南昌航空大学1-3次大作业心得
1. 前言
学新语言真的很难受很不适应,虽然题目简单但真的耗费了很多时间
对于前三次的作业:
第一次作业我认为最大的难点第一次接触java语言,各种语法和格式只能通过网络搜索+以前学过的语言的语法来尝试和理解;
第二次作业我认为最大的难点是java数组的特殊性,和String类的相关API的学习;
第三次作业我认为最大的难点是寻找好的方法,可以有更优的复杂度并且减少精度损失;
2. 设计与分析
2.1. practice 1
2.1.1. 身体质量指数(BMI)测算
- 思路
个人认为是输入输出题,简单判断和计算即可
- 实现
//身体质量指数(BMI)测算
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
float x=input.nextFloat();
float y=input.nextFloat();
if(x<=0||x>727||y<0||y>2.72)
System.out.println("input out of range");
else {
float z=x/(y*y);
if(z<18.5)
System.out.println("thin");
else if(z>=18.5&&z<24)
System.out.println("fit");
else if(z>=24&&z<28)
System.out.println("overweight");
else System.out.println("fat");
}
}
}
2.1.2. 长度质量计量单位换算
- 思路:
注意最后答案数据类型要转换为float型
- 实现:
//长度质量计量单位换算
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double x=input.nextDouble();
double y=input.nextDouble();
double z=x/0.45359237;
double t=y/0.0254;
System.out.print((float)z);
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.print((float)t);
}
}
2.1.3. 奇数求和
-
思路:
个人认为是想让我们设置一个数组记录所有数字,然后遍历数组求奇数和,但可以不断赋值给同一个值,然后判断就行,个人比较谨慎用了long类型的变量,注意负数的存在
-
实现:
//奇数求和
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
long sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
long x=input.nextLong();
if(x%2==1||x%2==-1)
sum+=x;
}
System.out.print(sum);
}
}
2.1.4. 房产税费计算2022
-
思路:
按题意模拟
-
实现:
//房产税费计算2022
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int x=input.nextInt();
int y=input.nextInt();
int z=input.nextInt();
double t=input.nextDouble();
double x1,x2,x3,x4;
if(x==1&&t<=144)
{
if(t<=90)
x1=100*z;
else x1=150*z;
}
else x1=300*z;
x2=y*5;
x3=3*t;
x4=1.36*t;
System.out.print((float)x1);
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.print((float)x2);
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.print((float)x3);
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.print((float)x4);
}
}
2.1.5. 游戏角色选择
- 思路:
两个变量强行if else判断
- 实现:
//游戏角色选择
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int x=input.nextInt();
int y=input.nextInt();
if(x<1||x>4||y<1||y>3)
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
else {
if(x==1)
System.out.printf("人类 ");
else if(x==2)
System.out.printf("精灵 ");
else if(x==3)
System.out.printf("兽人 ");
else if(x==4)
System.out.printf("暗精灵 ");
if(y==1)
System.out.printf("战士");
else if(y==2)
System.out.printf("法师");
else if(y==3)
System.out.printf("射手");
}
}
}
2.1.6.学号识别
-
思路:
写的时候不会处理字符串所以转化为字符数组了,强行对给的字符串进行if else判断
-
实现:
//学号识别
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
char[] stu=new char[10];
String s=input.next();
if(s.length()!=8)
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
else {
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
stu[i]=s.charAt(i);
if((stu[2]=='0'&&stu[3]=='1')||(stu[2]=='0'&&stu[3]=='2')||(stu[2]=='0'&&stu[3]=='3')||(stu[2]=='2'&&stu[3]=='0'))
{
System.out.printf("入学年份:20");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
System.out.print(stu[i]);
System.out.println("年");
if(stu[2]=='0'&&stu[3]=='1')
System.out.println("学院:材料学院");
else if(stu[2]=='0'&&stu[3]=='2')
System.out.println("学院:机械学院");
else if(stu[2]=='0'&&stu[3]=='3')
System.out.println("学院:外语学院");
else if(stu[2]=='2'&&stu[3]=='0')
System.out.println("学院:软件学院");
System.out.printf("班级:");
for(int i=4;i<6;i++)
System.out.print(stu[i]);
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("学号:");
for(int i=6;i<8;i++)
System.out.print(stu[i]);
}
else System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
2.1.7. 巴比伦法求平方根近似值
-
思路:
输入输出题,注意精度问题
-
实现:
//巴比伦法求平方根近似值
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
float x=input.nextFloat();
float y=input.nextFloat();
float z;
if(x<0||y<=0)
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
else {
z=(y+x/y)/2;
while(z-y>=0.00001||y-z>=0.00001)
{
y=z;
z=(y+x/y)/2;
}
System.out.print(y);
}
}
}
2.1.8. 二进制数值提取
-
思路:
暴力查找'-1'匹配到则输出之前存储的01串,没匹配到则输出Wrong Format
-
实现:
//二进制数值提取
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String s=input.nextLine();
char[] st=new char[1000];
int flag=0,j=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
if(s.charAt(i)=='-'&&s.charAt(i+1)=='1')
{
flag=1;
//System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
if(s.charAt(i)=='0'||s.charAt(i)=='1')
st[j++]=s.charAt(i);
}
if(flag==0)
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
else for(int i=0;i<j;i++)
System.out.print(st[i]);
}
}
2.1.9. 判断三角形类型
-
思路:
三个边硬判断即可,也可以存数组排序找出最大边后再判断,可以少很多条件
-
实现:
//判断三角形类型
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double x=input.nextDouble();
double y=input.nextDouble();
double z=input.nextDouble();
if(x<1||x>200||y<1||y>200||z<1||z>200)
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
else {
if(x+y<=z||x+z<=y||y+z<=x)
System.out.printf("Not a triangle");
else if(x==y&&y==z)
System.out.printf("Equilateral triangle");
else if((x==y&&Math.abs(x*x+y*y-z*z)<0.00001)||(x==z&&Math.abs(x*x+z*z-y*y)<0.00001)||(z==y&&Math.abs(y*y+z*z-x*x)<0.00001))
System.out.printf("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
else if(x==y||y==z||z==x)
System.out.printf("Isosceles triangle");
else if(x*x+y*y==z*z||z*z+y*y==x*x||x*x+z*z==y*y)
System.out.printf("Right-angled triangle");
else System.out.printf("General triangle");
}
}
}
复杂度分析
本次练习大多都是if else判断以及简单计算,复杂度并不高,省略了
2.2. practice 2
2.2.1. 字母-数字转换
-
思路:
循环遍历字符串判断是否合法;
利用String.charAt() - ‘a’ + 1转数字(大写则为String.charAt() - ‘A’ + 1) -
实现:
//字母-数字转换
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String s=input.nextLine();
int[] st=new int[1000];
int flag=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
if(s.charAt(i)>='a'&&s.charAt(i)<='z')
st[i]=(s.charAt(i)-'a')+1;
else if(s.charAt(i)>='A'&&s.charAt(i)<='Z')
st[i]=(s.charAt(i)-'A')+1;
else {
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==1)
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
else for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
System.out.print(st[i]);
}
}
2.2.2. 串口字符解析
-
思路:
一个信号由起始位(1),数据位(8),奇偶判断位(1),结束位(1)共 11 位组成;
先遍历字符串,设置一个flag代表有无信号出现,按照0的数量和字符串长度判断是否有信号的出现
在判断信号是否合法时先判断结束位是否为1,在判断奇偶位的正确性(注意:当数据位1的个数为奇数时,奇偶位为0,反之则为1)正确则输出并且将序号++; -
实现:
//串口字符解析
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String s=input.nextLine();
int[] st=new int[10];
int flag=0,ca=1;;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
if(s.charAt(i)=='0')
{
flag=1;
break;
}
if(s.length()<11||flag==0)
System.out.printf("null data");
else{
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
if(s.charAt(i)=='0'&&i<s.length()-10)
{
int j=i+1,sum=0,cnt=0;
for(;j<=i+8&&j<s.length()-2;j++)
{
st[cnt]=s.charAt(j)-'0';
sum+=st[cnt];
cnt++;
}
System.out.printf("%d:",ca);
if(s.charAt(j+1)!='1')
System.out.println("validate error");
else if((sum+1)%2!=(s.charAt(j)-'0'))
System.out.println("parity check error");
else {
for(int o=0;o<8;o++)
System.out.print(st[o]);
System.out.println("");
}
ca++;
i=j+1;
}
}
}
}
}
2.2.3. String的格式判断与内容提取
-
思路:
- 学生为17,18,19,20届软件学院人员,所以学号前四位在(2020,1920,1820,1720)中;
- 长度不是8位直接判错;
- 只要有一个学号不合法直接结束程序;
- 如果没提前结束则输出所有合法数据;
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String s=input.nextLine();
int[] st=new int[1000];
int j=0,flag=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i+=8)
{
if(i<s.length()&&i+8>s.length())
{
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
if(s.charAt(i+2)!='2'||s.charAt(i+3)!='0')
{
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
else if((s.charAt(i)=='2'&&s.charAt(i+1)=='0')||(s.charAt(i)=='1'&&s.charAt(i+1)=='9')||(s.charAt(i)=='1'&&s.charAt(i+1)=='8')||(s.charAt(i)=='1'&&s.charAt(i+1)=='7'))
{
if((s.charAt(i)=='2'&&s.charAt(i+1)=='0')&&((s.charAt(i+4)=='1'&&s.charAt(i+5)=='7')||(s.charAt(i+4)=='6'&&s.charAt(i+5)=='1')))
st[j++]=(s.charAt(i+4)-'0')*1000+(s.charAt(i+5)-'0')*100+(s.charAt(i+6)-'0')*10+(s.charAt(i+7)-'0');
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)
for(int i=0;i<j;i++)
{
System.out.print(st[i]);
if(i!=j-1)
System.out.printf(" ");
}
}
}
复杂度分析
按照要求,本次练习只分析第二题:

CogC是认知复杂度
ev(G)基本复杂度是用来衡量程序非结构化程度的。
Iv(G)模块设计复杂度是用来衡量模块判定结构,即模块和其他模块的调用关系。
v(G)是用来衡量一个模块判定结构的复杂程度,数量上表现为独立路径的条数。
2.3. practice 3
2.3.1. 点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离
-
思路:
-
采用正则表达式对每一个输入的点进行判断,有不满足的就输出“Wrong format”
-
采用Double.parsedouble函数将匹配成功字符串中的x,y提取出来,构成一个点
-
调用point.dis即可
-
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
point[] p=new point[10];
int i=0,flag=0;
String s=input.next();
String pt="[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)";
while(true)
{
if(s.matches(pt))
{
p[i] = new point();
p[i].getx(s);
i++;
if(!input.hasNext())
break;
s=input.next();
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
if(flag==0&&(i>2||i<=1))
System.out.printf("wrong number of points");
else if(i==2)
point.dis(p[0],p[1]);
input.close();
}
}
class point{
double x;
double y;
void getx(String t)
{
int tmp=0;
for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++)
if(t.charAt(i)==',')
{
tmp=i;
break;
}
x=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(0,tmp));
y=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(tmp+1,t.length()));
}
void pr()
{
System.out.printf("%f %f\n",x,y);
}
static void dis(point a,point b)
{
double te=Math.sqrt((b.x-a.x)*(b.x-a.x)+(b.y-a.y)*(b.y-a.y));
System.out.print(te);
}
}
2.3.2. 点线形系列2-线的计算
-
思路:
- 正则表达式和之前一致,多了一个判断开头的正则表达式,检测输入的函数变为了input.nextLine();
2.如果两点构成直线不成功(两点重合)则输出points coincide
-
op == 1: 调用line.prk函数
-
op == 2:调用line.dislp函数
-
cmd == 3:调用line.gongxian函数(通过判断点到直线距离来判断点是否在线上)
-
cmd == 4:调用Line.pingxing函数
-
cmd == 5:先调用Line.pingxing函数特判平行,在调用Line.jiaodian函数获取两线段交点,再调用Line.panduan函数判断交点是否在两条线段的任一条内
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
point[] p=new point[10];
int[] o={0,2,3,3,4,4};
int i=0,flag=0,op=0;
String s=input.nextLine();
String pt="[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)$";
String pt2="[1-5]:[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)$";
for(String te:s.split(" "))
{
if(i==0)
{
if(te.matches(pt2))
{
p[i] = new point();
op=(te.charAt(0)-'0');
p[i].setxy(te.substring(2,te.length()));
i++;
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
else{
if(te.matches(pt))
{
p[i] = new point();
p[i].setxy(te);
i++;
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
}
if(flag==0&&i!=o[op])
System.out.printf("wrong number of points");
else if(flag==0)
{
if(op==1)
{
line l=new line();
if(l.get(p[0],p[1])==1)
l.prk();
}
else if(op==2)
{
line l=new line();
if(l.get(p[1],p[2])==1)
l.dislp(p[0]);
}
else if(op==3)
{
line l=new line();
if(l.get(p[1],p[2])==1)
l.gongxian(p[0]);
}
else if(op==4)
{
line l=new line();
line l1=new line();
if(l.get(p[0],p[1])==1&&l1.get(p[2],p[3])==1)
{
if(line.pingxing(l,l1))
System.out.printf("true");
else System.out.printf("false");
}
}
else
{
line l=new line();
line l1=new line();
point te=new point();
if(l.get(p[0],p[1])==1&&l1.get(p[2],p[3])==1)
{
if(line.pingxing(l,l1))
System.out.printf("is parallel lines,have no intersection point");
else {
te=line.jiaodian(l,l1);
System.out.print(te.x+","+te.y);
if(l.panduan(te)&&l1.panduan(te))
System.out.printf(" false");
else System.out.printf(" true");
}
}
}
}
input.close();
}
}
class line {
double a,b,c;
point p1,p2;
public void prk()
{
if(this.b!=0)
System.out.print(-this.a/this.b);
else System.out.printf("Slope does not exist");
}
public void dislp(point d)
{
double ans=Math.abs(this.a*d.x+this.b*d.y+this.c)/Math.sqrt(this.a*this.a+this.b*this.b);
System.out.print(ans);
}
public boolean gongxian(point d)
{
double ans=Math.abs(this.a*d.x+this.b*d.y+this.c)/Math.sqrt(this.a*this.a+this.b*this.b);
if(Math.abs(ans)<=0.000001)
return true;
else return false;
}
public static boolean pingxing(line d,line e)
{
if(d.a==0)
{
if(e.a==0)
return true;
return false;
}
if(d.b==0)
{
if(e.b==0)
return true;
return false;
}
if(d.a*e.b==e.a*d.b)
return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean chonghe(line d,line e)
{
if(!line.pingxing(d,e))
return false;
if(d.a==0&&d.b*e.c==e.b*d.c)
return true;
if(d.a*e.c==e.a*d.c)
return true;
return false;
}
public static point jiaodian(line d,line e)
{
point te=new point();
te.x=(d.c*e.b-e.c*d.b)/(e.a*d.b-d.a*e.b);
if(d.b!=0)
te.y=-(d.a*te.x+d.c)/d.b;
else if(e.b!=0)
te.y=-(e.a*te.x+e.c)/e.b;
return te;
}
boolean panduan(point e)
{
double te=(p1.x-e.x)*(p2.x-e.x)+(p1.y-e.y)*(p2.y-e.y);
if(te<0)
return true;
return false;
}
boolean get(point d,point e)
{
if(point.sample(d,e))
{
//System.out.printf("points coincide");
return false;
}
a=d.y-e.y;
b=e.x-d.x;
c=-(a*d.x+b*d.y);
p1=d;
p2=e;
return true;
}
static double changdu(line e)
{
return Math.sqrt((e.p1.x-e.p2.x)*(e.p1.x-e.p2.x)+(e.p1.y-e.p2.y)*(e.p1.y-e.p2.y));
}
int shangxia (point e)
{
if(Math.abs(a*e.x+b*e.y+c)==0)
return 1;
if(a*e.x+b*e.y+c<0)
return 0;
return 2;
}
}
class point{
double x,y;
void setxy(String t)
{
int tmp=0;
for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++)
if(t.charAt(i)==',')
{
tmp=i;
break;
}
this.x=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(0,tmp));
this.y=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(tmp+1,t.length()));
}
public static void dis(point a,point b)
{
double te=Math.sqrt((b.x-a.x)*(b.x-a.x)+(b.y-a.y)*(b.y-a.y));
System.out.print(te);
}
public static boolean sample(point d,point e)
{
if(d.x==e.x&&d.y==e.y)
return true;
return false;
}
}
2.3.3. 点线形系列3-三角形的计算
-
思路:
-
前几点和前两题差不多,相当于初始化操作
-
op == 1:调用triangle.dengyao函数 和 triangle.dengbian函数即可
-
op == 2:调用triangle.zhouchang,triangle.mianji函数即可
-
op == 3:调用triangle.pdtype函数即可
-
op == 4:先判断直线是否能构成,再调用triangle.ltjiaodian函数即可(该函数判断三角形三条边和直线是否有交点,通过交点数量以及交的边来生成三角形算面积,再用大三角形面积减小三角形面积来求出另一部分的面积)
-
op == 5:调用triangle.ptpanduan函数即可
-
-
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
point[] p=new point[10];
int[] o={0,3,3,3,5,4};
int i=0,flag=0,op=0;
String s=input.nextLine();
String pt="[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)$";
String pt2="[1-5]:[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?),[-+]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?)$";
for(String te:s.split(" "))
{
if(i==0)
{
if(te.matches(pt2))
{
p[i] = new point();
op=(te.charAt(0)-'0');
p[i].setxy(te.substring(2,te.length()));
i++;
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
else{
if(te.matches(pt))
{
p[i] = new point();
p[i].setxy(te);
i++;
}
else {
flag=1;
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
}
input.close();
if(flag==0&&i!=o[op])
System.out.printf("wrong number of points");
else if(flag==0)
{
if(op==1)
{
triangle t=new triangle();
if(t.get(p[0],p[1],p[2]))
System.out.print(t.dengyao()+" "+t.dengbian());
}
else if(op==2)
{
triangle t=new triangle();
if(t.get(p[0],p[1],p[2]))
{
System.out.print(Main.zh(t.zhouchang())+" "+Main.zh(t.mianji())+" ");
point te=t.zhongxin();
System.out.print(Main.zh(te.x)+","+Main.zh(te.y));
}
}
else if(op==3)
{
triangle t=new triangle();
if(t.get(p[0],p[1],p[2]))
t.pdtype();
}
else if(op==4)
{
line l=new line();
if(!l.get(p[0],p[1]))
{
System.out.printf("points coincide");
return ;
}
triangle t=new triangle();
if(t.get(p[2],p[3],p[4]))
t.ltjiaodian(l);
}
else
{
triangle t=new triangle();
if(t.get(p[1],p[2],p[3]))
t.ptpanduan(p[0]);
}
}
}
public static String zh(double a){
String res = String.format("%.6f",a);
res = res.replaceAll("0+?$", "");
if(res.charAt(res.length()-1) == '.') res+='0';
return res;
}
}
class triangle{
point[] tp=new point[3];
line[] tl=new line[3];
double[] tlc=new double[3];
boolean get(point d,point e,point f)
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
tl[i]=new line();
if(tl[0].get(d,e)&&tl[1].get(f,e)&&tl[2].get(d,f))
{
if(line.pingxing(tl[0],tl[1]))
{
//System.out.printf("data error");
return false;
}
tp[0]=d;
tp[1]=e;
tp[2]=f;
tlc[0]=Math.sqrt((d.x-e.x)*(d.x-e.x)+(d.y-e.y)*(d.y-e.y));
tlc[1]=Math.sqrt((f.x-e.x)*(f.x-e.x)+(f.y-e.y)*(f.y-e.y));
tlc[2]=Math.sqrt((f.x-d.x)*(f.x-d.x)+(f.y-d.y)*(f.y-d.y));
return true;
}
//System.out.printf("data error");
return false;
}
boolean dengyao()
{
if(tlc[0]==tlc[1]||tlc[0]==tlc[2]||tlc[1]==tlc[2])
return true;
return false;
}
boolean dengbian()
{
if(tlc[0]==tlc[1]&&tlc[0]==tlc[2])
return true;
return false;
}
double zhouchang()
{
return tlc[0]+tlc[1]+tlc[2];
}
double mianji()
{
double p=(tlc[0]+tlc[1]+tlc[2])/2;
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-tlc[0])*(p-tlc[1])*(p-tlc[2]));
}
point zhongxin()
{
point te=new point();
te.x=(tp[0].x+tp[1].x+tp[2].x)/3;
te.y=(tp[0].y+tp[1].y+tp[2].y)/3;
return te;
}
void pdtype(){
Arrays.sort(tlc);
double tmp = tlc[0]*tlc[0]+tlc[1]*tlc[1]-tlc[2]*tlc[2];
if(Math.abs(tmp) < 0.0000001)
System.out.print("false true false");
else if(tmp < 0) System.out.print("true false false");
else System.out.print("false false true");
}
void ltjiaodian(line l)
{
point[] pt1=new point[3];
point[] pt2=new point[3];
point[] pt3=new point[3];
int cnt1=0,cnt2=0,cnt3=0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
if(line.chonghe(l, tl[i]))
{
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
System.exit(0);
}
if(!line.pingxing(tl[i], l)&&tl[i].panduan(line.jiaodian(l, tl[i])))
pt2[cnt2++]=line.jiaodian(l,tl[i]);
if(l.shangxia(tp[i])==1)
pt2[cnt2++]=tp[i];
else if(l.shangxia(tp[i])==0)
pt1[cnt1++]=tp[i];
else pt3[cnt3++]=tp[i];
}
System.out.print(cnt2);
if(cnt2==2)
{
if(cnt1==1)
{
triangle te=new triangle();
te.get(pt1[0],pt2[0],pt2[1]);
System.out.print(" "+Main.zh(Math.min(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji()))+" "+Main.zh(Math.max(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji())));
}
else
{
triangle te=new triangle();
te.get(pt3[0],pt2[0],pt2[1]);
System.out.print(" "+Main.zh(Math.min(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji()))+" "+Main.zh(Math.max(this.mianji()-te.mianji(),te.mianji())));
}
}
}
void ptpanduan(point p)
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
if(point.sample(p,tp[i])||(tl[i].gongxian(p)&&tl[i].panduan(p)))
{
System.out.print("on the triangle");
return ;
}
triangle t1=new triangle();
triangle t2=new triangle();
triangle t3=new triangle();
t1.get(tp[0],tp[1],p);
t2.get(tp[0],tp[2],p);
t3.get(tp[1],tp[2],p);
if(Math.abs(t1.mianji()+t2.mianji()+t3.mianji()-this.mianji())<=0.000001)
System.out.print("in the triangle");
else System.out.print("outof the triangle");
}
}
class line {
double a,b,c;
point p1,p2;
public void prk()
{
if(this.b!=0)
System.out.print(-this.a/this.b);
else System.out.printf("Slope does not exist");
}
public void dislp(point d)
{
double ans=Math.abs(this.a*d.x+this.b*d.y+this.c)/Math.sqrt(this.a*this.a+this.b*this.b);
System.out.print(ans);
}
public boolean gongxian(point d)
{
double ans=Math.abs(this.a*d.x+this.b*d.y+this.c)/Math.sqrt(this.a*this.a+this.b*this.b);
if(Math.abs(ans)<=0.000001)
return true;
else return false;
}
public static boolean pingxing(line d,line e)
{
if(d.a==0)
{
if(e.a==0)
return true;
return false;
}
if(d.b==0)
{
if(e.b==0)
return true;
return false;
}
if(d.a*e.b==e.a*d.b)
return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean chonghe(line d,line e)
{
if(!line.pingxing(d,e))
return false;
if(d.a==0&&d.b*e.c==e.b*d.c)
return true;
if(d.a*e.c==e.a*d.c)
return true;
return false;
}
public static point jiaodian(line d,line e)
{
point te=new point();
te.x=(d.c*e.b-e.c*d.b)/(e.a*d.b-d.a*e.b);
if(d.b!=0)
te.y=-(d.a*te.x+d.c)/d.b;
else if(e.b!=0)
te.y=-(e.a*te.x+e.c)/e.b;
return te;
}
boolean panduan(point e)
{
double te=(p1.x-e.x)*(p2.x-e.x)+(p1.y-e.y)*(p2.y-e.y);
if(te<0)
return true;
return false;
}
boolean get(point d,point e)
{
if(point.sample(d,e))
{
//System.out.printf("points coincide");
return false;
}
a=d.y-e.y;
b=e.x-d.x;
c=-(a*d.x+b*d.y);
p1=d;
p2=e;
return true;
}
static double changdu(line e)
{
return Math.sqrt((e.p1.x-e.p2.x)*(e.p1.x-e.p2.x)+(e.p1.y-e.p2.y)*(e.p1.y-e.p2.y));
}
int shangxia (point e)
{
if(Math.abs(a*e.x+b*e.y+c)==0)
return 1;
if(a*e.x+b*e.y+c<0)
return 0;
return 2;
}
}
class point{
double x,y;
void setxy(String t)
{
int tmp=0;
for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++)
if(t.charAt(i)==',')
{
tmp=i;
break;
}
this.x=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(0,tmp));
this.y=Double.parseDouble(t.substring(tmp+1,t.length()));
}
public static void dis(point a,point b)
{
double te=Math.sqrt((b.x-a.x)*(b.x-a.x)+(b.y-a.y)*(b.y-a.y));
System.out.print(te);
}
public static boolean sample(point d,point e)
{
if(d.x==e.x&&d.y==e.y)
return true;
return false;
}
}
复杂度分析
第一题:
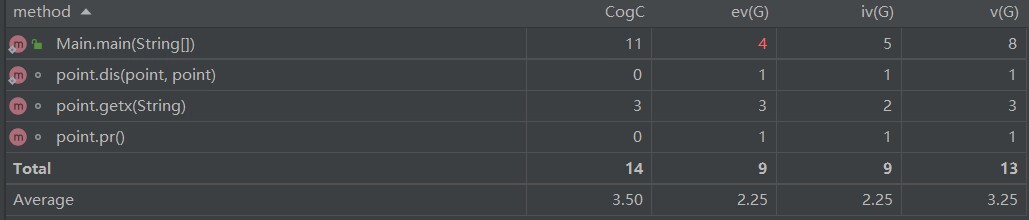
复杂度还ok
第二题:
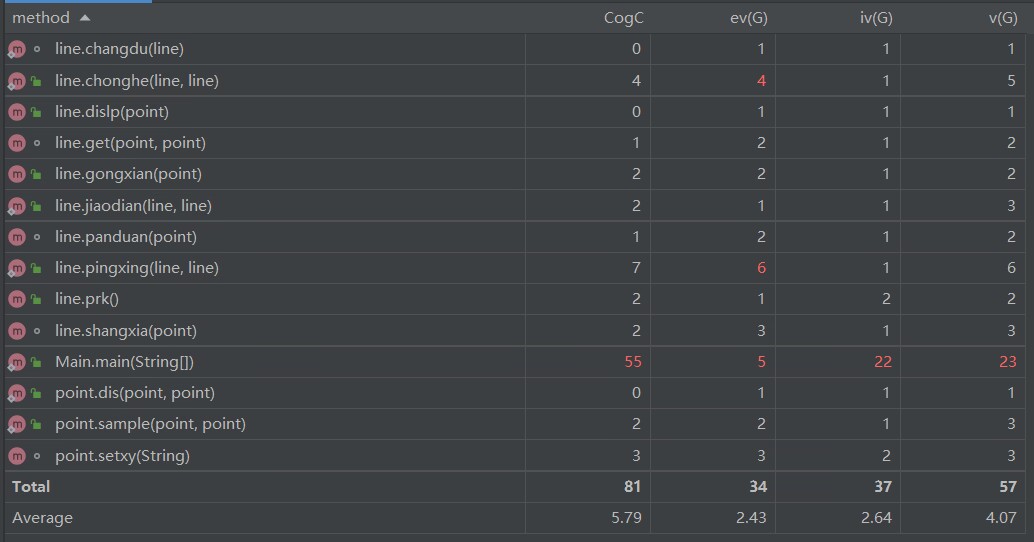
主函数复杂度很高(if else使用过多了),一片飘红
第三题:
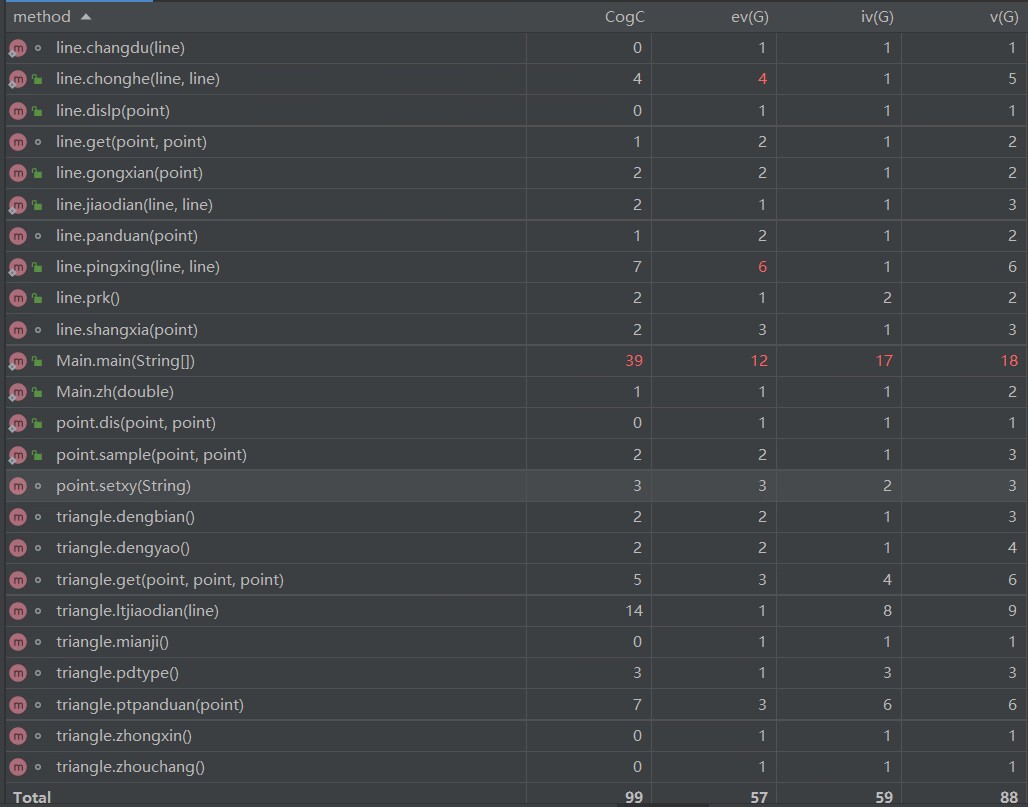
主函数复杂度很高(还是和第二题一样的问题),一片飘红
3. 踩坑心得
- 第一次作业中有许多题,最终输出必须采用float类型,不然会错,因为double类型精度更高,PTA测试点为文本对比,只有一模一样才算答案正确
- java方法中有很多大小写区分问题类似于nextLine()或者String或者charAt()这种,大小写错误就会报错
- 对于操作数的判断应该使用switch的,过多的if else导致了主函数圈复杂度过高
- 第三次作业在定义线段类时,使用点斜式会造成精度丢失(因为求斜率k时使用了除法,相当于在过程中就已经发生精度丢失),应该使用一般式Ax + By + C = 0,用点斜式永远有一个点过不去,最后考虑到后面还要用,用截距式重写了一遍line类
4. 改进建议
最能体现问题的还是第三次作业,明显难度和码量都提升了几个档次,在这种情况下,我虽然完成了但在后面的作业中又会出现不够完善的问题,最后又导致我重构原先写的类。所以在写函数的时候需要更多的考虑到精确度和复杂度还有辨识度的问题,一开始使用a,b,c这种没含义的变量还要f()这种没含义的方法导致写着写着就忘记有什么用了。
所以要将函数封装好,使用具有辨识度的变量和函数名是非常必要的,需要改掉随意取名的毛病,还有精度的问题,尽量避免除法或者开方这类会产生精度问题的计算方式,而且要减少对长if else的使用,减少圈复杂度
5. 总结
关于java中的数组
java中的数组声明方式为 类名+[]+数组名=new+类名+[数组长度]。对于每个成员都需要new一次否则会为空。
关于java中String类
String作为经常使用的非一般类数据类型,内置API相当之多,所以学习一些常用的API是非常有必要的,有时候只需要一个函数就能解决许多复杂的操作,使得代码更加简洁。
这三次作业让我了解到了java最基本的语法和格式,了解到了类和方法和对象之间的联系,虽然花费了很多时间但收获颇丰。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号