常用类(一)
一、String类构造函数
package com.JavaSE.homework.Day14.Demo01; public class pra1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "nba"; String s2 = "nba"; String s3 = new String("nba"); String s4 = new String("nba"); System.out.println(s1==s2);//true System.out.println(s1==s3);//false System.out.println(s3==s4);//false System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//true System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true //equals方法的toString被重写了,可以比较字符 } }
String类创建的对象是不可更改的,内存的地址(字符串序列)也不能改变
-
String()构造函数,创建一个空字符串 不是null
String s5=new String();
String s6=new String("");
System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));/true
//new String()和new String("")一样,都是输出空串
-
getbytes()把字符串转换byte[]字节数组,以当前的编码转换
String s7 = "ABC"; //65 66 67
byte[] b1=s7.getBytes();//字节数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b1));
-
String(byte[] byte);把一个字节数组作为参数,就能按照当前编码转换成字符串
String s8 = new String(b1);
System.out.println(s8);
-
getbytes(Charset charset); 把字符串转换成字节数组时,可以用指定的编码进行转换
byte[] s9 = s7.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8"));
byte[] s10 = s7.getBytes(Charset.forName("GBK"));
byte[] s11 = s7.getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s9));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s10));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s11));
-
String(byte[] byte,String 字符编码);
-
getbytes(String 字符编码);
//String s7 = "ABC";
//byte[] b1=s7.getBytes();
// String ss = "NBA";
// byte[] b2 = ss.getBytes("GBK");
// System.out.println(b2);
// String s14 = new String(b1,"GBK");
-
String(byte[] byte,起点,终点);
String s12 = new String(b1,0,2);//注意:不要角标越界
System.out.println(s12);
-
String(char[] arr) 把一个字符数组,转换成字符串
char[] c1 = {'我', '*', '*'};
String s15 = new String(c1);
System.out.println(s15);
前端html 字符编码 服务器 字符编码 数据库 字符编码----统一编码是最好的方式
二、字符串常用方法
-
charAt(int index) 根据索引返回字符串中的字符
char c2 = s7.charAt(1); System.out.println(c2);
-
compareTo(字符串) 两个字符串比较 0 负数 正数
前数减后数,返回值为负,说明前数小编码在前,为正则前数大编码在后
-
comareToIgnoreCass(字符串)忽略大小写
package com.JavaSE.homework.Day14.Demo02; public class func { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "LOL"; int a1 = s1.compareTo("DNF"); System.out.println(a1); int a2 = "a".compareToIgnoreCase("B");//忽略大小写 int a3 = "a".compareTo("B"); System.out.println(a2);//-1 System.out.println(a3);//31 } }
-
concat(“xxx”)拼接
String s2 = "haha".concat("hehe");
System.out.println(s2);
-
contain(CharSequence c); 参数使用多态
-
源码:String是CharSequence子类
boolean b1 = "haha".contains("ha");
System.out.println(b1);
//源码
public boolean contains(CharSequence s) {
return indexOf(s.toString()) > -1;
}
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
endswith(字符串) ; 参数字符串 判断是什么结尾
boolean b2 = "javac.exe".endsWith(".exe");
System.out.println(b2);
boolean b3 = "Hello.java.txt".endsWith(".java");
System.out.println(b3);
-
equals(Object obj) 比较两个字符串的字面值,不比较内存地址 ,重写Object的equals()
boolean admain = "admin".equals("admin");
System.out.println(admain);
String ss1=new String("root");
String ss2=new String("root");
System.out.println(ss1.equals(ss2));
System.out.println(ss1==ss2);
-
equalsIgnoreCase(Object obj);
//忽略大小写比较字面值
boolean root = "root".equalsIgnoreCase("ROOT");
System.out.println(root);
-
getChars(begin,end,数组名,数组位置) 把字符串部分放到数组中
char[] c1 = new char[10]; "asdfewfc".getChars(0,5,c1,3); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c1));
-
isEmpty(); 判断空串
//判断字符串是否为空串 boolean b2 = " ".isEmpty(); System.out.println(b2);
-
indexof(); 返回第一个匹配到的字符索引
-
lastindexof(int c);返回最后一个匹配到的字符索引
int a4 = "中三扽等动扽".indexOf('中');
System.out.println(a4);//0
int a5 = "中三扽等动扽中".lastIndexOf('中');
System.out.println(a5);//6
-
lenth() 返回字符串长度
//length()方法 数组.length size() int length = "ljkasdjflasdjladjsl".length(); System.out.println(length);
-
mathches(正则表达式); 能使用(javascript语言 也有校验,也用正则表达式)
boolean b4 = s11.matches("^1([38][0-9]|4[5-9]|5[0-3,5-9]|66|7[0-8]|9[89])[0-9]{8}$");
System.out.println(b4);
-
replace(老,新) 替换
-
split(表达式) 切割,返回一个数组
String s3="今天又搞到十点半!好慢!";//把今天替换成明天
String s4 = s2.replace('今', '明');
System.out.println(s4);
String s5="锐雯,德莱厄斯,德莱文,亚索";
String[] s6=s5.split(",");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s6));//
-
startwith(字符串);以什么前缀
System.out.println("----------------------");
boolean hello = "hello.java".startsWith("hello");
System.out.println(hello);
-
subString(开始的索引)
-
subString(开始索引,结束索引)
String s7 = "锐雯,德莱厄斯,德莱文,亚索,盖伦"; String sb1 = s7.substring(3); System.out.println(sb1); String sb2 = s7.substring(8, 11); System.out.println(sb2);
-
tocharArray(); 把字符串转换成数组
//字符串转换字符数组 char[] c2 = "一点寒芒先到,随后枪出如龙。".toCharArray(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c2));
-
toUpperCase(); 小转大
-
toLowerCase(); 大转小
System.out.println("------------------------");
String s9="hello";
System.out.println( s9.toUpperCase().toLowerCase());
-
trim()去除两端空格
//去除前后空格
String s9 = " 死亡如风, 常伴吾身 ".trim();
System.out.println(s9);
//去除全部空格
String s13=" 中 国 ";
String replace1 = s13.replace(" ", "");
System.out.println("|"+replace1+"|");
//只去除中间的空格
TrimMid.tm(s13);
-
tm() 只去除中间空格
package com.JavaSE.homework.Day14.trimmid; public class TrimMid { public static void tm(String s) { int a=0; int b=s.length()-1; for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { if (s.charAt(i) != ' ') { a=i+1; break; } } for (int j = s.length()-1; j >= 0; j--) { if (s.charAt(j) != ' ') { b=j; break; } } System.out.println(s.substring(0, a)+s.substring(b)); //如果多段字符和空格,则循环找出所有字符的位置append到数组里,然后拼接出来,0-a和b是空格,中间依次拼接 } }
-
valueOf(xxx) 把数据类型转换字符串
//把其他数据类型转为字符串 int a6=12; String s15 = String.valueOf(a6); System.out.println(s15); String s16 = a6 + "13"; System.out.println(s16);
对以上方法有一定的了解,不需要完全记忆,当遇到解决字符串问题的时候,去自己查api,调试使用
三、StringBuffer
StringBuffer的底层的char [] 是会发生变化的,如果一直追加,达到了数组的容量,会自动扩容
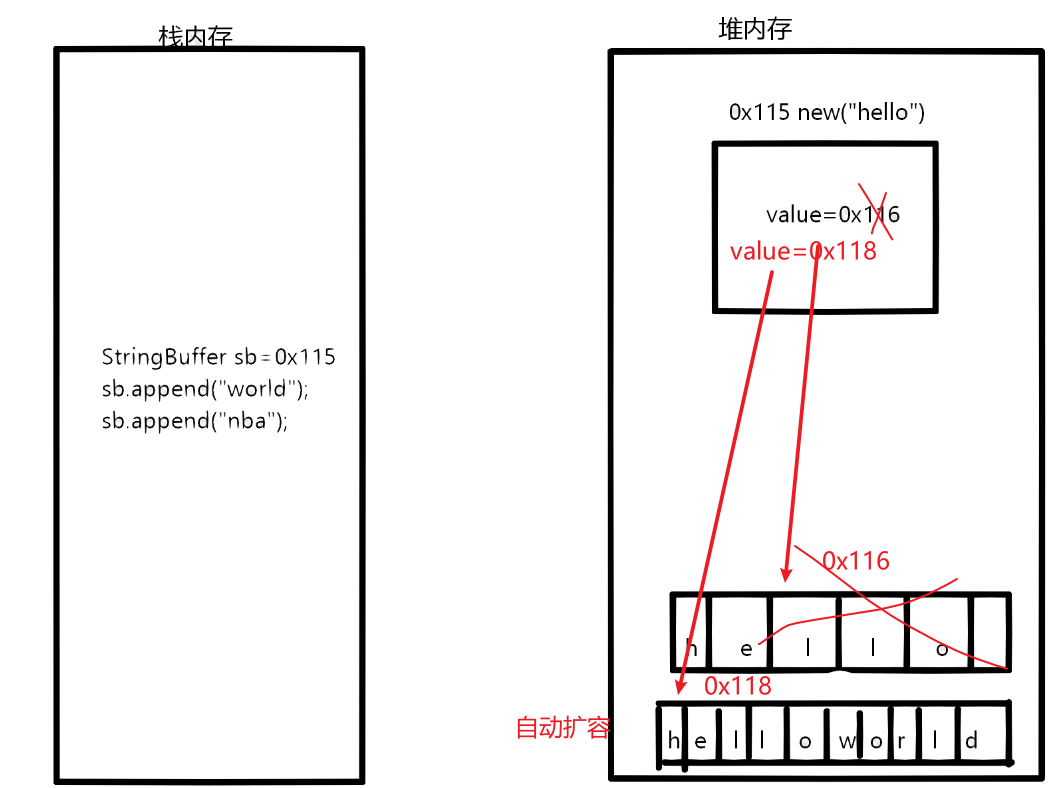
package com.JavaSE.homework.Day14.stringbufferdemo; public class TestStringBuffer { public static void main(String[] args) { // StringBuffer 引用的地址0x115,底层char[] 在扩容 StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("hello"); sb.append("world"); sb.append("abcdefjhigk"); sb.append("z"); System.out.println(sb); //String引用地址不可变 底层char[] 也是不可变的 String s1=new String("hello"); s1.concat("world"); System.out.println(s1); System.out.println("-----------------------"); StringBuffer sb1=new StringBuffer("abc");//16+3=19 //反转 sb1.reverse(); System.out.println(sb1); //把StringBuffer类型转换成String类型 String s = sb1.toString(); System.out.println(s); //字符串一直发生变化,用StringBuffer 操作,操作完成之后转换成String字符串 int i = sb1.capacity(); System.out.println(i); sb1.insert(2,"888"); System.out.println(sb1); sb1.delete(2,5); System.out.println(sb1); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号