可靠投递
原理
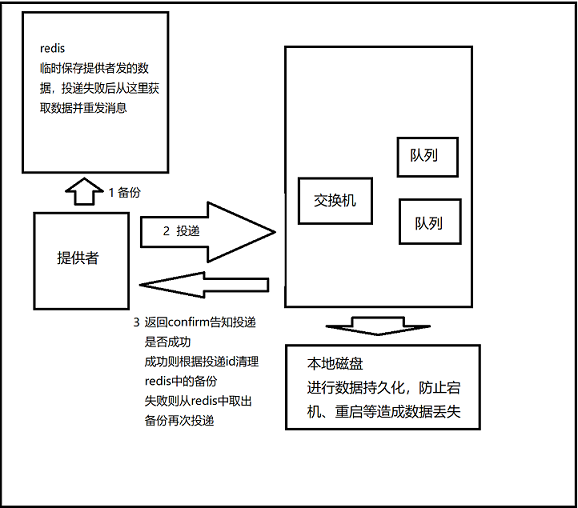
rabbitmq基于confirm模式、持久化策略,使用redis作为消息的临时储存空间
首先开启rabbitmq的confirm和持久化策略(可持久的对象为交换机、队列、消息)
1 开启confirm,在配置文件application.yml中
spring: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.200.128 publisher-confirms: true #开启confirm数据保护机制
2 开启交换机、队列、消息的持久化,在rabbitmq的配置类里
@Configuration public class RabbitMQConfig { public static final String SECKILL_ORDER_QUEUE ="seckill_order"; @Bean public Queue queue(){ return new Queue(SECKILL_ORDER_QUEUE,true);//true为开启队列持久化 } }
此处没有用交换机,如果想要开启交换机持久化参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/wrc-blog/p/14340064.html
消息默认就是持久的
编写一个增强spring自带的rabbitTemplate的类
使其在向队列发消息前,先往redis中备份数据
同时实现RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback接口,接收confirm模式下的回调函数,根据结果执行下一步操作
package com.changgou.seckill.config; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.UUID; //增强rabbitmq @Component public class ConfirmMessageSender implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; public static final String MESSAGE_CONFIRM_KEY="message_confirm_key"; //构造函数 public ConfirmMessageSender(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate) { this.rabbitTemplate = rabbitTemplate; rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this); } //开启生产者的confirm可靠投递时,用于接收rabbit服务器返回的通知 //参数1 消息的唯一标识,需要在发送消息时就传入,参见下方自定义发送方法 //参数2 发送是否成功 @Override public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) { if (ack){ //成功 删除redis中的相关数据 redisTemplate.delete(correlationData.getId()); redisTemplate.delete(MESSAGE_CONFIRM_KEY+correlationData.getId()); }else{ //失败 //从redis中获取失败的消息,重新发送 Map<String,String> map = ( Map<String,String>)redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(MESSAGE_CONFIRM_KEY + correlationData.getId()); String exchange = map.get("exchange"); String routingKey = map.get("routingKey"); String message = map.get("message"); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange,routingKey, JSON.toJSONString(message)); } } //自定义消息发送方法 先往redis里保存一份,再往消息队列里发送 public void sendMessage(String exchange,String routingKey,String message){ //将消息保存到redis中,在投递失败时重新取出再次投递 //设置消息的唯一标识,这个类由rabbit提供,用来为消息设置唯一标识,在上方confrim用于回调时区分消息 CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(correlationData.getId(),message); //将本次发送消息的元数据保存到redis Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("exchange",exchange); map.put("routingKey",routingKey); map.put("message",message); //注意这是哈希结构,你可以想为一大一小两个map,putAll会把上边定义的map作为小map的键值 redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(MESSAGE_CONFIRM_KEY+correlationData.getId(),map); //携带本次消息的唯一标识,发送到消息队列 //注意这里多了一个参数4,是我们上边定义的消息唯一标识,通过confirm模式确认可靠投递时,用corrlationData来区分不同的消息 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange,routingKey,message,correlationData); //这里的message是由外部传入的,如果是一个对象,要在外部先转为json } }
在需要进行可靠投递时,不用原生的rabbittemplate,而注入这个类,并调用sendMessage方法,回调函数会自动执行,并判断如何继续处理
可靠接收
默认为消费者一收到消息就立刻返回已收到,rabbit服务器会将消息从队列中删除
但是,万一消费者处理中宕机,则这条消息会丢失,所以我们希望在处理完后在签收这条消息
修改消费者的appication.yml
spring: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.200.128 listener: simple: acknowledge-mode: manual #开启消费者手动应答,rabbit接到应答后会删除队列中的消息,默认为自动,一接到就立刻应答
在监听者中手动签收消息 无需担心操作数据库但还未签收时,消息被重复获取的问题
package com.changgou.consumer.listener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.changgou.consumer.config.RabbitMQConfig; import com.changgou.consumer.service.SecKillOrderService; import com.changgou.seckill.pojo.SeckillOrder; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.io.IOException; @Component public class ConsumerListener { @Autowired private SecKillOrderService secKillOrderService; @RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.SECKILL_ORDER_QUEUE) public void receiveSecKillOrderMessage(Message message, Channel channel){//以往都是用String直接接收消息内容 //转换消息格式 SeckillOrder seckillOrder = JSON.parseObject(message.getBody(), SeckillOrder.class); //基于业务层完成同步musql的操作 int result = secKillOrderService.createOrder(seckillOrder); if(result>0){ //同步mysql成功 //向rabbitmq返回成功通知,rabbitmq会删除消息队列中的相关消息 try { //参数1 在消息队列中的唯一标识,参数2 开启批处理 channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),false); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }else { //同步mysql失败 try { //参数1 消息的唯一标识 //参数2 true所有的消费者都会拒绝这个消息 false只有当前的消费者拒绝这个消息 //参数3 true当前的消息会进入死信队列(延迟消息队列) false当前的消息会重新进入消息队列,默认在头部 channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),false,false); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
1
1




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号