
}
int judge_point(point p)
{
polygon[] t=new polygon[10];
double ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<line_cnt;i++)
if(point.sample(p,pp[i])||(pl[i].gongxian(p)&&pl[i].panduan(p)))
return 1;
for(int i=0;i<line_cnt;i++)
{
t[i]=new polygon();
point[] tp={pp[i],pp[(i+1)%line_cnt],p};
t[i].create_polygon(tp, 3);
ans+=t[i].mianji();
}
if(Math.abs(ans-this.mianji())<=0.000001)
return 0;
else return 2;
}
static boolean judge_sample(polygon p1,polygon p2)
{
if(p1.line_cnt!=p2.line_cnt)
return false;
int j;
for(int i=0;i<p1.line_cnt;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<p1.line_cnt;j++)
if(!point.sample(p1.pp[j],p2.pp[(i+j)%p1.line_cnt]))
break;
if(j==p1.line_cnt)
return true;
}
return false;
}
static boolean judge_inside(polygon p1,polygon p2)
{
int cnt1=0;
for(int i=0;i<p1.line_cnt;i++)
if(p2.judge_point(p1.pp[i])<=1)
cnt1++;
if(cnt1==p1.line_cnt)
return true;
return false;
}
static boolean judge_outside(polygon p1,polygon p2)
{
for(int i=0;i<p1.line_cnt;i++)
if(p2.judge_point(p1.pp[i])<=1)
return false;
for(int i=0;i<p1.line_cnt;i++)
for(int j=0;j<p2.line_cnt;j++)
if(!line.pingxing(p1.pl[i], p2.pl[j]))
{
point te=line.jiaodian(p1.pl[i], p2.pl[j]);
if(p1.pl[i].panduan(te)&&p2.pl[j].panduan(te))
return false;
}
return true;
}
static boolean judge_link(polygon p1,polygon p2)
{
int cnt=0;
point[] tp=new point[10];
for(int i=0;i<p1.line_cnt;i++)
if(p2.judge_point(p1.pp[i])<1)
return false;
else if(p2.judge_point(p1.pp[i])==1)
{
if(point.check(tp, p1.pp[i], cnt))
tp[cnt++]=p1.pp[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<p2.line_cnt;i++)
if(p1.judge_point(p2.pp[i])<1)
return false;
else if(p1.judge_point(p2.pp[i])==1)
{
if(point.check(tp, p2.pp[i], cnt))
tp[cnt++]=p2.pp[i];
}
if(cnt>2)
return false;
for(int i=0;i<p1.line_cnt;i++)
for(int j=0;j<p2.line_cnt;j++)
if(!line.pingxing(p1.pl[i], p2.pl[j]))
{
point te=line.jiaodian(p1.pl[i], p2.pl[j]);
if(p1.pl[i].panduan(te)&&p2.pl[j].panduan(te))
return false;
}
return true;
}
static int judge_relationship(polygon p1,polygon p2)
{
if(polygon.judge_sample(p1, p2))
return 2;
if(polygon.judge_inside(p1, p2))
return 3;
if(polygon.judge_inside(p2, p1))
return 5;
if(polygon.judge_outside(p2, p1))
return 0;
if(polygon.judge_link(p2, p1))
return 1;
return 4;
}
static point[] area(polygon p1,polygon p2)
{
int cnt=0;
point[] te=new point[10];
for(int i=0;i<p1.line_cnt;i++)
{
if(p2.judge_point(p1.pp[i])<=1)
{
if(point.check(te,p1.pp[i], cnt))
te[cnt++]=p1.pp[i];
}
if(p1.judge_point(p2.pp[i])<=1)
{
if(point.check(te,p2.pp[i], cnt))
te[cnt++]=p2.pp[i];
}
for(int j=0;j<p2.line_cnt;j++)
if(!line.pingxing(p1.pl[i], p2.pl[j]))
{
point tp=line.jiaodian(p1.pl[i], p2.pl[j]);
if(p1.pl[i].panduan(tp)&&p2.pl[j].panduan(tp))
te[cnt++]=tp;
}
}
return te;
}
static point[] sort(point[] p,int cnt)
{
point zx=new point();
line[] ll=new line[10];
zx.x=0;
zx.y=0;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++)
{
zx.x+=p[i].x;
zx.y+=p[i].y;
}
zx.x/=cnt;
zx.y/=cnt;
if(point.sample(p[0], zx))
{
point temp=new point();
temp=p[0];
p[0]=p[1];
p[1]=temp;
}
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++)
{
ll[i]=new line();
ll[i].get(zx, p[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<cnt;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<cnt;j++)
if(line.cos(ll[i],ll[0])>line.cos(ll[j],ll[0]))
{
point temp=new point();
temp=p[i];
p[i]=p[j];
p[j]=temp;
line temp1=new line();
temp1=ll[i];
ll[i]=ll[j];
ll[j]=temp1;
}
return p;
}
static double chmianji(polygon p1,polygon p2)
{
if(polygon.judge_inside(p1, p2))
return p1.mianji();
if(polygon.judge_inside(p2, p1))
return p2.mianji();
if(polygon.judge_outside(p2, p1))
return 0;
point[] tp=polygon.area(p1, p2);
int cnt=10;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
if(tp[i]==null)
{
cnt=i;
break;
}
if(cnt<=2)
return 0;
tp=polygon.sort(tp,cnt);
polygon ttp=new polygon();
ttp.create_polygon(tp,cnt);
return ttp.mianji();
}
}
class line {
double a,b,c;
point p1,p2;
public boolean gongxian(point d)
{
double ans=Math.abs(this.a*d.x+this.b*d.y+this.c)/Math.sqrt(this.a*this.a+this.b*this.b);
if(Math.abs(ans)==0)
return true;
else return false;
}
public static boolean pingxing(line d,line e)
{
if(d.a==0)
{
if(e.a==0)
return true;
return false;
}
if(d.b==0)
{
if(e.b==0)
return true;
return false;
}
if(d.a*e.b==e.a*d.b)
return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean chonghe(line d,line e)
{
if(!line.pingxing(d,e))
return false;
if(d.a==0)
if(d.b*e.c==e.b*d.c)
return true;
else return false;
if(d.a*e.c==e.a*d.c)
return true;
return false;
}
public static point jiaodian(line d,line e)
{
point te=new point();
te.x=(d.c*e.b-e.c*d.b)/(e.a*d.b-d.a*e.b);
if(d.b!=0)
te.y=-(d.a*te.x+d.c)/d.b;
else if(e.b!=0)
te.y=-(e.a*te.x+e.c)/e.b;
return te;
}
boolean panduan(point e)
{
double te=(p1.x-e.x)*(p2.x-e.x)+(p1.y-e.y)*(p2.y-e.y);
if(te<0)
return true;
return false;
}
boolean panduan1(point e)
{
double te=(p1.x-e.x)*(p2.x-e.x)+(p1.y-e.y)*(p2.y-e.y);
if(te<=0)
return true;
return false;
}
boolean get(point d,point e)
{
if(point.sample(d,e))
return false;
a=d.y-e.y;
b=e.x-d.x;
c=-(a*d.x+b*d.y);
p1=d;
p2=e;
return true;
}
static double changdu(line e)
{
return Math.sqrt((e.p1.x-e.p2.x)*(e.p1.x-e.p2.x)+(e.p1.y-e.p2.y)*(e.p1.y-e.p2.y));
}
int shangxia (point e)
{
if(a*e.x+b*e.y+c==0)
return 1;
if(a*e.x+b*e.y+c<0)
return 0;
return 2;
}
static double cos(line d,line e)
{
double te1=(d.p2.x-d.p1.x)*(e.p2.x-e.p1.x)+(d.p2.y-d.p1.y)*(e.p2.y-e.p1.y);
te1=te1/line.changdu(d)/line.changdu(e);
if(e.shangxia(d.p2)==0)
return 6.28-Math.acos(te1);
return Math.acos(te1);
}
}
class point{
double x,y;
void setxy(String t)
{
int tmp=0;
for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++)
if(t.charAt(i)==',')
{
tmp=i;
break;
}
this.x=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(0,tmp));
this.y=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(tmp+1,t.length()));
}
public static void dis(point a,point b)
{
double te=Math.sqrt((b.x-a.x)*(b.x-a.x)+(b.y-a.y)*(b.y-a.y));
System.out.print(te);
}
public static boolean sample(point d,point e)
{
if(d.x==e.x&&d.y==e.y)
return true;
return false;
}
static boolean check(point[] p,point tp,int cnt)
{
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++)
if(point.sample(p[i], tp))
return false;
return true;
}
}
复杂度分析
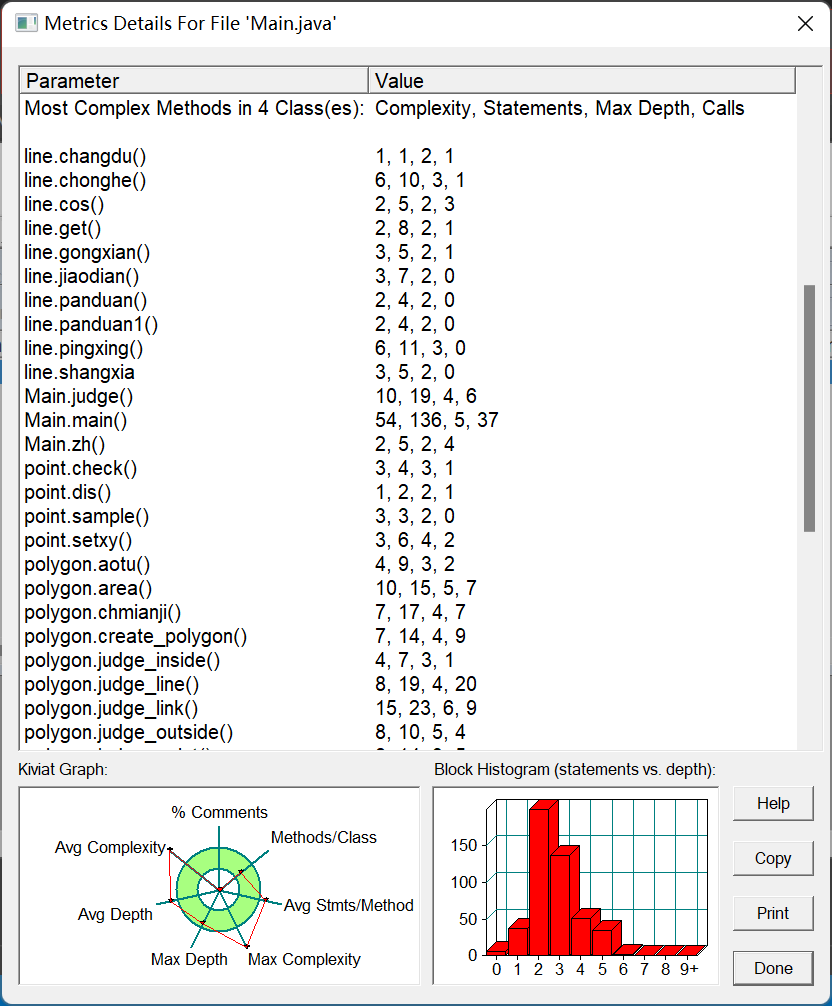
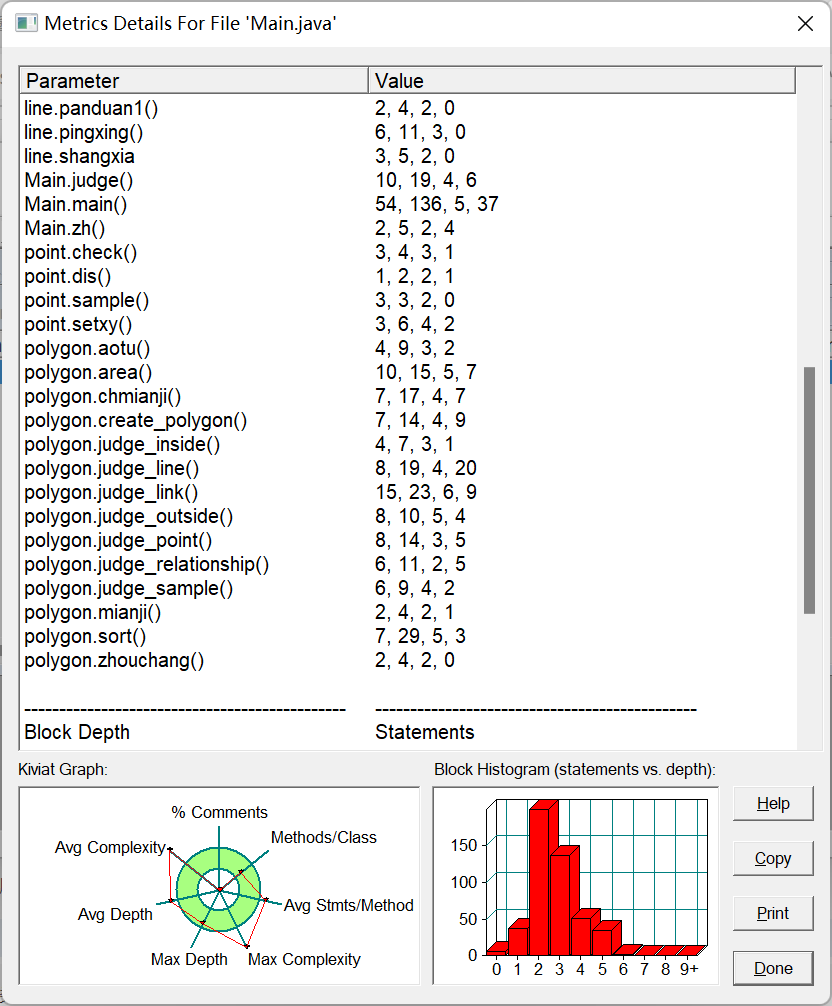
这次写的比较精简,但是老毛病还在,主函数圈复杂度很高,if else用的很麻...
2.3. 期中考试
2.3.1. 点与线(类设计)
-
思路:
按照给的类图编写即可
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double data;
Point p1=new Point();
Point p2=new Point();
data=input.nextDouble();
if(data<=0||data>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
data=Main.zh(data);
p1.setX(data);
data=input.nextDouble();
if(data<=0||data>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
data=Main.zh(data);
p1.setY(data);
data=input.nextDouble();
if(data<=0||data>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
data=Main.zh(data);
p2.setX(data);
data=input.nextDouble();
if(data<=0||data>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
data=Main.zh(data);
p2.setY(data);
String s=input.nextLine();
s=input.nextLine();
Line l1=new Line(p1,p2,s);
l1.display();
input.close();
}
public static double zh(double a){
String res = String.format("%.2f",a);
return Double.parseDouble(res);
}
}
class Line {
private Point point1,point2;
private String color;
public Line(){
}
public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
this.point1=p1;
this.point2=p2;
this.color=color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getDistance()
{
return Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY()));
}
public void display()
{
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
this.point1.display();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
this.point2.display();
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f",getDistance());
}
}
class Point{
private double x,y;
public Point(){
}
public Point(double x,double y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.getX(),this.getY());
}
}
2.3.2. 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
-
思路:
在上一题的基础上加了个抽象父类,还是不难,按照类图编写即可
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double data;
Element element;
Point p1=new Point();
Point p2=new Point();
data=input.nextDouble();
if(data<=0||data>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
p1.setX(data);
data=input.nextDouble();
if(data<=0||data>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
p1.setY(data);
data=input.nextDouble();
if(data<=0||data>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
p2.setX(data);
data=input.nextDouble();
if(data<=0||data>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
p2.setY(data);
String s=input.nextLine();
s=input.nextLine();
Line l1=new Line(p1,p2,s);
Plane plane=new Plane(s);
element=p1;
element.display();
element=p2;
element.display();
element=l1;
element.display();
element=plane;
element.display();
input.close();
}
public static double zh(double a){
String res = String.format("%.2f",a);
return Double.parseDouble(res);
}
}
abstract class Element{
abstract void display();
}
class Plane extends Element{
private String color;
public Plane(){
}
public Plane(String color){
this.color=color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public void display()
{
System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+this.getColor());
}
}
class Line extends Element{
private Point point1,point2;
private String color;
public Line(){
}
public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
this.point1=p1;
this.point2=p2;
this.color=color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getDistance()
{
return Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY()));
}
@Override
public void display()
{
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
this.point1.display();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
this.point2.display();
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n",Main.zh(getDistance()));
}
}
class Point extends Element{
private double x,y;
public Point(){
}
public Point(double x,double y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
@Override
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.getX(),this.getY());
}
}
2.3.3. 点线面问题再重构(容器类)
-
思路:
就多了个容器类...(你知道我想说什么吧) -
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String data,color,s;
double data1,data2;
Point p1,p2;
GeometryObject geometryObject=new GeometryObject();
int choice = input.nextInt();
while(choice != 0) {
s=input.nextLine();
switch(choice) {
case 1://insert Point object into list
data=input.nextLine();
data1=Double.parseDouble(data);
if(data1<=0||data1>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
data=input.nextLine();
data2=Double.parseDouble(data);
if(data2<=0||data2>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
p1=new Point(data1, data2);
geometryObject.add(p1);
break;
case 2://insert Line object into list
data=input.nextLine();
data1=Double.parseDouble(data);
if(data1<=0||data1>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
data=input.nextLine();
data2=Double.parseDouble(data);
if(data2<=0||data2>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
p1=new Point(data1, data2);
data=input.nextLine();
data1=Double.parseDouble(data);
if(data1<=0||data1>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
data=input.nextLine();
data2=Double.parseDouble(data);
if(data2<=0||data2>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
p2=new Point(data1, data2);
color=input.nextLine();
Line line=new Line(p1, p2, color);
geometryObject.add(line);
break;
case 3://insert Plane object into list
color=input.nextLine();
Plane plane=new Plane(color);
geometryObject.add(plane);
break;
case 4://delete index - 1 object from list
int index = input.nextInt();
if(index<=geometryObject.getList().size())
geometryObject.remove(index);
}
choice = input.nextInt();
}
for(Element element:geometryObject.getList())
element.display();
}
public static double zh(double a){
String res = String.format("%.2f",a);
return Double.parseDouble(res);
}
}
class GeometryObject{
private ArrayList<Element> list=new ArrayList<Element>();
public GeometryObject(){
}
public void add(Element element)
{
list.add(element);
}
public void remove(int index)
{
list.remove(index-1);
}
public ArrayList<Element> getList() {
return list;
}
}
abstract class Element{
abstract void display();
}
class Plane extends Element{
private String color;
public Plane(){
}
public Plane(String color){
this.color=color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public void display()
{
System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+this.getColor());
}
}
class Line extends Element{
private Point point1,point2;
private String color;
public Line(){
}
public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
this.point1=p1;
this.point2=p2;
this.color=color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getDistance()
{
return Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY()));
}
@Override
public void display()
{
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
this.point1.display();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
this.point2.display();
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n",Main.zh(getDistance()));
}
}
class Point extends Element{
private double x,y;
public Point(){
}
public Point(double x,double y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
@Override
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.getX(),this.getY());
}
}
复杂度分析
第一题:
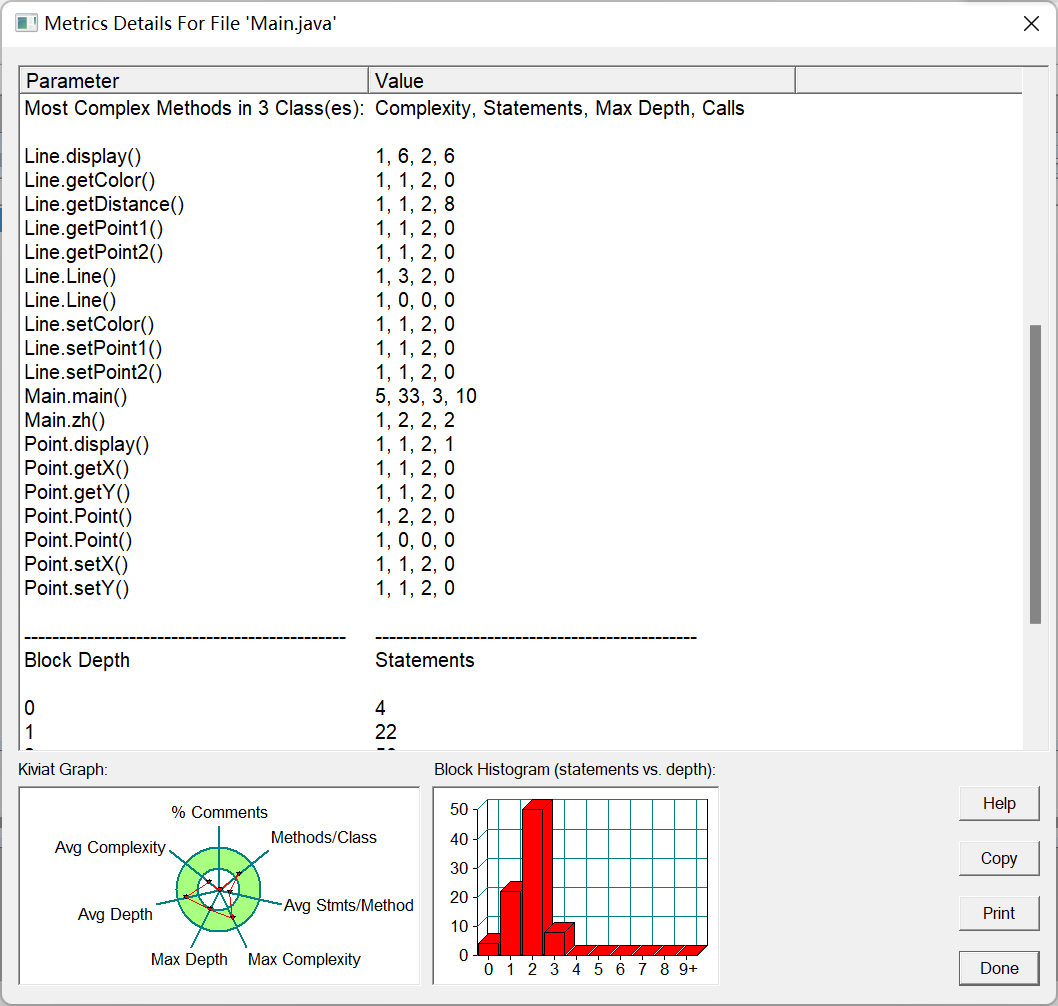
还行
第二题:
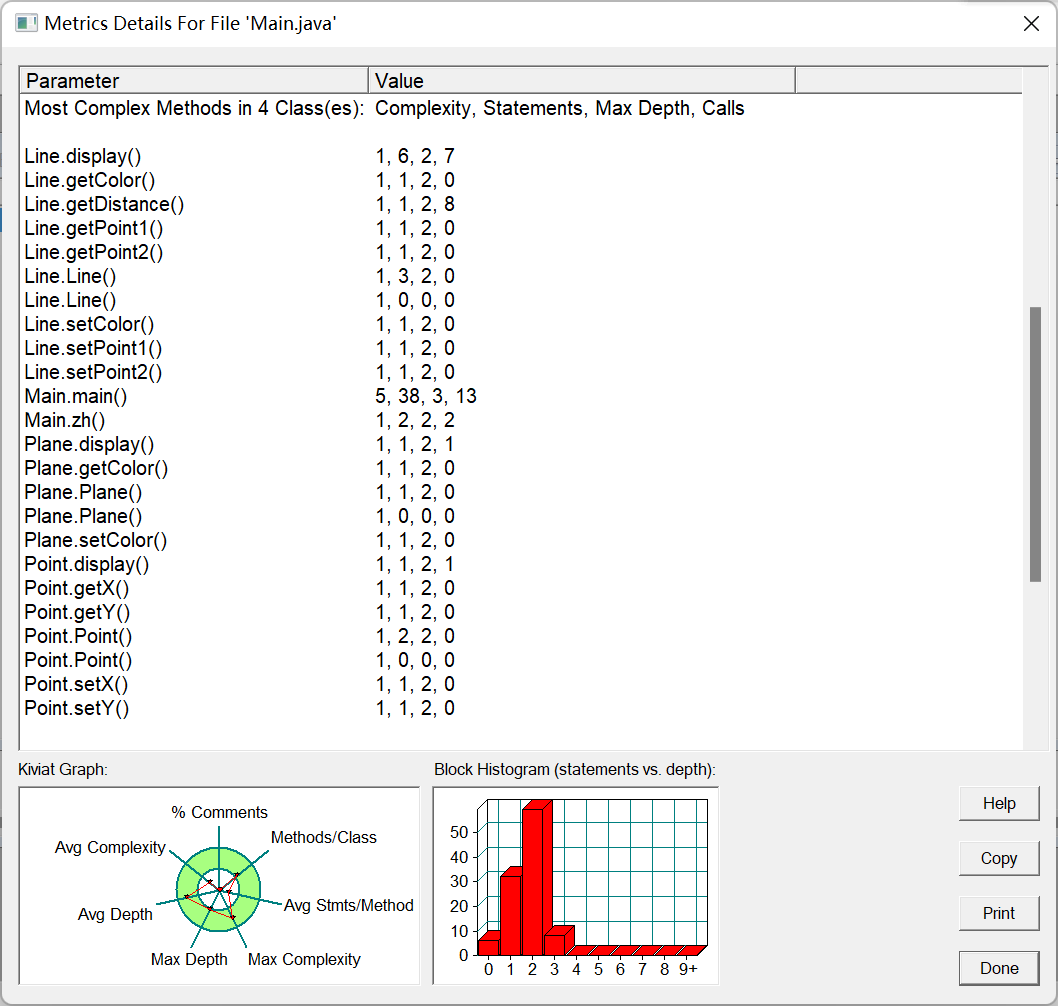
大多数处理都在主函数,所以主函数复杂度很高
第三题:
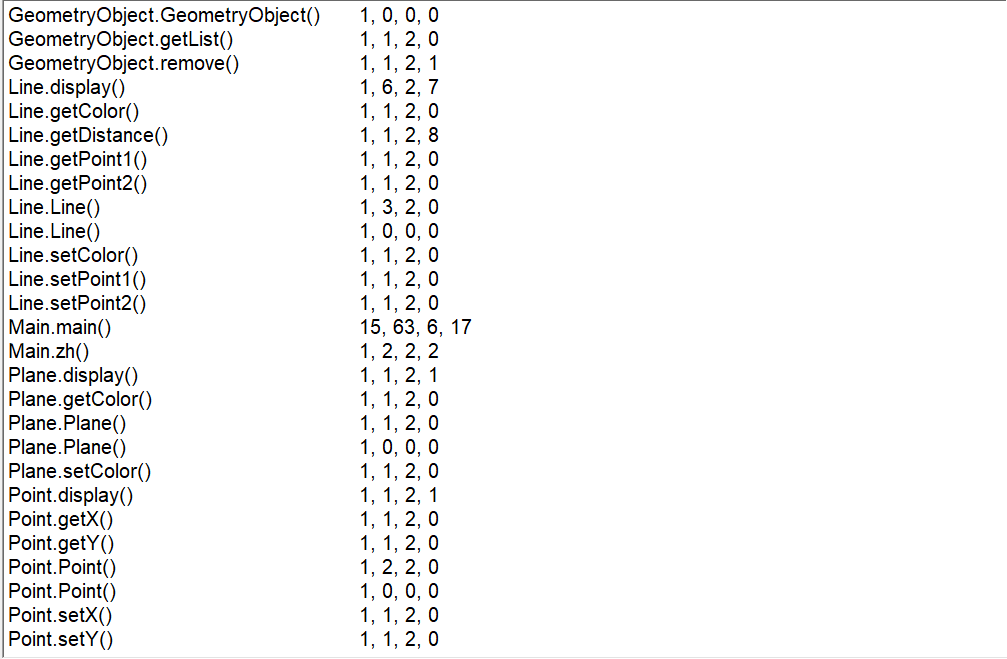
大多数处理都在主函数,所以主函数复杂度很高
3. 踩坑心得
其实前言里说的差不多了,也没有遇到很复杂的问题,对于图形类的计算主要还是本身这方面的知识少,才走了一大堆弯路,而输入输出的问题也是一个蛮大的要考虑的点,各种转格式啊类型转化啊还有判断输入是否合法,需要多加留意,免得出错
4. 改进建议
熟练运用父类与子类!!!可以减少很多问题,而且函数一定要封装好,用起来就会方便。后面也免得重写。
5. 总结
关于java中的父类与子类
子类是可以继承父类的方法的,而且抽象父类的方法可以在子类中改写,在实际运用的时候就非常方便不需要对于多种情况多种考虑,直接将具有相同属性的类继承同一个父类即可。
关于java中Arraylist类
Arraylist是链表,支持add,remove等多种已经写好的方法,作为一个不定长的数组非常的实用。
图形类一开始没写好导致多次重写,所以一定要慎重,要考虑全面,不然就会很难受。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号