13.多线程
一.线程
1.定义:能够独立运行程序的资源,理论上可以多线程并发运行
2.进程和线程的区别:进程是针对操作系统而言的,一个进程就是一个程序在后台运行,可以多进程并发运行。
一个进程可以包含多个线程
3.线程的实现方式:
a.写一个类继承Thread类,重写其run(); 调用该实例的start()启动线程
b.写一个类实现Runable接口,重写run();通过Thread(Runable)构造一个线程类,再调用start()
c.见案例demo1
4.线程的生命周期
a.新生:创建线程的实例
b.运行中:
运行正常
阻塞状态:睡眠(会自己醒来),IO阻塞(必须等到唤醒),等待锁状态(一定要拿到对象锁才会执行),唤醒
5.Thread的常用API
start 启动线程
sleep 睡眠,会自定唤醒,
currentThread():获取当前线程的引用
interrupt():中断线程 代替stop方法
setPriority(int newPriority):设置优先级
yield() :礼让,把cpu的资源放弃让其他线程占有
Object中对线程的操作:
wait:是将该对象上正在执行的线程阻塞,挂起,不能自己唤醒
notify:将该对象上阻塞的线程唤醒,此方法之唤醒一个线程
notifyall:就是将该对象上所有挂起的线程全部唤醒
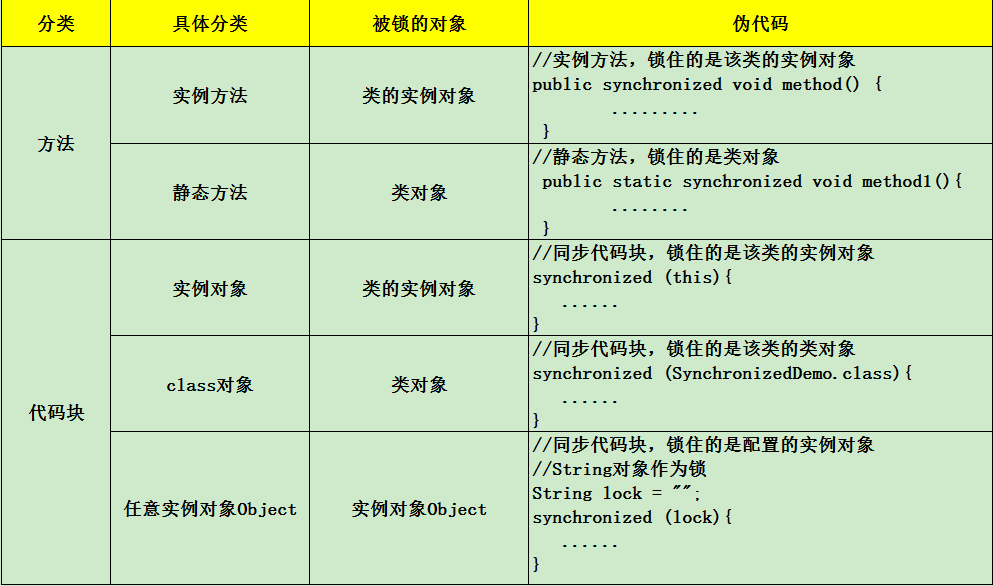
6.多线程操作:
a.每个对象都有对象锁,多线程安全就是让线程获得该对象的对象锁
b.其实现就是用同步关键字:synchronized
c.同步关键字的用法:可以用在方法和代码块
练习1:
创建两个线程:线程1每隔一秒执行一次,打印输出奇数(1-100)
线程2每隔一秒执行一次,打印输出偶数(1-100)
线程1:1
线程2:2
7.例子
创建线程举例:
1 package com.hwua.myThread; 2 3 public class Demo1 extends Thread{ 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 //此方法是核心方法,线程运行就是执行该方法 7 try { 8 Thread.sleep(1000); 9 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 10 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 System.out.println("线程1:你好"); 14 } 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 18 } 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * 线程实现的第一种方式 23 * @author allen 24 * 25 */ 26 class Demo2 extends Thread{ 27 public void run() { 28 //此方法是核心方法,线程运行就是执行该方法 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(2000); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } 35 System.out.println("线程2:你好,吃饭了没"); 36 } 37 } 38 39 /** 40 * 线程实现的第二种方式 41 * @author allen 42 * 43 */ 44 class Demo3 implements Runnable{ 45 @Override 46 public void run() { 47 try { 48 Thread.sleep(5000); 49 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 50 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } 53 System.out.println("线程3:吃没吃饭管你什么事?"); 54 } 55 56 } 57 58 class Test{ 59 public static void main(String[] args) { 60 Thread demo1 = new Demo1(); 61 Thread demo2 = new Demo2(); 62 Thread demo3 = new Thread(new Demo3()); 63 demo1.setPriority(10);//设置线程的优先级,但是优先级不具有具有绝对性,低优先级仍有机会执行只是概率变小 64 demo1.start();//该方法是启动线程的唯一方法 65 demo2.start(); 66 demo3.start(); 67 } 68 }
线程同步到方法上举例:
1 package com.hwua.myThread; 2 /** 3 * 线程同步案例。多线程访问同一资源的问题 4 * 线程安全是同步的过程 5 * 线程非安全是异步的过程 6 * @author allen 7 * 8 */ 9 public class SynchronizDemo { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 UserInfo user = new UserInfo(); 12 Thread a = new A(user); 13 Thread b = new B(user); 14 a.start(); 15 b.start(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 class A extends Thread{ 20 UserInfo user;//让多个线程公用同一个对象 21 public A(UserInfo user) { 22 this.user = user; 23 } 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 user.getMoney(1000); 27 } 28 } 29 30 class B extends Thread{ 31 UserInfo user;//让多个线程公用同一个对象 32 public B(UserInfo user) { 33 this.user = user; 34 } 35 @Override 36 public void run() { 37 user.getMoney(1000); 38 } 39 } 40 41 42 class UserInfo{ 43 private double balance = 1000;//余额 44 45 public double getBalance() { 46 return balance; 47 } 48 49 public void setBalance(double balance) { 50 this.balance = balance; 51 } 52 /** 53 * money:要取得数量 54 */ 55 public synchronized int getMoney(double money){ 56 if(money>balance){ 57 System.out.println("余额不足!不能取"); 58 return -1; 59 }else{ 60 try { 61 Thread.currentThread().sleep(2000); 62 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 63 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 balance -= money; 67 System.out.println("取款成功,取了:"+money+",余额:"+balance); 68 return 1; 69 } 70 } 71 }
线程死锁举例:
1 package com.hwua.myThread; 2 3 public class DeathThreadDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Thread aa = new AA(); 6 Thread bb = new BB(); 7 aa.start(); 8 bb.start(); 9 } 10 } 11 12 class Stu1 { 13 14 } 15 16 class Stu2 { 17 18 } 19 20 class AA extends Thread{ 21 @Override 22 public void run() { 23 synchronized (Stu1.class) {//该线程获取Stu1的对象锁 24 System.out.println("线程AA:获取Stu1的对象锁"); 25 try { 26 Thread.sleep(2000); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 28 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 System.out.println("线程AA:准备去获取Stu2的对象锁"); 32 synchronized (Stu2.class){ 33 System.out.println("线程AA:已经获取Stu2的对象锁"); 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 class BB extends Thread{ 40 @Override 41 public void run() { 42 synchronized (Stu2.class) {//该线程获取Stu1的对象锁 43 System.out.println("线程BB:获取Stu2的对象锁"); 44 try { 45 Thread.sleep(2000); 46 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 47 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } 50 System.out.println("线程BB:准备去获取Stu1的对象锁"); 51 synchronized (Stu1.class){ 52 System.out.println("线程BB:已经获取Stu1的对象锁"); 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 }
生产者和消费者举例:
1 package com.hwua.myThread; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 public class ProductCustomerDemo { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Basket basket = new Basket(); 9 Thread product = new Product(basket); 10 Thread customer = new Customer(basket); 11 product.start(); 12 customer.start(); 13 } 14 } 15 /** 16 * 数据类 17 * @author allen 18 * 19 */ 20 class Apple{ 21 int id; 22 23 public Apple(int id) { 24 this.id = id; 25 } 26 27 @Override 28 public String toString() { 29 return "Apple [id=" + id + "]"; 30 } 31 } 32 /** 33 * 容器类 34 * @author allen 35 * 36 */ 37 class Basket{ 38 List<Apple> list = new ArrayList<Apple>();//放数据的容器 39 //往里面放数据 40 public synchronized void addApple(){ 41 for (int i = 1; i < 21; i++) { 42 Apple apple = new Apple(i); 43 pushApple(apple); 44 } 45 } 46 47 //一个一个往篮子中放数据 48 //放到第五个暂停,并通知消费者来消费数据 49 private void pushApple(Apple apple) { 50 if(list.size()==5){//达到上限,通知消费者消费 51 try { 52 wait();//表示当前线程挂起,等待唤醒 53 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 54 e.printStackTrace(); 55 } 56 } 57 try { 58 Thread.sleep(500); 59 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 60 e.printStackTrace(); 61 } 62 list.add(apple);//模拟放数据,并且有时间延迟 63 System.out.println("生产者:生产"+apple.toString()); 64 notify();//唤醒当前对象被挂起的线程,第一个被挂起的线程 65 } 66 67 //消费数据 68 public synchronized void consumeApple(){ 69 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 70 getApple(); 71 } 72 } 73 74 private void getApple() { 75 if(list.size()==0){//通知生产者去生产 76 try { 77 wait(); 78 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 79 e.printStackTrace(); 80 } 81 } 82 try { 83 Thread.sleep(500); 84 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 85 e.printStackTrace(); 86 } 87 System.out.println("消费者:消费"+list.get(0).toString()); 88 list.remove(0); 89 notify(); 90 } 91 } 92 /** 93 * 生产线程 94 * @author allen 95 * 96 */ 97 class Product extends Thread{ 98 Basket b; 99 public Product(Basket b) { 100 this.b = b; 101 } 102 @Override 103 public void run() { 104 b.addApple(); 105 } 106 } 107 /** 108 * 消费线程 109 * @author allen 110 * 111 */ 112 class Customer extends Thread{ 113 Basket b; 114 public Customer(Basket b) { 115 this.b = b; 116 } 117 @Override 118 public void run() { 119 b.consumeApple(); 120 } 121 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号