破环单例模式
方式一:序列化
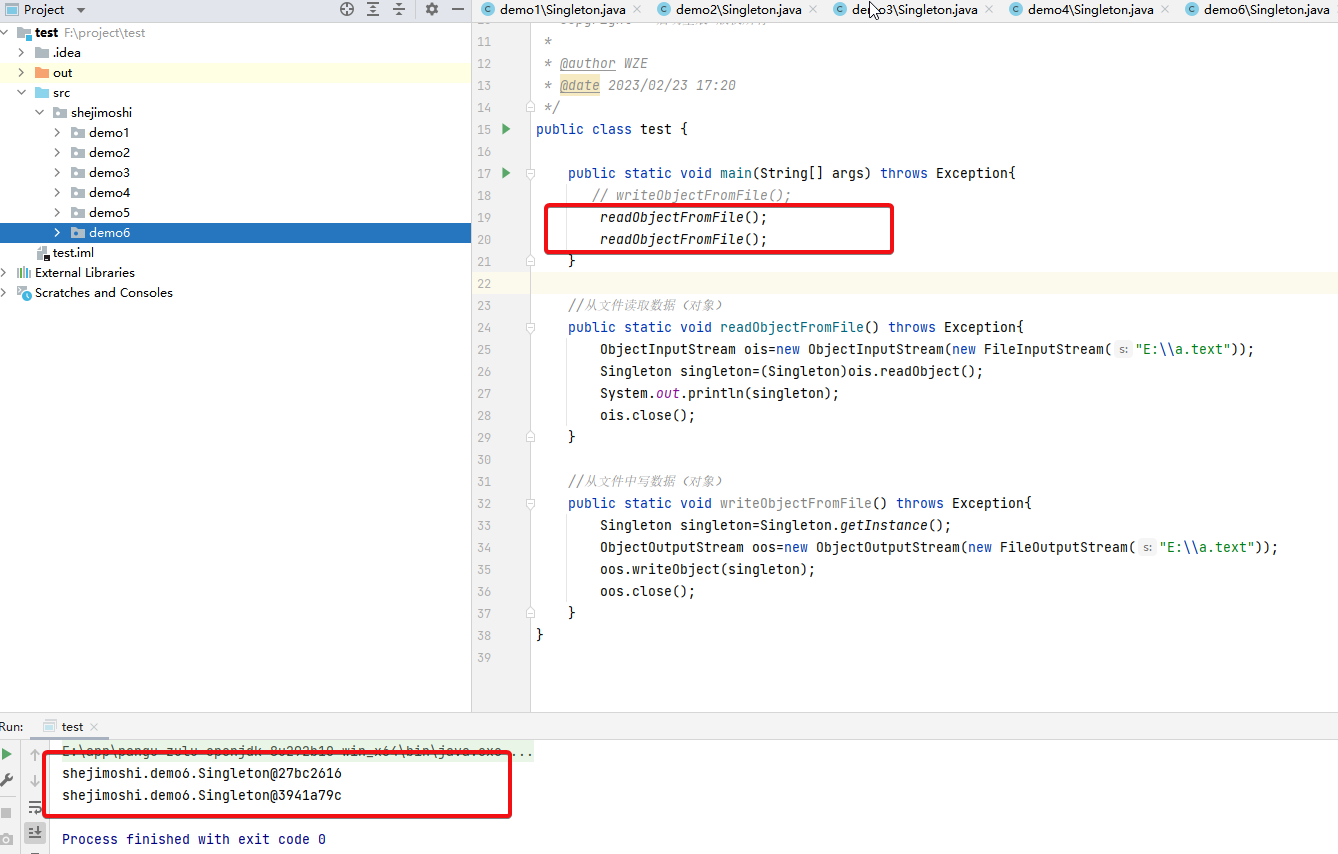
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// writeObjectFromFile();
readObjectFromFile();
readObjectFromFile();
}
//从文件读取数据(对象)
public static void readObjectFromFile() throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\a.text"));
Singleton singleton=(Singleton)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(singleton);
ois.close();
}
//从文件中写数据(对象)
public static void writeObjectFromFile() throws Exception{
Singleton singleton=Singleton.getInstance();
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\\a.text"));
oos.writeObject(singleton);
oos.close();
}
}
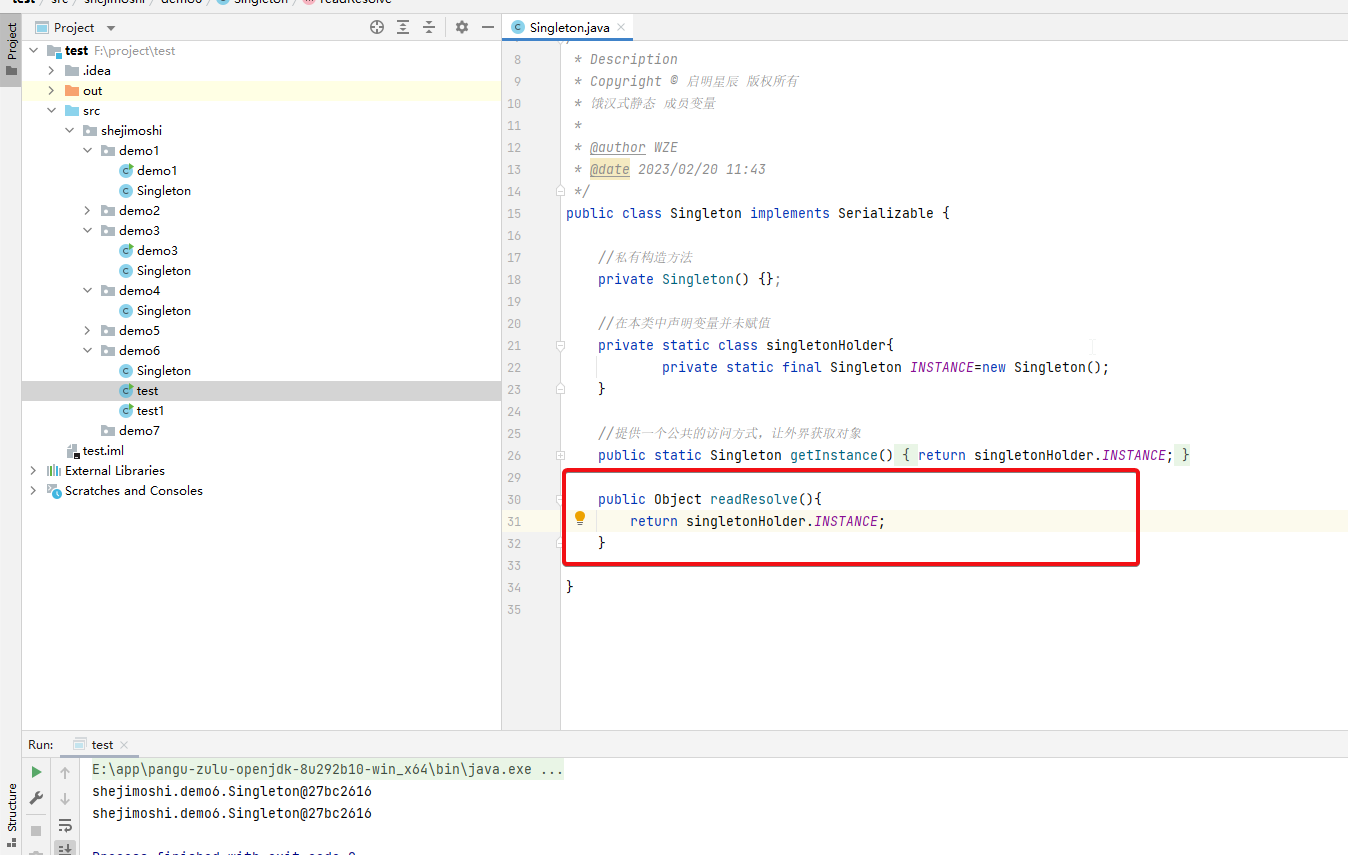
解决方案
public class Singleton implements Serializable {
//私有构造方法
private Singleton() {};
//在本类中声明变量并未赋值
private static class singletonHolder{
private static final Singleton INSTANCE=new Singleton();
}
//提供一个公共的访问方式,让外界获取对象
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return singletonHolder.INSTANCE;
}
public Object readResolve(){
return singletonHolder.INSTANCE;
}
}
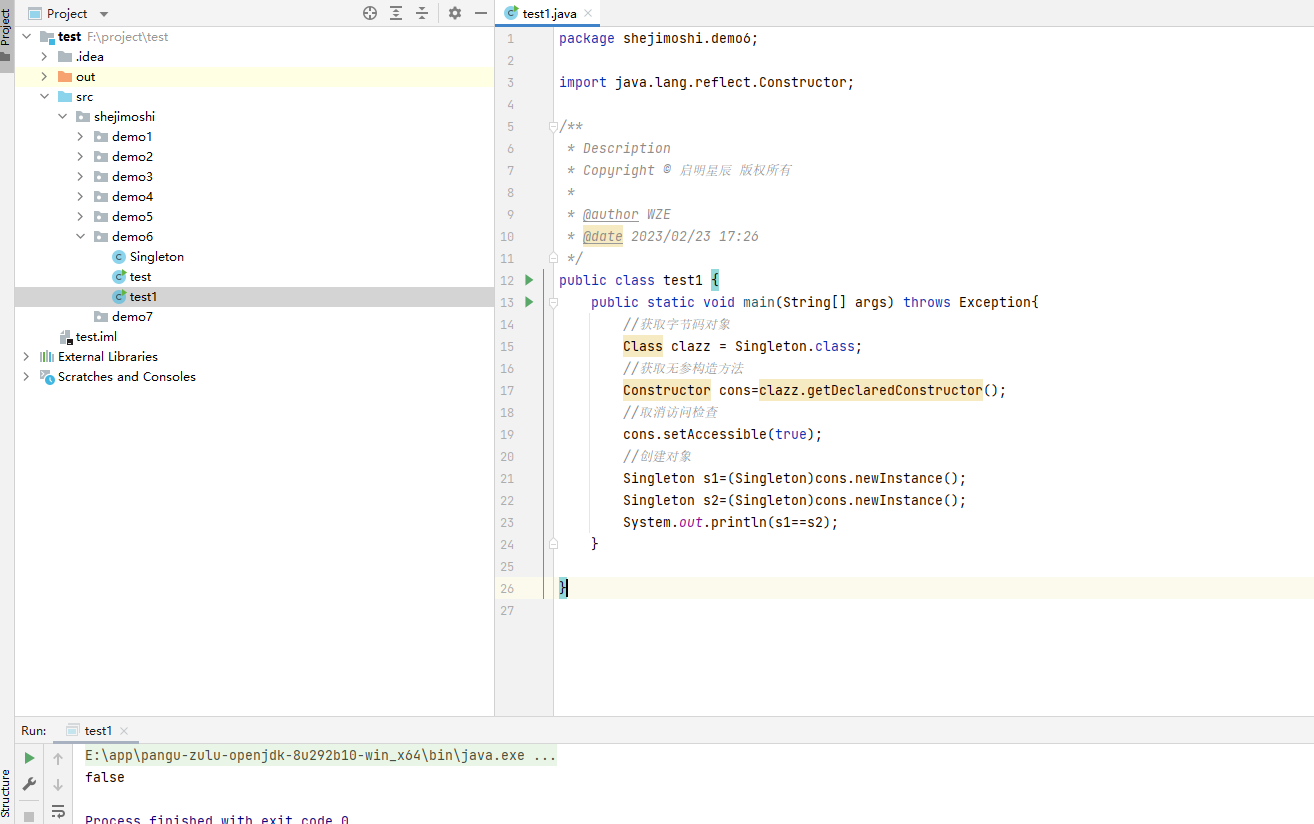
方式二:反射
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//获取字节码对象
Class clazz = Singleton.class;
//获取无参构造方法
Constructor cons=clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
//取消访问检查
cons.setAccessible(true);
//创建对象
Singleton s1=(Singleton)cons.newInstance();
Singleton s2=(Singleton)cons.newInstance();
System.out.println(s1==s2);
}
}
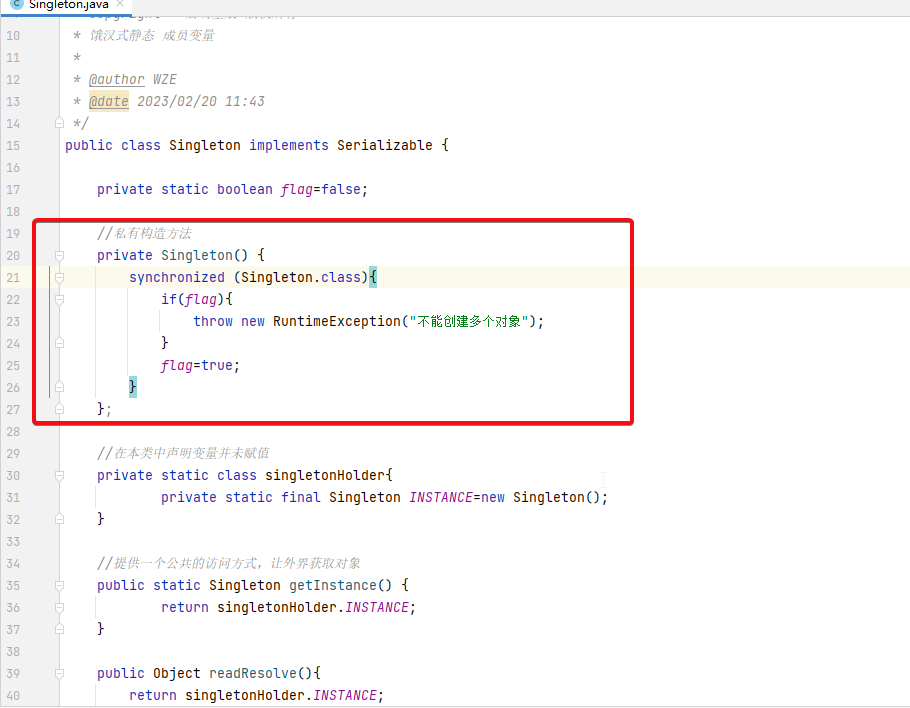
解决方案
public class Singleton implements Serializable {
private static boolean flag=false;
//私有构造方法
private Singleton() {
synchronized (Singleton.class){
if(flag){
throw new RuntimeException("不能创建多个对象");
}
flag=true;
}
};
//在本类中声明变量并未赋值
private static class singletonHolder{
private static final Singleton INSTANCE=new Singleton();
}
//提供一个公共的访问方式,让外界获取对象
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return singletonHolder.INSTANCE;
}
public Object readResolve(){
return singletonHolder.INSTANCE;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号