优化gcc
优化gcc
目的是改善程序的执行性能,通过编译选项\(On\)来控制优化代码生成,\(n\)是一个代表优化级别的整数,
典型的有\(0, 1, 2, 3\) 其中\(-O\)等价于\(-O_1\),
\(-O\)或\(-O_1\)编译时告诉gcc同时减少代码长度和执行时间, 一般是线程跳转或者延迟退栈
\(-O_2\) 是完成 \(-O_1\) 的工作外还要做一些额外工作,比如处理器调度等
\(-O_3\) 是完成 \(-O_2\) 的工作外,还要做包括循环展开和一些与处理器相关的优化工作
一般来说\(n\)越大,优化等级越高
比如如下这一个程序test.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long int counter;
unsigned long int result;
unsigned long int temp;
unsigned long int five;
for(counter = 0; counter < 2022 * 2022 * 100/4 + 2023; counter += (10 - 6) / 4)
{
temp=counter / 1979;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i ++)
{
five = 200 * 200 / 8000;
}
result = counter;
}
printf("Result is %ld\n", result);
return 0;
}
首先不加任何优化进行编译
gcc -Wall test.c -o in test # Wall 是为了让gcc显示更多的警告
time ./test # 显示各阶段执行时间, 优化通过这个体现
执行结果如下
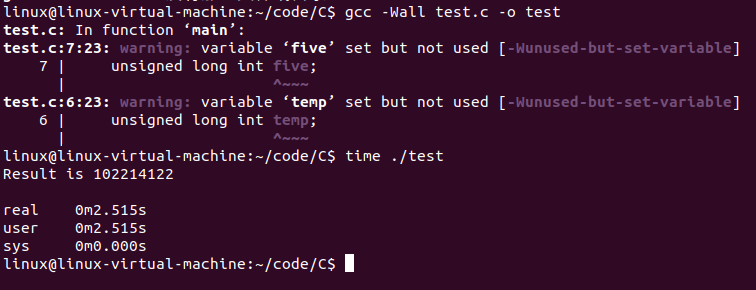
说明
real 进程总的执行时间
user 被测量的进程中的用户指令执行时间
sys 被测量进程中内核代用户执行的时间
sys 和 user 的和被称为CPU时间
加上\(-O1\)优化
gcc -Wall -O1 test.c -o in test
time ./time
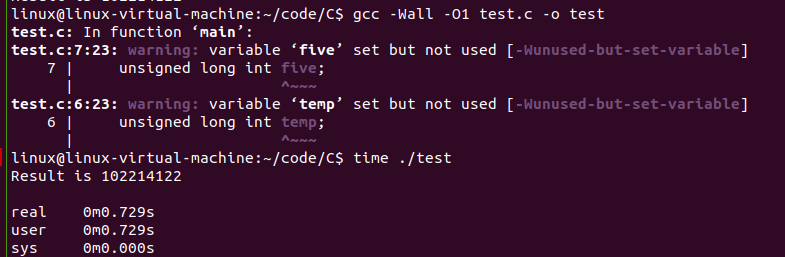
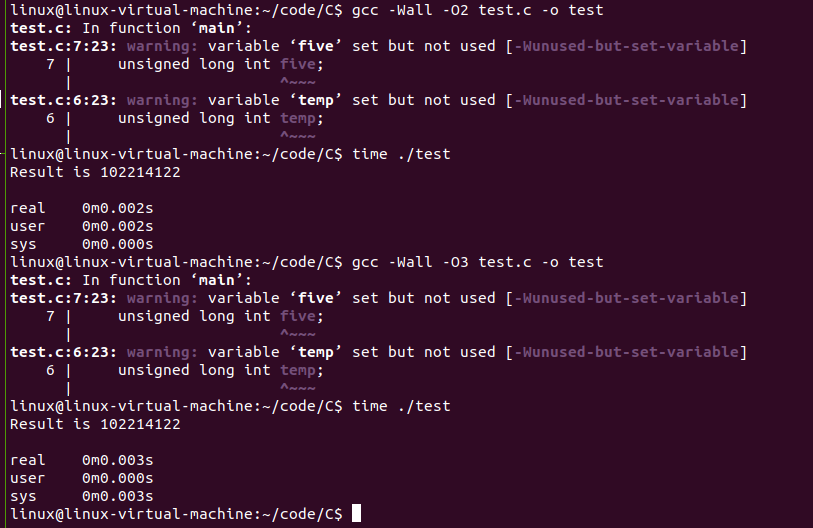
其他两种



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号