Java第二次bolg作业
一:前言
1.知识点:
题目集04:共有3道题目,难度较大,考察点线型系列的运算。
题目集06:共有5道题目,难度较小。主要考察字符串的解析及正则表达式的运用和学习。
题目集07:共有3道题,有些难度,主要考察类设计和几何图形相关的运算,及正则表达式的练习。
期中考试:共3道题,考察了类设计,继承与多态及容器类的使用。
链表练习:考察了对链表的理解及设计。
2.题量和难度:
总的来说题量和难度适中,题目也契合阶段性的java学习,考察内容精确,循序渐进,有很好的java学习引导和锻炼作用。
二:设计与分析
1.PTA 题目集07 7-2
图形类设计 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
要求:
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
以下为类设计:
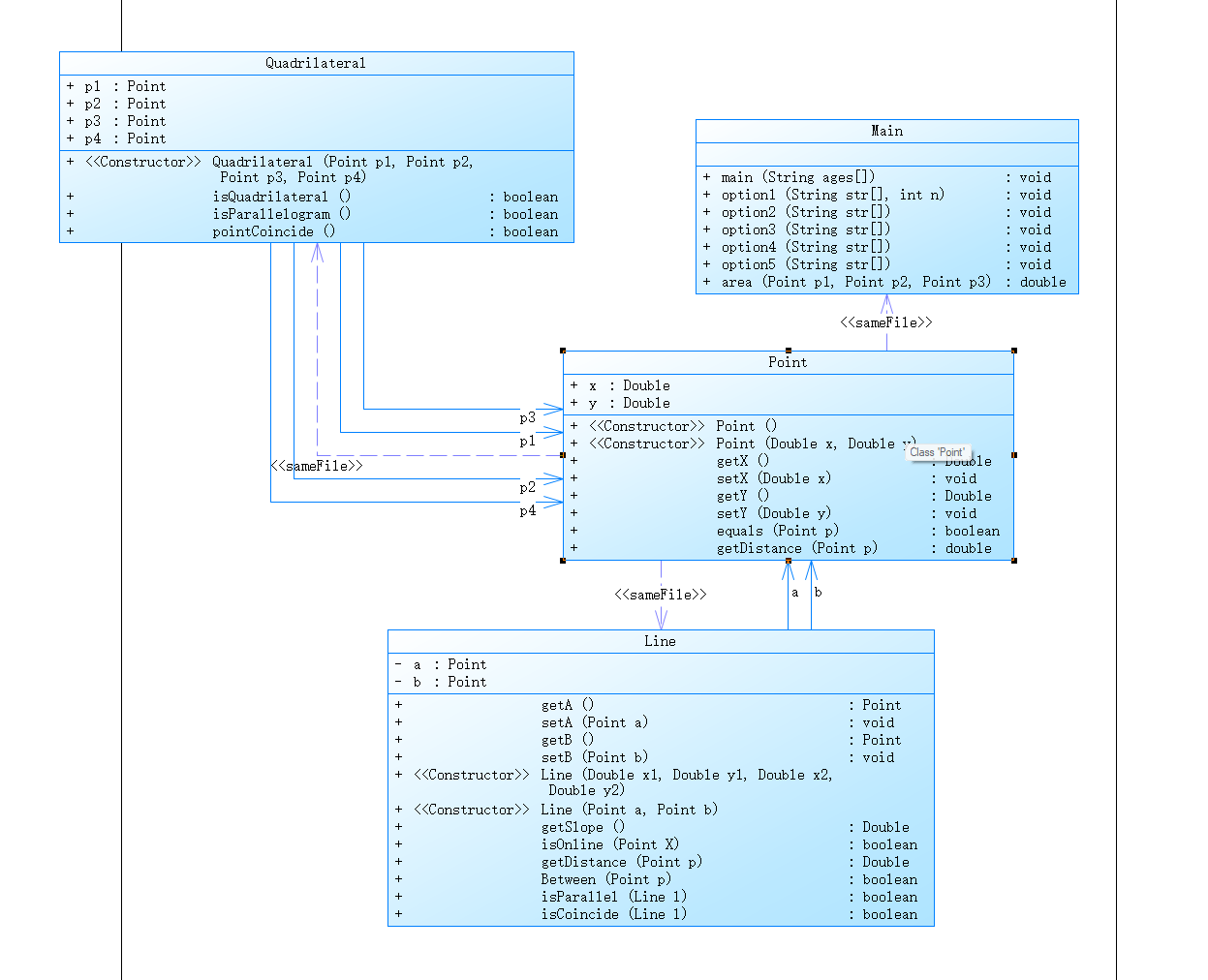
解释与心得:
设计了三个类:点类 Point 线类 Line 四边形类 Quadrilateral
Line 类传入两个Point 构成线 在类内完成两点距离,斜率,点线距离的计算 和判断点在线上,两线平行及是否重合的方法。
在 Quadrilateral 类内传入 4个Point 在类内完成判断是否构成四边形及平行四边形的方法。
采坑心得:
在输出数值的时候容易忽略小数位数的规定
如下:
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
if((((p1.getDistance(p2)+p2.getDistance(p3)+p3.getDistance(p4)+p4.getDistance(p1))*1e3)%10 != 0)) System.out.printf("%.3f ",p1.getDistance(p2)+p2.getDistance(p3)+p3.getDistance(p4)+p4.getDistance(p1)); else System.out.print(p1.getDistance(p2)+p2.getDistance(p3)+p3.getDistance(p4)+p4.getDistance(p1)+" ");
采用该方法进行判断后输出
以下为Point类的代码:
class Point { public Double x; public Double y; public Point(){ } public Point(Double x, Double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public Double getX() { return x; } public void setX(Double x) { this.x = x; } public Double getY() { return y; } public void setY(Double y) { this.y = y; } public boolean equals(Point p){ if(this.x.equals(p.getX()) && Objects.equals(this.y, p.getY())){ return true; } else return false; } public double getDistance(Point p){ return Math.sqrt((p.x-x)*(p.x-x)+(p.y-y)*(p.y-y)); } }
Line 类
class Line{ private Point a; private Point b; public Point getA() { return a; } public void setA(Point a) { this.a = a; } public Point getB() { return b; } public void setB(Point b) { this.b = b; } public Line(Double x1,Double y1, Double x2 ,Double y2){ this.a.setX(x1); this.a.setY(y1); this.b.setX(x2); this.b.setY(y2); } public Line(Point a, Point b) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } public Double getSlope(){ return (b.getY()-a.getY())/(b.getX()-a.getX()); } public boolean isOnline(Point X){//在延长线上 double slope1 = (X.y-a.y)/(X.x-a.x); if(slope1 == getSlope() && !Between(X)){ return true; } else return false; } public Double getDistance(Point p){ double l1 = a.getDistance(p); double l2 = b.getDistance(p); double l3 = a.getDistance(b); double l = (l1 + l2 + l3) / 2; double s = Math.sqrt(l * (l - l1) * (l - l2) * (l - l3));// 海伦公式 return 2 * s / l3;// 返回点到线的距离 用三角形面积求高 } public boolean Between(Point p){//在线内 return a.getDistance(p) + b.getDistance(p) == a.getDistance(b); } public boolean isParallel(Line l){ return Math.abs(getSlope()) == Math.abs(l.getSlope()); } public boolean isCoincide(Line l){//两线重合 return (a.equals(l.a) && b.equals(l.b)) || (a.equals(l.b) && b.equals(l.a)); } //public Point getIntersection(Line l){}//求两线交点 }
四边形类:
class Quadrilateral{ public Point p1; public Point p2; public Point p3; public Point p4; public Quadrilateral(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3, Point p4) { this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; this.p3 = p3; this.p4 = p4; } public boolean isQuadrilateral(){//任意三个顶点成直线,非四边形 if ((p4.y - p3.y) * (p4.x - p2.x) == (p4.y - p2.y) * (p4.x - p3.x)||(p4.y - p3.y) * (p4.x - p1.x) == (p4.y - p1.y) * (p4.x - p3.x)||(p4.y - p2.y) * (p4.x - p1.x) == (p4.y - p1.y) * (p4.x - p2.x)||(p3.y - p2.y) * (p3.x - p1.x) == (p3.y - p1.y) * (p3.x - p2.x)) { return false; } else return true; } public boolean isParallelogram(){ Line line1 = new Line(p1,p2); Line line2 = new Line(p2,p3); Line line3 = new Line(p3,p4); Line line4 = new Line(p4,p1); if(line1.isParallel(line3)&&p1.getDistance(p2)==p3.getDistance(p4)){//对边平行相等 return true; } else if(line2.isParallel(line4)&&p2.getDistance(p3)==p4.getDistance(p1)){ return true; } else{ return false; } } public boolean pointCoincide(){ if(p1.equals(p2)|| p3.equals(p4)|| p1.equals(p3)|| p1.equals(p4)||p2.equals(p3)||p2.equals(p4)){ return true; } else return false; } }
2.双向链表练习
要求:
实现双向链表的设计,要求实现如下功能
判断链表是否为空
获取当前链表节点数量
获取链表中第index个位置的节点的data值
删除链表最后一个节点
删除链表中第index位置的节点
在链表的第index个位置之前插入一个节点,值为theElement,index∈[1,size]
在链表尾插入节点,插入节点data值为element
获取第一个节点的data值
获取链表最后一个节点的data值
类图如下:
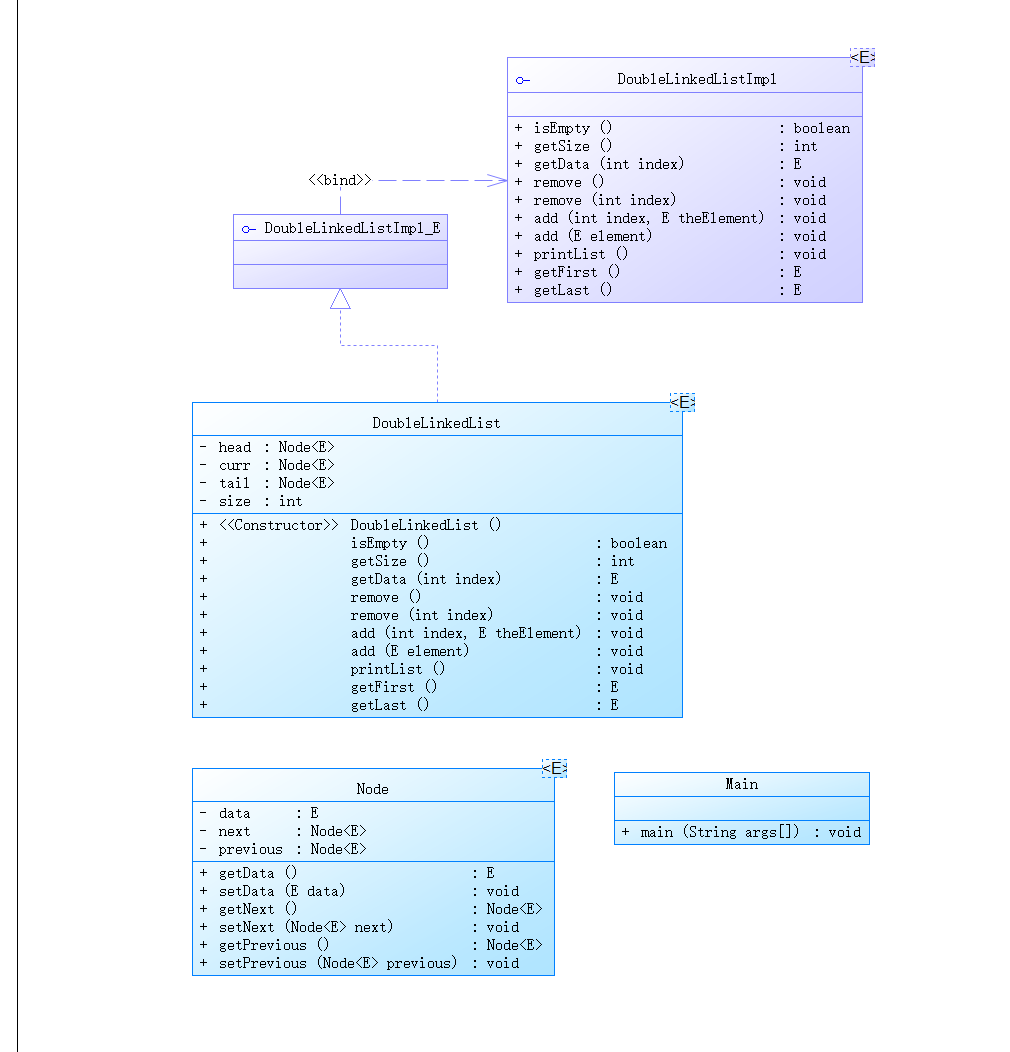
解释与分析:
话不多说 上代码:
删除某个节点 删除最后的节点只要删除尾节点
public void remove(int index) { if(index < 1||index>this.size) { return ; } curr = head; if(index == 1) { curr = head.getNext(); head.setNext(curr.getNext()); curr.getNext().setPrevious(head); } else if(index == this.size) {//设置tail tail.getPrevious().setNext(null); tail = tail.getPrevious(); } else { for(int i=1;i<index;i++) {//找到被删除节点的前一个节点 curr = curr.getNext(); } curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext()); curr.getNext().getNext().setPrevious(curr); } this.size--; }
在指定位置添加一个节点的数据
public void add(int index, E theElement) { //创建新增节点 Node<E> curr = new Node<>(); curr.setData(theElement); curr.setNext(null); if(index == 0) {//插入第一个位置 head.setNext(curr); curr.setPrevious(head); } else if(index == this.size ) {//插入最后一个位置 curr.setPrevious(tail); this.tail.setNext(curr); this.tail = curr; } else {//插入中间位置 Node<E> tempNoed =head; for(int i=0;i<index;i++) { tempNoed = tempNoed.getNext(); } curr.setNext(tempNoed.getNext()); tempNoed.getNext().setPrevious(curr); tempNoed.setNext(curr); curr.setPrevious(tempNoed); } this.size++; if(this.size == 1) { tail = curr; } }
输出链表:
public void printList() { curr = head.getNext(); for(int i = 0;i<size;i++) { System.out.print(curr.getData()+" "); curr = curr.getNext(); } System.out.println(); }
采坑心得:
注意在添加或删除后要注意将前后节点的 前驱引用(指针) 后继引用(指针)连接到相应位置。
3.期中考试题集
7-1:
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
``` The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值 ```
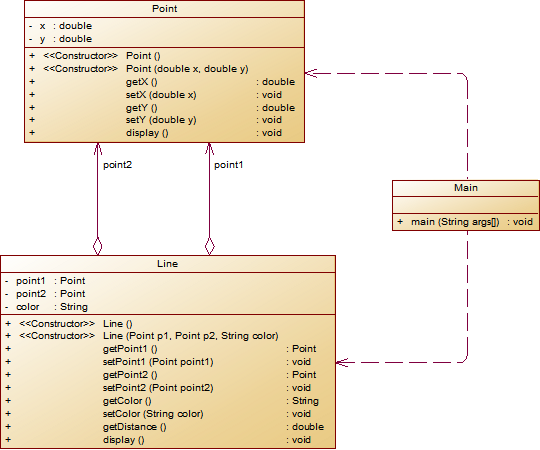
解释与心得:
line 类传入两点构成线并设置了颜色属性 及和Point 类都设计了display 输出内容
代码如下:
class Line { private Point a; private Point b; public Line() { } public Line(Point a, Point b, String color) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.color = color; } private String color; public Point getA() { return a; } public void setA(Point a) { this.a = a; } public Point getB() { return b; } public void setB(Point b) { this.b = b; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getDistance(){ return Math.sqrt((b.getX()-a.getX())*(b.getX()-a.getX())+(b.getY()-a.getY())*(b.getY()-a.getY())); } public void display(){ System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); a.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); b.display(); System.out.println("The line's length is:"+String.format("%.2f",getDistance())); } } class Point { private Double x; private Double y; public Point(){ } public Point(Double x, Double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public Double getX() { return x; } public void setX(Double x) { this.x = x; } public Double getY() { return y; } public void setY(Double y) { this.y = y; } public void display(){ System.out.printf("("+"%.2f"+","+"%.2f"+")",x,y); System.out.println(); } }
7-2 : 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
要求:
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display();
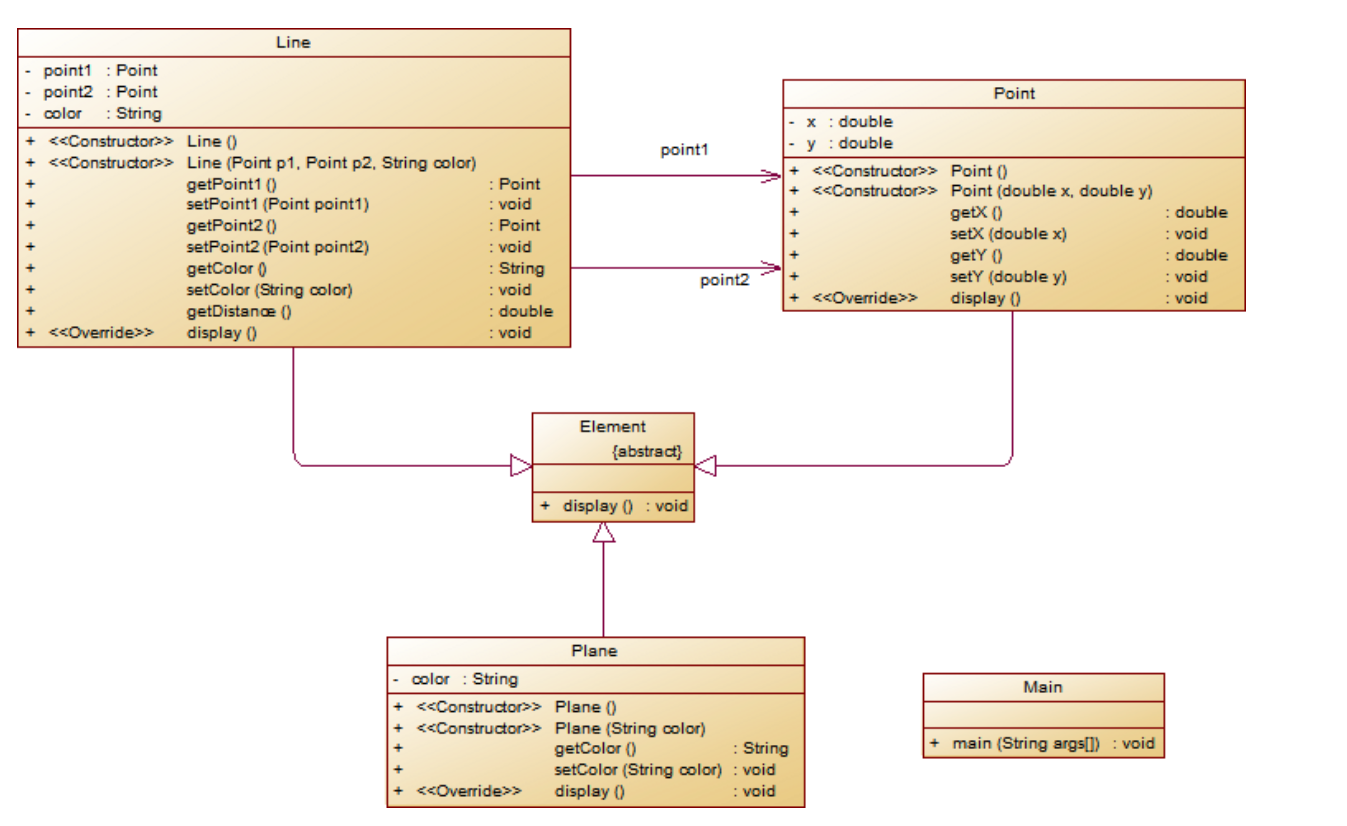
解释与分析:
设计了Point 和 Line 类共同的父类 Element 设置了一个抽象方法display以实现最后的多态。
代码如下:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] ages){ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); double x1 = in.nextDouble(); double y1 = in.nextDouble(); double x2 = in.nextDouble(); double y2 = in.nextDouble(); String str = in.next(); if(x1>0&&x1<=200&&x2>0&&x2<=200&&y1>0&&y1<=200&&y2>0&&y2<=200){ Element p1 = new Point(x1,y1); p1.display(); Element p2 = new Point(x2,y2); p2.display(); Element line = new Line(new Point(x1,y1),new Point(x2,y2),str); line.display(); Element color = new Plane(str); color.display(); } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Line extends Element{ private Point a; private Point b; public Line() { } public Line(Point a, Point b, String color) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.color = color; } private String color; public Point getA() { return a; } public void setA(Point a) { this.a = a; } public Point getB() { return b; } public void setB(Point b) { this.b = b; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getDistance(){ return Math.sqrt((b.getX()-a.getX())*(b.getX()-a.getX())+(b.getY()-a.getY())*(b.getY()-a.getY())); } public void display(){ System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); a.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); b.display(); System.out.println("The line's length is:"+String.format("%.2f",getDistance())); } } class Point extends Element{ private Double x; private Double y; public Point(){ } public Point(Double x, Double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public Double getX() { return x; } public void setX(Double x) { this.x = x; } public Double getY() { return y; } public void setY(Double y) { this.y = y; } public void display(){ System.out.printf("("+"%.2f"+","+"%.2f"+")",x,y); System.out.println(); } } abstract class Element{ public abstract void display(); } class Plane extends Element{ private String color; public Plane() { } public Plane(String str) { this.color = str; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } }
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) - 增加该类的
add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 - 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
- 0:输入结束
choice = input.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list ... break; case 2://insert Line object into list ... break; case 3://insert Plane object into list ... break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = input.nextInt(); ... } choice = input.nextInt(); }
同样有类图:
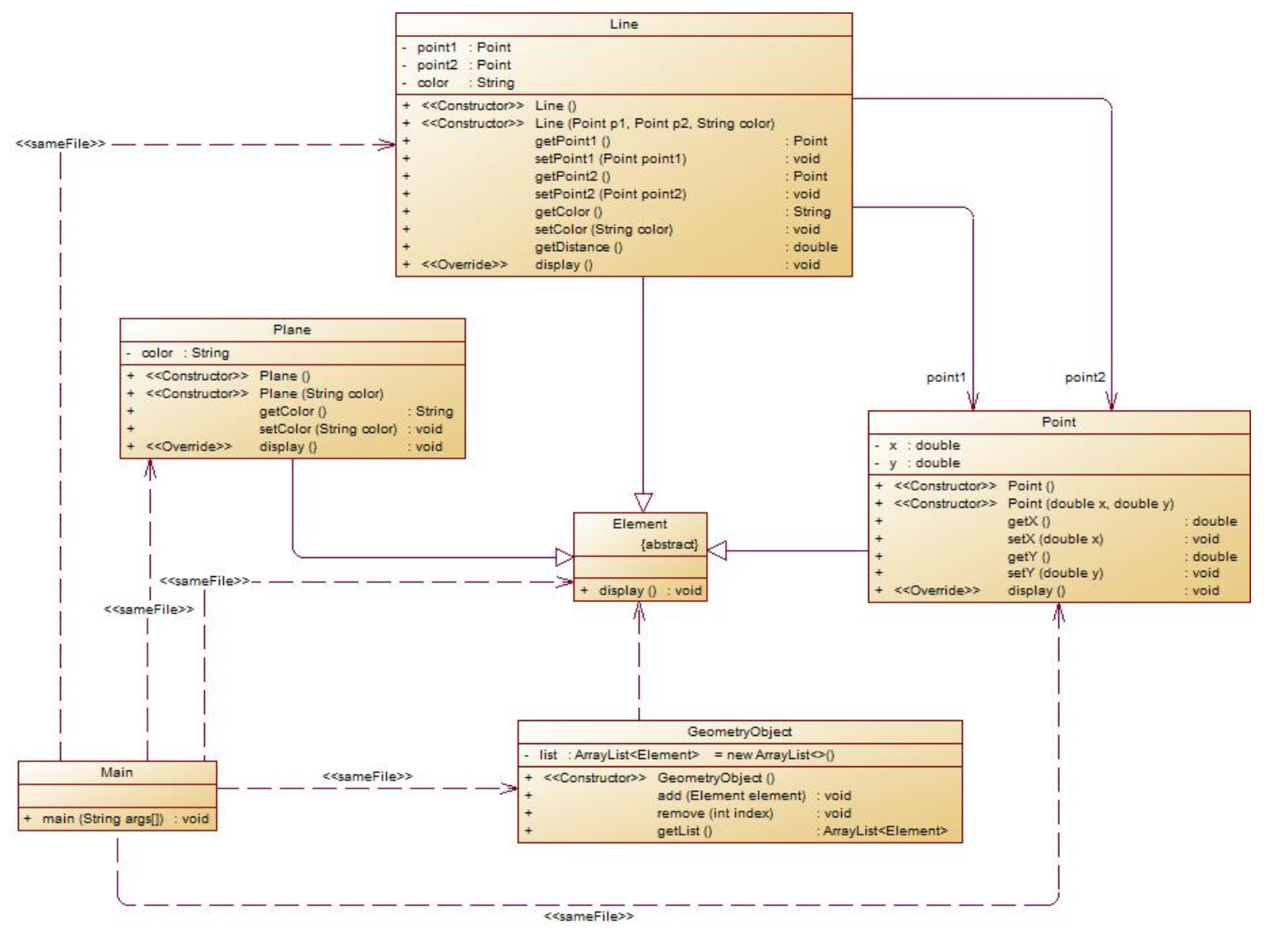
解释与心得:
代码如下:
容器类:
class GeometryObject{ private ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<>(); public ArrayList<Element> getList() { return list; } public void add(Element element){ list.add(element); } public void remove(int index){ list.remove(index); } }
主函数:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] ages){ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = in.nextInt(); GeometryObject g = new GeometryObject(); while(choice!=0){ switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list double x1 = in.nextDouble(); double y1 = in.nextDouble(); if(x1<=0||y1<=0||x1>200||y1>200){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } Element p1 = new Point(x1,y1); g.add(p1); break; case 2://insert Line object into list double x = in.nextDouble(); double y = in.nextDouble(); double x2 = in.nextDouble(); double y2 = in.nextDouble(); String str = in.next(); if(x<=0||y<=0||x>200||y>200||x2<=0||y2<=0||x2>200||y2>200){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } Element line = new Line(new Point(x,y),new Point(x2,y2),str); g.add(line); break; case 3://insert Plane object into list Element Plane = new Plane(in.next()); g.add(Plane); break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int i = in.nextInt(); if(i-1>= g.getList().size()||i-1<0){ choice = in.nextInt(); continue; } else{ g.remove(i-1); } break; default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } choice = in.nextInt(); } for(Element e: g.getList()){ e.display(); } } }
采坑❤得:
注意输出两位数和点的范围。注意删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作。
三:改进建议
在类设计上要符合单一职责原则,降低类与类间的耦合性,改进代码结构,让代码更加高效。
四:总结
在这阶段的学习中,学习了正则表达式的使用,加强了类设计,容器,继承与多态的练习。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号